

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 305-312.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18027 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18027
Special Issue: 药用植物专辑 (2018年53卷3期)
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhu Yujia1, Jiao Kaili1, Luo Xiujun1, Feng Shangguo1,2,*( ), Wang Huizhong1,2,*(
), Wang Huizhong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-01-28
Accepted:2018-05-09
Online:2018-05-01
Published:2018-06-05
Contact:
Feng Shangguo,Wang Huizhong
Zhu Yujia, Jiao Kaili, Luo Xiujun, Feng Shangguo, Wang Huizhong. Genetic Relationship of Physalis Plants Revealed by Simple Sequence Repeat Markers[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(3): 305-312.
| No. | Species name | Code | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physalis minima | XSJ1 | Qianxi, Tangshan, Hebei |
| 2 | P. minima | XSJ2 | Mudan, Heze, Shandong |
| 3 | P. minima | XSJ3 | Lou’an, Anhui |
| 4 | P. minima | XSJ4 | Lishui, Zhejiang |
| 5 | P. angulata | KZ1 | Jianggan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang |
| 6 | P. angulata | KZ2 | Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang |
| 7 | P. angulata | KZ3 | Luotian, Huanggang, Hubei |
| 8 | P. angulata | KZ4 | Honghe, Yunnan |
| 9 | P. angulata | KZ5 | Najing, Jiangsu |
| 10 | P. angulata | KZ6 | Linhai, Taizhou, Zhejiang |
| 11 | P. angulata | KZ7 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang |
| 12 | P. angulata | KZ8 | Pujiang, Jinhua, Zhejiang |
| 13 | P. angulata | KZ9 | Xiajin, Dezhou, Shandong |
| 14 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ1 | Faku, Shenyang, Liaoning |
| 15 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ2 | Donggang, Dandong, Liaoning |
| 16 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ3 | Nong’an, Changchun, Jilin |
| 17 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ4 | Zoucheng, Jinan, Shandong |
| 18 | P. pubescens | MSJ1 | Faku, Shenyang, Liaoning |
| 19 | P. pubescens | MSJ2 | Nong’an, Changchun, Jilin |
| 20 | P. pubescens | MSJ3 | Chaoyang, Zhaodong, Heilongjiang |
| 21 | P. pubescens | MSJ4 | Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang |
| 22 | P. pubescens | MSJ5 | Hulunbeir, Inner Mongolia |
Table 1 Twenty-two Physalis samples tested in this experiment
| No. | Species name | Code | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physalis minima | XSJ1 | Qianxi, Tangshan, Hebei |
| 2 | P. minima | XSJ2 | Mudan, Heze, Shandong |
| 3 | P. minima | XSJ3 | Lou’an, Anhui |
| 4 | P. minima | XSJ4 | Lishui, Zhejiang |
| 5 | P. angulata | KZ1 | Jianggan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang |
| 6 | P. angulata | KZ2 | Xiaoshan, Hangzhou, Zhejiang |
| 7 | P. angulata | KZ3 | Luotian, Huanggang, Hubei |
| 8 | P. angulata | KZ4 | Honghe, Yunnan |
| 9 | P. angulata | KZ5 | Najing, Jiangsu |
| 10 | P. angulata | KZ6 | Linhai, Taizhou, Zhejiang |
| 11 | P. angulata | KZ7 | Wenzhou, Zhejiang |
| 12 | P. angulata | KZ8 | Pujiang, Jinhua, Zhejiang |
| 13 | P. angulata | KZ9 | Xiajin, Dezhou, Shandong |
| 14 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ1 | Faku, Shenyang, Liaoning |
| 15 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ2 | Donggang, Dandong, Liaoning |
| 16 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ3 | Nong’an, Changchun, Jilin |
| 17 | P. alkekengi var. francheti | SJ4 | Zoucheng, Jinan, Shandong |
| 18 | P. pubescens | MSJ1 | Faku, Shenyang, Liaoning |
| 19 | P. pubescens | MSJ2 | Nong’an, Changchun, Jilin |
| 20 | P. pubescens | MSJ3 | Chaoyang, Zhaodong, Heilongjiang |
| 21 | P. pubescens | MSJ4 | Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang |
| 22 | P. pubescens | MSJ5 | Hulunbeir, Inner Mongolia |
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Repeat type | Tm | No. of loci | Polymorphic loci | Polymorphism rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR2 | F: CATTGGGTTTCGCATCCAT | AG | 60 | 6 | 6 | 100.0 |
| R: AGACAAGCCTAGGGGAAAGG | ||||||
| SSR9 | F: TGCTCCGAGTTTTAGGGTTC | AG | 60 | 8 | 7 | 87.5 |
| R: GCAGTTGGTAAAGTTGAGAGACG | ||||||
| SSR10 | F: GCTTCCTATTGTGTTGCCTGA | AT | 58 | 5 | 4 | 80.0 |
| R: ACTTTGGGTTTCGGGAATTG | ||||||
| SSR11 | F: CAGCTGAAATAAGAGAGTGATTGG | AG | 57 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: CCCTCTTTTTCTCCTCCGAGT | ||||||
| SSR13 | F: GCGGAATCCATTGTTTTTCA | AC | 58 | 9 | 8 | 88.9 |
| R: CCGATGGAGTATAGTCACGCAAA | ||||||
| SSR15 | F: GCTTGTTGATCAGCTTTCTTTG | AT | 57 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: TGGATCATAACCTTGCTAATGC | ||||||
| SSR36 | F: ATGAACCACATGTCGGAGGA | AG | 58 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: GGGGATCCAAACGAAGTGTA | ||||||
| SSR54 | F: CGGCTGGTATGCTTACAAAGAT | AC | 58 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: GCACTTCCACTGTTTTTAACTTCC | ||||||
| SSR55 | F: CACCTACATAGGCAGCCAAAA | AG | 58 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: ATTTGTGGGCGGAGGAAG | ||||||
| SSR57 | F: AGTGAAAAGCAGCCCATTCT | AT | 56 | 9 | 8 | 88.9 |
| R: GGCGAAGCTGAATTGAAAAA | ||||||
| SSR67 | F: GCTTCTGTTCCATTATTCACCA | AG | 56 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| R: GCAGTGTGGGATCAATCAAT | ||||||
| SSR68 | F: GAAGCAAACAACTACACCCAAA | AG | 56 | 8 | 8 | 100.0 |
| R: AAGCCTCGGATTTCATAGCA | ||||||
| SSR77 | F: CATACCATAACTCCCCATCTCTC | AG | 57 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: TGCCGATTCTGATTTCTTCC | ||||||
| SSR92 | F: TGGTTTGAGGATCAAGAAAGAA | AAG | 56 | 5 | 4 | 80.0 |
| R: GTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTGG | ||||||
| SSR107 | F: CATCCAACACCAGAAATACGC | AAG | 58 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: TCCAACTTTATCATTTCTTCCAC | ||||||
| SSR110 | F: CACCCATATCCCAATCTTCTTC | CTT | 60 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: GGGTAATTTTCACGGGGAAT | ||||||
| SSR112 | F: CTACGCCTACCACTTGCACA | TCT | 60 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| R: CAGTGGAAGCCTCAAGATCC | ||||||
| SSR118 | F: AATCAAGGGTCAGAAGAAATGG | ATC | 58 | 2 | 2 | 100.0 |
| R: GCAAGAATGGATGTGGGTGT | ||||||
| SSR123 | F: TCAGTGGAGCGCGTATATCT | ATC | 60 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| R: GCGATCTCACCAAACCTCTC | ||||||
| SSR127 | F: TTGGTTTGGCATAACTGCAA | AAT | 58 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: GGTTTGCAACTCTCATGCTG | ||||||
| Average | - | - | - | 5.9 | 5.4 | 90.4 |
| Total | - | - | - | 118 | 107 | - |
Table 2 Amplification results and polymorphism information of 20 simple sequence repeats (SSR) primer pairs
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Repeat type | Tm | No. of loci | Polymorphic loci | Polymorphism rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR2 | F: CATTGGGTTTCGCATCCAT | AG | 60 | 6 | 6 | 100.0 |
| R: AGACAAGCCTAGGGGAAAGG | ||||||
| SSR9 | F: TGCTCCGAGTTTTAGGGTTC | AG | 60 | 8 | 7 | 87.5 |
| R: GCAGTTGGTAAAGTTGAGAGACG | ||||||
| SSR10 | F: GCTTCCTATTGTGTTGCCTGA | AT | 58 | 5 | 4 | 80.0 |
| R: ACTTTGGGTTTCGGGAATTG | ||||||
| SSR11 | F: CAGCTGAAATAAGAGAGTGATTGG | AG | 57 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: CCCTCTTTTTCTCCTCCGAGT | ||||||
| SSR13 | F: GCGGAATCCATTGTTTTTCA | AC | 58 | 9 | 8 | 88.9 |
| R: CCGATGGAGTATAGTCACGCAAA | ||||||
| SSR15 | F: GCTTGTTGATCAGCTTTCTTTG | AT | 57 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: TGGATCATAACCTTGCTAATGC | ||||||
| SSR36 | F: ATGAACCACATGTCGGAGGA | AG | 58 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: GGGGATCCAAACGAAGTGTA | ||||||
| SSR54 | F: CGGCTGGTATGCTTACAAAGAT | AC | 58 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: GCACTTCCACTGTTTTTAACTTCC | ||||||
| SSR55 | F: CACCTACATAGGCAGCCAAAA | AG | 58 | 7 | 6 | 85.7 |
| R: ATTTGTGGGCGGAGGAAG | ||||||
| SSR57 | F: AGTGAAAAGCAGCCCATTCT | AT | 56 | 9 | 8 | 88.9 |
| R: GGCGAAGCTGAATTGAAAAA | ||||||
| SSR67 | F: GCTTCTGTTCCATTATTCACCA | AG | 56 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| R: GCAGTGTGGGATCAATCAAT | ||||||
| SSR68 | F: GAAGCAAACAACTACACCCAAA | AG | 56 | 8 | 8 | 100.0 |
| R: AAGCCTCGGATTTCATAGCA | ||||||
| SSR77 | F: CATACCATAACTCCCCATCTCTC | AG | 57 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: TGCCGATTCTGATTTCTTCC | ||||||
| SSR92 | F: TGGTTTGAGGATCAAGAAAGAA | AAG | 56 | 5 | 4 | 80.0 |
| R: GTGGTATCAACGCAGAGTGG | ||||||
| SSR107 | F: CATCCAACACCAGAAATACGC | AAG | 58 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: TCCAACTTTATCATTTCTTCCAC | ||||||
| SSR110 | F: CACCCATATCCCAATCTTCTTC | CTT | 60 | 4 | 4 | 100.0 |
| R: GGGTAATTTTCACGGGGAAT | ||||||
| SSR112 | F: CTACGCCTACCACTTGCACA | TCT | 60 | 11 | 11 | 100.0 |
| R: CAGTGGAAGCCTCAAGATCC | ||||||
| SSR118 | F: AATCAAGGGTCAGAAGAAATGG | ATC | 58 | 2 | 2 | 100.0 |
| R: GCAAGAATGGATGTGGGTGT | ||||||
| SSR123 | F: TCAGTGGAGCGCGTATATCT | ATC | 60 | 5 | 5 | 100.0 |
| R: GCGATCTCACCAAACCTCTC | ||||||
| SSR127 | F: TTGGTTTGGCATAACTGCAA | AAT | 58 | 4 | 3 | 75.0 |
| R: GGTTTGCAACTCTCATGCTG | ||||||
| Average | - | - | - | 5.9 | 5.4 | 90.4 |
| Total | - | - | - | 118 | 107 | - |
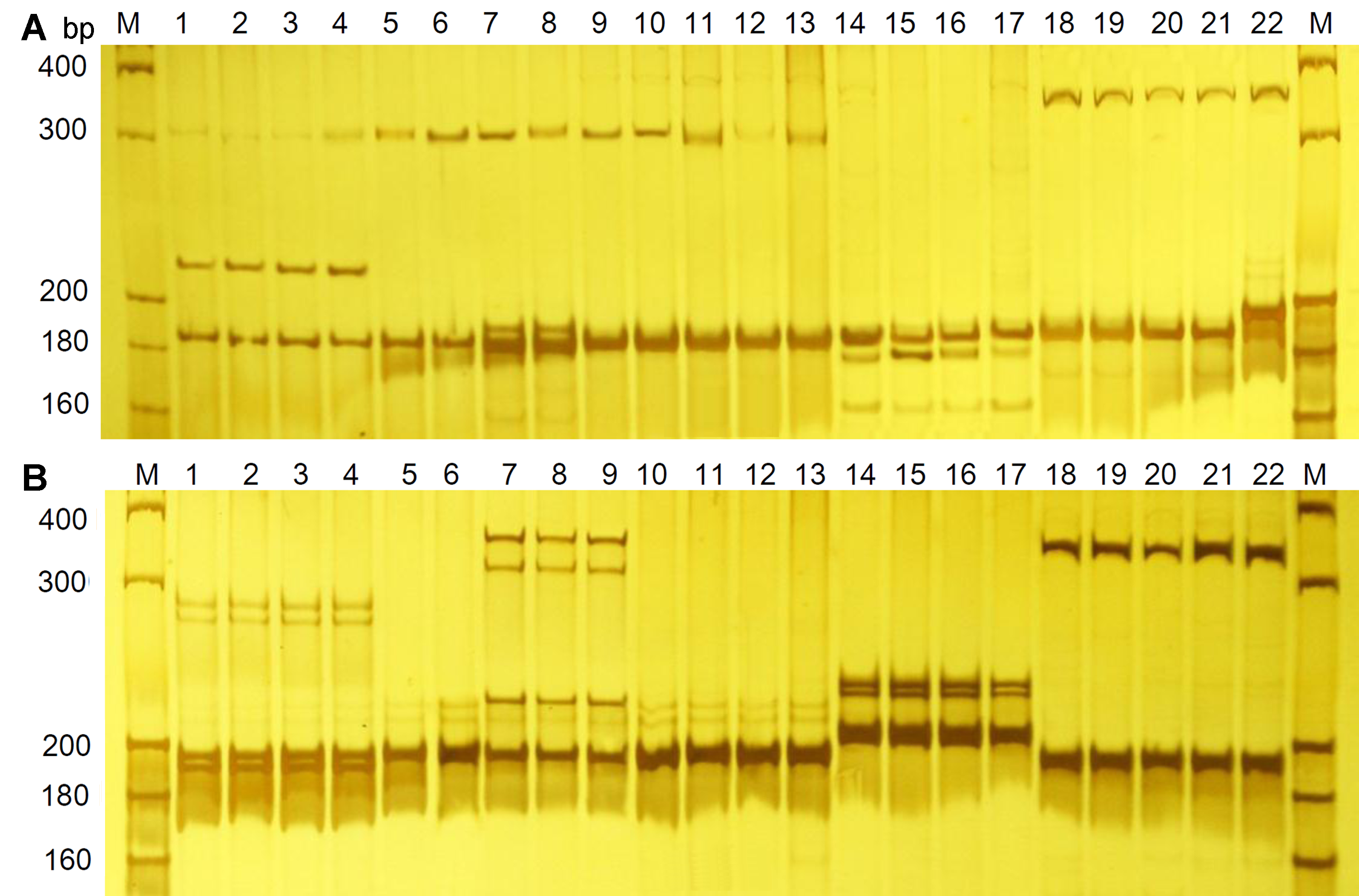
Figure 1 Amplification profile of primer SSR55 (A) and SSR112 (B) in Physalis samplesM: DNA molecular standards. Lane 1-22: The 22 Physalis samples (sample number is the same as in Table 1).
| Measurement | Similarity coefficient |
|---|---|
| Average interspecies genetic similarity coefficient | 0.501±0.074 |
| P. angulata vs P. minima | 0.600±0.042 |
| P. alkekengi var. francheti vs P. minima | 0.437±0.036 |
| P. pubescens vs P. minima | 0.570±0.037 |
| P. angulata vs P. alkekengi var. francheti | 0.444±0.044 |
| P. angulata vs P. pubescens | 0.514±0.043 |
| P. pubescens vs P. alkekengi var. francheti | 0.382±0.040 |
Table 3 Average interspecies genetic similarity coefficient in Physalis samples
| Measurement | Similarity coefficient |
|---|---|
| Average interspecies genetic similarity coefficient | 0.501±0.074 |
| P. angulata vs P. minima | 0.600±0.042 |
| P. alkekengi var. francheti vs P. minima | 0.437±0.036 |
| P. pubescens vs P. minima | 0.570±0.037 |
| P. angulata vs P. alkekengi var. francheti | 0.444±0.044 |
| P. angulata vs P. pubescens | 0.514±0.043 |
| P. pubescens vs P. alkekengi var. francheti | 0.382±0.040 |
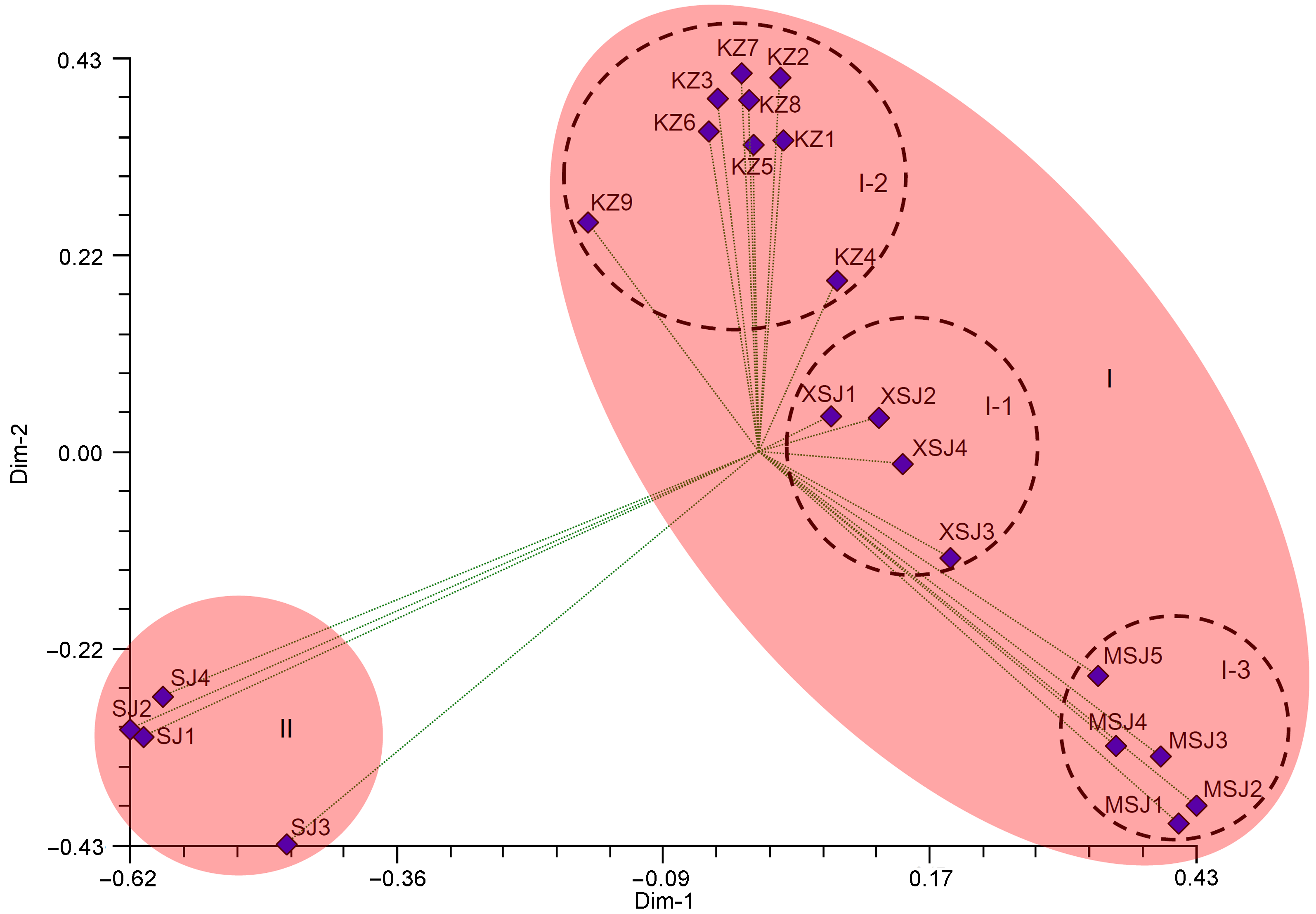
Figure 3 The analysis of PCoA for 22 Physalis samples based on simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers along the first two principal axesThe codes are the same as in Table 1.
| [1] | 国家药典委员会 (2015). 中华人民共和国药典(一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社. pp. 360-361. |
| [2] | 郭瑜, 吴东栋, 任志远, 王晓闻, 郭峰 (2017). 酸浆悬浮饮料的研制. 食品研究与开发 38(15), 89-92. |
| [3] | 贾远敏, 陈重, 许琼明, 李笑然, 杨世林 (2013). 毛酸浆浆果的化学成分研究. 中草药 9, 1086-1090. |
| [4] | 李晓岚, 陆嘉惠, 谢良碧, 张爱霞, 陈晓翠, 李学禹 (2015). 4种甘草属植物EST-SSR引物开发及其亲缘关系分析. 西北植物学报 35, 480-485. |
| [5] | 骆丽萍, 成凡钦, 季龙, 虞和永 (2015). 毛酸浆的化学成分研究. 中国中药杂志 22, 4424-4427. |
| [6] | 孙海涛, 高玉超 (2013). 毛酸浆番茄复合调味酱的研制. 中国调味品 38(12), 58-59, 67. |
| [7] | 王晓英, 刘长姣, 段连海, 霍岩 (2014). 毛酸浆开发利用的研究进展. 中国酿造 2, 5-8. |
| [8] | 王赢, 朱丹, 牛广财, 郑唯, 魏文毅, 刘鑫 (2017). 毛酸浆发酵果脯的研制. 中国酿造 36(8), 182-185. |
| [9] | 许亮, 王荣祥, 杨燕云, 王冰 (2009). 中国酸浆属植物药用资源研究. 中国野生植物资源 28, 21-23. |
| [10] | 杨金颖, 杨德草, 李津津 (2014). 酸浆的药理作用研究进展. 内蒙古中医药 33(25), 116-117. |
| [11] | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1978). 中国植物志(第67卷). 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 50. |
| [12] | Axelius B (1996). The phylogenetic relationships of the physaloid genera (Solanaceae) based on morphological data.Am J Bot 83, 118-124. |
| [13] | Ding H, Hu ZJ, Yu LY, Ma ZY, Ma XQ, Chen Z, Wang D, Zhao XF (2014). Induction of quinone reductase (QR) by withanolides isolated from Physalis angulata L. var. villosa Bonati (Solanaceae). Steroids 86, 32-38. |
| [14] | Feng SG, He RF, Lu JJ, Jiang MY, Shen XY, Jiang Y, Wang ZA, Wang HZ (2016a). Development of SSR markers and assessment of genetic diversity in medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivars. Front Genet 7, 113. |
| [15] | Feng SG, Jiang MY, Shi YJ, Jiao KL, Shen CJ, Lu JJ, Ying QC, Wang HZ (2016b). Application of the ribosomal DNA ITS2 region of Physalis ( Solanaceae): DNA barcoding and phylogenetic study. Front Plant Sci 7, 1047. |
| [16] | Feng SG, Jiao KL, Zhu YJ, Wang HF, Jiang MY, Wang HZ (2018). Molecular identification of species of Physalis ( Solanaceae) using a candidate DNA barcode: the chloroplast psbA-trnH intergenic region. Genome 61, 15-20. |
| [17] | Fu N, Wang PY, Liu XD, Shen HL (2014). Use of EST-SSR markers for evaluating genetic diversity and fingerprinting celery (Apium graveolens L.) cultivars. Molecules 19, 1939-1955. |
| [18] | Garzon-Martínez GA, Osorio-Guarín JA, Delgádillo-Duran P, Mayorga F, Enciso-Rodríguez FE, Landsman D, Mariño-Ramírez L, Barrero LS (2015). Genetic diversity and population structure in Physalis peruviana and related taxa based on InDels and SNPs derived from COSII and IRG markers. Plant Gene 4, 29-37. |
| [19] | Gower JC (1966). Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis.Biometrika 53, 325-338. |
| [20] | Ji L, Yuan YL, Ma ZJ, Chen Z, Gan LS, Ma XQ, Huang DS (2013). Induction of quinone reductase (QR) by withanolides isolated from Physalis pubescens L. ( Solanaceae). Steroids 78, 860-865. |
| [21] | Li X, Zhao JP, Yang M, Liu YL, Li ZC, Li RY, Li XR, Li N, Xu QM, Khan IA, Yang SL (2014). Physalins and withanolides from the fruits ofPhysalis alkekengi L. var. fran- chetii ( Mast.) Makino and the inhibitory activities against human tumor cells. Phytochem Lett 10, 95-100. |
| [22] | Maggie WPS, Manos PS (2005). Untangling Physalis ( Solanaceae) from the physaloids: a two-gene phylogeny of the Physalinae. Syst Bot 30, 216-230. |
| [23] | Nei M, Li WH (1979). Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76, 5269-5273. |
| [24] | Olmstead RG, Bohs L, Migid HA, Santiago-Valentin E, Garcia VF, Collier SM (2008). A molecular phylogeny of the Solanaceae.Taxon 57, 1159-1181. |
| [25] | Rohlf FJ (2000). NTSYS-PC: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.00. Setauket, New York:Exeter Software. |
| [26] | Simbaqueba J, Sánchez P, Sanchez E, Zarantes VMN, Chacon MI, Barrero LS, Mariño-Ramírez L (2011). Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for the cape gooseberry Physalis peruviana. PLoS One 6, e26719. |
| [27] | Sun CP, Nie XF, Kang N, Zhao F, Chen LX, Qiu F (2017). A new phenol glycoside from Physalis angulata. Nat Prod Res 31, 1059-1065. |
| [28] | Teshome A, Bryngelsson T, Dagne K, Geleta M (2015). Assessment of genetic diversity in Ethiopian field pea ( Pisum sativum L.) accessions with newly developed EST- SSR markers. BMC Genet 16, 102. |
| [29] | Wang F, Yang T, Burlyaeva M, Li L, Jiang JY, Fang L, Redden R, Zong XX (2015). Genetic diversity of grasspea and its relative species revealed by SSR markers.PLoS One 10, e0118542. |
| [30] | Wei JL, Hu XR, Yang JJ, Yang WC (2012). Identification of single-copy orthologous genes between Physalis and Solanum lycopersicum and analysis of genetic diversity in Physalis using molecular markers. PLoS One 7, e50164. |
| [31] | Xu XM, Guan YZ, Shan SM, Luo JG, Kong LY (2016). Withaphysalin-type withanolides from Physalis minima. Phytochem Lett 15, 1-6. |
| [32] | Yang YK, Xie SD, Xu WX, Nian Y, Liu XL, Peng XR, Ding ZT, Qiu MH (2016). Six new physalins from Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. Fitoterapia 112, 144-152. |
| [33] | Zamora-Tavares P, Vargas-Ponce O, Sanchez-Martínez J, Cabrera-Toledo D (2015). Diversity and genetic structure of the husk tomato ( Physalis philadelphica Lam.) in Wes- tern Mexico. Genet Res Crop Evol 62, 141-153. |
| [34] | Zhang WN, Tong WY (2016). Chemical constituents and biological activities of plants from the genus Physalis. Chem Biodivers 13, 48-65. |
| [1] | Chuanyong Wang, Dian Zhuang, Zhengda Song, Henghua Zhai, Naiwei Li, Fan Zhang. Structural and Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genome and Phylogenetic Inference of the Aronia melanocarpa [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | XU Hao, LIU Ming-Guo, DONG Sheng-Jun, WU Yue-Liang, ZHANG Hao-Kai. Diversity and geographical variations of germplasm resources of Armeniaca mandshurica [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2019, 43(7): 585-600. |
| [3] | Jieli He,Tiantian Shi,Ling Chen,Haigang Wang,Zhijun Gao,Meihong Yang,Ruiyun Wang,Zhijun Qiao. The Genetic Diversity of Common Millet (Panicum miliaceum) Germplasm Resources Based on the EST-SSR Markers [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 723-732. |
| [4] | Jing Zhang, Yuan Li, Na Song, Longshan Lin, Tianxiang Gao. Species identification and phylogenetic relationship of Thryssa species in the coastal waters of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(8): 888-895. |
| [5] | Xiao Luo, Feng Li, Jing Chen, Zhigang Jiang. The taxonomic status of badgers in the Qinghai Lake area and evolutionary history of Meles [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 694-700. |
| [6] | Yani Hu, Zongwen Zhang, Bin Wu, Jia Gao, Yanqin Li. Genetic relationships of buckwheat species based on the sequence analysis of ITS and ndhF-rpl32 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(3): 296-303. |
| [7] | Qi Guo, Dalong Guo, Lili Guo, Lin Zhang, Xiaogai Hou. Application of Simple Sequence Repeat Molecular Markers in the Study of Tree Peony [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(5): 652-664. |
| [8] | Gangbiao Xu,Yan Liang,Yan Jiang,Xiongsheng Liu,Shangli Hu,Yufei Xiao,Bobo Hao. Genetic diversity and population structure of Bretschneidera sinensis, an endangered species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 723-731. |
| [9] | Weimin Li, Sifeng Li, Bin Li. Genetic Diversity in Natural Populations of Abies chensiensis Based on Nuclear Simple Sequence Repeat Markers [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(4): 413-421. |
| [10] | Xiaohong He, Xiuli Han, Weijun Guan, Kechuan Tian, Wenbin Zhang, Yuehui Ma. Genetic variability and relationship of 10 Bactrian camel populations revealed by microsatellite markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(2): 199-206. |
| [11] | Hongmei Sun, Xiumei Xing, Min Rong, Bo Cong. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of rabbit breeds based on microsatellite DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(5): 492-497. |
| [12] | Xinjun Liao, Hong Chang, Guixiang Zhang, Donglei Wang, Weitao Song, Xu Han, Zifu Zhang. Genetic diversity of five native Chinese yak breeds based on microsatellite DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2008, 16(2): 156-165. |
| [13] | Lubin Li;Xiaojun Guo;Zhenhua Peng;Guanshui Liu;Hongshui Yuan;Baocheng Zhu;Kai Yang*. Effect of the Quantity of AFLP Primer Combinations on Accurately Identifying Bamboo Genetic Relationships [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(04): 449-454. |
| [14] | Ran Di, Xiaohong He, Jianlin Han, Weijun Guan, Yabin Pu, Qianjun Zhao, Baoling Fu, Yuehui Ma. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of Chinese cashmere goats based on microsatellite DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2007, 15(5): 470-478. |
| [15] | Yongfa Luo, Zhigang Wang, Jiaqi Li, Guixiang Zhang, Yaosheng Chen, Yong Liang, Fuqing Yu, Weitao Song, Zifu Zhang . Genetic variation and genetic relationship among 13 Chinese and intro-duced cattle breeds using microsatellite DNA markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2006, 14(6): 498-507. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||