

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 659-670.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23112 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23112
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yaqi Zhang1,2, Fuxi Rong2, Yuxin Shen2, Zheyuan Hong1,2, Lantian Zhang1,2, Liang Wu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-17
Accepted:2023-11-02
Online:2024-07-10
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
*E-mail: liangwu@zju.edu.cn
Yaqi Zhang, Fuxi Rong, Yuxin Shen, Zheyuan Hong, Lantian Zhang, Liang Wu. Research Advances of Structure and Function of HIPP Family in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 659-670.
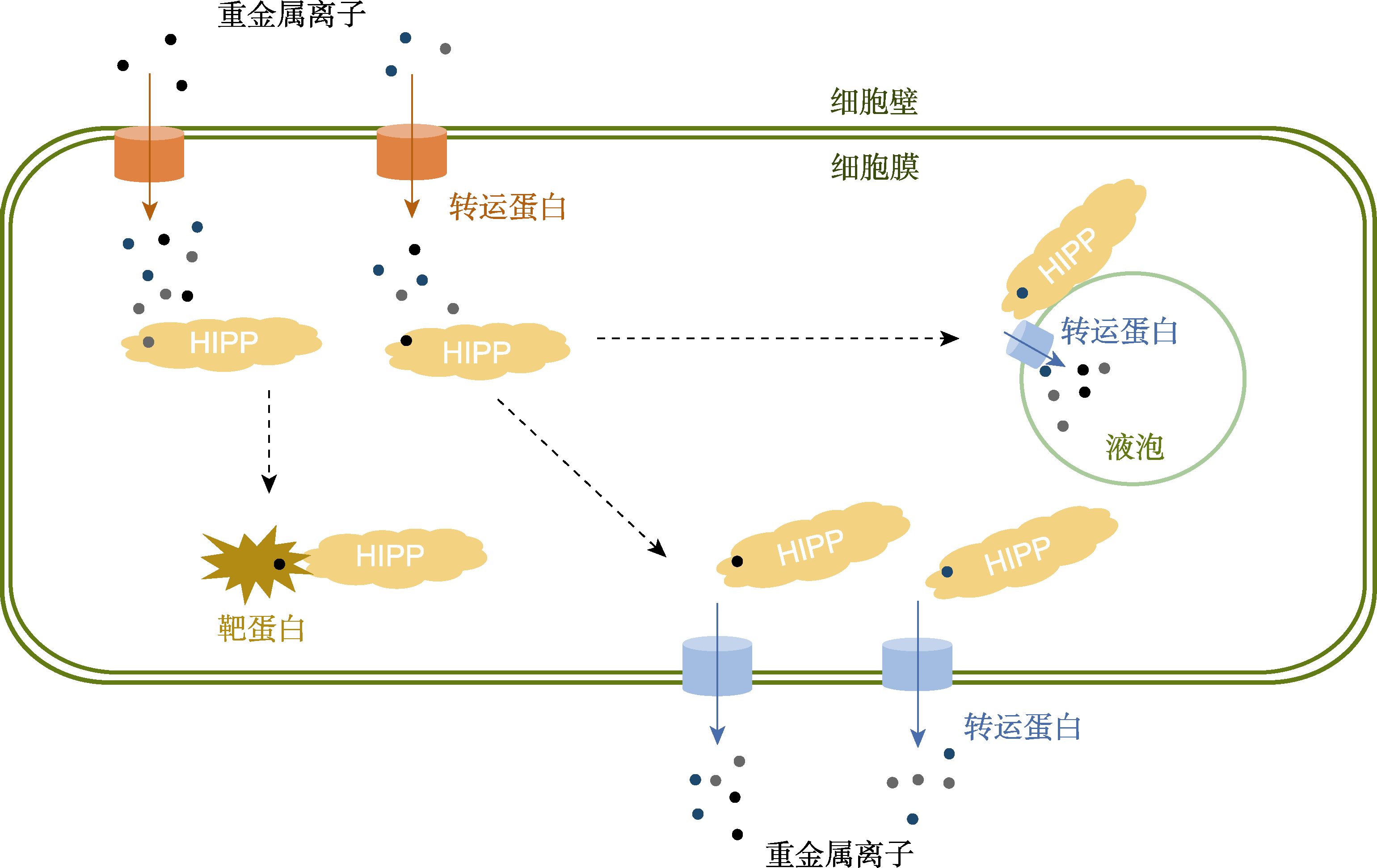
Figure 2 HIPPs are involved in the metal homeostasis regulation in plant cells Heavy metal ions enter the cells by metal transporters (such as ZIPs, and HMAs), which are actively chelated by HIPPs in the cytoplasm and then subsequently transported into target proteins. For excess or toxic metal ions, on the one hand, they can be actively transferred by HIPPs to the plasma membrane efflux transporters; on the other hand, they can be also isolated into the vacuole via vacuole membrane transporters (such as HMAs).
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHIPP07 | 结合Cu2+、Ni2+和Zn2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Dykema et al., |
| AtHIPP06 | 结合Cu2+和Hg2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Suzuki et al., | |
| AtHIPP26 | 结合Pb2+、Cd2+和Cu2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Gao et al., | |
| AtHIPP20/21/22 | 突变体植株对镉敏感 | Tehseen et al., | |
| AtHIPP27 | 增强酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Zhao et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | OsHIPP42 | 耐受镉胁迫 | Khan et al., |
| OsHIPP28 OsHIPP34 OsHIPP60 | 响应Zn2+和Fe2+诱导表达 | Khan et al., | |
| OsHIPP29 | 耐受镉和锌胁迫 | Zhang et al., | |
| OsHIPP24 | 结合Cd2+和Cu2+; 酵母异源表达体系耐受镉胁迫 | Chen and Xiong, | |
| OsHIPP56 | 耐受镉和锌胁迫 | Zhao et al., | |
| OsHIPP16 | 耐受镉胁迫 | Cao et al., | |
| OsHIPP33 | 维持水稻植株锌和铁稳态 | Cao et al., | |
| OsHIPP9 | 结合Cd2+和Cu2+; 增强酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Xiong et al., | |
| OsHIPP17 | 降低酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Shi et al., | |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | TaHIPP1 | 增强酵母盐胁迫和铜胁迫的耐受性 | Zhang et al., |
Table 1 Functions of HIPPs in maintaining heavy metal homeostasis and detoxification in plants
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHIPP07 | 结合Cu2+、Ni2+和Zn2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Dykema et al., |
| AtHIPP06 | 结合Cu2+和Hg2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Suzuki et al., | |
| AtHIPP26 | 结合Pb2+、Cd2+和Cu2+; 耐受镉胁迫 | Gao et al., | |
| AtHIPP20/21/22 | 突变体植株对镉敏感 | Tehseen et al., | |
| AtHIPP27 | 增强酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Zhao et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | OsHIPP42 | 耐受镉胁迫 | Khan et al., |
| OsHIPP28 OsHIPP34 OsHIPP60 | 响应Zn2+和Fe2+诱导表达 | Khan et al., | |
| OsHIPP29 | 耐受镉和锌胁迫 | Zhang et al., | |
| OsHIPP24 | 结合Cd2+和Cu2+; 酵母异源表达体系耐受镉胁迫 | Chen and Xiong, | |
| OsHIPP56 | 耐受镉和锌胁迫 | Zhao et al., | |
| OsHIPP16 | 耐受镉胁迫 | Cao et al., | |
| OsHIPP33 | 维持水稻植株锌和铁稳态 | Cao et al., | |
| OsHIPP9 | 结合Cd2+和Cu2+; 增强酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Xiong et al., | |
| OsHIPP17 | 降低酵母镉胁迫的耐受性 | Shi et al., | |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | TaHIPP1 | 增强酵母盐胁迫和铜胁迫的耐受性 | Zhang et al., |
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHIPP26 | 对干旱、盐和冷害胁迫转录响应; 与干旱胁迫相关转录因子AtHB29互作 | Barth et al., |
| AtHIPP03 | 调控水杨酸依赖的病原菌应答途径 | Zschiesche et al., | |
| AtHIPP01 | 触发细胞分裂素氧化/脱氢酶CKX1的降解 | Guo et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | OsHIPP09 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., |
| OsHIPP23 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP40 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP11 OsHIPP45 | 对冷害胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP41 | 对干旱和冷害胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP05 | 促进水稻体内稻瘟病菌生长 | Fukuoka et al., | |
| OsHIPP04 | 与寄生线虫效应蛋白MgMO289互作, 抑制植物免疫 | Song et al., | |
| OsHIPP19 | 与稻瘟病菌效应蛋白AVR-Pik的所有变体互作, 激活植物免疫 | Maidment et al., | |
| 大麦 (Hordeum vulgare) | HvFP1 | 对干旱、盐和冷害胁迫转录响应 | Barth et al., |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | TaHIPP1 | 对干旱、低温、强光、脱落酸胁迫和叶片衰老转录响应 | Zhang et al., |
| 葡萄 (Vitis vinifera) | VvHIPP21 | 降低植株对低温和干旱胁迫的耐受性 | Zheng et al., |
| 藜麦 (Chenopodium quinoa) | CqHIPP34 | 提高藜麦的耐旱性 | Sun et al., |
Table 2 Roles of identified HIPPs in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stress
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHIPP26 | 对干旱、盐和冷害胁迫转录响应; 与干旱胁迫相关转录因子AtHB29互作 | Barth et al., |
| AtHIPP03 | 调控水杨酸依赖的病原菌应答途径 | Zschiesche et al., | |
| AtHIPP01 | 触发细胞分裂素氧化/脱氢酶CKX1的降解 | Guo et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | OsHIPP09 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., |
| OsHIPP23 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP40 | 对干旱胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP11 OsHIPP45 | 对冷害胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP41 | 对干旱和冷害胁迫转录响应 | De Abreu-Neto et al., | |
| OsHIPP05 | 促进水稻体内稻瘟病菌生长 | Fukuoka et al., | |
| OsHIPP04 | 与寄生线虫效应蛋白MgMO289互作, 抑制植物免疫 | Song et al., | |
| OsHIPP19 | 与稻瘟病菌效应蛋白AVR-Pik的所有变体互作, 激活植物免疫 | Maidment et al., | |
| 大麦 (Hordeum vulgare) | HvFP1 | 对干旱、盐和冷害胁迫转录响应 | Barth et al., |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | TaHIPP1 | 对干旱、低温、强光、脱落酸胁迫和叶片衰老转录响应 | Zhang et al., |
| 葡萄 (Vitis vinifera) | VvHIPP21 | 降低植株对低温和干旱胁迫的耐受性 | Zheng et al., |
| 藜麦 (Chenopodium quinoa) | CqHIPP34 | 提高藜麦的耐旱性 | Sun et al., |

Figure 3 A working model of HIPP proteins in biotic and abiotic stress tolerance in plants The expressions of some HIPPs could be affected by environmental stress stimuli (such as light, drought, cold, salt and pathogen attack). Under abiotic stresses, HIPPs interact with target proteins to activate downstream signaling, such as drought/cold responses and salicylic acid synthesis pathway thereby to enhance plant resistance or tolerance. By contrast, in some biotic stresses, a couple of HIPPs with target proteins have been shown to play negative roles in plant immunity via protein-protein interactions.
| [1] | Abreu ME, Munné-Bosch S (2009). Salicylic acid deficiency in NahG transgenic lines and sid2 mutants increases seed yield in the annual plant Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 60, 1261-1271. |
| [2] | An TT, Huang D, Wang H, Zhang Y, Chen YL (2021). Research advances in plant physiological and biochemical mechanisms in response to cadmium stress. Chin Bull Bot 56, 347-362. (in Chinese) |
| 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 347-362. | |
| [3] |
Andrés-Colás N, Sancenón V, Rodríguez-Navarro S, Mayo S, Thiele DJ, Ecker JR, Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2006). The Arabidopsis heavy metal P-type ATPase HMA5 interacts with metallochaperones and functions in copper detoxification of roots. Plant J 45, 225-236.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M (2008). Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance. Genetics 180, 2267-2276.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Barth O, Vogt S, Uhlemann R, Zschiesche W, Humbeck K (2009). Stress induced and nuclear localized HIPP26 from Arabidopsis thaliana interacts via its heavy metal associated domain with the drought stress related zinc finger transcription factor ATHB29. Plant Mol Biol 69, 213-226.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Barth O, Zschiesche W, Siersleben S, Humbeck K (2004). Isolation of a novel barley cDNA encoding a nuclear protein involved in stress response and leaf senescence. Physiol Plant 121, 282-293.
PMID |
| [7] |
Berner N, Reutter KR, Wolf DH (2018). Protein quality control of the endoplasmic reticulum and ubiquitin-proteasome-triggered degradation of aberrant proteins: yeast pioneers the path. Annu Rev Biochem 87, 751-782.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Cao HW, Li C, Zhang BQ, Rono JK, Yang ZM (2022a). A metallochaperone HIPP33 is required for rice zinc and iron homeostasis and productivity. Agronomy 12, 488. |
| [9] | Cao HW, Zhao YN, Liu XS, Rono JK, Yang ZM (2022b). A metal chaperone OsHIPP16 detoxifies cadmium by repressing its accumulation in rice crops. Environ Pollut 311, 120058. |
| [10] | Chen GQ, Xiong S (2021). OsHIPP24 is a copper metallochaperone which affects rice growth. J Plant Biol 64, 145- 153. |
| [11] |
Clemens S (2006). Toxic metal accumulation, responses to exposure and mechanisms of tolerance in plants. Biochimie 88, 1707-1719.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Crowell DN (2000). Functional implications of protein isoprenylation in plants. Prog Lipid Res 39, 393-408.
PMID |
| [13] | Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001). Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411, 826- 833. |
| [14] |
De Abreu-Neto JB, Turchetto-Zolet AC, Bodanese Zanettini MH, Margis-Pinheiro M (2013). Heavy metal-associated isoprenylated plant protein (HIPP): characterization of a family of proteins exclusive to plants. FEBS J 280, 1604-1616.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Dykema PE, Sipes PR, Marie A, Biermann BJ, Crowell DN, Randall SK (1999). A new class of proteins capable of binding transition metals. Plant Mol Biol 41, 139-150.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Feng SJ, Liu XS, Ma LY, Khan IU, Rono JK, Yang ZM (2020). Identification of epigenetic mechanisms in paddy crop associated with lowering environmentally related cadmium risks to food safety. Environ Pollut 256, 113464. |
| [17] | Feng SJ, Liu XS, Tao H, Tan SK, Chu SS, Oono Y, Zhang XD, Chen J, Yang ZM (2016). Variation of DNA methylation patterns associated with gene expression in rice (Oryza sativa) exposed to cadmium. Plant Cell Environ 39, 2629-2649. |
| [18] | Fukuoka S, Okuno K (2001). QTL analysis and mapping of pi21, a recessive gene for field resistance to rice blast in Japanese upland rice. Theor Appl Genet 103, 185-190. |
| [19] |
Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Yano M (2009). Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 325, 998-1001.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Gao W, Xiao S, Li HY, Tsao SW, Chye ML (2009). Arabidopsis thaliana acyl-CoA-binding protein ACBP2 interacts with heavy-metal-binding farnesylated protein AtFP6. New Phytol 181, 89-102. |
| [21] | Guo TQ, Weber H, Niemann MCE, Theisl L, Leonte G, Novák O, Werner T (2021). Arabidopsis HIPP proteins regulate endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of CKX proteins and cytokinin responses. Mol Plant 14, 1918-1934. |
| [22] | Hu YA, Cheng HF, Tao S (2016). The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review. Environ Int 92-93, 515-532. |
| [23] |
Huffman DL, O’Halloran TV (2001). Function, structure, and mechanism of intracellular copper trafficking proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 70, 677-701.
PMID |
| [24] |
Hung IH, Casareno RLB, Labesse G, Mathews FS, Gitlin JD (1998). HAH1 is a copper-binding protein with distinct amino acid residues mediating copper homeostasis and antioxidant defense. J Biol Chem 273, 1749-1754.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329. |
| [26] | Jones JDG, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016). Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354, aaf6395. |
| [27] | Kanzaki H, Yoshida K, Saitoh H, Fujisaki K, Hirabuchi A, Alaux L, Fournier E, Tharreau D, Terauchi R (2012). Arms race co-evolution of Magnaporthe oryzae AVR-Pik and rice Pik genes driven by their physical interactions. Plant J 72, 894-907. |
| [28] | Khan IU, Rono JK, Liu XS, Feng SJ, Li H, Chen X, Yang ZM (2020). Functional characterization of a new metallochaperone for reducing cadmium concentration in rice crop. J Clean Prod 272, 123152. |
| [29] |
Khan IU, Rono JK, Zhang BQ, Liu XS, Wang MQ, Wang LL, Wu XC, Chen X, Cao HW, Yang ZM (2019). Identification of novel rice (Oryza sativa) HPP and HIPP genes tolerant to heavy metal toxicity. Ecotox Environ Safe 175, 8-18.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Komárek M, Vaněk A, Ettler V (2013). Chemical stabiliza-tion of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides-a review. Environ Pollut 172, 9-22. |
| [31] |
Lee S, Kim YY, Lee Y, An G (2007). Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol 145, 831-842.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Li H, Luo N, Li YW, Cai QY, Li HY, Mo CH, Wong MH (2017). Cadmium in rice: transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ Pollut 224, 622-630.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Liu H, Zhao HX, Wu LH, Liu AN, Zhao FJ, Xu WZ (2017). Heavy metal ATPase 3 (HMA3) confers cadmium hyper-tolerance on the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. New Phytol 215, 687-698. |
| [34] | Liu XS, Feng SJ, Zhang BQ, Wang MQ, Cao HW, Rono JK, Chen X, Yang ZM (2019). OsZIP1 functions as a metal efflux transporter limiting excess zinc, copper and cadmium accumulation in rice. BMC Plant Biol 19, 283. |
| [35] | Longya A, Chaipanya C, Franceschetti M, Maidment JHR, Banfield MJ, Jantasuriyarat C (2019). Gene dupli-cation and mutation in the emergence of a novel aggres-sive allele of the AVR-Pik effector in the rice blast fungus. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 32, 740-749. |
| [36] | Maidment JHR, Franceschetti M, Maqbool A, Saitoh H, Jantasuriyarat C, Kamoun S, Terauchi R, Banfield MJ (2021). Multiple variants of the fungal effector AVR-Pik bind the HMA domain of the rice protein OsHIPP19, provi-ding a foundation to engineer plant defense. J Biol Chem 296, 100371. |
| [37] | Maqbool A, Saitoh H, Franceschetti M, Stevenson CEM, Uemura A, Kanzaki H, Kamoun S, Terauchi R, Banfield MJ (2015). Structural basis of pathogen recognition by an integrated HMA domain in a plant NLR immune receptor. eLife 4, e08709. |
| [38] |
Moyroud E, Kusters E, Monniaux M, Koes R, Parcy F (2010). LEAFY blossoms. Trends Plant Sci 15, 346-352.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Muller PAJ, Klomp LWJ (2009). ATOX1: a novel copper- responsive transcription factor in mammals? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41, 1233-1236. |
| [40] | Nakao M, Nakamura R, Kita K, Inukai R, Ishikawa A (2011). Non-host resistance to penetration and hyphal growth of Magnaporthe oryzae in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 1, 171. |
| [41] | Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32, 268-274. |
| [42] |
Pufahl RA, Singer CP, Peariso KL, Lin SJ, Schmidt PJ, Fahrni CJ, Culotta VC, Penner-Hahn JE, O’Halloran TV (1997). Metal ion chaperone function of the soluble Cu(I) receptor Atx1. Science 278, 853-856.
PMID |
| [43] |
Robinson NJ, Winge DR (2010). Copper metallochaperones. Annu Rev Biochem 79, 537-562.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Rodríguez-Concepción M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W (1999). Protein prenylation in plants: old friends and new targets. Plant Mol Biol 39, 865-870.
PMID |
| [45] | Rono JK, Sun D, Yang ZM (2022). Metallochaperones: a critical regulator of metal homeostasis and beyond. Gene 822, 146352. |
| [46] | Rono JK, Wang LL, Wu XC, Cao HW, Zhao YN, Khan IU, Yang ZM (2021). Identification of a new function of metallothionein-like gene OsMT1e for cadmium detoxification and potential phytoremediation. Chemosphere 265, 129136. |
| [47] |
Schmülling T, Werner T, Riefler M, Krupková E, Bartrina Y, Manns I (2003). Structure and function of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes of maize, rice, Arabidopsis and other species. J Plant Res 116, 241-252.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Shi Y, Jiang WJ, Li MY, Jiang N, Huang YY, Wang MT, Du ZY, Chen J, Li JH, Wu LY, Zhong M, Yang J, Huang J (2023). Metallochaperone protein OsHIPP17 regulates the absorption and translocation of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Biol Macromol 116, 125607. |
| [49] | Song HD, Lin BR, Huang QL, Sun LH, Chen JS, Hu LL, Zhuo K, Liao JL (2021). The Meloidogyne graminicola effector MgMO289 targets a novel copper metallochaperone to suppress immunity in rice. J Exp Bot 72, 5638- 5655. |
| [50] |
Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Lepiniec L, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2001). LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes a B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 11806-11811.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Strasser R (2018). Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 147-172.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Sun WJ, Wei JL, Wu GM, Xu HS, Chen Y, Yao M, Zhan JY, Yan J, Wu N, Chen H, Bu TL, Tang ZZ, Li QF (2022). CqZF-HD14 enhances drought tolerance in quinoa seed-lings through interaction with CqHIPP34 and CqNAC79. Plant Sci 323, 111406. |
| [53] | Suzuki N, Yamaguchi Y, Koizumi N, Sano H (2002). Functional characterization of a heavy metal binding pro-tein CdI19 from Arabidopsis. Plant J 32, 165-173. |
| [54] | Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Ogo Y, Senoura T, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H (2012). The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ 35, 1948-1957. |
| [55] | Tehseen M, Cairns N, Sherson S, Cobbett CS (2010). Metallochaperone-like genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Metallomics 2, 556-564. |
| [56] | van der Hoorn RAL, Kamoun S (2008). From guard to decoy: a new model for perception of plant pathogen effe-ctors. Plant Cell 20, 2009-2017. |
| [57] |
Villiers F, Ducruix C, Hugouvieux V, Jarno N, Ezan E, Garin J, Junot C, Bourguignon J (2011). Investigating the plant response to cadmium exposure by proteomic and metabolomic approaches. Proteomics 11, 1650-1663.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Wu WH, Wang L, Zhang S, Li ZK, Zhang Y, Lin F, Pan QH (2014). Stepwise arms race between AvrPik and Pik alle-les in the rice blast pathosystem. Mol Plant Microbe Inte-ract 27, 759-769. |
| [59] |
Wu XD, Rapoport TA (2018). Mechanistic insights into ER-associated protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 53, 22-28.
DOI PMID |
| [60] | Xiong S, Kong XH, Chen GQ, Tian LH, Qian DD, Zhu Z, Qu LQ (2023). Metallochaperone OsHIPP9 is involved in the retention of cadmium and copper in rice. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1946-1961. |
| [61] |
Yalovsky S, Rodrı́guez-Concepción M, Gruissem W (1999). Lipid modifications of proteins-slipping in and out of membranes. Trends Plant Sci 4, 439-445.
PMID |
| [62] | Yoshida K, Saitoh H, Fujisawa S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Tosa Y, Chuma I, Takano Y, Win J, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2009). Association genetics reveals three novel avirulence genes from the rice blast fungal pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell 21, 1573- 1591. |
| [63] | Zhang BQ, Liu XS, Feng SJ, Zhao YN, Wang LL, Rono JK, Li H, Yang ZM (2020). Developing a cadmium resis-tant rice genotype with OsHIPP29 locus for limiting cad-mium accumulation in the paddy crop. Chemosphere 247, 125958. |
| [64] | Zhang X, Feng H, Feng C, Xu H, Huang X, Wang Q, Duan X, Wang X, Wei G, Huang L, Kang Z (2015). Isolation and characterisation of cDNA encoding a wheat heavy metal-associated isoprenylated protein involved in stress responses. Plant Biol 17, 1176-1186. |
| [65] | Zhao JF, Zhou HP, Li XY (2013). Ubiquitin-specific protease16 interacts with a heavy metal associated isopreny-lated plant protein27 and modulates cadmium tolerance. Plant Signal Behav 8, e25680. |
| [66] | Zhao XX, Huang SQ, Tan WB, Xing W, Liu DL (2023). Identification and relative expression profile of HIPPs gene family cadmium stress in sugar beet. Acta Agronomica Sinica 49, 3302-3314. (in Chinese) |
|
赵晓鑫, 黄烁淇, 谭文勃, 兴旺, 刘大丽 (2023). 甜菜HIPPs基因家族鉴定与镉胁迫下的表达分析. 作物学报 49, 3302-3314.
DOI |
|
| [67] | Zhao YN, Wang MQ, Li C, Cao HW, Rono JK, Yang ZM (2022). The metallochaperone OsHIPP56 gene is requi-red for cadmium detoxification in rice crops. Environ Exp Bot 193, 104680. |
| [68] | Zheng QL, Yu QH, Wu N, Yao WK, Li JD, Lv K, Xu WR (2023). A grape VvHOS1-interacting HIPP protein (VvHIPP21) negatively regulates cold and drought stress. En-viron Exp Bot 207, 105203. |
| [69] |
Zschiesche W, Barth O, Daniel K, Böhme S, Rausche J, Humbeck K (2015). The zinc-binding nuclear protein HIPP3 acts as an upstream regulator of the salicylate- dependent plant immunity pathway and of flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 207, 1084-1096.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | HAO Shang-Hua, LUO Meng-Xiang, CAO Hong-Li, ZHANG Sen, WANG Ming-Dao. Effects of Penicillium oxalicum C11 on Rehmannia glutinosa growth and its metabolites analysis [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(6): 809-816. |
| [2] | Chunyan Miao, Mingming Li, Xin Zuo, Ning Ding, Jiafang Du, Juan Li, Zhongyi Zhang, Fengqing Wang. Establishment of CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing System in Rehmannia henryi [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 905-916. |
| [3] | Run Liu, Zhaohui Zhang, Jiachen Shen, Zhihui Wang. Community characteristics of bryophyte in Karst caves and its effect on heavy metal pollution: A case study of Zhijin Cave, Guizhou Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(12): 1277-1288. |
| [4] | Quan CHEN, Ke-Ming MA. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on enrichment of sedimental heavy metals in a mangrove wetland and the underlying mechanisms [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2017, 41(4): 409-417. |
| [5] | Xiaoli Zhang, Ping Li, Caiyun Zhou, Mingxia Chen, Xiting Zhao, Mingjun Li. Growth Characters, Yield and Quality of Virus-free Rehmannia glutinosa Seedlings in the Field [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(4): 474-479. |
| [6] | Yanqing Zhou, Wanshen Wang, Xiangnan Wang, Hongying Duan. Recent Progress in DNA Molecular Markers and Gene Functions of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(5): 665-672. |
| [7] | HUANG Yi, WANG Dong-Wei, CAI Jia-Liang, ZHENG Wei-Shuang. Review of glomalin-related soil protein and its environmental function in the rhizosphere [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2011, 35(2): 232-236. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zhong-Yi, YIN Wen-Jia, LI Juan, DU Jia-Fang, Yang Yan-Hui, CHEN Xin-Jian, LIN Wen-Xiong. Physio-ecological properties of continuous cropping Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2010, 34(5): 547-554. |
| [9] | WANG Ming-Dao, CHEN Hong-Ge, LIU Xin-Yu, GAO Yu-Qian, WU Kun, JIA Xin-Cheng. ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF ALLELOCHEMICALS FROM REHMANNIA GLUTINOSA THAT AFFECT SESAMUM INDICUM [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2009, 33(6): 1191-1198. |
| [10] | LI Jian, MA Jian-Hua, SONG Bo. HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION AND HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT IN THE ROADSIDE SOIL-WHEAT SYSTEM ALONG ZHENGZHOU-KAIFENG HIGH-WAY, CHINA [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2009, 33(3): 624-628. |
| [11] | Zhigang Nie;Yan Wang;Shaoshan Li. Heavy Metal-induced DNA Damage in Arabidopsis thaliana Protoplasts Measured by Single-cell Gel Electrophoresis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(01): 117-123. |
| [12] | Jianmin Ma;Ping Jin;Zhenbin Wu. Absorption and Purification of Heavy Metals by Submerged Macrophytes and Its Mechanism [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(02): 232-239. |
| [13] | Mingjun Li;Xin Xu;Min Xia;Xiaoli Zhang;Jun Liu;Conghua Xie. The Influence of PP333 in Combination with Benzylaminopurine on Growth of Rehmannia glutinosa Plantlets [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2006, 23(1): 56-59. |
| [14] | LUO Chun-Ling SHEN Zhen-Guo. The Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Uptake and Accumulation in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 20(01): 59-66. |
| [15] | WANG Jian-Hong MA Mi. Biological Mechanisms of Phytoremediation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2000, 17(06): 504-510. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||