

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 444-456.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22088 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22088
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhang Mingzhu1, Qin Huaguang1, Mu Dan1, Yang Longyu1, Li Hu1, Qi Zehua1, Wang Yuxi1, Zhang Yongcheng1, Ye Lili1, Yin Wenjing2, Wang Shuyuan1, Rao Yuchun2,*( ), Wu Yan1,*(
), Wu Yan1,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-26
Revised:2022-06-28
Online:2022-07-01
Published:2022-07-14
Contact:
Rao Yuchun,Wu Yan
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Zhang Mingzhu, Qin Huaguang, Mu Dan, Yang Longyu, Li Hu, Qi Zehua, Wang Yuxi, Zhang Yongcheng, Ye Lili, Yin Wenjing, Wang Shuyuan, Rao Yuchun, Wu Yan. Antioxidant Activity of Tea Polysaccharide and Its Protective Mechanism Against Oxidative Damage[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 444-456.
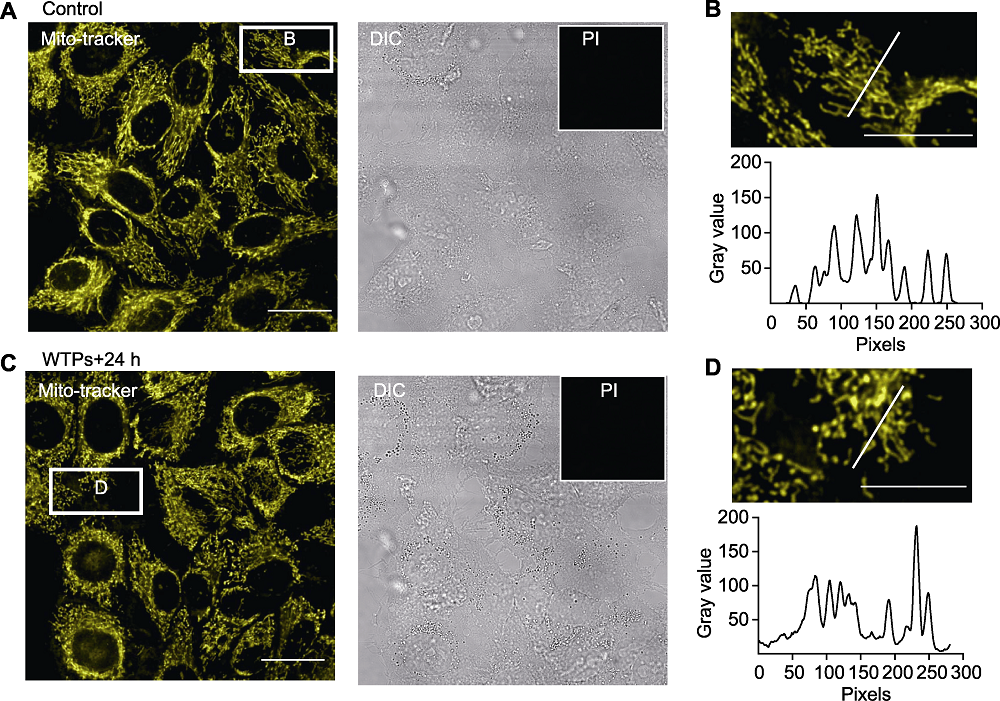
Figure 3 Effects of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on cell physiological state (A) Morphology of mitochondria in control cells; (B) Zoom in micrograph from selected regions from different treated cells and their intensity analysis; (C) Morphology of mitochondria in WTPs incubated cells; (D) Zoom in micrograph from selected regions from different treated cells and their intensity analysis. DIC: Differential interference contrast. Bars=20 μm
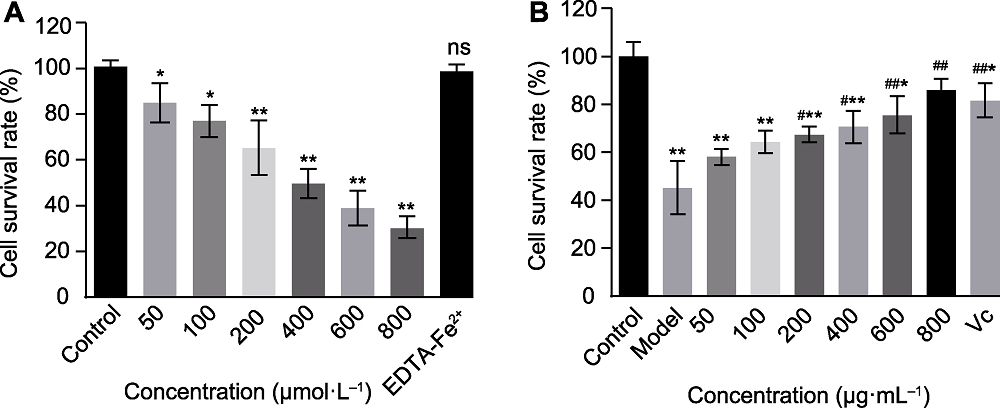
Figure 4 Protective effect of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on demaged cells (A) Effects of different concentrations of exogenous ·OH on the survival rate of HepG-2 cells; (B) Effects of different concentrations of WTPs on HepG-2 cell survival rate induced by ·OH. Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01
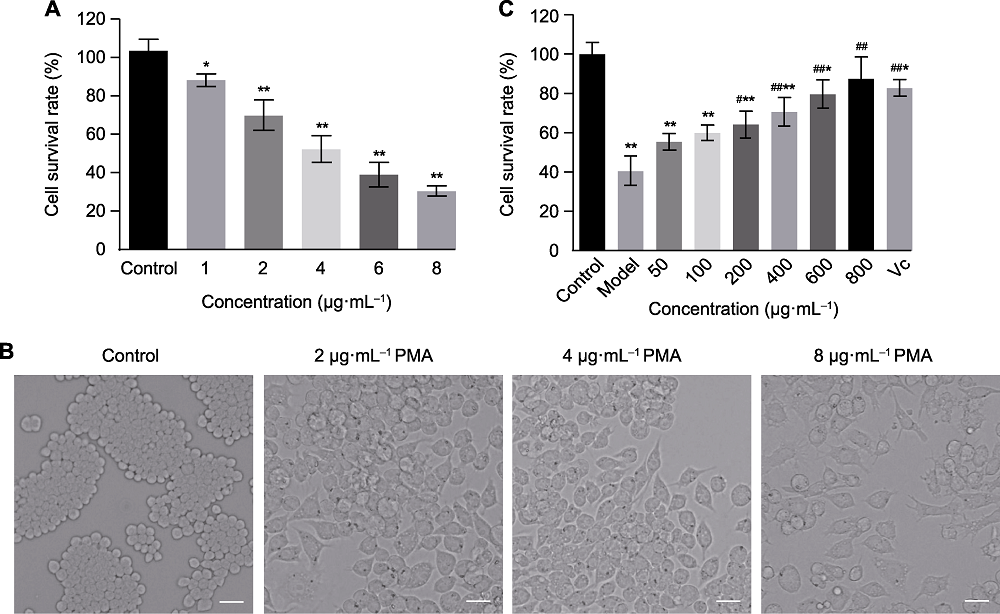
Figure 5 Effect of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on the viability of RAW264.7 cells induced by PMA (A) Effects of endogenous ·OH induced by different concentration of PMA on the survival rate of RAW264.7 cells; (B) The effect of different concentration of PMA on morphological changes of RAW264.7 cells (bars=20 μm); (C) Effects of different concentration of WTPs on RAW264.7 cells survival rate induced by endogenous ·OH. Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01
| Group | GSH-PX | CAT |
|---|---|---|
| (U∙mL-1) | (U∙mL-1) | |
| Control | 0.45±0.08 | 1.08±0.12 |
| Model | 0.13±0.04** | 0.59±0.04** |
| 100 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.16±0.04** | 0.57±0.06** |
| 200 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.15±0.04** | 0.60±0.07** |
| 400 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.12±0.03** | 0.62±0.05** |
| 800 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.13±0.02** | 0.57±0.08** |
Table 1 Effects of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on the content of glutathione reductase (GSH-PX) and catalase (CAT) in oxidation-damaged RAW264.7 cells (means±SD)
| Group | GSH-PX | CAT |
|---|---|---|
| (U∙mL-1) | (U∙mL-1) | |
| Control | 0.45±0.08 | 1.08±0.12 |
| Model | 0.13±0.04** | 0.59±0.04** |
| 100 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.16±0.04** | 0.57±0.06** |
| 200 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.15±0.04** | 0.60±0.07** |
| 400 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.12±0.03** | 0.62±0.05** |
| 800 µg∙mL-1 WTPs | 0.13±0.02** | 0.57±0.08** |
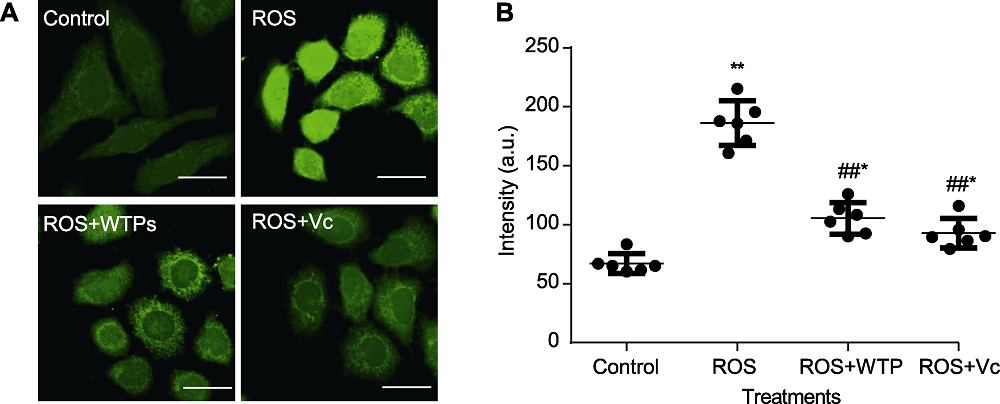
Figure 6 Repair effect of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on oxidative damage of HepG-2 cells (A) Confocal imaging of ·OH content in cells of different treatment groups (bars=20 μm); (B) Comparison of fluorescence intensity of ·OH in cells of different treatment groups. Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01.
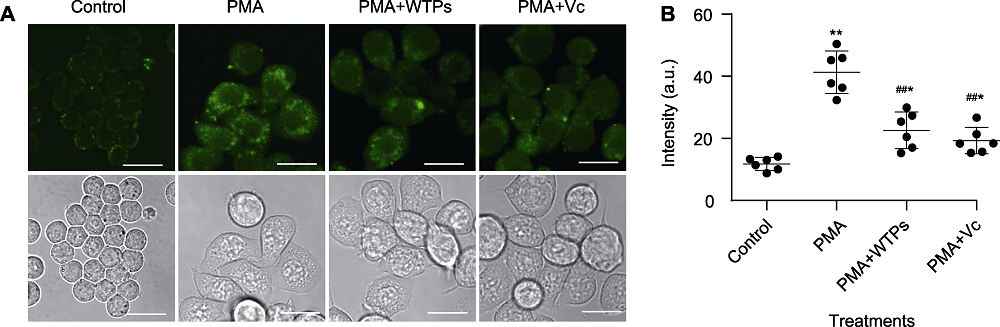
Figure 7 Effect of Wan tea polysaccharides (WTPs) on PMA-induced oxidative damage of RAW264.7 macrophages (A) Confocal imaging of ·OH content in cells of different treatment groups (bars=20 μm); (B) Comparison of fluorescence intensity of ·OH in cells of different treatment groups. Compared with control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; compared with model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01
| [1] | 陈宗懋 (2018). 新时代中国茶产业的创新与发展. 农学学报 8(1), 89-92. |
| [2] | 郝渊鹏, 李静一, 杨瑞, 李慧, 白红彤, 石雷 (2020). 芳香植物精油的抗菌性及在动物生产中的应用. 植物学报 55, 644-657. |
| [3] | 李布青, 张慧玲, 舒庆龄, 张部昌, 葛盛芳 (1996). 中低档绿茶中茶多糖的提取及降血糖作用. 茶叶科学 (1), 67-72. |
| [4] | 黎善铭, 桂海霞, 梅朋飞, 刘鸿艳, 陈世坚, 吴文嫱 (2021). 毛薯多糖提取分离工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究. 热带作物学报(网络首发) http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.S.20211026.2212.002.html. |
| [5] | 李勇, 孔令青, 高洪, 严玉霖 (2008). 自由基与疾病研究进展. 动物医学进展 29(4), 85-88. |
| [6] | 刘丹奇, 任发政, 李景明, 侯彩云 (2019). 几种茶多糖降血糖活性的研究. 茶叶科学 39, 652-660. |
| [7] |
刘亮, 钟云凯, 曹少谦, 戚向阳, 罗彤 (2016). 紫菜多糖抗氧化活性及体外免疫调节作用研究. 核农学报 30, 2355-2362.
DOI |
| [8] | 刘仲华 (2019). 中国茶叶深加工产业发展历程与趋势. 茶叶科学 39, 115-122. |
| [9] |
马丹颖, 季东超, 徐勇, 陈彤, 田世平 (2019). 活性氧调控植物细胞自噬的研究进展. 植物学报 54, 81-92.
DOI |
| [10] |
穆丹, 岂泽华, 李沁, 梁可欣, 华绍贵, 朱星雨, 焦梦婕, 饶玉春, 孙廷哲 (2021). 茶树花挥发物对叶蝉三棒缨小蜂的引诱增强效应. 植物学报 56, 559-572.
DOI |
| [11] | 孙红梅 (2014). 茶多糖对中国式摔跤女运动员赛前训练自由基代谢和无氧运动能力的影响及相关性研究. 山东体育学院学报 30(3), 61-66. |
| [12] | 孙廷哲, 岂泽华, 梁可欣, 李沁, 饶玉春, 穆丹 (2021). 蚜害茶树挥发物组分变化的聚类分析. 植物学报 56, 422-432. |
| [13] | 魏楠, 朱强强, 陈际名, 李彤, 李亦凡, 黄业伟, 马啸, 王宣军, 盛军 (2016). 茶多糖对阿霉素抑制肺癌A549细胞增殖作用的影响. 茶叶科学 36, 477-483. |
| [14] | 韦铮, 贺燕, 黄先智, 沈以红, 丁晓雯 (2022). 茶多糖-茶多酚对小鼠肠道氧化应激的改善与作用机制. 食品科学 43(11), 149-155. |
| [15] | 翁蔚, 李书魁, 张琴梅, 朱俊峰 (2021). 茶多糖的组成与保健功效研究进展. 中华中医药杂志 36, 7261-7264. |
| [16] | 吴存兵, 吴君艳, 李家春, 杨岚, 王梦媛 (2021). 黑乌龙茶茶多糖提取工艺的优化及其抗氧化与抑菌性分析. 安徽农业大学学报 48, 1005-1012. |
| [17] | 杨艾华, 宋姗姗, 王微微 (2021). 湄潭白茶多糖抗氧化活性及稳定性研究. 食品科技 46(10), 194-199. |
| [18] | 杨军国, 王丽丽, 陈林 (2018). 茶叶多糖的药理活性研究进展. 食品工业科技 39, 301-307. |
| [19] |
杨小青, 黄晓琴, 韩晓阳, 刘腾飞, 岳晓伟, 伊冉 (2020). 外源物质对茶树耐寒及蔗糖代谢关键基因表达的影响. 植物学报 55, 21-30.
DOI |
| [20] |
张凤培, 徐慧, 邱绍峰, 张君丽, 吴小平, 傅俊生 (2021). 鹿茸菇多糖抗氧化保肝研究. 生物技术通报 37, 92-100.
DOI |
| [21] | 中国茶叶流通协会 (2019). 中国茶叶行业发展报告. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社. pp. 55-62. |
| [22] |
Bai XY, Huang YY, Lu MY, Yang D (2017). HKOH-1: a highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for detecting endogenous hydroxyl radicals in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 56, 12873-12877.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chen XY, Sun-Waterhouse D, Yao WZ, Li X, Zhao MM, You LJ (2021). Free radical-mediated degradation of polysaccharides: mechanism of free radical formation and degradation, influence factors and product properties. Food Chem 365, 130524.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Fan MH, Zhu JX, Qian YL, Yue W, Xu Y, Zhang DD, Yang YQ, Gao XY, He HY, Wang DF (2020). Effect of purity of tea polysaccharides on its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities. J Food Biochem 44, e13277. |
| [25] |
Lu XS, Zhao Y, Sun YF, Yang S, Yang XB (2013). Characterisation of polysaccharides from green tea of Huangshan Maofeng with antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects. Food Chem 141, 3415-3423.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Qin HA, Huang L, Teng JW, Wei BY, Xia N, Ye Y (2021). Purification, characterization, and bioactivity of Liupao tea polysaccharides before and after fermentation. Food Chem 353, 129419.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Ray PD, Huang BW, Tsuji Y (2012). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal 24, 981-990.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Wang HS, Chen JR, Ren PF, Zhang YW, Onyango SO (2021). Ultrasound irradiation alters the spatial structure and improves the antioxidant activity of the yellow tea polysaccharide. Ultrason Sonochem 70, 105355.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang YF, Mao FF, Wei XL (2012). Characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from leaves, flowers and seeds of green tea. Carbohyd Polym 88, 146-153.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Xu LL, Chen Y, Chen ZQ, Gao XD, Wang CL, Panichayupakaranant P, Chen HX (2020). Ultrafiltration isolation, physicochemical characterization, and antidiabetic activities analysis of polysaccharides from green tea, oolong tea, and black tea. J Food Sci 85, 4025-4032.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Yang GQ, Liu ZJ, Zhang RL, Tian XH, Chen J, Han GM, Liu BH, Han XY, Fu Y, Hu ZJ, Zhang ZP (2020). A multi-responsive fluorescent probe reveals mitochondrial nucleoprotein dynamics with reactive oxygen species regulation through super-resolution imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 59, 16154-16160.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Zhang LY, Yu JL, Xu Q, Zhu JY, Zhang H, Xia GQ, Zang H (2021). Evaluation of total phenolic, flavonoid, carbohydrate contents and antioxidant activities of various solvent extracts from Angelica amurensis root. Nat Prod Res 35, 4084-4088.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Zhang MZ, Su RN, Zhang Q, Hu L, Tian XH, Chen Y, Zhou HP, Wu JY, Tian YP (2018). Ultra-bright intercellular lipidspseudo di-BODIPY probe with low molecular weight, high quantum yield and large two-photon action cross- sections. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 261, 161-168.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Jianhong Tian, Yan Liu, Mengqi Yin, Jing Wang, Ting Chen, Yan Wang, Xiaocheng Jiang. OsWAK16 Regulates Seed Anti-aging Ability by Modulating Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 17-32. |
| [2] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [3] | DU Xu-Long, HUANG Jin-Xue, YANG Zhi-Jie, XIONG De-Cheng. Effects of warming on oxidative damage and defense characteristics and their correlation in leaf and fine root of plants: a review [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(2): 135-146. |
| [4] | YU Yu-Rong, WU Hao, GAO Ya-Fei, ZHAO Yuan-Bo, LI Xiao-Ling, BU Gui-Jun, XUE Dan, LIU Zheng-Xiang, WU Hai-Wen, WU Lin. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on physiological and morphological characteristics of Sphagnum in wetland, southwestern Hubei Province, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2023, 47(11): 1493-1506. |
| [5] | Qi Wang, Yanli Xu, Peng Yan, Haosheng Dong, Wei Zhang, Lin Lu, Zhiqiang Dong. Effects of PAC on Soil Nitrogen Supply and Leaf Antioxidant Properties in Foxtail Millet at Anthesis Stage [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 90-107. |
| [6] | Xinlu Xu, Dandan Li, Yuandan Ma, Jianyun Zhai, Jianfei Sun, Yan Gao, Rumin Zhang. Responses of the Antioxidant Defense System of Osmanthus fragrans cv. ‘Tian Xiang TaiGe’ to Drought, Heat and the Synergistic Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 72-81. |
| [7] | Yan Pan, Jirui Gong, Taogetao Baoyin, Qinpu Luo, Zhanwei Zhai, Sha Xu, Yihui Wang, Min Liu, Lili Yang. Effect of Seasonal Grazing on Trade-off Among Plant Functional Traits in Root, Stem and Leaf of Leymus chinensis in the Temperate Grassland of Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(3): 307-321. |
| [8] | Meng-Meng LIU, Li JIA, Lu-Yun CHENG, Hong-Qin ZHANG, Xiao-Lin ZANG, Taogetao BAOYIN, Ru-Min ZHANG, Yan GAO. Responses of phenolic acid and defensive enzyme activities to mechanical damage in Artemisia frigida [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2017, 41(2): 219-230. |
| [9] | Siyu Chen, Peng Liu, Mo Zhu, Dongdong Xia, Liang Li, Kezhang Xu, Zhanyu Chen, Zhian Zhang. Seed Vigor and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities During Germination in Different Canopies of Soybean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 24-30. |
| [10] | HU Jun-Jing,CHEN Shuang-Lin,GUO Zi-Wu,CHEN Wei-Jun,YANG Qing-Ping,LI Ying-Chun. Divergent ramet ratio affects water physiological integration in Indocalamus decorus: Activity of antioxidant system and photosynthetic pigment content [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(7): 762-772. |
| [11] | YIN Ben-Feng,ZHANG Yuan-Ming. Impacts of freeze-thaw processes on antioxidant activities and osmolyte contents of Syntrichia caninervis under different desert microhabitats [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(5): 517-529. |
| [12] | MENG De-Yun,HOU Lin-Lin,YANG Sha,MENG Jing-Jing,GUO Feng,LI Xin-Guo,WAN Shu-Bo. Exogenous polyamines alleviating salt stress on peanuts (Arachis hypogaea) grown in pots [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(12): 1209-1215. |
| [13] | GUO Hui-Yuan, MA Yuan-Dan, WANG Dan, ZUO Zhao-Jiang, GAO Yan, ZHANG Ru-Min, WANG Yu-Kui. Effects of simulated acid rain on the activity of antioxidant enzyme and the emission of induced green leaf volatiles in Phyllostachys pubescens [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(8): 896-903. |
| [14] | XING Bing-Yu,ZHU Nan,ZHANG Hong-Pei,YANG Xi-Ling,DONG Juan-E. Effects of methyl viologen on the antioxidant system in cultured Salvia miltiorrhiza cells [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(5): 507-514. |
| [15] | Dongmei Geng, Lishan Shan, Yi Li, Жигунов Анатолий Васильевич. Effect of Soil Water Stress on Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in Reaumuria soongorica Seedlings [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(3): 282-291. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||