

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 93-101.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18044 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18044
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ming Wei1,2,Xinwei Wang1,Bo Chen1,Chengwei Song1,Liang Du1,Jianwei Xiao1,Jinxing Lin1,*( )
)
Received:2018-02-09
Accepted:2018-05-23
Online:2019-01-01
Published:2019-07-31
Contact:
Jinxing Lin
Ming Wei,Xinwei Wang,Bo Chen,Chengwei Song,Liang Du,Jianwei Xiao,Jinxing Lin. Research Progress into the Function of Purple Acid Phosphatase Gene Family in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(1): 93-101.
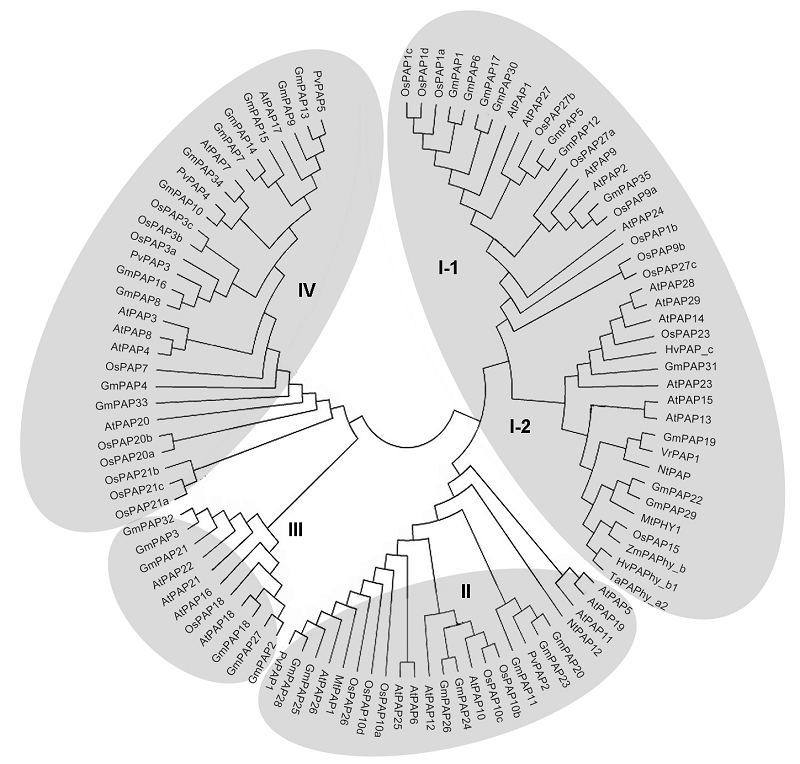
Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationships of plant PAPs (modified from Tian and Liao, 2015) At: Arabidopsis thaliana; Os: Oryza sativa; Gm: Glycine max; Mt: Medicago truncatula; Nt: Nicotiana tabacum; Zm: Zea mays; Hv: Hordeum vulgare; Ta: Triticum aestivum; Vr: Vigna radiata; Pv: Phaseolus vulgaris
| 蛋白 | 物种 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AtPAP2 | 拟南芥 | 碳代谢 | Sun et al., 2012a |
| AtPAP10 | 拟南芥 | 参与初生壁合成 | Kaida et al., 2003 |
| AtPAP12 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Wang et al., 2014 |
| AtPAP15 | 拟南芥 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Zhang et al., 2008 |
| AtPAP25 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Del Vecchio et al., 2014 |
| AtPAP26 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Wang et al., 2014 |
| GmPAP3 | 大豆 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Li et al., 2008 |
| GmPAP4 | 大豆 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Kong et al., 2014 |
| NtPAP12 | 烟草 | 参与初生壁合成 | Kaida et al., 2010 |
| PvPAP3 | 菜豆 | 磷代谢 | Liang et al., 2010 |
| StPAP1 | 马铃薯 | 磷代谢 | Zimmermann et al., 2004 |
Table 1 Biochemical properties functions of plant PAPs (modified from Tian and Liao, 2015)
| 蛋白 | 物种 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AtPAP2 | 拟南芥 | 碳代谢 | Sun et al., 2012a |
| AtPAP10 | 拟南芥 | 参与初生壁合成 | Kaida et al., 2003 |
| AtPAP12 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Wang et al., 2014 |
| AtPAP15 | 拟南芥 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Zhang et al., 2008 |
| AtPAP25 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Del Vecchio et al., 2014 |
| AtPAP26 | 拟南芥 | 磷代谢 | Wang et al., 2014 |
| GmPAP3 | 大豆 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Li et al., 2008 |
| GmPAP4 | 大豆 | 响应非生物逆境胁迫 | Kong et al., 2014 |
| NtPAP12 | 烟草 | 参与初生壁合成 | Kaida et al., 2010 |
| PvPAP3 | 菜豆 | 磷代谢 | Liang et al., 2010 |
| StPAP1 | 马铃薯 | 磷代谢 | Zimmermann et al., 2004 |
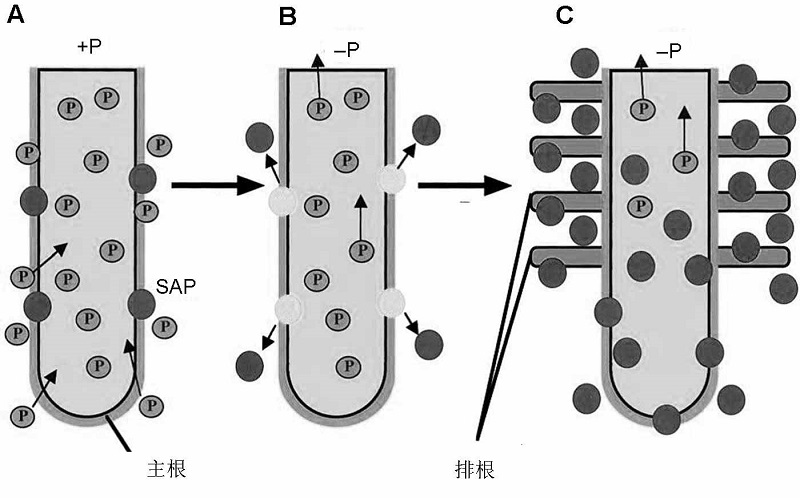
Figure 3 Schematic model of SAP expression and formation of cluster root under phosphorus deficiency (modified from Wasaki et al., 2003) (A) Under sufficient P conditions, SAP localizes around the epidermal cells of roots, and only a small amount of SAP is secreted; (B) After P stress treatment, SAP is released from roots rapidly within 12 h, however, SAP secretion remains at a low level for a long time; (C) After the decrease of P content in tissues, cluster roots form and SAP secretion significantly increases.
| 1 |
刘涛, 陈海英, 余海英, 李廷轩, 高尚卿, 陈光登 ( 2016). 低磷胁迫下大麦叶片磷素利用特征. 植物学报 51, 504-514.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
卢坤, 张凯, 柴友荣, 陆俊杏, 唐章林, 李加纳 ( 2010). 甘蓝和白菜紫色酸性磷酸酶17基因家族的克隆和比较分析. 作物学报 36, 517-525.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
周志高, 汪金舫, 周健民 ( 2005). 植物磷营养高效的分子生物学研究进展. 植物学报 22, 82-91.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Cakmak I ( 2002). Plant nutrition research: priorities to meet human needs for food in sustainable ways. Plant Soil 247, 3-24.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Del Vecchio HA, Ying S, Park J, Knowles VL, Kanno S, Tanoi K, She YM, Plaxton WC ( 2014). The cell wall- targeted purple acid phosphatase AtPAP25 is critical for acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to nutritional phosphorus deprivation.Plant J 80, 569-581.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 |
Hammond JP, Broadley MR, White PJ ( 2004). Genetic responses to phosphorus deficiency. Ann Bot 94, 323-332.
DOI URL PMID |
| 7 |
Hur YJ, Jin BR, Nam J, Chung YS, Lee JH, Choi HK, Yun DJ, Yi G, Kim YH, Kim DH ( 2010). Molecular characterization of OsPAP2: transgenic expression of a purple acid phosphatase up-regulated in phosphate-deprived rice sus- pension cells.Biotechnol Lett 32, 163-170.
DOI URL PMID |
| 8 |
James J, David WL ( 1992). Dependence of photosynthesis of sunflower and maize leaves on phosphate supply, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity, and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate pool size. Plant Physiol 98, 801-807.
DOI URL PMID |
| 9 |
Jarenmark M, Haukka M, Demeshko S, Tuczek F, Zuppiroli L, Meyer F, Nordlander E ( 2011). Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity studies of heterodinuclear complexes modeling active sites in purple acid phospha- tases. Inorg Chem 50, 3866-3887.
DOI URL PMID |
| 10 |
Kaida R, Hayashi T, Kaneko TS ( 2008). Purple acid phosphatase in the walls of tobacco cells. Phytochemistry 69, 2546-2551.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 |
Kaida R, Sage-Ono K, Kamada H, Okuyama H, Syono K, Kaneko TS ( 2003). Isolation and characterization of four cell wall purple acid phosphatase genes from tobacco cells. Biochim Biophys Acta-Gene Regul Mech 1625, 134-140.
DOI URL PMID |
| 12 |
Kaida R, Satoh Y, Bulone V, Yamada Y, Kaku T, Hayashi T, Kaneko TS ( 2009). Activation of β-glucan synthases by wall-bound purple acid phosphatase in tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 150, 1822-1830.
DOI URL PMID |
| 13 |
Kaida R, Serada S, Norioka N, Norioka S, Neumetzler L, Pauly M, Sampedro J, Zarra I, Hayashi T, Kaneko TS ( 2010). Potential role for purple acid phosphatase in the dephosphorylation of wall proteins in tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 153, 603-610.
DOI URL PMID |
| 14 |
Klabunde T, Stahl B, Suerbaum H, Hahner S, Karas M, Hillenkamp F, Krebs B, Witzel H ( 1994). The amino acid sequence of the red kidney bean Fe(III)-Zn(II) purple acid phosphatase. Determination of the amino acid sequence by a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ioni- zation mass spectrometry and automated Edman sequ- encing. Eur J Biochem 226, 369-375.
DOI URL PMID |
| 15 |
Klabunde T, Sträter N, Krebs B, Witzel H ( 1995). Structural relationship between the mammalian Fe(III)-Fe(II) and the Fe(III)-Zn(II) plant purple acid phosphatases. FEBS Lett 367, 56-60.
DOI URL PMID |
| 16 | Kong YB, Li XH, Ma J, Li WL, Yan GJ, Zhang CY ( 2014). GmPAP4, a novel purple acid phosphatase gene isolated from soybean ( Glycine max), enhanced extracellular phytate utilization in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Rep 33, 655-667. |
| 17 |
Kuang RB, Chan KH, Yeung E, Lim BL ( 2009). Molecular and biochemical characterization of AtPAP15, a purple acid phosphatase with phytase activity, in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151, 199-209.
DOI URL PMID |
| 18 |
Kusudo T, Sakaki T, Inouye K ( 2003). Purification and characterization of purple acid phosphatase PAP1 from dry powder of sweet potato. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67, 1609-1611.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Law YS, Zhang RS, Guan XQ, Cheng SF, Sun F, Duncan O, Murcha MW, Whelan J, Lim BL ( 2015). Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the presequence of precursor MULTIPLE ORGANELLAR RNA EDITING FACTOR3 during import into mitochondria from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169, 1344-1355.
DOI URL PMID |
| 20 |
Li CC, Gui SH, Yang T, Walk T, Wang XR, Liao H ( 2012). Identification of soybean purple acid phosphatase genes and their expression responses to phosphorus availability and symbiosis. Ann Bot 109, 275-285.
DOI URL PMID |
| 21 |
Li DP, Zhu HF, Liu KF, Liu X, Leggewie G, Udvardi M, Wang DW ( 2002). Purple acid phosphatases of Arabidopsis thaliana.Comparative analysis and differential regulation by phosphate deprivation. J Biol Chem 277, 27772-27781.
DOI URL PMID |
| 22 |
Li WYF, Shao GH, Lam HM ( 2008). Ectopic expression of GmPAP3 alleviates oxidative damage caused by salinity and osmotic stresses.New Phytol 178, 80-91.
DOI URL PMID |
| 23 |
Liang C, Liu X, Sun YZ, Yiu SM, Lim BL ( 2014). Global small RNA analysis in fast-growing Arabidopsis thaliana with elevated concentrations of ATP and sugars.BMC Genomics 15, 116.
DOI URL PMID |
| 24 |
Liang C, Zhang YJ, Cheng SF, Osorio S, Sun YZ, Fernie AR, Cheung CY, Lim BL ( 2015). Impacts of high ATP supply from chloroplasts and mitochondria on the leaf metabolism of Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci 6, 922.
DOI URL PMID |
| 25 |
Liang CY, Tian J, Lam HM, Lim BL, Yan XL, Liao H ( 2010). Biochemical and molecular characterization of PvPAP3, a novel purple acid phosphatase isolated from common bean enhancing extracellular ATP utilization. Plant Physiol 152, 854-865.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Liao H, Wong FL, Phang TH, Cheung MY, Li WYF, Shao GH, Yan XL, Lam HM ( 2003). GmPAP3, a novel purple acid phosphatase-like gene in soybean induced by NaCl stress but not phosphorus deficiency. Gene 318, 103-111.
DOI URL PMID |
| 27 | Nakazato H, Okamoto T, Nishikoori M, Washio K, Morita N, Haraguchi K, Thompson GA, Okuyama H ( 1998). The glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored phosphatase from Spirodela oligorrhiza is a purple acid phosphatase.Plant Physiol 118, 1015-1020. |
| 28 |
Olczak M, Morawiecka B, Watorek W ( 2003). Plant purple acid phosphatases-genes, structures and biological function. Acta Biochim Pol 50, 1245-1256.
DOI URL PMID |
| 29 | Ravichandran S, Stone SL, Bernhard B, Prithiviraj B ( 2013). Purple acid phosphatase 5 is required for maintaining basal resistance against Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol 13, 107. |
| 30 |
Robinson WD, Carson I, Ying S, Ellis K, Plaxton WC ( 2012a). Eliminating the purple acid phosphatase AtPAP26 in Arabidopsis thaliana delays leaf senescence and impairs phosphorus remobilization.New Phytol 196, 1024-1029.
DOI URL PMID |
| 31 |
Robinson WD, Park J, Tran HT, Del Vecchio HA, Ying S, Zins JL, Patel K, McKnight TD, Plaxton WC ( 2012 b). The secreted purple acid phosphatase isozymes AtPAP12 and AtPAP26 play a pivotal role in extracellular phosphate-scavenging by Arabidopsis thaliana.J Exp Bot 63, 6531-6542.
DOI URL PMID |
| 32 |
Rubio V, Linhares F, Solano R, Martín AC, Iglesias J, Leyva A, Paz-Ares J ( 2001). A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev 15, 2122-2133.
DOI URL |
| 33 | Schenk G, Elliott TW, Leung E, Carrington LE, Mitic N, Gahan LR, Guddat LW ( 2008). Crystal structures of a purple acid phosphatase, representing different steps of this enzyme’s catalytic cycle. BMC Struct Biol 8, 6. |
| 34 |
Schenk G, Guddat LW, Ge Y, Carrington LE, Hume DA, Hamilton S, de Jersey J ( 2000 a). Identification of mammalian-like purple acid phosphatases in a wide range of plants. Gene 250, 117-125.
DOI URL PMID |
| 35 |
Schenk G, Korsinczky MLJ, Hume DA, Hamilton S, DeJersey J ( 2000 b). Purple acid phosphatases from bacteria: similarities to mammalian and plant enzymes. Gene 255, 419-424.
DOI URL PMID |
| 36 |
Smith VH, Schindler DW ( 2009). Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24, 201-207.
DOI URL PMID |
| 37 | Strater N, Klabunde T, Tucker P, Witzel H, Krebs B ( 1995). Crystal structure of a purple acid phosphatase containing a dinuclear Fe(III)-Zn(II) active site. Science 268, 1489-1492. |
| 38 |
Sun F, Carrie C, Law S, Murcha MW, Zhang R, Law YS, Suen PK, Whelan J, Lim BL ( 2012 b). AtPAP2 is a tail-anchored protein in the outer membrane of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Plant Signal Behav 7, 927-932.
DOI URL PMID |
| 39 | Sun F, Liang C, Whelan J, Yang J, Zhang P, Lim BL ( 2013). Global transcriptome analysis of AtPAP2-overex- pressing Arabidopsis thaliana with elevated ATP.BMC Genomics 14, 752. |
| 40 |
Sun F, Suen PK, Zhang YJ, Liang C, Carrie C, Whelan J, Ward JL, Hawkins ND, Jiang LW, Lim BL ( 2012a). A dual-targeted purple acid phosphatase in Arabidopsis thaliana moderates carbon metabolism and its overexpression leads to faster plant growth and higher seed yield.New Phytol 194, 206-219.
DOI URL PMID |
| 41 |
Sun YZ, Law YS, Cheng SF, Lim BL ( 2017). RNA editing of cytochrome c maturation transcripts is responsive to the energy status of leaf cells in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mitochondrion 35, 23-34.
DOI URL PMID |
| 42 |
Tian J, Liao H (2015). The role of intracellular and secreted purple acid phosphatases in plant phosphorus scavenging and recycling. In: Plaxton WC, Lambers H, eds. Annual Plant Reviews Volume 48: Phosphorus Metabolism in Plants, Vol. 48. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd,. Ltd. pp. 265-287.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Tran HT, Hurley BA, Plaxton WC ( 2010 a). Feeding hungry plants: the role of purple acid phosphatases in phosphate nutrition. Plant Sci 179, 14-27.
DOI URL |
| 44 | Tran HT, Qian WQ, Hurley BA, She YM, Wang DW, Plaxton WC ( 2010 b). Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP12 and AtPAP26: the predominant purple acid phosphatase isozymes secreted by phosphate- starved Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Environ 33, 1789-1803. |
| 45 |
Vance CP ( 2001). Symbiotic nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition. plant nutrition in a world of declining renewable resources. Plant Physiol 127, 390-397.
DOI URL PMID |
| 46 |
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL ( 2003). Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157, 423-447.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Bragg J, Finnegan PM, Lovelock CE, Plaxton WC, Price CA, Scheible WR, Shane MW, White PJ, Raven JA ( 2012). Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytol 195, 306-320.
DOI URL PMID |
| 48 | Wang LS, Li Z, Qian WQ, Guo WL, Gao X, Huang LL, Wang H, Zhu HF, Wu JW, Wang DW, Liu D ( 2011). The Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase AtPAP10 is predominantly associated with the root surface and plays an important role in plant tolerance to phosphate limitation. Plant Physiol 157, 1283-1299. |
| 49 | Wang LS, Lu S, Zhang Y, Li Z, Du XQ, Liu D ( 2014). Comparative genetic analysis of Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatases AtPAP10, AtPAP12, and AtPAP26 provides new insights into their roles in plant adaptation to phosphate deprivation. J Integr Plant Biol 56, 299-314. |
| 50 |
Wasaki J, Yamamura T, Shinano T, Osaki M ( 2003). Secreted acid phosphatase is expressed in cluster roots of lupin in response to phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 248, 129-136.
DOI URL |
| 51 |
Zhang Q, Wang C, Tian J, Li K, Shou H ( 2011). Identification of rice purple acid phosphatases related to phosphate starvation signaling. Plant Biol 13, 7-15.
DOI URL PMID |
| 52 |
Zhang RS, Guan XQ, Law YS, Sun F, Chen S, Wong KB, Lim BL ( 2016). AtPAP2 modulates the import of the small subunit of Rubisco into chloroplasts. Plant Signal Behav 11, e1239687.
DOI URL PMID |
| 53 |
Zhang WY, Gruszewski HA, Chevone BI, Nessler CL ( 2008). An Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase with phytase activity increases foliar ascorbate. Plant Physiol 146, 431-440.
DOI URL PMID |
| 54 |
Zhang YJ, Sun F, Fettke J, Schottler MA, Ramsden L, Fernie AR, Lim BL ( 2014). Heterologous expression of AtPAP2 in transgenic potato influences carbon metabolism and tuber development.FEBS Lett 588, 3726-3731.
DOI URL PMID |
| 55 |
Zhang YJ, Yu L, Yung KF, Leung DYC, Sun F, Lim BL ( 2012). Over-expression of AtPAP2 in Camelina sativa leads to faster plant growth and higher seed yield.Biotechnol Biofuels 5, 219.
DOI URL PMID |
| 56 |
Zhou J, Jiao FC, Wu ZC, Li YY, Wang XM, He XW, Zhong WQ, Wu P ( 2008). OsPHR2 is involved in phosphate- starvation signaling and excessive phosphate accumulation in shoots of plants. Plant Physiol 146, 1673-1686.
DOI URL PMID |
| 57 |
Zhu HF, Qian WQ, Lu XZ, Li DP, Liu X, Liu KF, Wang DW ( 2005). Expression patterns of purple acid phosphatase genes in Arabidopsis organs and functional analysis of AtPAP23 predominantly transcribed in flower.Plant Mol Biol 59, 581-594.
DOI URL PMID |
| 58 |
Zimmermann P, Regierer B, Kossmann J, Frossard E, Amrhein N, Bucher M ( 2004). Differential expression of three purple acid phosphatases from potato. Plant Biol 6, 519-528.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | Haitao Hu, Yue Wu, Ling Yang. Research Progress on the NAD(P)+ Biosynthesis and Function in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [2] | Jia Hu, Chunlin Liu. Research Advances in Plant Oil Body [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(5): 669-679. |
| [3] | Hongmei Xi, Wenzhong Xu, Mi Ma. Advances in Biological Function of Arabidopsis Bifunctional Enzyme SAL1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(3): 377-386. |
| [4] | Le Yu1, Yonghai Liu, Weichao Yuan, Liping Zhou, Changlian Peng. Recent Advances in the Study of Accumulation of Ascorbic Acid and Its Molecular Mechanism in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(3): 396-410. |
| [5] | Linya Liu, Yacheng Huang, Xiaolong Huang, Dongyi Huang. Advances in Study of Dioscorins as Special Proteins in Yam Tuber [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 274-280. |
| [6] | Haijiao Liu, Liqun Du, Jinxing Lin, Ruili Li. Recent Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Ion Channels with their Functions in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(6): 779-789. |
| [7] | Kaien Zhai, Weihuai Pan, Xiaofan Ye, Jianwei Pan. Biological Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms of Local Auxin Biosynthesis in Higher Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 149-158. |
| [8] | Ming Li, Changsheng Li, Chuanzhi Zhao, Aiqin Li, Xingjun Wang. Research Advances in Plant SPL Transcription Factors [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 107-116. |
| [9] | Runhua Liu;Wenbo Jiang;Diqiu Yu . Structure, Metabolic Pathway and Function of Sphingolipids in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(05): 619-628. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||