

赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”
收稿日期: 2023-03-25
录用日期: 2023-04-18
网络出版日期: 2023-04-26
基金资助
国家自然科学基金创新群体(31921005)
Coordinated Regulation of Gibberellin and Brassinosteroid Signalings Drives Toward a Sustainable “Green Revolution” by Breeding the New Generation of High-yield Wheat
Received date: 2023-03-25
Accepted date: 2023-04-18
Online published: 2023-04-26
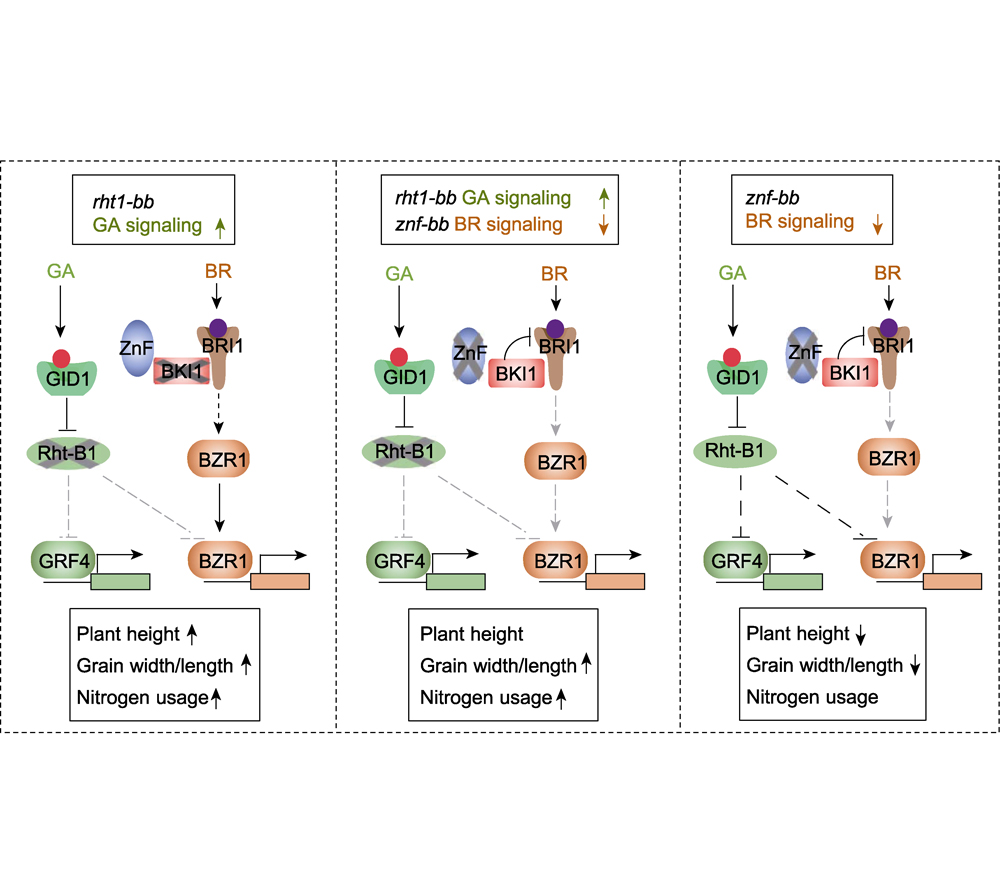
自20世纪60年代以来, 半矮秆基因Rht-B1b和Rht-D1b的利用显著提高了小麦(Triticum aestivum)抗倒伏能力和收获指数, 使得全世界小麦产量翻了一番, 引发了农业第1次“绿色革命”。Rht-B1b和Rht-D1b编码植物生长抑制因子DELLA蛋白, 是赤霉素(GA)信号转导途径的负调控因子。DELLA蛋白积累抑制细胞分裂和细胞伸长, 导致矮化表型; 同时也抑制光合作用并降低氮素利用效率, 导致半矮化品种需要较高的化肥投入才能获得高产。如何“减肥增效”是实现低碳绿色农业所面临的重大问题。最近, 中国农业大学倪中福团队发现了具有育种应用价值的新型“半矮秆”基因模块, 证明通过对赤霉素和油菜素内酯(BR)信号通路的双重调控可实现矮秆高产小麦新品种培育。该团队鉴定并克隆了1个控制小麦株高和粒重的数量性状位点(QTL), 该QTL在衡597中存在1个约500 kb的r-e-z大片段缺失, 其中包括Rht-B1b基因和1个编码RING E3泛素连接酶的ZnF-B基因。研究发现, ZnF-B蛋白与油菜素内酯信号转导途径的抑制因子TaBKI1相互作用, 诱导TaBKI1降解, 从而促进BR信号转导。ZnF-B单敲除导致小麦株高和粒重降低, 影响小麦产量; ZnF-B1和Rht-B1b双敲除植株株高不变, 但小麦粒重和氮肥利用效率增高。该研究不仅揭示了BR信号转导调控的新机制, 而且提出了通过调控GA和BR双重信号转导机制实现农业可持续发展的育种新策略, 助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”。
白明义 , 彭金荣 , 傅向东 . 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023 , 58(2) : 194 -198 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB23038
Since the 1960s, the utilization of semi-dwarfing genes Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b has significantly improved the lodging resistance and harvest index of wheat (Triticum aestivum), leading to a doubling of global wheat production and triggering the “Green Revolution” in agriculture. Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b encode plant growth-inhibiting factors, DELLA proteins, which are negative regulatory factors in the gibberellin (GA) signaling pathway. Accumulation of DELLA proteins not only inhibits cell division and elongation, leading to a dwarf phenotype, but also suppresses photosynthesis and nitrogen use efficiency, resulting in semi-dwarf varieties requiring higher fertilizer inputs to achieve high yields. Addressing the challenge of “reducing fertilizer inputs while increasing efficiency” is a crucial issue for achieving green and low-carbon agriculture. Recently, Zhongfu Ni and his colleagues from China Agricultural University identified a novel “semi-dwarfing” regulatory module with potential breeding applications and demonstrated that reducing brassinosteroid (BR) signaling could enhance grain yield of wheat “Green Revolution” varieties (GRVs). They isolated and characterized a major QTL responsible for plant height and 1000-grain weight in wheat. Positional cloning and functional analysis revealed that this QTL was associated with a ~500 kb fragment deletion in the Heng597 genome, designated as r-e-z, which contains Rht-B1 and ZnF-B (encoding a RING E3 ligase). ZnF-B was found to positively regulate BR signaling by triggering the degradation of BR signaling repressor BRI1 Kinase Inhibitor (TaBKI1). Further experiments showed that deletion of ZnF-B not only caused the semi-dwarf phenotypes in the absence of Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b alleles, but also enhanced grain yield at low nitrogen fertilization levels. Thus, manipulation of GA and BR signaling provides a new breeding strategy to improve grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of wheat GRVs without affecting beneficial semi-dwarfism, which will drive toward a new “Green Revolution” in wheat.

Key words: wheat; Green Revolution; plant height; gibberellin; brassinosteroid
| [1] | Bai MY, Shang JX, Oh E, Fan M, Bai Y, Zentella R, Sun TP, Wang ZY (2012). Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 14, 810-817. |
| [2] | Gallego-Bartolome J, Minguet EG, Grau-Enguix F, Abbas M, Locascio A, Thomas SG, Alabadi D, Blázquez MA (2012). Molecular mechanism for the interaction between gibberellin and brassinosteroid signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 13446-13451. |
| [3] | Han C, Wang LY, Lyu J, Shi W, Yao LM, Fan M, Bai MY (2023). Brassinosteroid signaling and molecular crosstalk with nutrients in plants. J Genet Genomics doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2023.03.004. |
| [4] | Khush GS (1999). Green revolution: preparing for the 21st century. Genome 42, 646-655. |
| [5] | Li QF, Wang CM, Jiang L, Li S, Sun SSM, He JX (2012). An interaction between BZR1 and DELLAs mediates direct signaling crosstalk between brassinosteroids and gibberellins in Arabidopsis. Sci Signal 5, ra72. |
| [6] | Li S, Tian YH, Wu K, Ye YF, Yu JP, Zhang JQ, Liu Q, Hu MY, Li H, Tong YP, Harberd NP, Fu XD (2018). Modulating plant growth-metabolism coordination for sustainable agriculture. Nature 560, 595-600. |
| [7] | Liu Q, Wu K, Song WZ, Zhong N, Wu YZ, Fu XD (2022). Improving crop nitrogen use efficiency toward sustainable green revolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol 73, 523-551. |
| [8] | Peng JR, Richards DE, Hartley NM, Murphy GP, Devos KM, Flintham JE, Beales J, Fish LJ, Worland AJ, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape JW, Gale MD, Harberd NP (1999). ‘Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400, 256-261. |
| [9] | Pingali PL (2012). Green revolution: impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 12302-12308. |
| [10] | Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2002). Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416, 701-702. |
| [11] | Song L, Liu J, Cao BL, Liu B, Zhang XP, Chen ZY, Dong CQ, Liu XQ, Zhang ZH, Wang WX, Chai LL, Liu J, Zhu J, Cui SB, He F, Peng HR, Hu ZR, Su ZQ, Guo WL, Xin MM, Yao YY, Yan Y, Song YM, Bai GH, Sun XX, Ni ZF (2023). Reducing brassinosteroid signaling enhances gr- ain yield in semi-dwarf wheat. Nature 617, 118-124. |
| [12] | Spielmeyer W, Ellis MH, Chandler PM (2002). Semidwarf (sd-1), "green revolution" rice, contains a defective gibberellin 20-oxidase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 9043-9048. |
| [13] | Tong HN, Chu CC (2018). Functional specificities of brassinosteroid and potential utilization for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 23, 1016-1028. |
| [14] | Tong HN, Xiao YH, Liu DP, Gao SP, Liu LC, Yin YH, Jin Y, Qian Q, Chu CC (2014). Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell 26, 4376-4393. |
| [15] | Wu K, Wang SS, Song WZ, Zhang JQ, Wang Y, Liu Q, Yu JP, Ye YF, Li S, Chen JF, Zhao Y, Wang J, Wu XK, Wang MY, Zhang YJ, Liu BM, Wu YJ, Harberd NP, Fu XD (2020). Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice. Science 367, eaaz2046. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |