

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 605-612.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20030 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20030
刘建飞1, 刘炎1, 刘克俭2, 池阳3, 霍志发3, 霍永洪3, 由香玲1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-26
接受日期:2020-06-05
出版日期:2020-09-01
发布日期:2020-09-03
通讯作者:
由香玲
作者简介:E-mail: 185064633@qq.com基金资助:
Jianfei Liu1, Yan Liu1, Kejian Liu2, Yang Chi3, Zhifa Huo3, Yonghong Huo3, Xiangling You1,*( )
)
Received:2020-02-26
Accepted:2020-06-05
Online:2020-09-01
Published:2020-09-03
Contact:
Xiangling You
摘要: 以长白落叶松(Larix olgensis)未成熟合子胚为外植体诱导胚性愈伤组织, 通过调节影响体胚发生的营养物质和植物生长调节剂配比, 进行愈伤组织的胚性恢复与保持以及体胚发生再生体系的优化。结果表明: 不同无性系之间胚性愈伤组织诱导率差异显著, 胚性愈伤组织在S+0.2 mg·L -1NAA+0.5 mg·L -1BA+0.5 mg·L -1KT+0.5 g·L -1谷氨酰胺+0.5 g·L -1水解酪蛋白+30 g·L -1蔗糖及3.0 g·L -1植物凝胶培养条件下, 可以恢复胚性并长久保持。在S+20 mg·L -1ABA+60 g·L -1PEG4000+60 g·L -1蔗糖及3.0 g·L -1植物凝胶条件下分化培养6周, 体胚发生率可达100%。将正常发育的体胚先在WPM+ 6 mg·L -1间苯三酚+1.0 g·L -1活性炭+3.0 mg·L -1VB1+20 g·L -1蔗糖及3.0 g·L -1植物凝胶条件下培养2周, 再转接至B5+ 0.4 mg·L -1NAA+1.0 mg·L -1IBA+0.5 mg·L -1GA3+2.0 mg·L -1VB1+1.0 g·L -1活性炭+20 g·L -1蔗糖及3.0 g·L -1植物凝胶条件下培养2周, 可见子叶舒展、下胚轴伸长且根系正常的体胚苗。该研究建立了长白落叶松胚性愈伤组织胚性恢复与保持方法, 并进一步优化了体胚发生的植株再生体系, 为林木资源快速繁育和遗传改良奠定了基础。
刘建飞, 刘炎, 刘克俭, 池阳, 霍志发, 霍永洪, 由香玲. 长白落叶松体胚发生再生体系优化. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 605-612.
Jianfei Liu, Yan Liu, Kejian Liu, Yang Chi, Zhifa Huo, Yonghong Huo, Xiangling You. Optimization of the Regeneration System from Somatic Embryogenesis in Larix olgensis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 605-612.
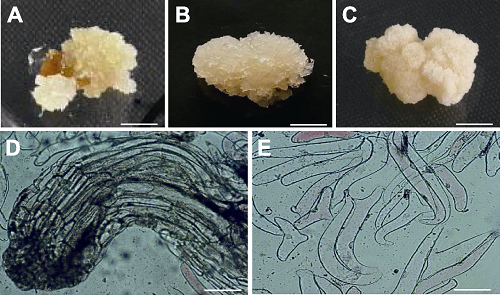
图1 长白落叶松愈伤组织及镜检结构 (A) 愈伤组织; (B) 胚性愈伤组织; (C) 非胚性愈伤组织; (D) 胚性愈伤组织显微图像; (E) 非胚性愈伤组织显微图像。 (A)- (C) Bars=3 mm; (D) Bar=200 μm; (E) Bar=500 μm
Figure 1 Callus and its microscopic images of Larix olgensis (A) Callus; (B) Embryogenic callus; (C) Non-embryogenic callus; (D) The image of embryogenic callus; (E) The image of non-embryogenic callus. (A)-(C) Bars=3 mm; (D) Bar= 200 μm; (E) Bar=500 μm
| Excellent trees | Callus induction rate (%) | Embryogenic callus formation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 061-1009 | 89.43±48.59 a | 0 |
| 091-1008 | 81.56±47.91 c | 0 |
| 058-842 | 91.25±53.17 a | 4.53±2.73 a |
| 024-922 | 85.91±37.29 b | 0 |
表1 不同长白落叶松株系愈伤组织与胚性愈伤组织诱导(平均值±标准差)
Table 1 Callus and embryogenic callus induction in different Larix olgensis lines (means±SD)
| Excellent trees | Callus induction rate (%) | Embryogenic callus formation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 061-1009 | 89.43±48.59 a | 0 |
| 091-1008 | 81.56±47.91 c | 0 |
| 058-842 | 91.25±53.17 a | 4.53±2.73 a |
| 024-922 | 85.91±37.29 b | 0 |
| The combination of plant growth regulators in the medium | Somatic embryogenesis (%) | Somatic embryo amount (numbers·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mg?L-1 2,4-D+0.04 mg·L-1 BA+0.02 mg·L-1 KT | 45.27±23.31 | 16.47±1.67 |
| 0.5 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 52.65±31.83 b | 25.31±9.85 c |
| 0.4 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 57.38±15.41 ab | 31.53±5.37 b |
| 0.3 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 64.41±11.79 a | 39.74±4.29 ab |
| 0.2 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 72.36±10.57 a | 48.56±3.77 a |
| 0.1 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 63.70±43.86 a | 41.92±7.22 a |
表2 不同浓度配比的植物生长调节剂对长白落叶松体胚发生率和体胚数量的影响(平均值±标准差)
Table 2 Effects of plant growth regulators at different concentration ratios on somatic embryogenesis and somatic embryo amount in Larix olgensis (means±SD)
| The combination of plant growth regulators in the medium | Somatic embryogenesis (%) | Somatic embryo amount (numbers·g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mg?L-1 2,4-D+0.04 mg·L-1 BA+0.02 mg·L-1 KT | 45.27±23.31 | 16.47±1.67 |
| 0.5 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 52.65±31.83 b | 25.31±9.85 c |
| 0.4 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 57.38±15.41 ab | 31.53±5.37 b |
| 0.3 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 64.41±11.79 a | 39.74±4.29 ab |
| 0.2 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 72.36±10.57 a | 48.56±3.77 a |
| 0.1 mg?L-1 NAA+0.5 mg·L-1 BA+0.5 mg·L-1 KT | 63.70±43.86 a | 41.92±7.22 a |

图2 长白落叶松体胚成熟过程 (A) 培养2周; (B) 培养4周; (C) 培养6周。Bars=2.5 mm
Figure 2 Maturation of somatic embryos of Larix olgensis (A) Cultured for 2 weeks; (B) Cultured for 4 weeks; (C) Cultured for 6 weeks. Bars=2.5 mm
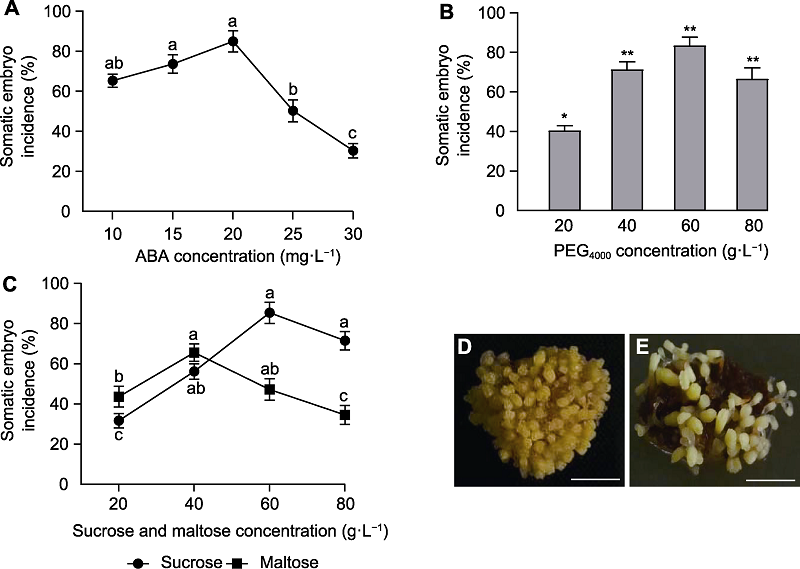
图3 不同因素对长白落叶松体胚发生率的影响(平均值±标准误) (A) ABA; (B) PEG4000; (C) 蔗糖和麦芽糖; (D) 添加蔗糖后培养6周; (E) 添加麦芽糖后培养6周。 (D), (E) Bars=2.5 mm。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。* P<0.05; ** P<0.01
Figure 3 Effects of different factors on the rate of somatic embryogenesis in Larix olgensis (means±SE) (A) ABA; (B) PEG4000; (C) Sucrose and maltose; (D) Cultured with sucrose for 6 weeks; (E) Cultured with maltose for 6 weeks. (D), (E) Bars=2.5 mm. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). * P<0.05; ** P<0.01

图4 长白落叶松不同发育状态的体胚苗及其移栽 (A) 子叶胚; (B) 子叶胚萌发; (C) 对照体胚苗; (D) 优化体胚苗; (E) 生根体胚苗; (F) 移栽体胚苗。 (A) Bar=1.5 mm; (B) Bar=6.5 mm; (C), (D) Bars=1.0 cm; (E), (F) Bars=1.5 cm
Figure 4 Somatic embryo seedlings at different developmental states of Larix olgensis and their transplanting (A) Cotyledonary embryo; (B) Cotyledons germinate; (C) Control of somatic embryo seedling; (D) Optimization somatic embryo seedling; (E) Rooting somatic embryo seedlings; (F) Transplanting somatic embryo seedling. (A) Bar=1.5 mm; (B) Bar=6.5 mm; (C), (D) Bars=1.0 cm; (E), (F) Bars=1.5 cm
| Growth regulator combination | Somatic embryo seedlings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Seedling rate (%) | Stem length (mm) | Main root length (mm) |
| 0.4 | 0.5 | 38.83±29.38 ab | 1.59±1.44 c | 16.38±12.74 b |
| 0.4 | 1.0 | 46.21±41.29 a | 1.75±0.77 ab | 19.17±14.52 a |
| 0.4 | 1.5 | 35.37±33.34 b | 1.67±1.75 b | 12.60±10.34 c |
| 0.8 | 0.5 | 22.57±25.43 c | 1.76±0.91 ab | 12.31±9.54 c |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 22.65±15.83 c | 1.81±0.88 a | 15.18±13.37 bc |
| 0.8 | 1.5 | 21.43±19.68 c | 1.78±0.67 ab | 11.40±8.53 c |
表3 生长调节剂组合对长白落叶松体胚苗生长的影响(平均值±标准差)
Table 3 Effects of growth regulator combination on the growth of somatic embryo seedling in Larix olgensis (means±SD)
| Growth regulator combination | Somatic embryo seedlings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAA (mg·L-1) | IBA (mg·L-1) | Seedling rate (%) | Stem length (mm) | Main root length (mm) |
| 0.4 | 0.5 | 38.83±29.38 ab | 1.59±1.44 c | 16.38±12.74 b |
| 0.4 | 1.0 | 46.21±41.29 a | 1.75±0.77 ab | 19.17±14.52 a |
| 0.4 | 1.5 | 35.37±33.34 b | 1.67±1.75 b | 12.60±10.34 c |
| 0.8 | 0.5 | 22.57±25.43 c | 1.76±0.91 ab | 12.31±9.54 c |
| 0.8 | 1.0 | 22.65±15.83 c | 1.81±0.88 a | 15.18±13.37 bc |
| 0.8 | 1.5 | 21.43±19.68 c | 1.78±0.67 ab | 11.40±8.53 c |
| Plant regeneration | GA3 concentration (mg·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| Seedling rate (%) | 45.61±52.27 b | 55.44±37.91 a | 45.91±35.81 b |
| Stem length (mm) | 1.63±1.33 b | 2.65±2.61 a | 0.91±1.11 c |
| Main root length (mm) | 17.98±14.22 a | 12.41±16.55 b | 8.65±5.49 c |
表4 不同浓度GA3对长白落叶松体胚苗生长的影响(平均值±标准差)
Table 4 Effects of different concentration of GA3 on the growth of somatic embryo seedling in Larix olgensis (means± SD)
| Plant regeneration | GA3 concentration (mg·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| Seedling rate (%) | 45.61±52.27 b | 55.44±37.91 a | 45.91±35.81 b |
| Stem length (mm) | 1.63±1.33 b | 2.65±2.61 a | 0.91±1.11 c |
| Main root length (mm) | 17.98±14.22 a | 12.41±16.55 b | 8.65±5.49 c |
| [1] | 黄健秋, 卫志明, 许智宏 ( 1995). 马尾松成熟合子胚的体细胞胚胎发生和植株再生. 科学通报 40, 72-75. |
| [2] | 齐力旺 ( 2000). 华北落叶松体细胞胚胎发生与遗传转化系统建立的研究. 博士论文. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. pp. 44-74. |
| [3] | 宋跃, 甄成, 张含国, 李淑娟 ( 2016). 长白落叶松胚性愈伤组织诱导及体细胞胚胎发生. 林业科学 52(10), 45-54. |
| [4] | 王伟达, 李成浩, 杨静莉, 张含国, 张淑玲 ( 2009). 杂种落叶松未成熟胚的体细胞胚发生和植株再生. 林业科学 12(8), 34-38. |
| [5] |
Attree SM, Pomeroy MK, Fowke LC ( 1992). Manipulation of conditions for the culture of somatic embryos of white spruce for improved triacylglycerol biosynthesis and desiccation tolerance. Planta 187, 395-404.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Chalupa V, Durzan DJ, Vithayasai C ( 1976). Growth and metabolism of cells and tissue of Jack pine ( Pinus banksiana). 2. The quantitative analysis of the growth of callus from hypocotyls and radicles. Can J Bot 54, 446-455.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Durzan DJ, Gupta PK ( 1987). Somatic embryogenesis and polyembryogenesis in Douglas-fir cell suspension cultures. Plant Sci 52, 229-235.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Hakman I, Fowke LC, Von Arnold S, Eriksson T ( 1985). The development of somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos of Picea abies (Norway Spruce). Plant Sci 38, 53-59.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Kim YW, Youn Y, Noh ER, Kim JC ( 1998). Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Japanese larch (Larix leptolepis). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 55, 95-101.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Klimaszewska K ( 1989). Plantlet development from immature zygotic embryos of hybrid larch through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci 63, 95-103.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Klimaszewska K, Devantier Y, Lachance D, Lelu MA, Charest PJ ( 1997). Larix laricinar (tamarack): somatic embryogenesis and genetic transformation. Can J For Res 27, 538-550. |
| [12] | Klimaszewska K, Hargreaves C, Lelu-Walter MA, Trontin JF (2016). Advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis since year 2000. In: Germana MA, Lambardi M, eds. In Vitro Embryogenesis in Higher Plants. New York: Humana Press. pp. 131-162. |
| [13] |
Klimaszewska K, Smith DR ( 1997). Maturation of somatic embryos of Pinus strobus is promoted by a high concentration of gellan gum. Physiol Plant 100, 949-957.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Kvaalen H, von Arnold S ( 1991). Effects of various partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide on different stages of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 27, 49-57.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Lelu MA, Klimaszewska K, Charest PJ ( 1994). Somatic embryogenesis from immature and mature zygotic embryos and from cotyledons and needles of somatic plantlets of Larix. Can J For Res 24, 100-106.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li QF, Deng C, Zhu TQ, Li JJ, Zhang HG, Kong LS, Zhang SG, Wang JH, Chen XY ( 2019). Dynamics of physiological and miRNA changes after long-term proliferation in somatic embryogenesis of Picea balfouriana. Trees 33, 469-480.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Lulsdorf MM, Tautorus TE, Kikcio SI, Bethune TD, Dunstan DI ( 1993). Germination of encapsulated embryos of interior spruce (Picea glauca engelmannii complex) and black spruce (Picea mariana Mill.). Plant Cell Rep 12, 385-389.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Montalbán IA, De Diego N, Moncaleán P ( 2010). Bottlenecks in Pinus radiata somatic embryogenesis: improving maturation and germination. Trees 24, 1061-1071.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Nunes S, Marum L, Farinha N, Pereira VT, Almeida T, Sousa D, Mano N, Figueiredo J, Dias MC, Santos C ( 2018). Somatic embryogenesis of hybrid Pinus elliottii var. elliottii × P. caribaea var. hondurensis and ploidy assessment of somatic plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 132, 71-84.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Plačková L, Hrdlička J, Smýkalová I, Cvečková M, Novák O, Griga M, Doležal K ( 2015). Cytokinin profiling of long-term in vitro pea (Pisum sativum L.) shoot cultures. Plant Growth Regul 77, 125-132.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Roberts DR, Sutton BCS, Flinn BS ( 1990). Erratum: synchronous and high frequency germination of interior spruce somatic embryos following partial drying at high relative humidity. Can J Bot 68, 1832.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Stasolla C, Yeung EC ( 2003). Recent advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis: improving somatic embryo quality. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74, 15-35.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Tautorus TE, Fowke LC, Dunstan DI ( 1991). Somatic embryogenesis in conifers. Can J Bot 69, 1873-1899.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Thompson RG, von Aderkas P ( 1992). Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature embryos of western larch. Plant Cell Rep 11, 379-385.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Tret’yakova IN, Barsukova AV ( 2012). Somatic embryogenesis in in vitro culture of three larch species. Russ J Dev Biol 43, 353-361. |
| [26] | von Aderkas P, Bonga JM, Nagmani R ( 1987). Promotion of embryogenesis in cultured megagametophytes of Larix decidua. Can J For Res 17, 1293-1296. |
| [27] | Yang XY, Zhang XL ( 2010). Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29, 36-57. |
| [1] | 李宇琛, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 黄馨田, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 赵彦, 付春祥. 根癌农杆菌介导的蒙古冰草稳定遗传转化体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [2] | 刘小飞, 孙映波, 黄丽丽, 杨钰钗, 朱根发, 于波. 黑鹅绒海芋体细胞胚发生和植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 750-759. |
| [3] | 和璐璐, 张萱, 章毓文, 王晓霞, 刘亚栋, 刘岩, 范子莹, 何远洋, 席本野, 段劼. 辽东山区不同坡向长白落叶松人工林树冠特征与林木生长关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(11): 1523-1539. |
| [4] | 解雅麟, 王海燕, 雷相东. 基于过程模型的气候变化对长白落叶松人工林净初级生产力的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 826-839. |
| [5] | 于健, 徐倩倩, 刘文慧, 罗春旺, 杨君珑, 李俊清, 刘琪璟. 长白山东坡不同海拔长白落叶松径向生长对气候变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(1): 24-35. |
| [6] | 刘琳, 俞斌, 黄鹏燕, 贾军, 赵华, 彭俊华, 陈鹏, 彭良才. 芒不同基因型愈伤组织诱导及分化的差异[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(2): 192-198. |
| [7] | 陈书安, 王晓东, 赵兵, 王玉春. 应用稀土调控藏红花胚性愈伤组织的生长与分化[J]. 植物学报, 2010, 45(05): 609-614. |
| [8] | 冷文芳, 贺红士, 布仁仓, 胡远满. 中国东北落叶松属3种植物潜在分布对气候变化的敏感性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(5): 825-833. |
| [9] | 曲丽娜 王秋玉 杨传平. 兴安、长白及华北落叶松RAPD 分子标记的物种特异性鉴定[J]. 植物学报, 2007, 24(04): 498-504. |
| [10] | 陈雄文 周广胜 王凤友. 长白落叶松幼苗在受控条件下干物质积累的模拟[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 17(03): 246-250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||