

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 816-830.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24135 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24135
黄雨欣1, 谢涛2, 王省芬3, 郭惠明2, 程红梅2, 马伯军1, 陈析丰1,*( ), 苏晓峰2,*(
), 苏晓峰2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-04
接受日期:2024-10-30
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2024-11-15
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:中国农业科学院生物技术研究所微生物智能设计与合成创新团队程红梅课题组, 长期致力于作物黄萎病综合防治及新型基因编辑器在棉花中的评估和应用研究。近年来, 该课题组成功建立了病原菌精准监测预警方法, 系统解析了病原菌致病力、植物防御反应和环境微生物三者之间的互作机制, 从而利用合成生物学及纳米技术进行作物黄萎病的综合防治。课题组先后主持国家转基因重大专项、973计划、国家自然科学基金、公益性行业科技专项和国家重点研发等项目。在Nature Communications、Plant Biotechnology Journal、Chemical Engineering Journal和International Journal of Biological Macromolecules等国际知名及中文核心期刊上发表论文80余篇。获国家发明专利授权20余项, 为作物黄萎病的综合防控相关研究做出了重要贡献
基金资助:
Huang Yuxin1, Xie Tao2, Wang Xingfen3, Guo Huiming2, Cheng Hongmei2, Ma Bojun1, Chen Xifeng1,*( ), Su Xiaofeng2,*(
), Su Xiaofeng2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-04
Accepted:2024-10-30
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2024-11-15
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要: 由大丽轮枝菌(Verticillium dahliae)引起的黄萎病是棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)生产中最主要的威胁之一, 其可导致棉花大幅减产和纤维品质严重下降。前期对接种大丽轮枝菌的拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)进行转录组分析, 表明DIR1类蛋白基因AT3G53980.2受病原菌强烈诱导表达。该研究发现, 棉花脂质转移蛋白编码基因GhDIR1 (Gh_A09G180700.1)与AT3G53980.2表现出高度的同源性。生物信息学分析表明, GhDIR1开放阅读框(ORF)为351 bp, 编码116个氨基酸残基。亚细胞定位结果显示GhDIR1定位于细胞膜。分析GhDIR1在大丽轮枝菌V991侵染后的表达模式, 发现其能快速响应大丽轮枝菌侵染。利用病毒诱导的基因沉默(VIGS)技术下调该基因表达后, 棉花对黄萎病菌的抗性显著降低。野生型和GhDIR1沉默植株转录组测序结果表明, 差异表达基因主要在类黄酮生物合成、倍半萜和三萜生物合成以及α-亚麻酸代谢3个途径富集; 同时, 荧光定量PCR结果表明, 3个途径中的6个关键基因(GhCHS、GhDFR、GhCAD、GhSEQ、GhLOX和GhAOC)在GhDIR1沉默植株中均下调表达, 与转录组数据一致。推测GhDIR1可能通过介导类黄酮和萜类化合物的合成途径, 并调节茉莉酸(JA)等植物激素的次级代谢来激活相关信号通路, 进而影响植株抗病性。综上, GhDIR1作为棉花抗黄萎病的正向调控因子, 通过参与多种激素和抗病信号网络调控植物的免疫反应。
黄雨欣, 谢涛, 王省芬, 郭惠明, 程红梅, 马伯军, 陈析丰, 苏晓峰. 棉花抗黄萎病相关基因GhDIR1的生物学功能分析. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 816-830.
Huang Yuxin, Xie Tao, Wang Xingfen, Guo Huiming, Cheng Hongmei, Ma Bojun, Chen Xifeng, Su Xiaofeng. Functional Verification of GhDIR1 Gene Against Verticillium Wilt in Cotton. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 816-830.
| Primer names | Primer sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| GhDIR1-F | ATGGCAGCTGCAATGAAACTC |
| GhDIR1-R | TCAAGGAAGTGTATATGCTCCAC |
| qGhDIR1-F | CCTGGGAAAGGTGGTTGATG |
| qGhDIR1-R | TCTCAGGCTTGATTCCAGATGC |
| qGhCHS-F | GCTGCTGTTATAGTAGGTGCGGATC |
| qGhCHS-R | CTCAGCTAGGCTCTTTTCAATGTTC |
| qGhDFR-F | GCTCTGGGTTCATTGGTTCATGG |
| qGhDFR-R | CCTCTTCAGCTAAATCTGCTTTCC |
| qGhCAD-F | CCTGGCATTTGGGGAGATATCTTC |
| qGhCAD-R | GACACCCAACCTTTGGACTGC |
| qGhSEQ-F | GCAAAGGAGAATGCTCGCCTG |
| qGhSEQ-R | CCTGGCTGCAACAGTTCTCCAAC |
| qGhLOX-F | GATCGTGCTTGATGGTCTCACTG |
| qGhLOX-R | CGTTCCCTCTCAATGCCTGC |
| qGhAOC-F | CGGATAGGAATAACAGCAGGGATG |
| qGhAOC-R | GCCAGATCCACCAGTAATAGCG |
| Vd-ITS-F | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| Vd-ITS-R | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
| GhDIR1-VIGS-F | TCTGTGAGTAAGGTTACC GAATTCG- TTCTGGGATTGATTGTGCTTATT |
| GhDIR1-VIGS-R | ACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACC GGAT C C- ATGCTCCACATCTGTAACCGACT |
| p1132-GhDIR1-F | TCTGTGAGTAAGGTTACC GAATTCC- CTGGGAAAGGTGGTTGATG |
| p1132-GhDIR1-R | ACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACC GGATCC- TCTCAGGCTTGATTCCAGATGC |
| UBQ-F | AGCTCGGATACGATTGATAACG |
| UBQ-R | GAAGACGAAGAACAAGGGGAAG |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| Primer names | Primer sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| GhDIR1-F | ATGGCAGCTGCAATGAAACTC |
| GhDIR1-R | TCAAGGAAGTGTATATGCTCCAC |
| qGhDIR1-F | CCTGGGAAAGGTGGTTGATG |
| qGhDIR1-R | TCTCAGGCTTGATTCCAGATGC |
| qGhCHS-F | GCTGCTGTTATAGTAGGTGCGGATC |
| qGhCHS-R | CTCAGCTAGGCTCTTTTCAATGTTC |
| qGhDFR-F | GCTCTGGGTTCATTGGTTCATGG |
| qGhDFR-R | CCTCTTCAGCTAAATCTGCTTTCC |
| qGhCAD-F | CCTGGCATTTGGGGAGATATCTTC |
| qGhCAD-R | GACACCCAACCTTTGGACTGC |
| qGhSEQ-F | GCAAAGGAGAATGCTCGCCTG |
| qGhSEQ-R | CCTGGCTGCAACAGTTCTCCAAC |
| qGhLOX-F | GATCGTGCTTGATGGTCTCACTG |
| qGhLOX-R | CGTTCCCTCTCAATGCCTGC |
| qGhAOC-F | CGGATAGGAATAACAGCAGGGATG |
| qGhAOC-R | GCCAGATCCACCAGTAATAGCG |
| Vd-ITS-F | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| Vd-ITS-R | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
| GhDIR1-VIGS-F | TCTGTGAGTAAGGTTACC GAATTCG- TTCTGGGATTGATTGTGCTTATT |
| GhDIR1-VIGS-R | ACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACC GGAT C C- ATGCTCCACATCTGTAACCGACT |
| p1132-GhDIR1-F | TCTGTGAGTAAGGTTACC GAATTCC- CTGGGAAAGGTGGTTGATG |
| p1132-GhDIR1-R | ACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACC GGATCC- TCTCAGGCTTGATTCCAGATGC |
| UBQ-F | AGCTCGGATACGATTGATAACG |
| UBQ-R | GAAGACGAAGAACAAGGGGAAG |
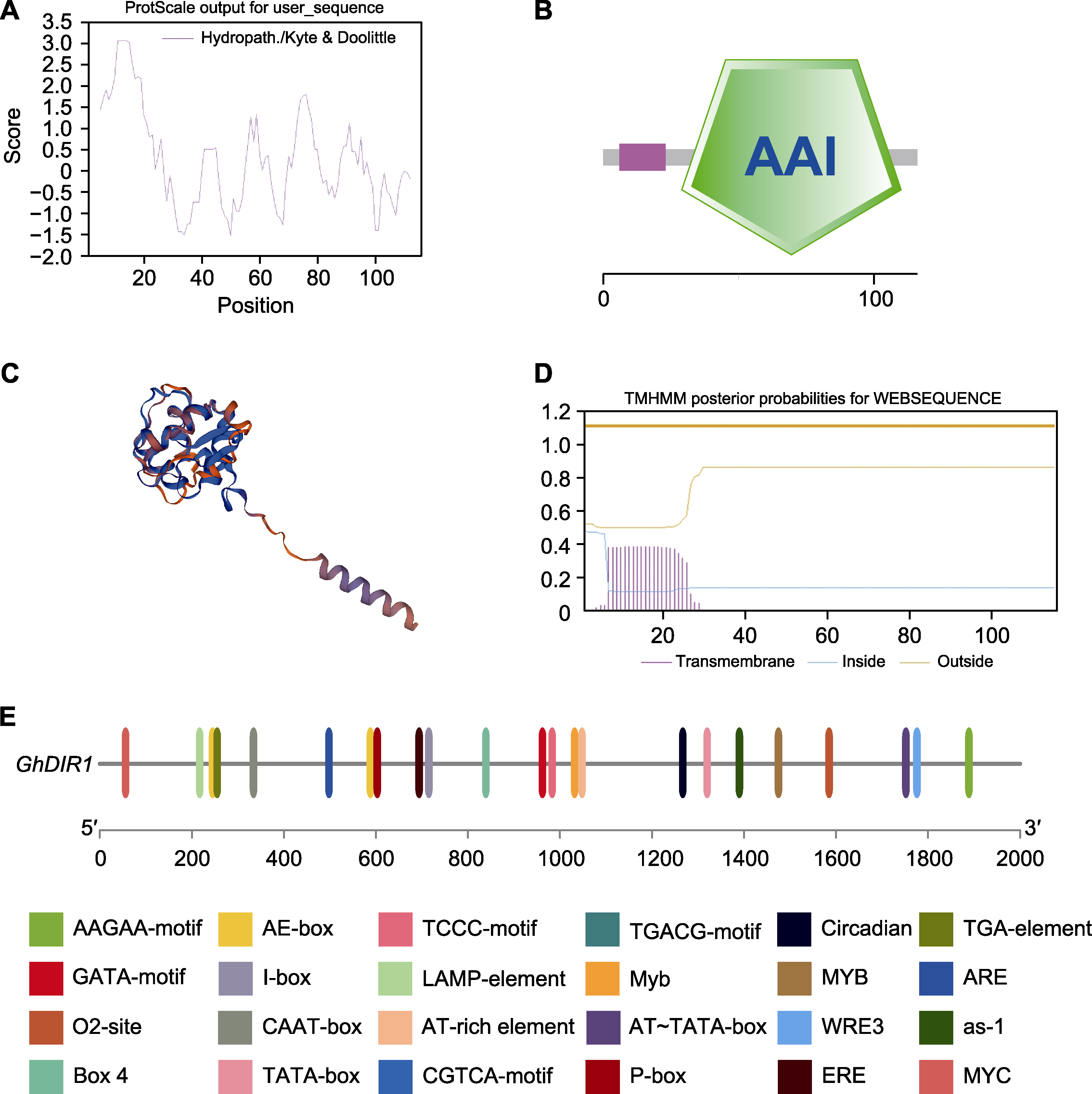
图1 GhDIR1蛋白质理化性质及基因上游启动子顺式作用元件分析 (A) GhDIR1蛋白亲疏水性分析; (B) GhDIR1结构域分析; (C) GhDIR1蛋白的三级结构预测; (D) GhDIR1蛋白跨膜结构域预测; (E) GhDIR1基因启动子顺式作用元件分析
Figure 1 Physicochemical properties of GhDIR1 and analysis of cis-acting element of the GhDIR1 gene promoter (A) Hydrophilicity analysis of GhDIR1 protein; (B) GhDIR1 structural domain analysis; (C) Tertiary structure prediction of GhDIR1 protein; (D) Transmembrane structural domain prediction of GhDIR1 protein; (E) Analysis of cis-acting element of the GhDIR1 gene promoter
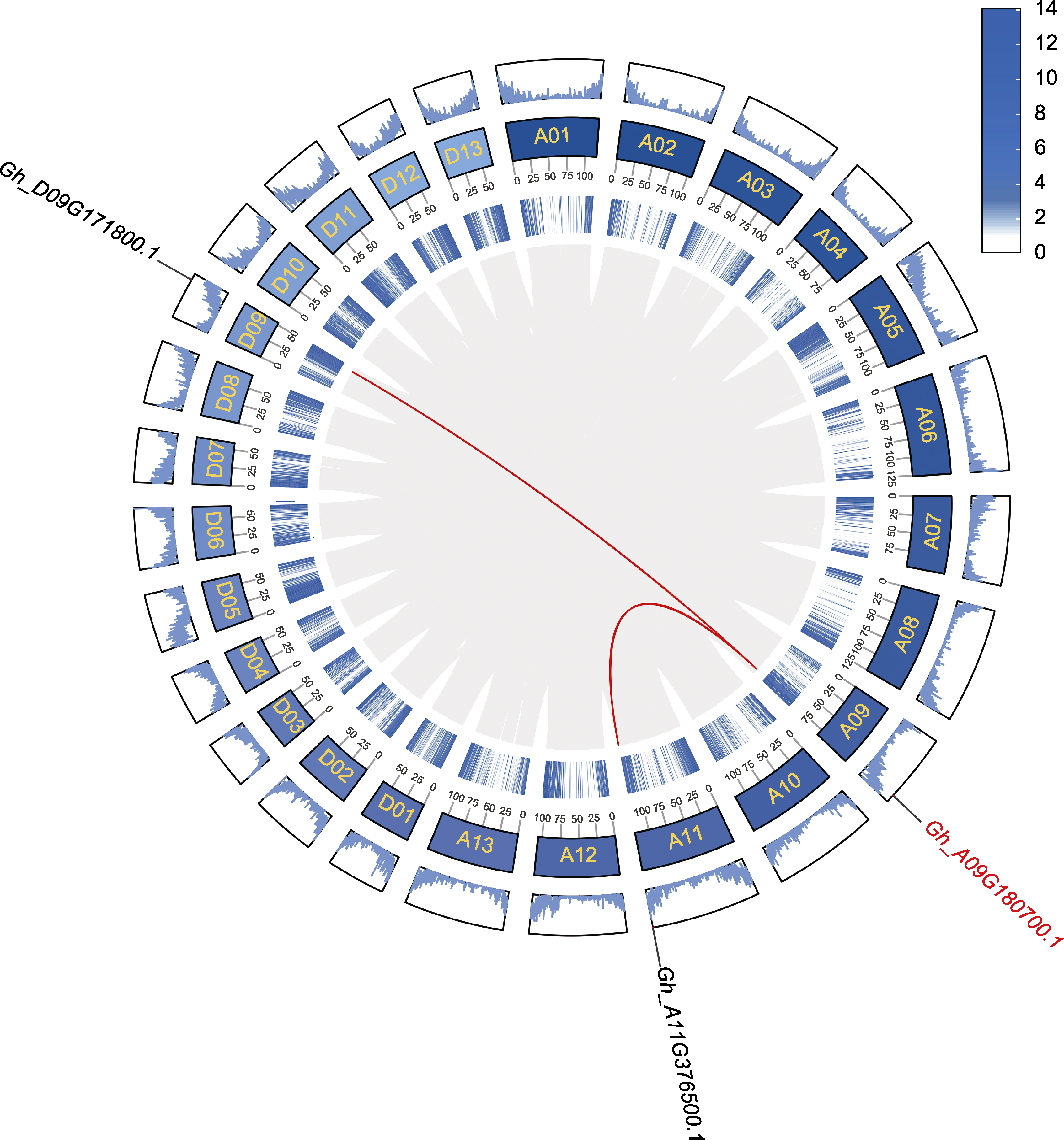
图2 GhDIR1的基因组共线性分析 深蓝色区域为陆地棉染色体。灰线描绘了陆地棉26条染色体中的所有共线性对。红色线条为与目的基因存在片段重复的共线性基因对, 最内圈及最外圈浅蓝色区域为基因密度的2种不同表现形式。
Figure 2 Genome collinearity analysis of GhDIR1 Dark blue regions represent the chromosomes of Gossypium hirsutum. The gray lines depict all collinear pairs across the 26 chromosomes. The red lines highlight collinear gene pairs associated with segmental duplications of the target gene. The innermost and outermost light blue rings illustrate two distinct representations of gene density.
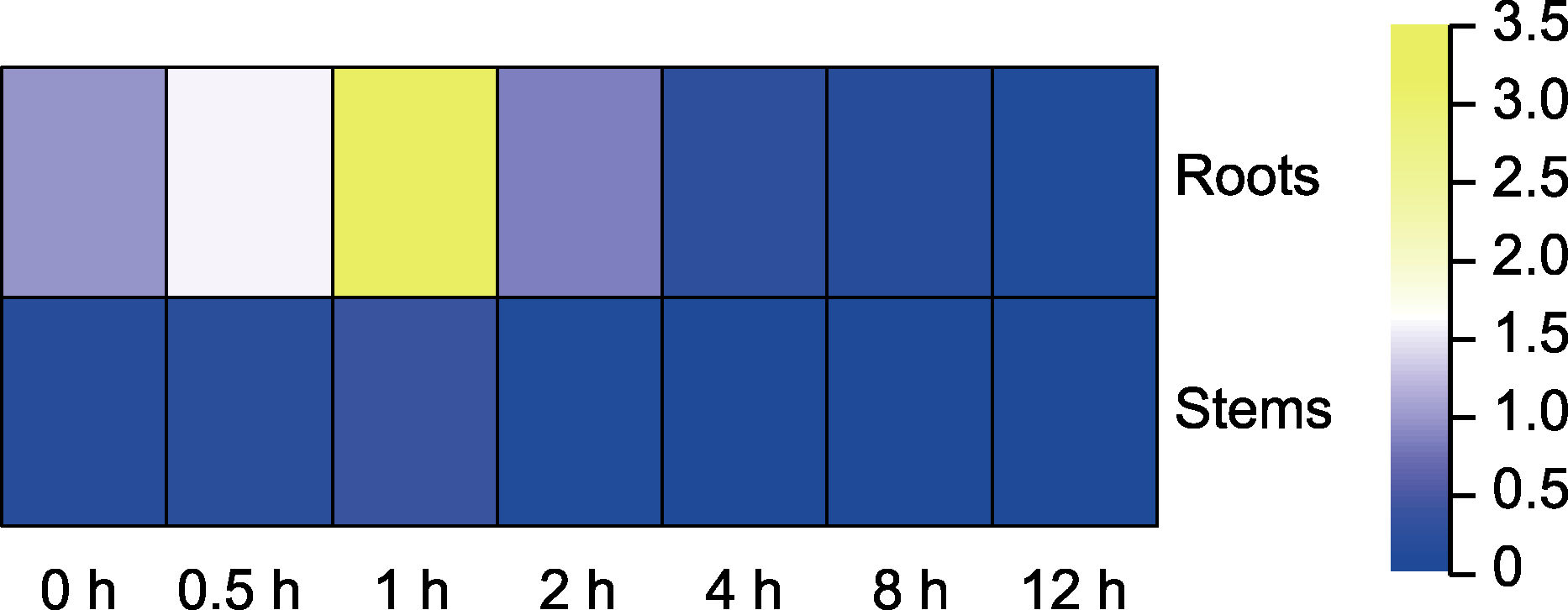
图3 GhDIR1在接种大丽轮枝菌棉花中的表达 热图分析GhDIR1基因在不同器官(根、茎)和不同接种时间(0、0.5、1、2、4、8和12小时)棉花中的表达水平。从蓝色到黄色表示低表达到高表达。
Figure 3 Expression of GhDIR1 in cotton inoculated with Verticillium dahliae Heat map analysis of GhDIR1 gene expressions in different organs (roots, stems) and different inoculation times (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 12 h) of Gossypium hirsutum with V. dahliae. The color from blue to yellow indicates low to high level of expression.
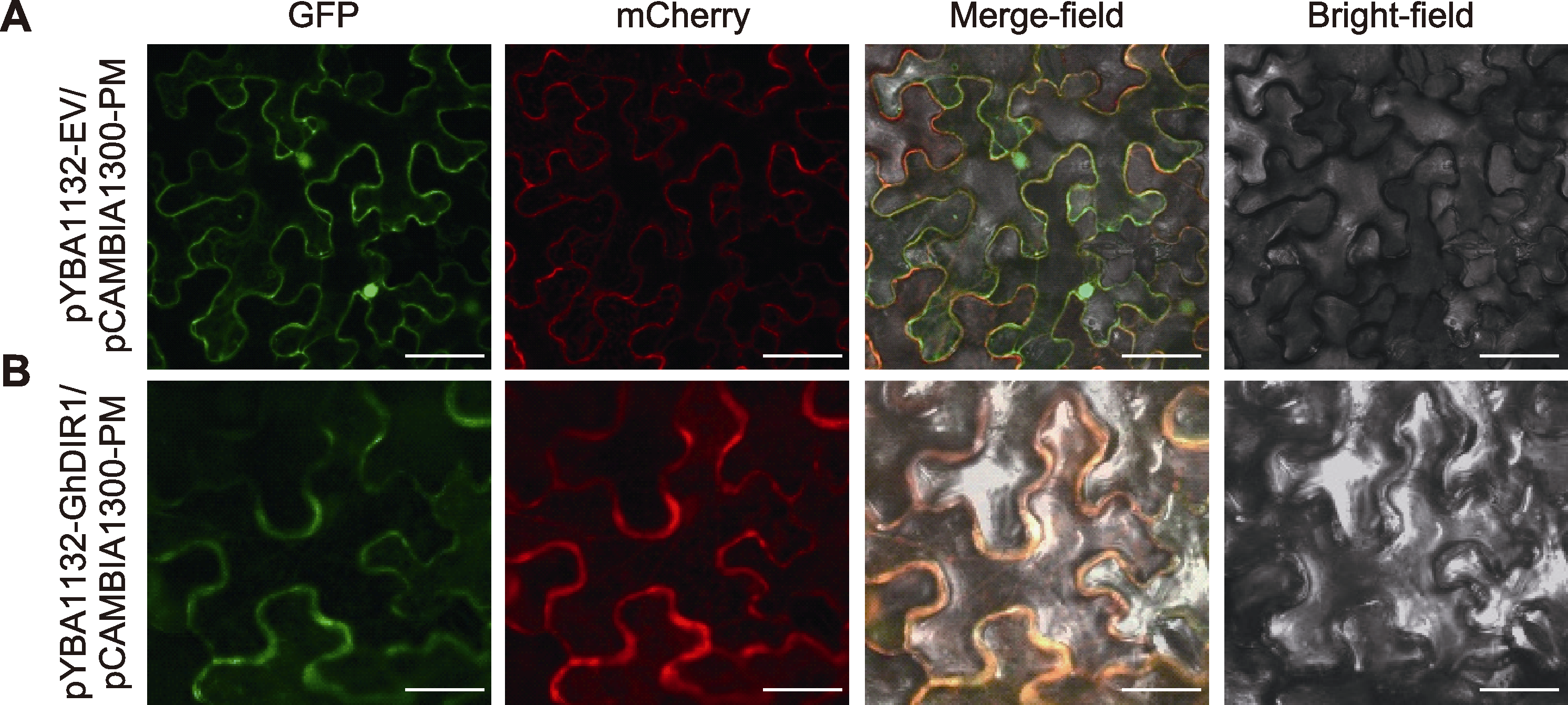
图4 GhDIR1的亚细胞定位 将GFP、GhDIR1-GFP融合表达蛋白分别与PM-mCherry膜定位marker共定位于烟草; GFP和GhDIR1-GFP融合表达蛋白在绿色荧光通道产生绿色荧光, PM-mCherry膜定位marker只在红色荧光通道mCherry中产生红色信号。(A) GFP亚细胞定位图(bars= 20 μm); (B) GhDIR1-GFP亚细胞定位图(bars=10 μm)
Figure 4 Subcellular localization of GhDIR1 The fusion proteins GFP and GhDIR1-GFP were co-localized with the PM-mCherry membrane localization marker in tobacco. The GFP and GhDIR1-GFP fusion proteins exhibited green fluorescence in the green fluorescence channel, while the PM-mCherry membrane localization marker displayed red fluorescence in the mCherry channel only. (A) GFP subcellular localization map (bars=20 μm); (B) GhDIR1-GFP subcellular localization map (bars=10 μm)
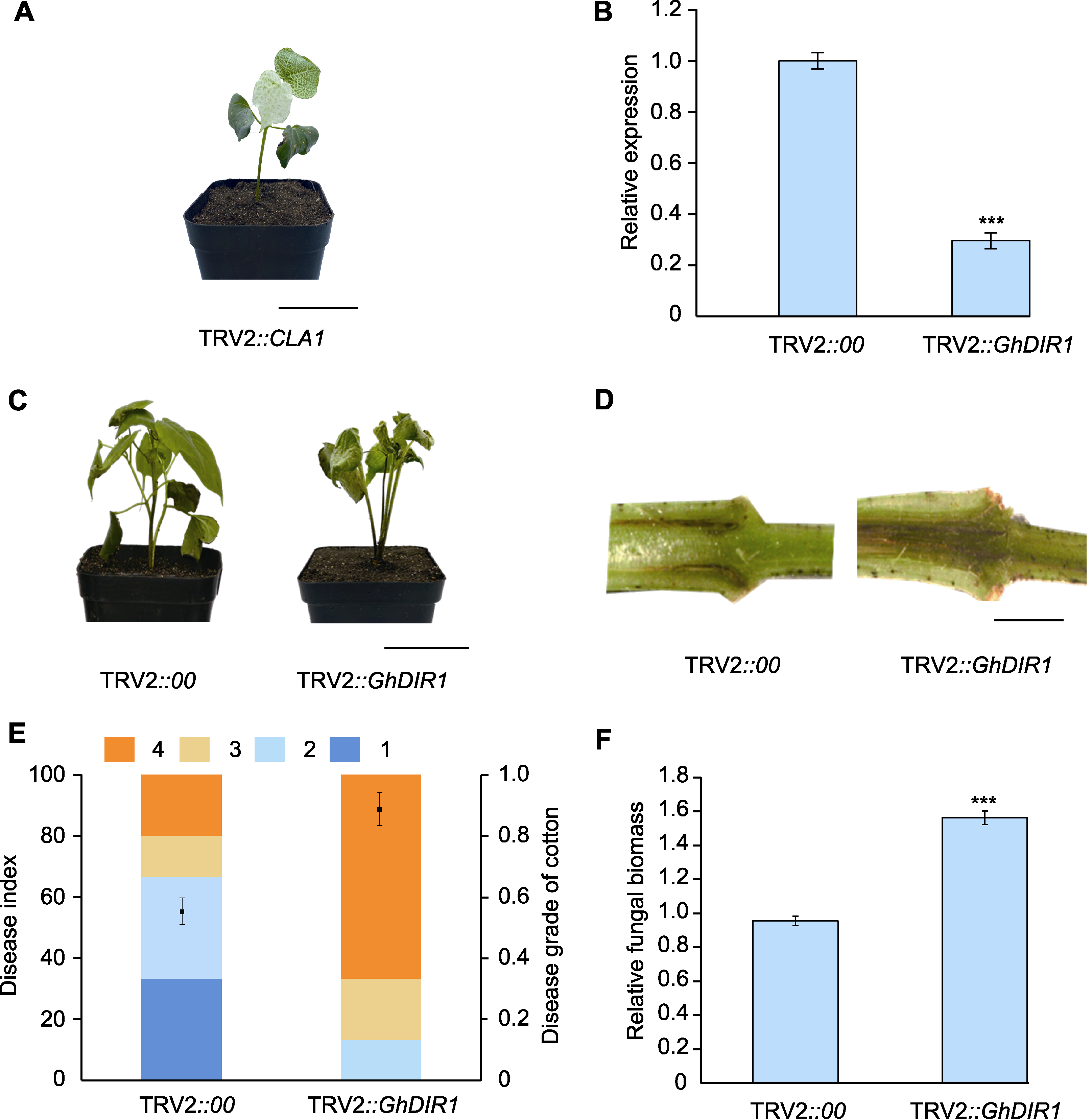
图5 GhDIR1基因沉默效率检测及其对棉花黄萎病抗性的影响 (A) TRV2::CLA1植株(bar=5 cm); (B) GhDIR1在沉默组棉花植株中的表达水平(3次生物学重复(n=3); 统计分析方法为ANOVA; *** P<0.001); (C) 大丽轮枝菌侵染14天后TRV2::00和TRV2::GhDIR1植株表型(bar=5 cm); (D) 大丽轮枝菌侵染14天后TRV2::00和TRV2::GhDIR1茎秆表型(bar=1 cm); (E) 接种14天后TRV2::00和TRV2::GhDIR1棉花植株病情指数统计(1-4分别为病情指数分级。1: 子叶变黄, 真叶无病症; 2: 子叶全部出现病症, 1-3片真叶出现病斑; 3: 包括子叶在内, 超过5片棉花叶片出现病症; 4: 所有叶片均表现病症, 叶片脱落, 植株枯死); (F) 接种14天后TRV2::00和TRV2::GhDIR1棉花植株相对真菌生物量测定(3次生物学重复(n=3); 统计分析方法为ANOVA; *** P<0.001)
Figure 5 Detection of GhDIR1 gene silencing efficiency and the resistant analysis of GhDIR1 silenced seedlings against cotton Verticillium wilt (A) TRV2::CLA1 plants (bar=5 cm); (B) Gene expression of GhDIR1 in silenced cotton plants (three biological replicates (n=3); ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis; *** P<0.001); (C) Phenotype of TRV2::00 and TRV2::GhDIR1 plants at 14 days post inoculation (dpi) with Verticillium dahliae (bar=5 cm); (D) Stem phenotype of TRV2::00 and TRV2::GhDIR1 plants at 14 dpi with V. dahliae (bar=1 cm); (E) Statistical analysis of disease index in cotton plants of TRV2::00 and TRV2::GhDIR1 at 14 dpi (grades 1-4 represent disease severity classifications. 1: Cotyledons turn yellow, no symptoms on true leaves; 2: All cotyledons show symptoms, 1-3 true leaves show necrosis or chlorosis; 3: More than 5 cotton leaves, including cotyledons, show symptoms; 4: All leaves show symptoms, and leaves fall off/plant dies); (F) Fungal biomass of TRV2::00 and TRV2::GhDIR1 plants at 14 dpi with V. dahliae (three biological replicates (n=3); ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis; *** P<0.001)
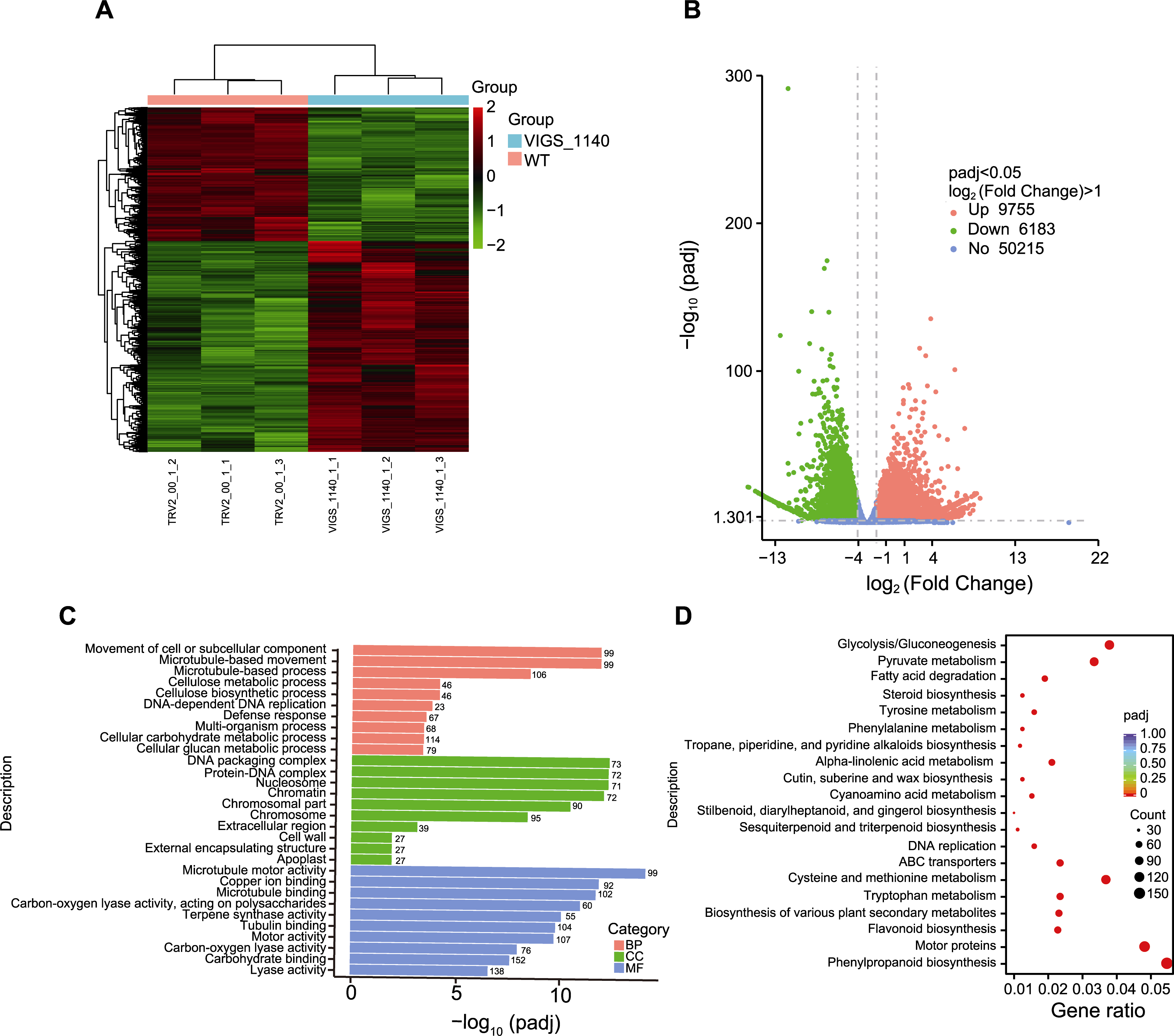
图6 TRV2::00和TRV2::GhDIR1棉花RNA-seq分析 (A) 每个样本中差异表达基因(DEGs)热图; (B) DEGs火山图; (C) GO分析; (D) KEGG分析。WT: 野生型; VIGS: 病毒诱导的基因沉默植株; BP: 生物过程; CC: 细胞成分; MF: 分子功能
Figure 6 RNA-seq comparison between TRV2::00 and TRV2::GhDIR1 cottons (A) Heat map of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in each sample; (B) Volcano map of DEGs; (C) GO terms; (D) KEGG terms. WT: Wild type; VIGS: Virus-induced gene silencing plant; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function
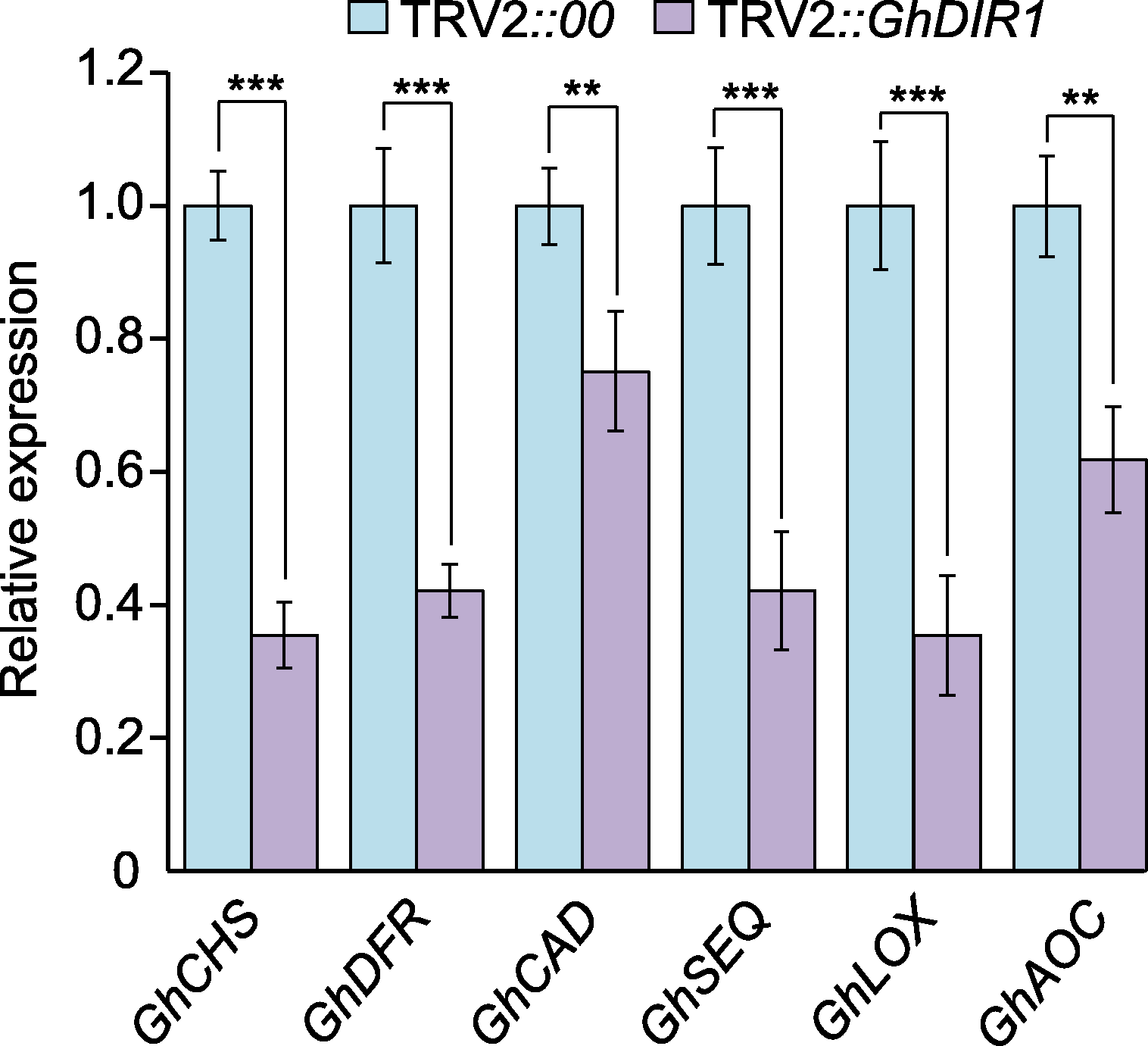
图7 qRT-PCR验证6个关键差异表达基因(DEGs)的表达水平 蓝色柱子表示TRV2::00中基因相对表达水平, 标定为1, 作为对照组。紫色柱子为TRV2::GhDIR1中基因相对表达水平。3次生物学重复(n=3)。统计分析方法为ANOVA。** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
Figure 7 qRT-PCR verification of the expression levels of six key differentially expressed genes (DEGs) The blue bars represent the relative expression levels of genes in TRV2::00, normalized to 1, serving as the control group. The purple bars indicate the relative expression levels of genes in TRV2::GhDIR1. Three biological replicates (n= 3). ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis. ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
| [1] | Anderson JP, Badruzsaufari E, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Desmond OJ, Ehlert C, Maclean DJ, Ebert PR, Kazan K (2004). Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 3460-3479. |
| [2] |
Chen B, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhang M, Ma QM, Wang XF, Ma ZY (2021). The G-protein α subunit GhGPA positively regulates Gossypium hirsutum resistance to Verticillium dahliae via induction of SA and JA signaling pathways and ROS accumulation. Crop J 9, 823-833.
DOI |
| [3] | Chen LB, Ji CH, Zhou DG, Gou X, Tang JN, Jiang YJ, Han JL, Liu YG, Chen LY, Xie YY (2022). OsLTP47 may function in a lipid transfer relay essential for pollen wall development in rice. J Genet Genomics 49, 481-491. |
| [4] | Dai PH, Hu ZY, Li XQ, Lei JF, Liu C, Liu XD, Li Y (2022). Cloning and functional analysis of GhMYB6 gene related to cotton Verticillium wilt resistance. J South Agric 53, 3020-3027. (in Chinese) |
| 代培红, 胡子曜, 李秀青, 雷建峰, 刘超, 刘晓东, 李月 (2022). 棉花黄萎病相关基因GhMYB6的克隆与功能分析. 南方农业学报 53, 3020-3027. | |
| [5] | David L, Kang JN, Nicklay J, Dufresne C, Chen SX (2021). Identification of DIR1-dependant cellular responses in guard cell systemic acquired resistance. Front Mol Biosci 8, 746523. |
| [6] | Dong YM, Zhang WY, Ling ZY, Li JR, Bai HT, Li H, Shi L (2020). Advances in transcription factors regulating plant terpenoids biosynthesis. Chin Bull Bot 55, 340-350. (in Chinese) |
|
董燕梅, 张文颖, 凌正一, 李靖锐, 白红彤, 李慧, 石雷 (2020). 转录因子调控植物萜类化合物生物合成研究进展. 植物学报 55, 340-350.
DOI |
|
| [7] | Fan YP, Zhang YX, Rui C, Xu N, Zhang H, Wang J, Malik WA, Han MG, Zhao LJ, Lu XK, Chen XG, Chen C, Ye WW (2021). Zinc finger transcription factor ZAT family genes confer multi-tolerances in Gossypium hirsutum L. J Cotton Res 4, 24. |
| [8] | Fradin EF, Thomma BPHJ (2006). Physiology and molecular aspects of Verticillium wilt diseases caused by V. dahliae and V. albo-atrum. Mol Plant Pathol 7, 71-86. |
| [9] |
Gao SQ, Shao WK, Zhao Z, Shao PX, Hu WR, Huang QS (2023). Functional analysis of cotton calcineurin B-like protein GhCBL3-A01 in regulating the resistance to Verticillium wilt. Cotton Sci 35, 447-458. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
高升旗, 邵武奎, 赵准, 邵盘霞, 胡文冉, 黄全生 (2023). 类钙调磷酸酶B亚基蛋白GhCBL3-A01调控棉花黄萎病抗性的功能分析. 棉花学报 35, 447-458.
DOI |
|
| [10] | Gautam H, Sharma A, Trivedi PK (2023). The role of flavonols in insect resistance and stress response. Curr Opin Plant Biol 73, 102353. |
| [11] | Gfeller A, Dubugnon L, Liechti R, Farmer EE (2010). Jasmonate biochemical pathway. Sci Signal 3, cm3. |
| [12] | Harms K, Atzorn R, Brash A, Kuhn H, Wasternack C, Willmitzer L, Pena-Cortes H (1995). Expression of a flax allene oxide synthase cDNA leads to increased endogenous jasmonic acid (JA) levels in transgenic potato plants but not to a corresponding activation of JA-responding genes. Plant Cell 7, 1645-1654. |
| [13] | Hu XQ, Shi ZY, Zhu YT, Gao LY, Wang P, Wang HW, Hou YX (2023). Mechanism of the cotton GhRAR1 gene regulating the resistance of cotton to Verticillium wilt. Plant Prot 49(2), 39-47, 56. (in Chinese) |
| 胡晓倩, 石志钰, 朱玉涛, 高琳颖, 王平, 王宏伟, 侯玉霞 (2023). 棉花GhRAR1基因调控棉花抗黄萎病机理的研究. 植物保护 49(2), 39-47, 56. | |
| [14] | Hu ZY, Li XQ, Dai PH, Lei JF, Liu JF, Zhao Y, Deng JH, Liu C, Liu XD, Li Y (2022). Functional verification of GhP450-94C1 that a Verticillium wilt resistant gene in Gossypium hirsutum L. Acta Agric Bor-Sin 37(6), 72-81. (in Chinese) |
|
胡子曜, 李秀青, 代培红, 雷建峰, 柳建飞, 赵燚, 邓嘉辉, 刘超, 刘晓东, 李月 (2022). 陆地棉细胞色素P450基因GhP450-94C1黄萎病抗性功能验证. 华北农学报 37(6), 72-81.
DOI |
|
| [15] |
Huang H, Liu B, Liu LY, Song SS (2017). Jasmonate action in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 68, 1349-1359.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Huang Y, Xie FJ, Cao X, Li MY (2021). Research progress in biosynthesis and regulation of plant terpenoids. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 35, 1799-1808. |
| [17] |
Huffaker A, Kaplan F, Vaughan MM, Dafoe NJ, Ni XZ, Rocca JR, Alborn HT, Teal PEA, Schmelz EA (2011). Novel acidic sesquiterpenoids constitute a dominant class of pathogen-induced phytoalexins in maize. Plant Physiol 156, 2082-2097.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Jacq A, Pernot C, Martinez Y, Domergue F, Payré B, Jamet E, Burlat V, Pacquit VB (2017). The Arabidopsis lipid transfer protein 2 (AtLTP2) is involved in cuticle-cell wall interface integrity and in etiolated hypocotyl permeability. Front Plant Sci 8, 263. |
| [19] | Kim J, Lee WJ, Vu TT, Jeong CY, Hong SW, Lee H (2017). High accumulation of anthocyanins via the ectopic expression of AtDFR confers significant salt stress tolerance in Brassica napus L. Plant Cell Rep 36, 1215-1224. |
| [20] | Kumar V, Nadda G, Kumar S, Yadav SK (2013). Transgenic tobacco overexpressing tea cDNA encoding dihydroflavonol 4-reductase and anthocyanidin reductase induces early flowering and provides biotic stress tolerance. PLoS One 8, e65535. |
| [21] | Li MJ (2021). Functional Verification of Cotton GhIQM1, GhNAC90 and GhBsr-d1 Genes in Resistance to Verticillium Wilt. Master’s thesis. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University. pp. 23-24. (in Chinese) |
| 李名江 (2021). 棉花GhIQM1、GhNAC90和GhBsr-d1基因在抗黄萎病中的功能验证. 硕士论文. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学. pp. 23-24. | |
| [22] | Liao ZH, Wang L, Li CZ, Cao MJ, Wang JN, Yao ZL, Zhou SY, Zhou GX, Zhang DY, Lou YG (2022). The lipoxygenase gene OsRCI-1 is involved in the biosynthesis of herbivore-induced JAs and regulates plant defense and growth in rice. Plant Cell Environ 45, 2827-2840. |
| [23] | Liu DF, Shi SP, Hao ZJ, Xiong WT, Luo MZ (2019). OsbZIP81, a homologue of Arabidopsis VIP1, may positively regulate JA levels by directly targetting the genes in JA signaling and metabolism pathway in rice. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2360. |
| [24] | Liu PP, von Dahl CC, Park SW, Klessig DF (2011). Interconnection between methyl salicylate and lipid-based long-distance signaling during the development of systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant Physiol 155, 1762-1768. |
| [25] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Lu XR, Jia XY, Niu JH (2018). The present situation and prospects of cotton industry development in China. Sci Agric Sin 51, 26-36. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
卢秀茹, 贾肖月, 牛佳慧 (2018). 中国棉花产业发展现状及展望. 中国农业科学 51, 26-36.
DOI |
|
| [27] | Maldonado AM, Doerner P, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Cameron RK (2002). A putative lipid transfer protein involved in systemic resistance signaling in Arabidopsis. Nature 419, 399-403. |
| [28] | Mansfeld BN, Colle M, Kang YY, Jones AD, Grumet R (2017). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses of cucumber fruit peels reveal a developmental increase in terpenoid glycosides associated with age-related resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Hortic Res 4, 17022. |
| [29] | Mo HJ, Wang XF, Zhang Y, Zhang GY, Zhang JF, Ma ZY (2015). Cotton polyamine oxidase is required for spermine and camalexin signaling in the defence response to Verticillium dahliae. Plant J 83, 962-975. |
| [30] |
Qanmber G, Lu LL, Liu Z, Yu DQ, Zhou KH, Huo P, Li FG, Yang ZR (2019). Genome-wide identification of GhAAI genes reveals that GhAAI66 triggers a phase transition to induce early flowering. J Exp Bot 70, 4721-4736.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Sanchez S, Demain AL (2008). Metabolic regulation and overproduction of primary metabolites. Microb Biotechnol 1, 283-319.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Seo SB, McNamara P, Heo S, Turner A, Lane WS, Chakravarti D (2001). Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the set oncoprotein. Cell 104, 119-130.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Song RR, Li JP, Xie CJ, Jian W, Yang XY (2020). An overview of the molecular genetics of plant resistance to the Verticillium wilt pathogen Verticillium dahliae. Int J Mol Sci 21, 1120. |
| [34] | Su XF, Lu GQ, Guo HM, Zhang KX, Li XK, Cheng HM (2018). The dynamic transcriptome and metabolomics profiling in Verticillium dahliae inoculated Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Rep 8, 15404. |
| [35] | Thayale Purayil F, Rajashekar B, Kurup SS, Cheruth AJ, Subramaniam S, Hassan Tawfik N, Amiri KMA (2020). Transcriptome profiling of Haloxylon persicum (Bunge ex Boiss and Buhse) an endangered plant species under PEG-induced drought stress. Genes (Basel) 11, 640. |
| [36] | Tholl D (2015). Biosynthesis and biological functions of terpenoids in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 148, 63-106. |
| [37] | Waadt R, Seller CA, Hsu PK, Takahashi Y, Munemasa S, Schroeder JI (2022). Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23, 680-694. |
| [38] | Wang J, Dong JZ, Chen H, Zheng LS, Wang M (2018). Analysis and forecast of global cotton import and export trade. Cotton Text Technol 46(3), 81-84. (in Chinese) |
| 王健, 董俊哲, 陈浩, 郑丽莎, 王铭 (2018). 全球棉花进出口贸易分析及展望. 棉纺织技术 46(3), 81-84. | |
| [39] | Wang LL, Xu GJ, Li LH, Ruan MY, Bennion A, Wang GL, Li R, Qu SH (2023). The OsBDR1-MPK3 module negatively regulates blast resistance by suppressing the jasmonate signaling and terpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2211102120. |
| [40] |
Wang Q, Cao R, Zhang YN, Qi PY, Wang LZ, Fang SM (2021). Biosynthesis and regulation of terpenoids from basidiomycetes: exploration of new research. AMB Express 11, 150.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Wang XF (2007). Studies on Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein Receptors on Rice Cell Membranes. PhD dissertation. Shanghai: Fudan University. pp. 64-65. (in Chinese) |
| 汪笑峰 (2007). 水稻细胞膜上非特异性脂质转移蛋白受体的研究. 博士论文. 上海: 复旦大学. pp. 64-65. | |
| [42] | Xie JW, Cao XY, Pan WQ, Du LJ (2024). Advances in plant flavonoid transport and accumulation mechanism. Chin Bull Bot 59, 463-480. (in Chinese) |
|
谢靖雯, 曹晓云, 潘婉琪, 杜灵娟 (2024). 植物类黄酮转运与积累机制的研究进展. 植物学报 59, 463-480.
DOI |
|
| [43] | Xu YH, Wang JW, Wang S, Wang JY, Chen XY (2004). Characterization of GaWRKY1, a cotton transcription factor that regulates the sesquiterpene synthase gene (+)-δ-cadinene synthase-A. Plant Physiol 135, 507-515. |
| [44] |
Yamaguchi Y, Barona G, Ryan CA, Pearce G (2011). GmPep914, an eight-amino acid peptide isolated from soybean leaves, activates defense-related genes. Plant Physiol 156, 932-942.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Yang G, Sun MH, Wang ZF, Hu QY, Guo JJ, Yu J, Lei CZ, Dang RH (2023). Comparative genomics identifies the evolutionarily conserved gene TPM3 as a target of eca-miR-1 involved in the skeletal muscle development of donkeys. Int J Mol Sci 24, 15440. |
| [46] | Yang YX, Ahammed GJ, Wu CJ, Fan SY, Zhou YH (2015). Crosstalk among jasmonate, salicylate and ethylene signaling pathways in plant disease and immune responses. Curr Protein Pept Sci 16, 450-461. |
| [47] |
Yu KS, Soares JM, Mandal MK, Wang CX, Chanda B, Gifford AN, Fowler JS, Navarre D, Kachroo A, Kachroo P (2013). A feedback regulatory loop between G3P and lipid transfer proteins DIR1 and AZI1 mediates azelaic-acid-induced systemic immunity. Cell Rep 3, 1266-1278.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Yu TF, Hou ZH, Wang HL, Chang SY, Song XY, Zheng WJ, Zheng L, Wei JT, Lu ZW, Chen J, Zhou YB, Chen M, Sun SL, Jiang QY, Jin LG, Ma YZ, Xu ZS (2024). Soybean steroids improve crop abiotic stress tolerance and increase yield. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 2333-2347. |
| [49] | Zhang M, Zhang J, Zhang XY, Wang GN, Wang XF, Zhang Y (2023). Cloning and functional analysis of GhNAC1 in upland cotton involved in Verticillium wilt resistance. J Agric Sci Technol 25(10), 35-44. (in Chinese) |
| 张曼, 张进, 张新雨, 王国宁, 王省芬, 张艳 (2023). 陆地棉GhNAC1基因的克隆及抗黄萎病功能分析. 中国农业科技导报 25(10), 35-44. | |
| [50] | Zhu YT, Hu XQ, Wang P, Wang HW, Ge XY, Li FG, Hou YX (2022). GhODO1, an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor, positively regulates cotton resistance to Verticillium dahliae via the lignin biosynthesis and jasmonic acid signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 201, 580-591. |
| [51] | Zulfiqar S, Farooq MA, Zhao TT, Wang PP, Tabusam J, Wang YH, Xuan SX, Zhao JJ, Chen XP, Shen SX, Gu AX (2023). Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS): a powerful tool for crop improvement and its advancement towards epigenetics. Int J Mol Sci 24, 5608. |
| [1] | 赵蔓雅, 孙倩楠, 徐晶晶, 段恬妮, 蔡锦涛, 周婧, 范婷婷, 萧浪涛, 王若仲. 一个新的黄瓜叶色突变体鉴定、初定位及转录组分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 515-532. |
| [2] | 郭宝生, 刘素恩, 赵存鹏, 王兆晓, 王凯辉, 李丹, 刘旭, 杜海英, 耿军义. 转FBP7::iaaM基因陆地棉种质冀资139纤维品质性状杂种优势分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 166-174. |
| [3] | 阿曼古丽·买买提阿力, 拉扎提·努尔布拉提, 高丽丽, 张巨松, 田立文. 盐胁迫对海岛棉和陆地棉幼苗生长及 生理特性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(4): 465-473. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||