

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (6): 888-900.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24161 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24161
靳佳瑞1,2, 刘玉萍1,2,3, 苏旭1,2,3,*( ), 刘涛4,*(
), 刘涛4,*( ), 余明君1,2, 杨倩1,2, 曲荣举1,2, 张朋辉1,2, 才让扎西1,2, 南措加1, 周乐怡1
), 余明君1,2, 杨倩1,2, 曲荣举1,2, 张朋辉1,2, 才让扎西1,2, 南措加1, 周乐怡1
收稿日期:2024-10-23
接受日期:2025-01-20
出版日期:2025-11-10
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
*苏旭, 博士后, 教授, 博士生导师, 青海师范大学生命科学学院副院长, 青海省青藏高原生物多样性形成机制与综合利用重点实验室主任, 教育部基础教育教学指导委员会委员; 青海青年五四奖章获得者, 青海省“昆仑英才·高端创新创业人才”项目培养领军人才, 首届青海省高教领域“昆仑英才·教学名师”, 青海省自然科学与工程技术学科带头人, 青海省高等院校“135高层次人才培养工程”拔尖学科带头人, 青海省省级骨干教师。长期从事高山植物系统发育、物种形成及适应进化机制等研究。主持国家自然科学基金3项; 科技基础项目2项以及省部级科研项目10余项。在国内外学术期刊上发表论文70余篇; 编写学术专著5部。授权发明专利5件; 获青海省自然科学三等奖和第二届青海省科学成果创新驱动奖各1项。E-mail: xusu8527972@126.com;E-mail: 532226527@qq.com
基金资助:
Jiarui Jin1,2, Yuping Liu1,2,3, Xu Su1,2,3,*( ), Tao Liu4,*(
), Tao Liu4,*( ), Mingjun Yu1,2, Qian Yang1,2, Rongju Qu1,2, Penghui Zhang1,2, Zhaxi Cairang1,2, Cuojia Nan1, Leyi Zhou1
), Mingjun Yu1,2, Qian Yang1,2, Rongju Qu1,2, Penghui Zhang1,2, Zhaxi Cairang1,2, Cuojia Nan1, Leyi Zhou1
Received:2024-10-23
Accepted:2025-01-20
Online:2025-11-10
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
*E-mail: xusu8527972@126.com;E-mail: 532226527@qq.com
摘要: 黄缨菊(Xanthopappus subacaulis)是菊科(Asteraceae)黄缨菊属(Xanthopappus)多年生高原特有单属种药用植物, 具有重要的经济、生态和药用价值。为确定适合黄缨菊全基因组测序的技术策略, 利用流式细胞术和基因组Survey分析评估黄缨菊基因组大小、杂合率、重复序列比例、GC含量和长末端重复反转录转座子(long terminal repeat retrotransposons, LTR-RTs)等信息。结果表明: (1) 以长裂太行菊(Opisthopappus longilobus)和番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)为参考物种, 采用流式细胞术预估黄缨菊为二倍体, 基因组大小分别为1.94 G和1.75 G, DNA-C值为0.99 pg; (2) 高通量测序得到约100.3 G的Clean reads, 其Q20均大于97.1%, Q30均高于90.8%, AT和GC碱基含量无明显分离, GC含量为38.5%, 测序质量良好; (3) K核苷酸序列分析(K-mer analysis, K-mer)显示黄缨菊基因组大小为2 198.50 Mb, 杂合度为0.69%, 重复序列占比为80.15%, 属于微杂合、高重复序列的复杂基因组; (4) LTR-RTs鉴定表明Copia家族数量最多, 占全基因组的30.72%, Gypsy家族和Unknown分别占全基因组的33.66%和16.54%, 插入时间始于约3 Mya, 在1 Mya内产生大量扩增。综上, 研究结果表明LTR的大量插入是导致黄缨菊基因组复杂化的重要原因之一; 测序数据和研究结果可为黄缨菊高质量基因组遗传图谱构建和关键功能基因挖掘提供重要参考。
靳佳瑞, 刘玉萍, 苏旭, 刘涛, 余明君, 杨倩, 曲荣举, 张朋辉, 才让扎西, 南措加, 周乐怡. 基于流式细胞术和基因组Survey的黄缨菊基因组大小及特征分析. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 888-900.
Jiarui Jin, Yuping Liu, Xu Su, Tao Liu, Mingjun Yu, Qian Yang, Rongju Qu, Penghui Zhang, Zhaxi Cairang, Cuojia Nan, Leyi Zhou. Genome Size and Characteristics Analysis of Xanthopappus subacaulis Based on Flow Cytometry and Genome Survey. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(6): 888-900.
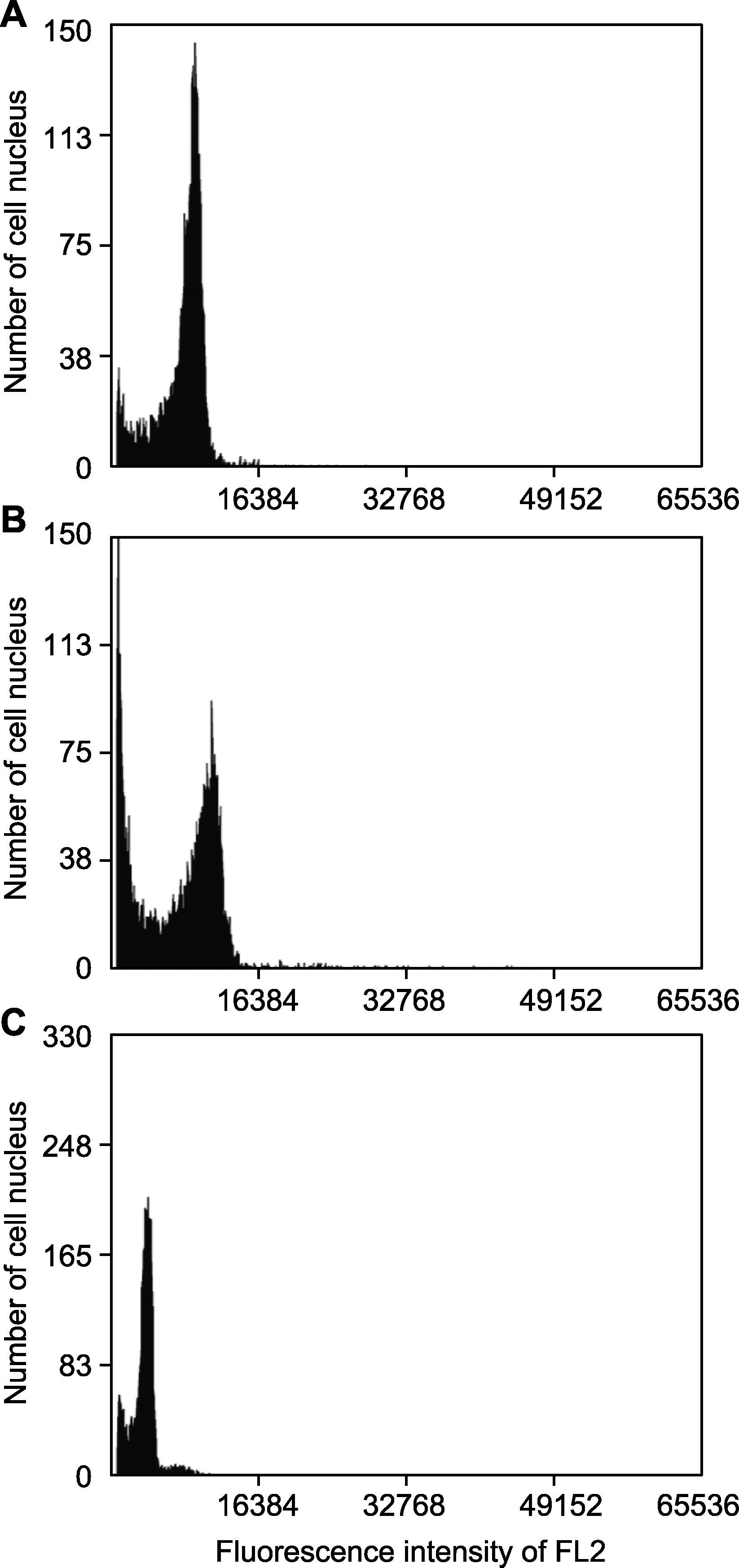
图1 流式细胞术(FCM)荧光信号图 (A) 黄缨菊; (B) 长裂太行菊; (C) 番茄
Figure 1 Flow cytometry (FCM) fluorescence pattern of different samples (A) Xanthopappus subacaulis; (B) Opisthopappus longilobus; (C) Solanum lycopersicum
| Date type | Library name | Read number | Base count (bp) | Read length (bp) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw data | Xanthopappus subacaulis | 710885064 | 106632759600 | 150; 150 | 98.7; 97.2 | 95.4; 91.0 | 38.6; 38.5 |
| Clean data | X. subacaulis | 669190080 | 100378512000 | 150; 150 | 98.6; 97.1 | 95.3; 90.8 | 38.5; 38.5 |
表1 黄缨菊测序数据统计
Table 1 Squencing data statistics of Xanthopappus subacaulis
| Date type | Library name | Read number | Base count (bp) | Read length (bp) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw data | Xanthopappus subacaulis | 710885064 | 106632759600 | 150; 150 | 98.7; 97.2 | 95.4; 91.0 | 38.6; 38.5 |
| Clean data | X. subacaulis | 669190080 | 100378512000 | 150; 150 | 98.6; 97.1 | 95.3; 90.8 | 38.5; 38.5 |
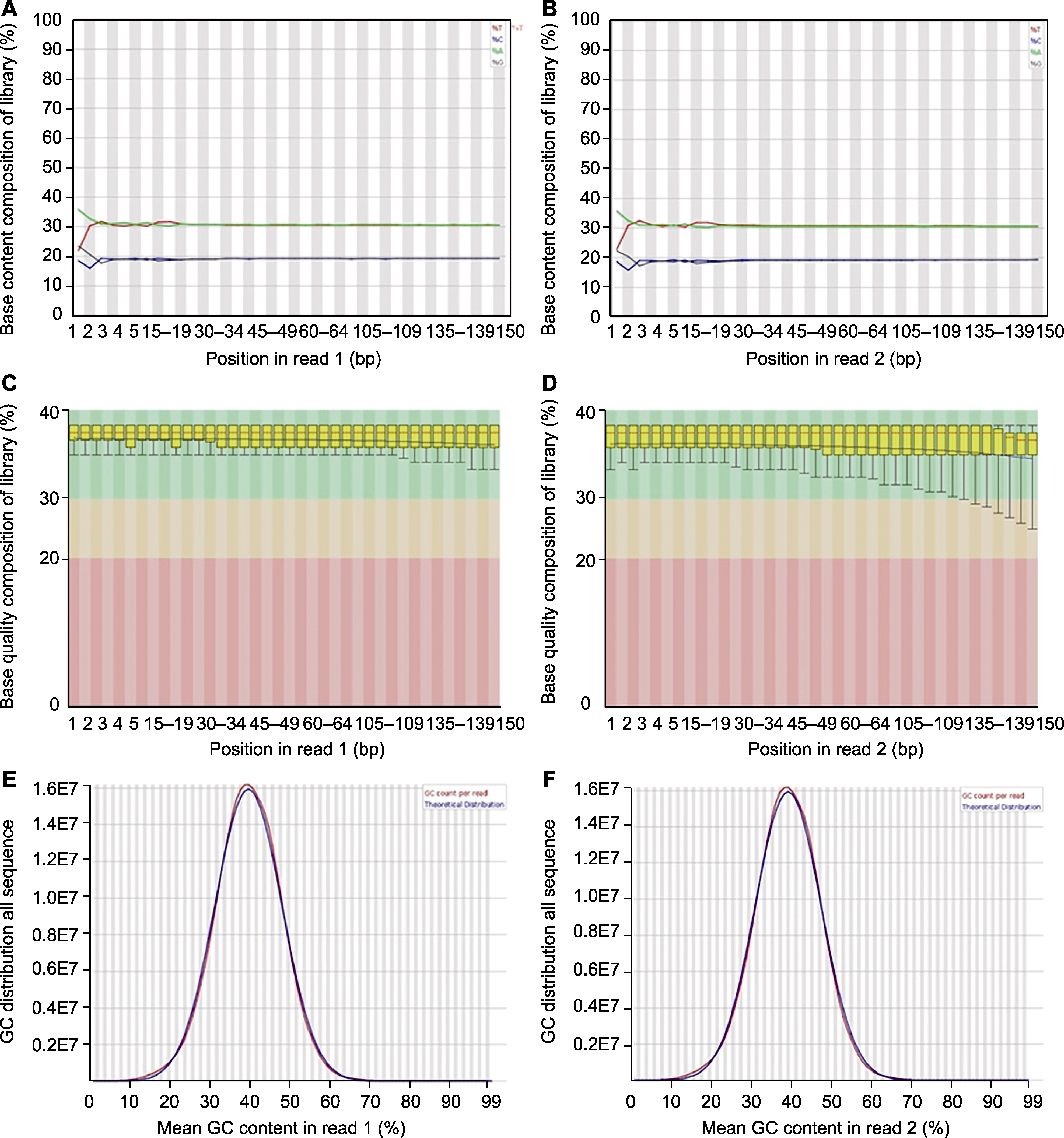
图2 黄缨菊测序质量检测与评估 (A), (B) Reads碱基分布图; (C), (D) Reads碱基质量分布图; (E), (F) Reads GC含量密度图
Figure 2 Sequencing quality evaluation for Xanthopappus subacaulis (A), (B) Base distribution plot; (C), (D) Base quality distribution plot; (E), (F) GC content density plot
| Species | Comparison rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Dolomiaea souliei | 2.36 |
| Cynara cardunculus | 1.96 |
| Gynoxys mandonii | 0.97 |
| Sonchus asper | 0.58 |
| D. edulis | 0.48 |
表2 NCBI核苷酸数据库比对
Table 2 NCBI nucleotide database BLAST
| Species | Comparison rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Dolomiaea souliei | 2.36 |
| Cynara cardunculus | 1.96 |
| Gynoxys mandonii | 0.97 |
| Sonchus asper | 0.58 |
| D. edulis | 0.48 |
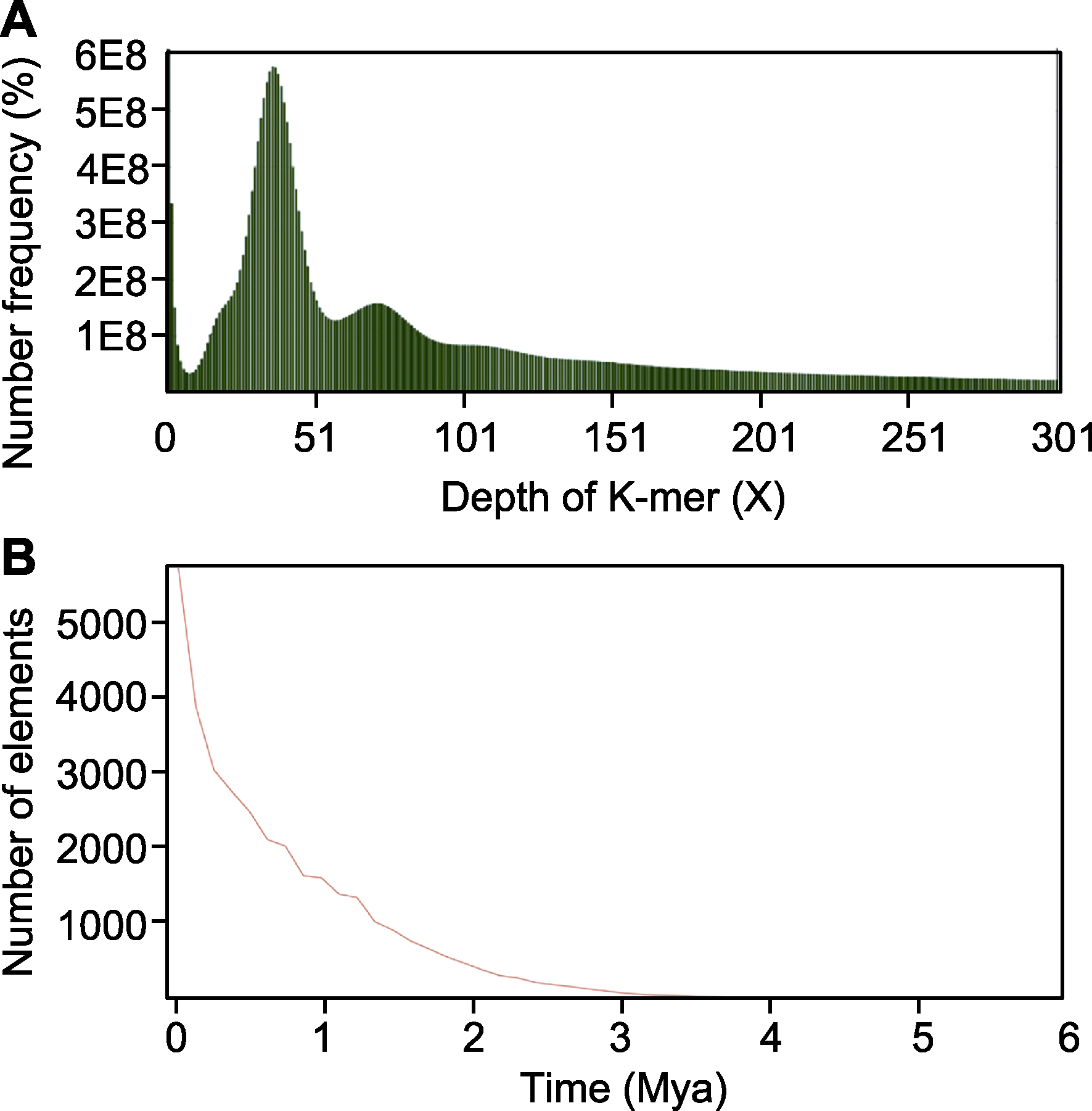
图3 黄缨菊基因组特征分析 (A) K-mer深度频率分布图; (B) 长末端重复反转录转座子(LTR-RTs)插入时间分析
Figure 3 Genomic characterization analysis of Xanthopappus subacaulis (A) Depth frequency distribution of K-mer; (B) Insertion time estimation of long terminal repeat retrotransposons (LTR-RTs)
| Transposable element | Class | Number | Base count (bp) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTR-RTs | Copia | 95073 | 674533731 | 30.72 |
| LTR-RTs | Gypsy | 73190 | 739177424 | 33.66 |
| LTR-RTs | Unknown | 70092 | 363196738 | 16.54 |
表3 黄缨菊基因组长末端重复反转录转座子(LTR-RTs)分类与特征
Table 3 Classification and characterization of long terminal repeat retrotransposons (LTR-RTs) in the genome of Xanthopappus subacaulis
| Transposable element | Class | Number | Base count (bp) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTR-RTs | Copia | 95073 | 674533731 | 30.72 |
| LTR-RTs | Gypsy | 73190 | 739177424 | 33.66 |
| LTR-RTs | Unknown | 70092 | 363196738 | 16.54 |
| [1] |
Amy Lyu MJ, Tang QM, Wang YJ, Essemine J, Chen FM, Ni XX, Chen GY, Zhu XG (2023). Evolution of gene regulatory network of C4 photosynthesis in the genus Flaveria reveals the evolutionary status of C3-C4 intermediate species. Plant Commun 4, 100426.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Badouin H, Gouzy J, Grassa CJ, Murat F, Staton SE, Cottret L, Lelandais-Brière C, Owens GL, Carrère S, Mayjonade B, Legrand L, Gill N, Kane NC, Bowers JE, Hubner S, Bellec A, Bérard A, Bergès H, Blanchet N, Boniface MC, Brunel D, Catrice O, Chaidir N, Claudel C, Donnadieu C, Faraut T, Fievet G, Helmstetter N, King M, Knapp SJ, Lai Z, Le Paslier MC, Lippi Y, Lorenzon L, Mandel JR, Marage G, Marchand G, Marquand E, Bret-Mestries E, Morien E, Nambeesan S, Nguyen T, Pegot-Espagnet P, Pouilly N, Raftis F, Sallet E, Schiex T, Thomas J, Vandecasteele C, Varès D, Vear F, Vautrin S, Crespi M, Mangin B, Burke JM, Salse J, Muños S, Vincourt P, Rieseberg LH, Langlade NB (2017). The sunflower genome provides insights into oil metabolism, flowering and Asterid evolution. Nature 546, 148-152.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bancheva S, Greilhuber J (2006). Genome size in Bulgarian Centaurea s.l. (Asteraceae). Plant Syst Evol 257, 95-117.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chen TT (2023). Ploidy Identification and Genome Size Determination of the Genus Aspidistra Based on Flow Cytometry. Master’s thesis. Nanning: Guangxi Minzu University. pp. 1-60. (in Chinese) |
| 陈婷婷 (2023). 基于流式细胞术对蜘蛛抱蛋属植物的倍性鉴定及其基因组大小测定的研究. 硕士论文. 南宁: 广西民族大学. pp. 1-60. | |
| [5] | Chen YX, Chen YS, Shi CM, Huang ZB, Zhang Y, Li SK, Li Y, Ye J, Yu C, Li Z, Zhang XQ, Wang J, Yang HM, Fang L, Chen Q (2018). SOAPnuke: a MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 7, gix120. |
| [6] | Deng HK, Luo L, Wang RQ, Gao SY, Zhang WJ (2023). Genome size determination of Scirpus mariqueter and its related species. Guihaia 43, 1838-1848. (in Chinese) |
| 邓颢珂, 罗凌, 王若秋, 高少羽, 张文驹 (2023). 海三棱藨草及其近缘种基因组大小的测定. 广西植物 43, 1838-1848. | |
| [7] | Dong CC, Wang S, Zhang H, Liu JQ, Li MJ (2022). Karyotype evolution of the Asterids insights from the first genome sequences of the family Cornaceae. DNA Res 30, dsac051. |
| [8] |
Ellinghaus D, Kurtz S, Willhoeft U (2008). LTRharvest, an efficient and flexible software for de novo detection of LTR retrotransposons. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 18.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Fei XY, Zhao H, Du Y, Duan MQ, Wang CC, Zhang B, Liu X, Li DY, Xu LX (2022). Genome size estimation and genome survey sequencing of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). Acta Agrestia Sin 30, 3207-3214. (in Chinese) |
|
费星宇, 赵泓, 杜洋, 段梦琪, 王晨晨, 张彬, 刘雪, 李大勇, 许立新 (2022). 菊苣的基因组大小估算及基因组调查测序. 草地学报 30, 3207-3214.
DOI |
|
| [10] |
Finnegan DJ (1989). Eukaryotic transposable elements and genome evolution. Trends Genet 5, 103-107.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Fomicheva M, Domblides E (2023). Mastering DNA content estimation by flow cytometry as an efficient tool for plant breeding and biodiversity research. Methods Protoc 6, 18.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Gao SH, Yu HY, Wu SY, Wang S, Geng JN, Luo YF, Hu SN (2018). Advances of sequencing and assembling technologies for complex genomes. Hereditas (Beijing) 40, 944-963. (in Chinese) |
| 高胜寒, 禹海英, 吴双阳, 王森, 耿佳宁, 骆迎峰, 胡松年 (2018). 复杂基因组测序技术研究进展. 遗传 40, 944-963. | |
| [13] | Garcia S, Leitch IJ, Anadon-Rosell A, Canela MÁ, Gálvez F, Garnatje T, Gras A, Hidalgo O, Johnston E, Mas de Xaxars G, Pellicer J, Siljak-Yakovlev S, Vallès J, Vitales D, Bennett MD (2014). Recent updates and developments to plant genome size databases. Nucleic Acids Res 42, D1159-D1166. |
| [14] |
Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR (2016). Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat Rev Genet 17, 333-351.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Guo SL, Yu J, Li DD, Zhou P, Fang Q, Yin LP (2015). DNA C-values of 138 herbaceous species and their biological significance. Acta Ecol Sin 35, 6516-6529. (in Chinese) |
| 郭水良, 于晶, 李丹丹, 周平, 方其, 印丽萍 (2015). 长三角及邻近地区138种草本植物DNA C-值测定及其生物学意义. 生态学报 35, 6516-6529. | |
| [16] | Huang AJ, Zhou JY, Li TZ, Xing YD, Gao F, Zhou YJ (2019). Flow cytometry and K-mer analysis estimates of genome size of Sophora alopecuroides. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 50, 6098-6102. (in Chinese) |
| 黄阿晶, 周佳熠, 李天泽, 邢怡德, 高飞, 周宜君 (2019). 基于流式细胞术和K-mer分析的苦豆子基因组大小估测. 中草药 50, 6098-6102. | |
| [17] | Huang SY, Zhang SW, Yang TW, Gao MR, Zhang XJ, Li T, Yu WH, Shi Q, Meng P (2023). Genome size estimates of medicinal and edible plant Erythropalum scandens based on flow cytometry and genome survey. Mol Plant Breed 21, 5281-5288. (in Chinese) |
| 黄诗宇, 张尚文, 杨天为, 高曼熔, 张向军, 李婷, 庾韦花, 石前, 蒙平 (2023). 基于流式细胞术和基因组Survey测定药食同源植物赤苍藤的基因组大小. 分子植物育种 21, 5281-5288. | |
| [18] | Kong XM, Zhang Y, Wang ZY, Bao ST, Feng YS, Wang JQ, Yu ZJ, Long F, Xiao ZJ, Hao YN, Gao XT, Li YF, Ding Y, Wang JY, Lei TY, Xu CY, Wang JP (2023). Two-step model of paleohexaploidy, ancestral genome reshuffling and plasticity of heat shock response in Asteraceae. Hortic Res 10, uhad073. |
| [19] |
Lander ES, Waterman MS (1988). Genomic mapping by fingerprinting random clones: a mathematical analysis. Genomics 2, 231-239.
PMID |
| [20] | Leitch IJ, Johnston E, Pellicer J, Hidalgo O, Bennett MD (2019). Plant DNA C-values database (Release 7.1). https://cvalues.science.kew.org/. 2019-04. |
| [21] |
Li A, Liu A, Du X, Chen JY, Yin M, Hu HY, Shrestha N, Wu SD, Wang HQ, Dou QW, Liu ZP, Liu JQ, Yang YZ, Ren GP (2020). A chromosome-scale genome assembly of a diploid alfalfa, the progenitor of autotetraploid alfalfa. Hortic Res 7, 194.
DOI |
| [22] | Li T, Tang SJ, Li W, Zhang SB, Wang JL, Pan DF, Lin ZL, Ma X, Chang YN, Liu B, Sun J, Wang XF, Zhao MJ, You CQ, Luo HF, Wang MJ, Ye XG, Zhai JX, Shen ZB, Du HL, Song XW, Huang G, Cao XF (2023). Genome evolution and initial breeding of the Triticeae grass Leymus chinensis dominating the Eurasian steppe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2308984120. |
| [23] | Liang FP, Wen XN, Gao HY, Zhang Y (2018). Analysis of chloroplast genomes features of Asteraceae species. Genomics Appl Biol 37, 5437-5447. (in Chinese) |
| 梁凤萍, 文祥宁, 高赫一, 张颖(2018). 菊科植物叶绿体基因组特征分析. 基因组学与应用生物学 37, 5437-5447. | |
| [24] |
Liu B, Yan J, Li WH, Yin LJ, Li P, Yu HX, Xing LS, Cai ML, Wang HC, Zhao MX, Zheng J, Sun F, Wang ZZ, Jiang ZY, Ou QJ, Li SB, Qu L, Zhang QL, Zheng YP, Qiao X, Xi Y, Zhang Y, Jiang F, Huang C, Liu CH, Ren YW, Wang S, Liu HW, Guo JY, Wang HH, Dong H, Peng CL, Qian WQ, Fan W, Wan FH (2020). Mikania micrantha genome provides insights into the molecular mechanism of rapid growth. Nat Commun 11, 340.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Liu T, Liu YP, Fu G, Lü T, Liu F, Zhang Y, Su DD, Wang YN, Zheng CY, Su X (2022). Estimation of genome size for Psammochloa villosa by flow cytometry and K-mer analysis. Acta Pratacult Sin 31(12), 133-145. (in Chinese) |
|
刘涛, 刘玉萍, 富贵, 吕婷, 刘峰, 张雨, 苏丹丹, 王亚男, 郑长远, 苏旭 (2022). 基于流式细胞法和K-mer分析法检测沙鞭基因组大小. 草业学报 31(12), 133-145.
DOI |
|
| [26] | Ma PJ, Zhou JY, Sun HG, Ma DD, Gao F, Zhou YJ, Zhang GF (2018). Estimation of jojoba genome’s size by flow cytometry and K-mer analysis. J Beijing Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 54, 733-737. (in Chinese) |
| 马鹏举, 周佳熠, 孙会改, 马丹丹, 高飞, 周宜君, 张根发 (2018). 基于流式细胞术和K-mer分析的好好芭基因组大小估测. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版) 54, 733-737. | |
| [27] | Ma ZL, Liu F, Zhang Y, Su X (2020). Research progress and germplasm collection of Xanthopappus subacaulis which is endemic species from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J Qinghai Norm Univ (Nat Sci) 36(2), 41-44. (in Chinese) |
| 马子兰, 刘峰, 张阳, 苏旭 (2020). 青藏高原特有植物黄缨菊研究现状及种质资源收集. 青海师范大学学报(自然科学版) 36(2), 41-44. | |
| [28] | Mao CQ, Sha XF, Huang J, Tao S, Peng F, Li Q, Zhang C, Yuan C (2023). Genome survey and characteristic analysis of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 54, 907-914. (in Chinese) |
| 毛常清, 沙秀芬, 黄静, 陶珊, 彭芳, 李群, 张超, 袁灿 (2023). 川芎基因组survey测序及其特征分析. 中草药 54, 907-914. | |
| [29] |
Mascher M, Gundlach H, Himmelbach A, Beier S, Twardziok SO, Wicker T, Radchuk V, Dockter C, Hedley PE, Russell J, Bayer M, Ramsay L, Liu H, Haberer G, Zhang XQ, Zhang QS, Barrero RA, Li L, Taudien S, Groth M, Felder M, Hastie A, Šimková H, Staňková H, Vrána J, Chan S, Muñoz-Amatriaín M, Ounit R, Wanamaker S, Bolser D, Colmsee C, Schmutzer T, Aliyeva-Schnorr L, Grasso S, Tanskanen J, Chailyan A, Sampath D, Heavens D, Clissold L, Cao SJ, Chapman B, Dai F, Han Y, Li H, Li X, Lin CY, McCooke JK, Tan C, Wang PH, Wang SB, Yin SY, Zhou GF, Poland JA, Bellgard MI, Borisjuk L, Houben A, Doležel J, Ayling S, Lonardi S, Kersey P, Langridge P, Muehlbauer GJ, Clark MD, Caccamo M, Schulman AH, Mayer KFX, Platzer M, Close TJ, Scholz U, Hansson M, Zhang GP, Braumann I, Spannagl M, Li CD, Waugh R, Stein N (2017). A chromosome conformation capture ordered sequence of the barley genome. Nature 544, 427-433.
DOI URL |
| [30] | McEvoy SL, Meyer RS, Hasenstab-Lehman KE, Guilliams CM (2024). The reference genome of an endangered Asteraceae, Deinandra increscens subsp. villosa, endemic to the Central Coast of California. G3 (Bethesda) 14, jkae117. |
| [31] |
Mishiba KI, Ando T, Mii M, Watanabe H, Kokubun H, Hashimoto G, Marchesi E (2000). Nuclear DNA content as an index character discriminating taxa in the genus Petunia sensu Jussieu (Solanaceae). Ann Bot 85, 665-673.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Morabito C, Aiese Cigliano R, Maréchal E, Rébeillé F, Amato A (2020). Illumina and PacBio DNA sequencing data, de novo assembly and annotation of the genome of Aurantiochytrium limacinum strain CCAP_4062/1. Data Brief 31, 105729.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Natali L, Cossu RM, Barghini E, Giordani T, Buti M, Mascagni F, Morgante M, Gill N, Kane NC, Rieseberg L, Cavallini A (2013). The repetitive component of the sunflower genome as shown by different procedures for assembling next generation sequencing reads. BMC Genomics 14, 686.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Ou SJ, Jiang N (2018). LTR_retriever: a highly accurate and sensitive program for identification of long terminal repeat retrotransposons. Plant Physiol 176, 1410-1422.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Peng YH, Lai Z, Lane T, Nageswara-Rao M, Okada M, Jasieniuk M, O’Geen H, Kim RW, Sammons RD, Rieseberg LH, Stewart CN Jr (2014). De novo genome assembly of the economically important weed horseweed using integrated data from multiple sequencing platforms. Plant Physiol 166, 1241-1254. |
| [36] |
Qiu F, Ungerer MC (2018). Genomic abundance and transcriptional activity of diverse gypsy and copia long terminal repeat retrotransposons in three wild sunflower species. BMC Plant Biol 18, 6.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Scaglione D, Reyes-Chin-Wo S, Acquadro A, Froenicke L, Portis E, Beitel C, Tirone M, Mauro R, Lo Monaco A, Mauromicale G, Faccioli P, Cattivelli L, Rieseberg L, Michelmore R, Lanteri S (2016). The genome sequence of the outbreeding globe artichoke constructed de novo incorporating a phase-aware low-pass sequencing strategy of F1 progeny. Sci Rep 6, 19427.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Shen Q, Zhang LD, Liao ZH, Wang SY, Yan TX, Shi P, Liu M, Fu XQ, Pan QF, Wang YL, Lv ZY, Lu X, Zhang FY, Jiang WM, Ma YN, Chen MH, Hao XL, Li L, Tang YL, Lv G, Zhou Y, Sun XF, Brodelius PE, Rose JKC, Tang KX (2018). The genome of Artemisia annua provides insight into the evolution of Asteraceae family and artemisinin biosynthesis. Mol Plant 11, 776-788.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Shi HL (2011). Study on the resistance indexes of four kinds of desert plants in Qinghai Lake area. J Anhui Agric Sci 39, 14227-14229. (in Chinese) |
| 史惠兰 (2011). 青海湖地区4种荒漠植物抗逆性指标的研究. 安徽农业科学 39, 14227-14229. | |
| [40] |
Staton SE, Burke JM (2015). Evolutionary transitions in the Asteraceae coincide with marked shifts in transposable element abundance. BMC Genomics 16, 623.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Sun HN, Li MY, Liu DY, Wang X, Tian L, Wu FF (2021). Chromosome number identification and karyotype analysis of Coreopsis L. Acta Agrestia Sin 29, 2477-2485. (in Chinese) |
|
孙浩男, 李明阳, 刘冬云, 王鑫, 田琳, 吴芳芳 (2021). 不同种(品种)金鸡菊的染色体数目鉴定及核型分析. 草地学报 29, 2477-2485.
DOI |
|
| [42] | Tian YQ, Zhuang LD, Xu HH (2008). A new screening method for photo-activated insecticidal plants. J Huazhong Agric Univ 27, 370-372. (in Chinese) |
| 田永清, 庄流东, 徐汉虹 (2008). 光活化杀虫植物的1种新型筛选方法. 华中农业大学学报 27, 370-372. | |
| [43] |
Vurture GW, Sedlazeck FJ, Nattestad M, Underwood CJ, Fang H, Gurtowski J, Schatz MC (2017). GenomeScope: fast reference-free genome profiling from short reads. Bioinformatics 33, 2202-2204.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Wang YJ, Liu JQ, Miehe G (2007). Phylogenetic origins of the Himalayan endemic Dolomiaea, Diplazoptilon and Xanthopappus (Asteraceae: Cardueae) based on three DNA regions. Ann Bot 99, 311-322.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Wang YL, Zang E, Zhang H, Liu ZX, Lan YF, He S, Hao WL, Cao YL (2022). Genome sizes and characteristics of cliff plants Opisthopappus taihangensis and O. longilobus on Taihang Mountains. Guihaia 42, 1582-1589. (in Chinese) |
| 王祎玲, 臧恩, 张昊, 刘志霞, 兰亚飞, 何珊, 郝伟丽, 曹艳玲 (2022). 崖壁植物太行菊与长裂太行菊全基因组大小及特征分析. 广西植物 42, 1582-1589. | |
| [46] | Xia CJ, Li YG, Xia S, Pang W, Chen CL (2024). Flow cytometric analysis and sorting in plant genomics. Chin Bull Bot 59, 774-782. (in Chinese) |
|
夏春皎, 李运广, 夏姝, 庞伟, 陈春丽 (2024). 植物基因组学中的流式细胞分析及分选技术. 植物学报 59, 774-782.
DOI |
|
| [47] | Xie M, Yu J, Guo SL (2018). Latitudinal variation patterns of plant nuclear DNA amount on a global scale and their environmental adaptation significance: a case study with Asteraceae. Acta Ecol Sin 38, 3453-3461. (in Chinese) |
| 解梦, 于晶, 郭水良 (2018). 植物核DNA含量在全球尺度上的纬度变异式样及其气候适应意义——以菊科植物为例. 生态学报 38, 3453-3461. | |
| [48] | Xin HB, Ji FF, Wu J, Zhang SY, Yi CJ, Zhao SW, Cong RC, Zhao LJ, Zhang H, Zhang Z (2023). Chromosome-scale genome assembly of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.): an ornamental plant and feedstock for industrial lutein production. Hortic Plant J 9, 1119-1130. |
| [49] | Xu Z, Wang H (2007). LTR_FINDER: an efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res 35, W265-W268. |
| [50] | Yang W, Si YY, Xu RW, Chen XH (2023). Characterization of microsatellites and polymorphic marker development in ragworm (Tylorrhynchus heterochaetus) based on genome survey data. South China Fish Sci 19(5), 123-133. (in Chinese) |
| 杨尉, 司圆圆, 许瑞雯, 陈兴汉 (2023). 基于基因组survey数据的疣吻沙蚕微卫星特征分析及多态标记开发. 南方水产科学 19(5), 123-133. | |
| [51] | Yang YH, Zhang YX, Zhang T, Xu XY, Sun YM, Wang XM, Tong HY, Yuan HY (2023). Fluorescence microscopy and transcriptome analysis on self-pollinated stigmas of self- incompatible and self-compatible clones of Stevia rebaudiana. J Plant Resour Environ 32(4), 25-32. (in Chinese) |
| 杨永恒, 张永侠, 张婷, 徐晓洋, 孙玉明, 王小敏, 佟海英, 原海燕 (2023). 甜菊自交不亲和及自交亲和无性系自花授粉柱头的荧光显微观察和转录组分析. 植物资源与环境学报 32(4), 25-32. | |
| [52] |
Yang YY, Li SN, Xing YP, Zhang ZG, Liu T, Ao WLJ, Bao GH, Zhan ZL, Zhao R, Zhang TT, Zhang DC, Song YY, Bian C, Xu L, Kang TG (2022). The first high-quality chromosomal genome assembly of a medicinal and edible plant Arctium lappa. Mol Ecol Resour 22, 1493-1507.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Zhang FJ, Chen FD, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS, Teng NJ (2023). The nature and genomic landscape of repetitive DNA classes in Chrysanthemum nankingense shows recent genomic changes. Ann Bot 131, 215-228.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Zhang JD, Feng M (2023). A plant sample optimal pretreatment for flow cytometric analysis. Chin Bull Bot 58, 285-297. (in Chinese) |
|
张晋丹, 冯旻 (2023). 一种提升流式细胞术分析效果的前处理方法. 植物学报 58, 285-297.
DOI |
|
| [55] | Zhang L (2014). Studies on Secondary Metabolites and Their Biological Activity of Three Medicinal Plants. PhD dissertation. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. pp. 1-160. (in Chinese) |
| 张丽 (2014). 三种药用植物次生代谢物结构及其生物活性研究. 博士论文. 兰州: 兰州大学. pp. 1-160. | |
| [56] |
Zhang L, Chen CJ, Chen J, Zhao QQ, Li Y, Gao K(2014). Thiophene acetylenes and furanosesquiterpenes from Xanthopappus subacaulis and their antibacterial activities. Phytochemistry 106, 134-140.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Zhang X, Ping PY, Hutvagner G, Blumenstein M, Li JY (2021). Aberration-corrected ultrafine analysis of miRNA reads at single-base resolution: a K-mer lattice approach. Nucleic Acids Res 49, e106. |
| [58] | Zhang Y, Ma ZL, Xu SS, Su X, Li MY (2022). Phylogeography of Xanthopappus subacaulis (Asteraceae), an endemic species from the northeastern of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Bull Bot Res 42, 565-573. (in Chinese) |
|
张阳, 马子兰, 徐珊珊, 苏旭, 李梅英 (2022). 青藏高原东北部黄缨菊的谱系地理学. 植物研究 42, 565-573.
DOI |
|
| [59] | Zhao L, Zhu YH, Wang M, Han YG, Ma LG, Feng WS, Zheng XK (2021). Estimation of Rehmannia glutinosa genome size based on flow cytometry and genome survey analysis. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 52, 821-826. (in Chinese) |
| 赵乐, 朱畇昊, 王敏, 韩永光, 马利刚, 冯卫生, 郑晓珂 (2021). 基于流式细胞术和基因组survey分析的地黄基因组研究. 中草药 52, 821-826. | |
| [60] | Zhao RR (2023). Genome Survey Analysis and Genetic Marker Identification of the White-Spotted Bamboo Shark Chiloscyllium Plagiosum. Master’s thesis. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University. pp. 1-82. (in Chinese) |
| 赵蕊蕊 (2023). 条纹斑竹鲨基因组survey分析及遗传标记开发. 硕士论文. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学. pp. 1-82. | |
| [61] | Zheng CY (2023). Development of SSR Molecular Markers and Analyses of Genetic Diversity in Xanthopappus Subacaulis (Asteraceae). Master’s thesis. Xining: Qinghai Normal University. pp. 1-64. (in Chinese) |
| 郑长远 (2023). 黄缨菊SSR分子标记开发及遗传多样性研究. 硕士论文. 西宁: 青海师范大学. pp. 1-64. | |
| [62] | Zhou HQ (2014). Analysis of the Relationship Between Genomic GC Content and Patterns of Base Usage, Codon Usage and Amino Acid Usage in Prokaryotes. Master’s thesis. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. pp. 1-55. (in Chinese) |
| 周慧琦 (2014). 基因组GC含量与碱基、密码子和氨基酸使用偏好的关系. 硕士论文. 成都: 电子科技大学. pp. 1-55. | |
| [63] |
Zhou P, Zhang Q, Li J, Li F, Huang J, Zhang M (2023). A first insight into the genomic background of Ilex pubescens (Aquifoliaceae) by flow cytometry and genome survey sequencing. BMC Genomics 24, 270.
DOI |
| [1] | 夏春皎, 李运广, 夏姝, 庞伟, 陈春丽. 植物基因组学中的流式细胞分析及分选技术[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 774-782. |
| [2] | 张晋丹, 冯旻. 一种提升流式细胞术分析效果的前处理方法[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 285-297. |
| [3] | 刘维仲, 王洁茹, 胡勇. 连续光照转暗培养联合药物处理实现衣藻细胞的高水平同步化[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(3): 363-371. |
| [4] | 张鹏, 王刚, 张涛, 陈年来. 祁连山两种优势乔木叶片δ13C的海拔响应及其机理[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(2): 125-133. |
| [5] | 黄建辉, 林光辉, 韩兴国. 不同生境间红树科植物水分利用效率的比较研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(4): 530-536. |
| [6] | 韦莉莉, 张小全, 侯振宏, 徐德应, 余雪标. 杉木苗木光合作用及其产物分配对水分胁迫的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(3): 394-402. |
| [7] | 陈世苹, 白永飞, 韩兴国, 安吉林, 郭富存. 沿土壤水分梯度黄囊苔草碳同位素组成及其适应策略的变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(4): 515-522. |
| [8] | 渠春梅, 韩兴国, 苏波, 黄建辉, 蒋高明. 西双版纳片断化热带雨林常绿乔木幼树水分利用效率的边缘效应研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2001, 25(1): 1-5. |
| [9] | 苏波, 韩兴国, 李凌浩, 黄建辉, 白永飞, 渠春梅. 中国东北样带草原区植物δ13C值及水分利用效率对环境梯度的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(6): 648-655. |
| [10] | 李卫华, 张承烈. 泡泡刺叶磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶季节性聚态变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(3): 283-288. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||