

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 635-650.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23136 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23136
收稿日期:2023-10-07
接受日期:2024-03-05
出版日期:2024-07-10
发布日期:2024-07-10
通讯作者:
*谢启光/徐小冬, 河南大学生命科学学院教授、博士生导师、省部共建作物逆境适应与改良国家重点实验室/生物节律团队课题组长; 2002-2015年分别于美国Vanderbilt U和美国Dartmouth College从事时间生物学研究。团队研究方向为生物钟调控农艺性状的遗传学机理。研究成果在Science、Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America、Plant Cell、Plant, Cell & Environment、Theoretical and Applied Genetics、Journal of Integrative Plant Biology和Genetics等期刊发表, 共计50余篇; 先后发现植物生物钟TTFL的激活环路及揭示生物钟蛋白时序表达的动态调控机理, 2次更新植物生物钟分子机制模型, 入选Plant Cell (2020-2021年度) 15篇高影响力论文; 授权国家发明专利7项、授权国家农业农村部植物新品种1项。两位课题组长历任中国细胞生物学学会生物节律分会副会长、常务委员和学术委员。E-mail: qiguang.xie@henu.edu.cn; xiaodong.xu@henu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Qiguang Xie*( ), Xiaodong Xu*(
), Xiaodong Xu*( )
)
Received:2023-10-07
Accepted:2024-03-05
Online:2024-07-10
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
*E-mail: qiguang.xie@henu.edu.cn; xiaodong.xu@henu.edu.cn
摘要: 当前全球变暖趋势不可逆转, 异常气候导致的温度胁迫频繁发生, 给农业高产及稳产带来了巨大挑战。生物钟作为内源性且可遗传的计时机制, 赋予了植物预测和快速响应环境因子周期性变化的能力, 以确保诸多生理生化途径与环境同步, 极大增强了植物的生存和繁衍能力。温度响应和补偿现象不仅涉及生物钟与环境信号“同步化”, 而且涉及农业生产中作物适应温度胁迫的实际应用。生物钟温度补偿是指在较宽范围的生理温度内, 通过转录和转录后机制, 生物钟可基本维持近日节律周期的长度不变, 确保计时机制准确运行。自然环境中, 光照、温度和湿度紧密耦联, 作为授时因子将环境信号经过输入途径传递给生物钟核心振荡器, 影响植物生长发育的全过程。该文回顾了植物生物钟温度响应和补偿机制的研究历史, 详述了最新研究进展, 展望了其在作物遗传育种和田间管理等方面的应用前景, 为解决农作物温度胁迫适应性问题提供了全新的思路和方案。
谢启光, 徐小冬. 植物生物钟在农业生产中应对全球变暖的应用. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 635-650.
Qiguang Xie, Xiaodong Xu. Plant Circadian Clock in Agricultural Production in Response to Global Warming. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 635-650.
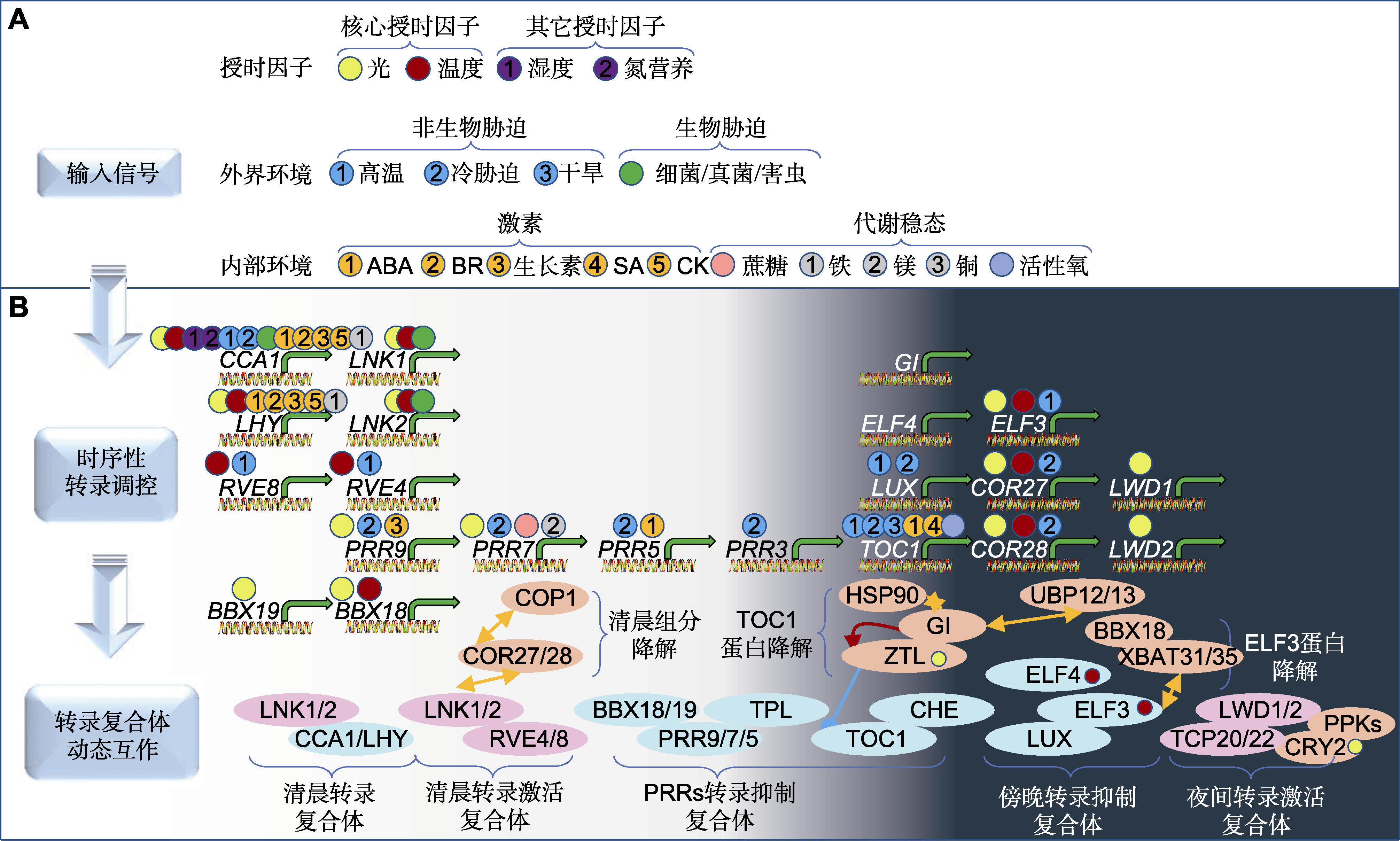
图1 植物生物钟核心振荡器响应内外环境信号并时序性形成转录蛋白复合体 植物生物钟系统输入途径的内外环境信号, 包括已经公认的授时因子、外部环境胁迫因子和内环境中的激素和代谢组分。生物钟核心组分展示出基因时序表达和蛋白动态周转机制。转录本和蛋白复合体按照1天24小时的时相次序排布。ABA: 脱落酸; BR: 油菜素甾醇; SA: 水杨酸; CK: 细胞分裂素
Figure 1 Circadian core oscillators respond to internal and external environmental cues and temporally form transcriptional protein complexes in plants Internal and external environmental signals in the input pathways of plant clock system include well-recognized timing factors, external environmental stressors, and internal hormonal and metabolic components. The core oscillators of the circadian clock exhibit temporal gene expression and dynamic protein turnover mechanisms. The transcripts and protein complexes are sequentially shown according to the circadian phases of a 24 h day. ABA: Abscisic acid; BR: Brassinosteroid; SA: Salicylic acid; CK: Cytokinin
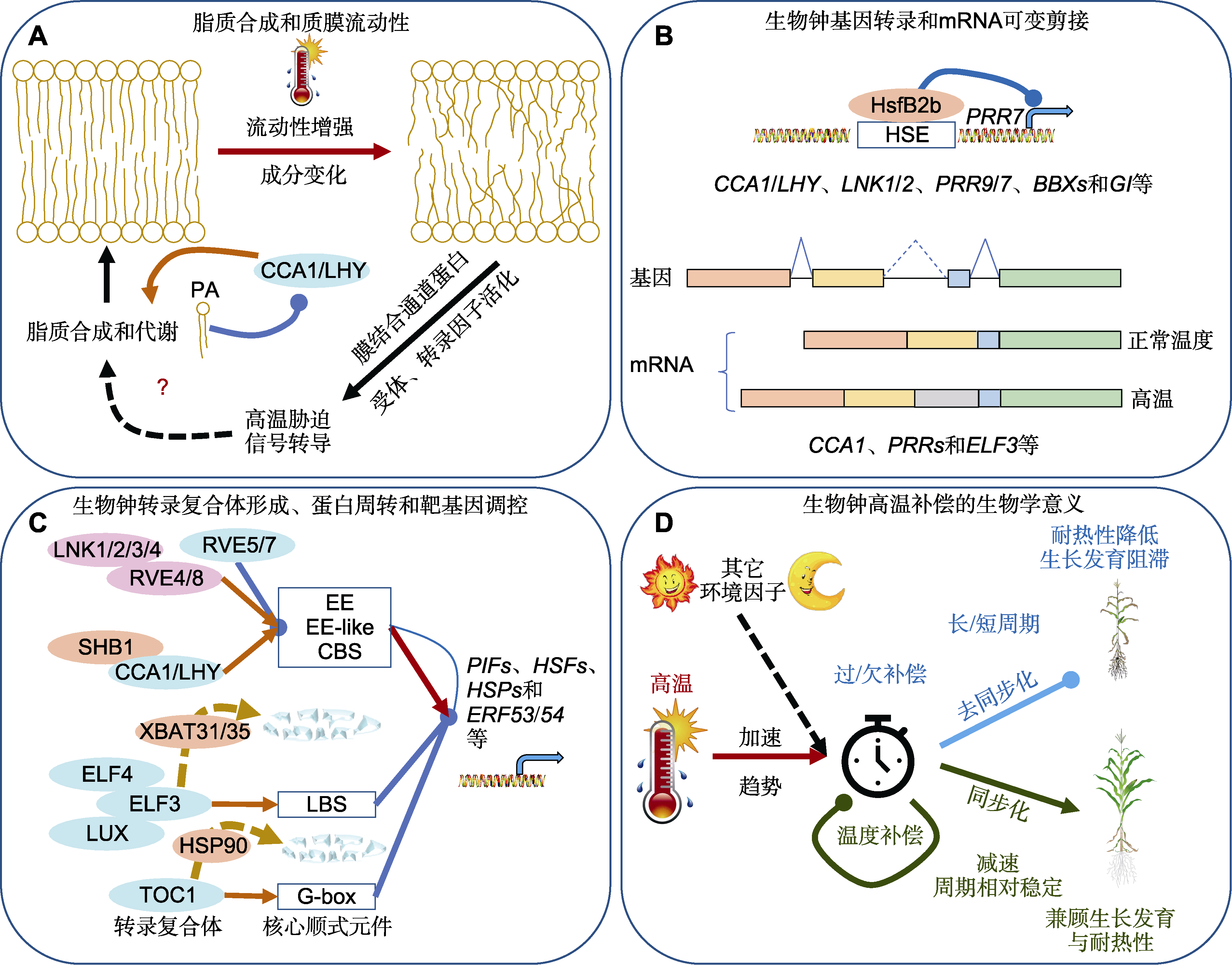
图2 生物钟感知昼夜温度变化、调控高温胁迫及周期长度温度补偿示意图 信号途径中带箭头实线表示直接或间接激活作用, 不带箭头实线表示直接或间接抑制作用, 黑色带箭头虚线表示可能存在的信号途径, C图中棕色带箭头虚线表示蛋白降解途径。PA: 磷脂酸; EE: 夜间元件; CBS: CCA1结合位点; LBS: LUX结合位点
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the circadian clock that anticipates diel temperature fluctuations, regulates the responses to high-temperature stress and temperature compensation of the circadian period length Solid lines with arrows in signaling pathways indicate direct or indirect activation, solid lines without arrows indicate direct or indirect inhibition, black dotted lines with arrows indicate possible signaling pathways, and brown dotted lines with arrows in Figure 2C indicate protein degradation pathways. PA: Phosphatidic acid; EE: Evening element; CBS: CCA1-binding site; LBS: LUX-binding site
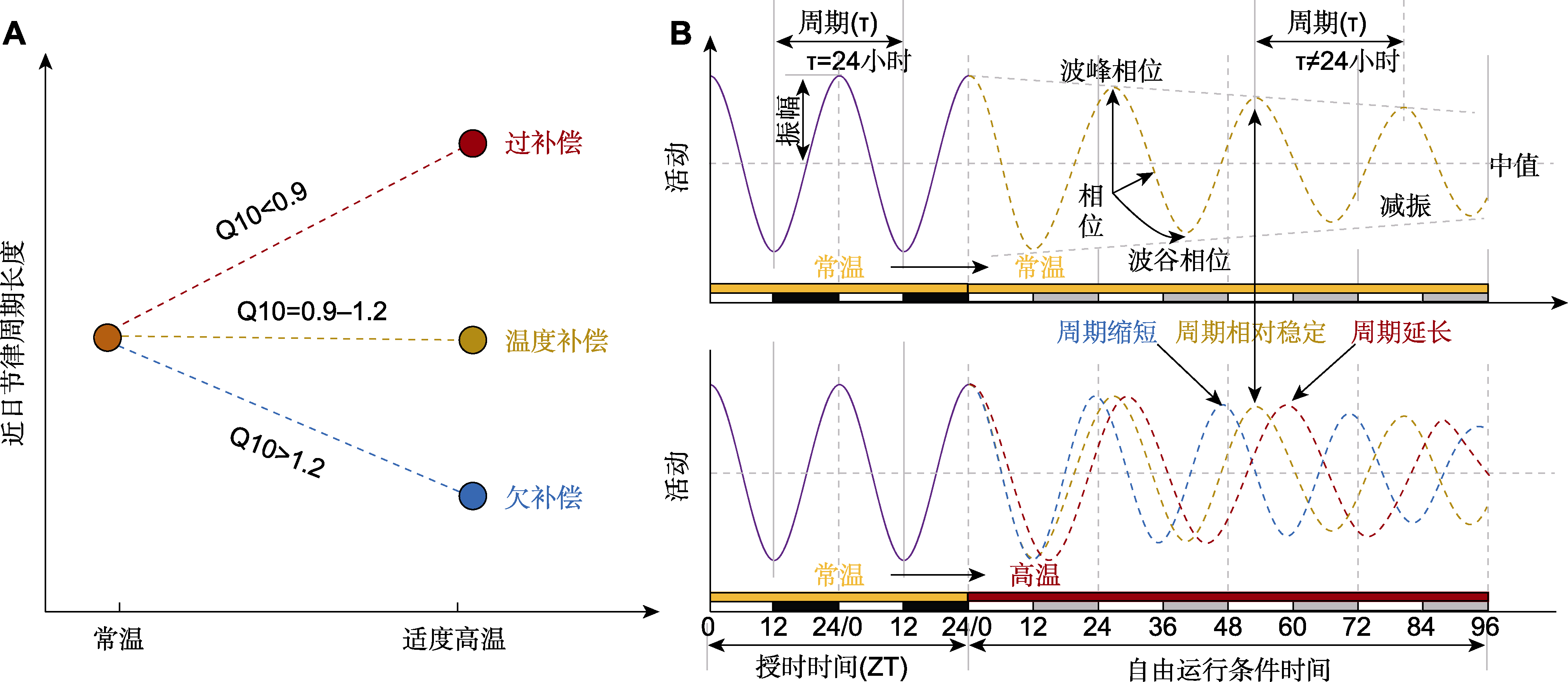
图3 温度补偿的计算及近日节律表型 (A) 从常温转入高温后, 自由振荡条件下检测的近日节律可能出现3种温度补偿现象; (B) 昼夜条件下, 生物钟每天被重置, 周期固定为24小时; 自由振荡条件下(如恒温和持续光照), 内源性节律周期并不等于24小时。近日节律的关键参数包括周期长度、相位、振幅和中值。ZT: 授时时间
Figure 3 Temperature compensation calculations and circadian rhythm phenotypes (A) Three types of temperature compensation may occur when the circadian rhythm is detected under free-running conditions after a transition from normal to higher temperature; (B) In light/dark cycles, the circadian clock is reset each day with a fixed 24 h period length; under free-running conditions (e.g., constant temperature and continuous light), the period length of endogenous circadian rhythm is not equal to 24 h. Key parameters of the circadian rhythmicity include period length, phase, amplitude, and mesor. ZT: Zeitgeber time
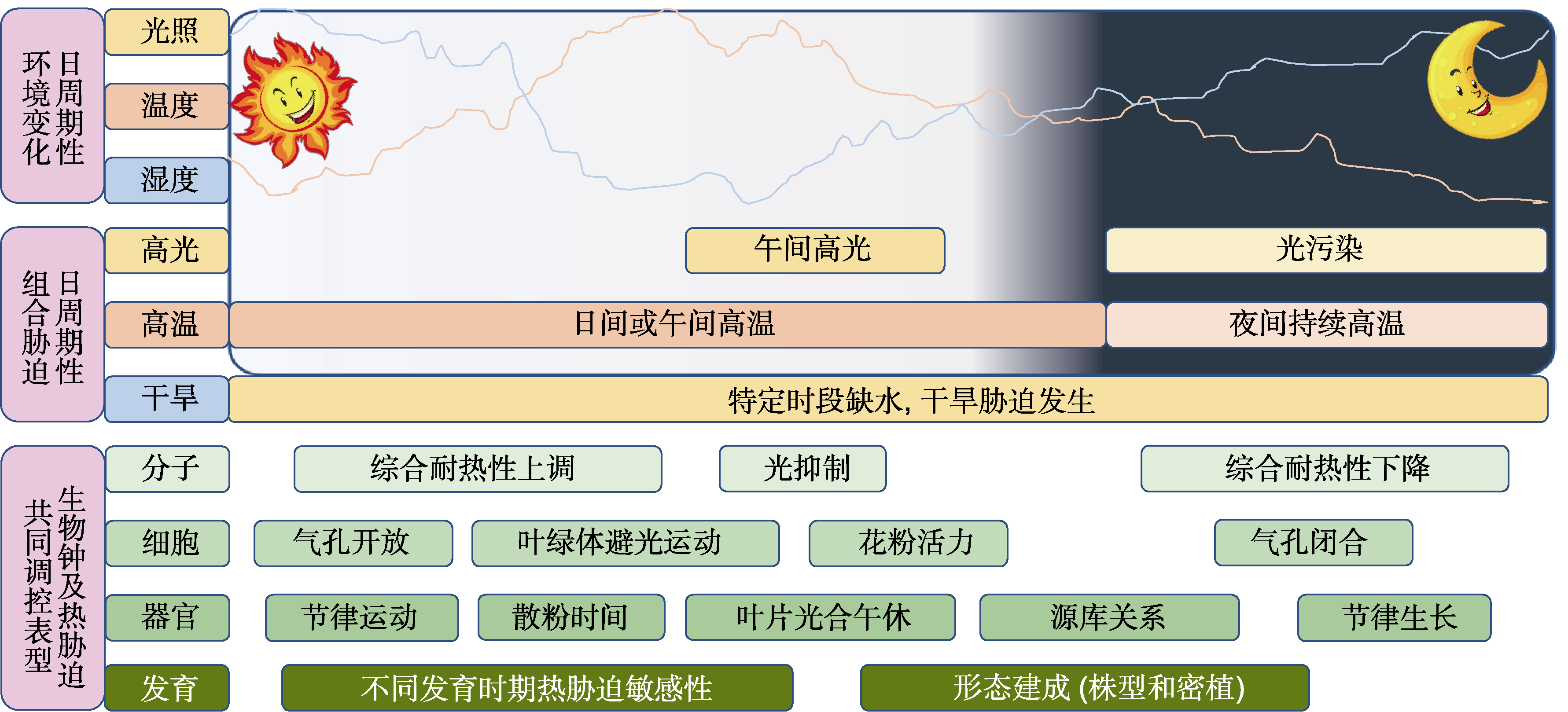
图4 生物钟调控的高温胁迫相关环境因子及生理表型 环境中光照、温度和湿度存在昼夜节律性变化, 其中光照和温度具有较强的正相关性, 温度和湿度具有较强的负相关性。在特定时段突破植物生理阈值的光照、温度和湿度会导致发生时间特异性胁迫。热激如果在1天中不同时段或作物不同生长时期发生, 最终均会对产量和品质产生一定程度的影响。
Figure 4 The circadian clock respond to environmental factors related to high temperature stress and regulate physiological processes Light, temperature and humidity in the environment show daily oscillations, with a strong positive correlation between light and temperature and a strong negative correlation between temperature and humidity. When physiological thresholds are exceeded at specific times of a day, light, temperature and humidity can lead to time-specific stresses in plants. Heat shock, if it occurs at different times of the day or at different growth periods, will eventually affect yield and quality to some extent in crops.
| [1] |
Agnolucci P, Rapti C, Alexander P, De Lipsis V, Holland RA, Eigenbrod F, Ekins P (2020). Impacts of rising temperatures and farm management practices on global yields of 18 crops. Nat Food 1, 562-571.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Belbin FE, Hall GJ, Jackson AB, Schanschieff FE, Archibald G, Formstone C, Dodd AN (2019). Plant cir-cadian rhythms regulate the effectiveness of a glyphosate-based herbicide. Nat Commun 10, 3704.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Bonnot T, Nagel DH (2021). Time of the day prioritizes the pool of translating mRNAs in response to heat stress. Plant Cell 33, 2164-2182. |
| [4] | Buckley CR, Li X, Martí MC, Haydon MJ (2023). A bitter-sweet symphony: metabolic signals in the circadian sys-tem. Curr Opin Plant Biol 73, 102333. |
| [5] | Cha JY, Kim J, Kim TS, Zeng QN, Wang L, Lee SY, Kim WY, Somers DE (2017). GIGANTEA is a co-chaperone which facilitates maturation of ZEITLUPE in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Nat Commun 8, 3. |
| [6] |
Chen WW, Takahashi N, Hirata Y, Ronald J, Porco S, Davis SJ, Nusinow DA, Kay SA, Mas P (2020). A mobile ELF4 delivers circadian temperature information from shoots to roots. Nat Plants 6, 416-426.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Choudhary MK, Nomura Y, Wang L, Nakagami H, Somer-s DE (2015). Quantitative circadian phosphoproteomic analysis of Arabidopsis reveals extensive clock control of key components in physiological, metabolic, and signaling pathways. Mol Cell Proteomics 14, 2243-2260.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Desai JS, Lawas LMF, Valente AM, Leman AR, Grinevich DO, Jagadish SVK, Doherty CJ (2021). Warm nights disrupt transcriptome rhythms in field-grown rice panicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2025899118. |
| [9] | Ding YL, Li H, Zhang XY, Xie Q, Gong ZZ, Yang SH (2015). OST1 kinase modulates freezing tolerance by enhancing ICE1 stability in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 32,278- 289. |
| [10] |
Edwards KD, Anderson PE, Hall A, Salathia NS, Locke JCW, Lynn JR, Straume M, Smith JQ, Millar AJ (2006). FLOWERING LOCUS C mediates natural variation in the high-temperature response of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 18, 639-650.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Edwards KD, Lynn JR, Gyula P, Nagy F, Millar AJ (2005). Natural allelic variation in the temperature-compensation mechanisms of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock. Genetics 170, 387-400.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Ezer D, Jung JH, Lan H, Biswas S, Gregoire L, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Lai XL, Stöckle D, Zubieta C, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2017). The evening complex coordinates environmental and endogenous signals in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 3, 17087. |
| [13] | Ford B, Deng WW, Clausen J, Oliver S, Boden S, Hem-ming M, Trevaskis B (2016). Barley (Hordeum vulgare) circadian clock genes can respond rapidly to temperature in an EARLY FLOWERING 3-dependent manner. J Exp Bot 67, 5517-5528. |
| [14] | Frank A, Matiolli CC, Viana AJC, Hearn TJ, Kusakina J, Belbin FE, Wells Newman D, Yochikawa A, Cano- Ramirez DL, Chembath A, Cragg-Barber K, Haydon MJ, Hotta CT, Vincentz M, Webb AAR, Dodd AN (2018). Circadian entrainment in Arabidopsis by the sugar- responsive transcription factor bZIP63. Curr Biol 28, 2597- 2606. |
| [15] | Gil KE, Kim WY, Lee HJ, Faisal M, Saquib Q, Alatar AA, Park CM (2017). ZEITLUPE contributes to a thermore-sponsive protein quality control system in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29, 2882-2894. |
| [16] | Gil KE, Park CM (2019). Thermal adaptation and plasticity of the plant circadian clock. New Phytol 221, 1215-1229. |
| [17] |
Goodspeed D, Liu JD, Chehab EW, Sheng ZJ, Francisco M, Kliebenstein DJ, Braam J (2013). Postharvest circa-dian entrainment enhances crop pest resistance and phy-tochemical cycling. Curr Biol 23, 1235-1241.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Gould PD, Locke JCW, Larue C, Southern MM, Davis SJ, Hanano S, Moyle R, Milich R, Putterill J, Millar AJ, Hall A (2006). The molecular basis of temperature compensa-tion in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 18, 1177-1187. |
| [19] | Gould PD, Ugarte N, Domijan M, Costa M, Foreman J, Macgregor D, Rose K, Griffiths J, Millar AJ, Finkens-tädt B, Penfield S, Rand DA, Halliday KJ, Hall AJW (2013). Network balance via CRY signaling controls the Arabidopsis circadian clock over ambient temperatures. Mol Syst Biol 9, 650. |
| [20] |
Greenham K, McClung CR (2015). Integrating circadian dynamics with physiological processes in plants. Nat Rev Genet 16, 598-610.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Gutiérrez RA, Stokes TL, Thum K, Xu XD, Obertello M, Katari MS, Tanurdzic M, Dean A, Nero DC, McClung CR, Coruzzi GM (2008). Systems approach identifies an organic nitrogen-responsive gene network that is regula-ted by the master clock control gene CCA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 4939-4944.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Hansen LL, Imrie L, Le Bihan T, van den Burg HA, van Ooijen G (2017a). Sumoylation of the plant clock transcription factor CCA1 suppresses DNA binding. J Biol Rhythms 32, 570-582. |
| [23] | Hansen LL, van den Burg HA, van Ooijen G (2017b). Sumoylation contributes to timekeeping and temperature compensation of the plant circadian clock. J Biol Rhythms 32, 560-569. |
| [24] | Haydon MJ, Mielczarek O, Robertson FC, Hubbard KE, Webb AAR (2013). Photosynthetic entrainment of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock. Nature 502, 689-692. |
| [25] | Haydon MJ, Román Á, Arshad W (2015). Nutrient homeo-stasis within the plant circadian network. Front Plant Sci 6, 299. |
| [26] | Hong S, Song HR, Lutz K, Kerstetter RA, Michael TP, McClung CR (2010). Type II protein arginine methyltrans-ferase 5 (PRMT5) is required for circadian period deter-mination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 21211-21216. |
| [27] | Hsu PY, Devisetty UK, Harmer SL (2013). Accurate time-keeping is controlled by a cycling activator in Arabidopsis. eLife 2, e00473. |
| [28] |
Huang H, Alvarez S, Bindbeutel R, Shen ZX, Naldrett MJ, Evans BS, Briggs SP, Hicks LM, Kay SA, Nusinow DA (2016). Identification of evening complex associated pro-teins in Arabidopsis by affinity purification and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 15, 201-217.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Jones MA, Morohashi K, Grotewold E, Harmer SL (2019). Arabidopsis JMJD5/JMJ30 acts independently of LUX ARRHYTHMO within the plant circadian clock to enable temperature compensation. Front Plant Sci 10, 57. |
| [30] | Jung JH, Barbosa AD, Hutin S, Kumita JR, Gao MJ, Derwort D, Silva CS, Lai XL, Pierre E, Geng F, Kim SB, Baek S, Zubieta C, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2020). A prion-like domain in ELF3 functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis. Nature 585, 256-260. |
| [31] |
Jung JH, Domijan M, Klose C, Biswas S, Ezer D, Gao MJ, Khattak AK, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Kumar M, Grant A, Locke JCW, Schäfer E, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2016). Phytochromes function as thermosen-sors in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 886-889.
PMID |
| [32] | Kidokoro S, Konoura I, Soma F, Suzuki T, Miyakawa T, Tanokura M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2023). Clock-regulated coactivators selectively control gene expression in response to different temperature stress conditions in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2216183120. |
| [33] | Kim SC, Nusinow DA, Sorkin ML, Pruneda-Paz J, Wang XM (2019). Interaction and regulation between lipid me-diator phosphatidic acid and circadian clock regulators. Plant Cell 31, 399-416. |
| [34] | Kim TS, Kim WY, Fujiwara S, Kim J, Cha JY, Park JH, Lee SY, Somers DE (2011). HSP90 functions in the circadian clock through stabilization of the client F-box protein ZEITLUPE. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 16843-16848. |
| [35] | Kolmos E, Chow BY, Pruneda-Paz JL, Kay SA (2014). HsfB2b-mediated repression of PRR7 directs abiotic stress responses of the circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 16172-16177. |
| [36] | Kon N, Wang HT, Kato YS, Uemoto K, Kawamoto N, Kawasaki K, Enoki R, Kurosawa G, Nakane T, Sugiya-ma Y, Tagashira H, Endo M, Iwasaki H, Iwamoto T, Kume K, Fukada Y (2021). Na+/Ca2+ exchanger mediates cold Ca2+ signaling conserved for temperature-compensated circadian rhythms. Sci Adv 7, eabe8132. |
| [37] | Kong YM, Han L, Liu X, Wang HF, Wen LZ, Yu XL, Xu XD, Kong FJ, Fu CX, Mysore KS, Wen JQ, Zhou C (2020). The nodulation and nyctinastic leaf movement is orchest-rated by clock gene LHY in Medicago truncatula. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 1880-1895. |
| [38] | Legris M, Klose C, Burgie ES, Rojas CCR, Neme M, Hilt-brunner A, Wigge PA, Schäfer E, Vierstra RD, Casal JJ (2016). Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 897-900. |
| [39] | Li BJ, Gao ZH, Liu XY, Sun DY, Tang WQ (2019). Trans-criptional profiling reveals a time-of-day-specific role of REVEILLE 4/8 in regulating the first wave of heat shock- induced gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 31, 2353-2369. |
| [40] | Li W, Tian YY, Li JY, Yuan L, Zhang LL, Wang ZY, Xu XD, Davis SJ, Liu JX (2023). A competition-attenuation mechanism modulates thermoresponsive growth at warm temperatures in plants. New Phytol 237, 177-191. |
| [41] | Li Y, Wang LB, Yuan L, Song Y, Sun JQ, Jia Q, Xie QG, Xu XD (2020). Molecular investigation of organ-autonomous expression of Arabidopsis circadian oscillators. Plant Cell Environ 43, 1501-1512. |
| [42] |
Liu XL, Covington MF, Fankhauser C, Chory J, Wagner DR (2001). ELF3 encodes a circadian clock-regulated nuclear protein that functions in an Arabidopsis PHYB signal transduction pathway. Plant Cell 13, 1293-1304.
PMID |
| [43] |
Lou P, Xie Q, Xu X, Edwards CE, Brock MT, Weinig C, McClung CR (2011). Genetic architecture of the circadian clock and flowering time in Brassica rapa. Theor Appl Genet 123, 397-409.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Ma Y, Dai XY, Xu YY, Luo W, Zheng XM, Zeng DL, Pan YJ, Lin XL, Liu HH, Zhang DJ, Xiao J, Guo XY, Xu SJ, Niu YD, Jin JB, Zhang H, Xu X, Li LG, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K (2015). COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160, 1209-1221. |
| [45] | Marshall CM, Tartaglio V, Duarte M, Harmon FG (2016). The Arabidopsis sickle mutant exhibits altered circadian clock responses to cool temperatures and temperature- dependent alternative splicing. Plant Cell 28, 2560-2575. |
| [46] | Mizuno T, Nakamichi N (2005). Pseudo-response regula-tors (PRRs) or True oscillator components (TOCs). Plant Cell Physiol 46, 677-685. |
| [47] | Mody T, Bonnot T, Nagel DH (2020). Interaction between the circadian clock and regulators of heat stress responses in plants. Genes (Basel) 11, 156. |
| [48] |
Moshelion M, Becker D, Biela A, Uehlein N, Hedrich R, Otto B, Levi H, Moran N, Kaldenhoff R (2002). Plasma membrane aquaporins in the motor cells of Samanea saman: diurnal and circadian regulation. Plant Cell 14, 727- 739.
PMID |
| [49] | Mwimba M, Karapetyan S, Liu LJ, Marqués J, McGinnis EM, Buchler NE, Dong XN (2018). Daily humidity oscil-lation regulates the circadian clock to influence plant physiology. Nat Commun 9, 4290. |
| [50] |
Nagel DH, Pruneda-Paz JL, Kay SA (2014). FBH1 affects warm temperature responses in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 14595-14600.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Nusinow DA, Helfer A, Hamilton EE, King JJ, Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Farré EM, Kay SA (2011). The ELF4-ELF3- LUX complex links the circadian clock to diurnal control of hypocotyl growth. Nature 475, 398-402. |
| [52] | Park YJ, Kim JY, Lee JH, Lee BD, Paek NC, Park CM (2020). GIGANTEA shapes the photoperiodic rhythms of thermomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 13, 459-470. |
| [53] |
Patnaik A, Alavilli H, Rath J, Panigrahi KCS, Panigrahy M (2022). Variations in circadian clock organization & func-tion: a journey from ancient to recent. Planta 256, 91.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Portolés S, Más P (2010). The functional interplay between protein kinase CK2 and CCA1 transcriptional activity is essential for clock temperature compensation in Arabi-dopsis. PLoS Genet 6, e1001201. |
| [55] | Prado K, Cotelle V, Li GW, Bellati J, Tang N, Tournaire-Roux C, Martinière A, Santoni V, Maurel C (2019). Oscillating aquaporin phosphorylation and 14-3-3 proteins mediate the circadian regulation of leaf hydraulics. Plant Cell 31, 417-429. |
| [56] | Rawat R, Takahashi N, Hsu PY, Jones MA, Schwartz J, Salemi MR, Phinney BS, Harmer SL (2011). REVEILLE8 and PSEUDO-REPONSE REGULATOR5 form a negative feedback loop within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. PLoS Genet 7, e1001350. |
| [57] |
Rikin A, Dillwith JW, Bergman DK (1993). Correlation between the circadian rhythm of resistance to extreme temperatures and changes in fatty acid composition in cot- ton seedlings. Plant Physiol 101, 31-36.
PMID |
| [58] | Salomé PA, Weigel D, McClung CR (2010). The role of the Arabidopsis morning loop components CCA1, LHY, PRR7, and PRR9 in temperature compensation. Plant Cell 22, 3650-3661. |
| [59] | Sanchez SE, Kay SA (2016). The plant circadian clock: from a simple timekeeper to a complex developmental manager. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8, a027748. |
| [60] | Sanchez SE, Rugnone ML, Kay SA (2020). Light percep-tion: a matter of time. Mol Plant 13, 363-385. |
| [61] |
Schaffer R, Ramsay N, Samach A, Corden S, Putterill J, Carré IA, Coupland G (1998). The late elongated hypo-cotyl mutation of Arabidopsis disrupts circadian rhythms and the photoperiodic control of flowering. Cell 93, 1219- 1229.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Schlaen RG, Mancini E, Sanchez SE, Perez-Santángelo S, Rugnone ML, Simpson CG, Brown JWS, Zhang X, Chernomoretz A, Yanovsky MJ (2015). The spliceosome assembly factor GEMIN2 attenuates the effects of temperature on alternative splicing and circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 9382-9387.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Seo PJ, Park MJ, Lim MH, Kim SG, Lee M, Baldwin IT, Park CM (2012). A self-regulatory circuit of CIRCADIAN CLOCK-ASSOCIATED1 underlies the circadian clock regulation of temperature responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 2427-2442. |
| [64] | Simon NML, Graham CA, Comben NE, Hetherington AM, Dodd AN (2020). The circadian clock influences the long- term water use efficiency of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 183, 317-330. |
| [65] |
Somers DE, Webb AAR, Pearson M, Kay SA (1998). The short-period mutant, toc1-1, alters circadian clock regula-tion of multiple outputs throughout development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 125, 485-494.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Steed G, Ramirez DC, Hannah MA, Webb AAR (2021). Chronoculture, harnessing the circadian clock to improve crop yield and sustainability. Science 372, eabc9141. |
| [67] |
Sun QB, Wang SL, Xu G, Kang XJ, Zhang M, Ni M (2019). SHB1 and CCA1 interaction desensitizes light responses and enhances thermomorphogenesis. Nat Commun 10, 3110.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Takase T, Ishikawa H, Murakami H, Kikuchi J, Sato-Nara K, Suzuki H (2011). The circadian clock modulates water dynamics and aquaporin expression in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell Physiol 52, 373-383. |
| [69] | Verslues PE, Bailey-Serres J, Brodersen C, Buckley TN, Conti L, Christmann A, Dinneny JR, Grill E, Hayes S, Heckman RW, Hsu PK, Juenger TE, Mas P, Munnik T, Nelissen H, Sack L, Schroeder JI, Testerink C, Tyer-man SD, Umezawa T, Wigge PA (2023). Burning ques-tions for a warming and changing world: 15 unknowns in plant abiotic stress. Plant Cell 35, 67-108. |
| [70] | Wang F, Han TW, Song QX, Ye WX, Song XG, Chu JF, Li JY, Chen ZJ (2020a). The rice circadian clock regulates tiller growth and panicle development through strigolactone signaling and sugar sensing. Plant Cell 32, 3124-3138. |
| [71] | Wang XH, Zhao C, Müller C, Wang CZ, Ciais P, Janssens I, Peñuelas J, Asseng S, Li T, Elliott J, Huang Y, Li L, Piao S (2020b). Emergent constraint on crop yield res-ponse to warmer temperature from field experiments. Nat Sustain 3, 908-916. |
| [72] | Wang XX, Wu FM, Xie QG, Wang HM, Wang Y, Yue YL, Gahura O, Ma SS, Liu L, Cao Y, Jiao YL, Puta F, McClung CR, Xu XD, Ma LG (2012). SKIP is a compo-nent of the spliceosome linking alternative splicing and the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 3278-3295. |
| [73] |
Wang ZY, Tobin EM (1998). Constitutive expression of the CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1) gene dis-rupts circadian rhythms and suppresses its own expres-sion. Cell 93, 1207-1217.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Wei H, Wang Y, Liu BH, Wang L (2018). Deciphering the underlying mechanism of the plant circadian system and its regulation on plant growth and development. Chin Bull Bot 53, 456-467. (in Chinese) |
|
魏华, 王岩, 刘宝辉, 王雷 (2018). 植物生物钟及其调控生长发育的研究进展. 植物学报 53, 456-467.
DOI |
|
| [75] | Wu JF, Tsai HL, Joanito I, Wu YC, Chang CW, Li YH, Wang Y, Hong JC, Chu JW, Hsu CP, Wu SH (2016). LWD-TCP complex activates the morning gene CCA1 in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 7, 13181. |
| [76] | Xie QG, Wang P, Liu X, Yuan L, Wang LB, Zhang CG, Li Y, Xing HY, Zhi LY, Yue ZL, Zhao CS, McClung CR, Xu XD (2014). LNK1 and LNK2 are transcriptional coactive-tors in the Arabidopsis circadian oscillator. Plant Cell 26, 2843-2857. |
| [77] | Xu XD, Hotta CT, Dodd AN, Love J, Sharrock R, Lee YW, Xie QG, Johnson CH, Webb AAR (2007). Distinct light and clock modulation of cytosolic free Ca2+ oscillations and rhythmic CHLOROPHYLL A/B BINDING PROTEIN2 promoter activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 3474-3490. |
| [78] | Xu XD, Yuan L, Xie QG (2022a). The circadian clock ticks in plant stress responses. Stress Biol 2, 15. |
| [79] | Xu XD, Yuan L, Yang X, Zhang X, Wang L, Xie QG (2022b). Circadian clock in plants: linking timing to fitness. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 792-811. |
| [80] |
Yanovsky MJ, Izaguirre M, Wagmaister JA, Gatz C, Jackson SD, Thomas B, Casal JJ (2000). Phytochrome A resets the circadian clock and delays tuber formation under long days in potato. Plant J 23, 223-232.
PMID |
| [81] | Yuan L, Hu Y, Li SL, Xie QG, Xu XD (2021). PRR9 and PRR7 negatively regulate the expression of EC compo-nents under warm temperature in roots. Plant Signal Be-hav 16, 1855384. |
| [82] | Zhang HT, Kumimoto RW, Anver S, Harmer SL (2023). XAP5 CIRCADIAN TIMEKEEPER regulates RNA splicing and the circadian clock by genetically separable pathway-s. Plant Physiol 192, 2492-2506. |
| [83] | Zhang LL, Li W, Tian YY, Davis SJ, Liu JX (2021a). The E3 ligase XBAT35 mediates thermoresponsive hypocotyl growth by targeting ELF3 for degradation in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 63,1097-1103. |
| [84] | Zhang LL, Luo AN, Davis SJ, Liu JX (2021b). Timing to grow: roles of clock in thermomorphogenesis. Trends Plant Sci 26, 1248-1257. |
| [85] | Zhou M, Wang W, Karapetyan S, Mwimba M, Marqués J, Buchler NE, Dong XN (2015). Redox rhythm reinforces the circadian clock to gate immune response. Nature 523, 472-476. |
| [1] | 苏晨, 牛钰凡, 徐航, 王希岭, 于英俊, 何雨晴, 王雷. 生物钟与光温环境信号互作网络研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 315-341. |
| [2] | 于英俊,徐航,王雷. 生物发光成像无损伤研究植物生物钟的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 177-181. |
| [3] | 魏华, 王岩, 刘宝辉, 王雷. 植物生物钟及其调控生长发育的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 456-467. |
| [4] | 彭波, 孙艳芳, 陈报阳, 孙瑞萌, 孔冬艳, 庞瑞华, 李先文, 宋晓华, 李慧龙, 李金涛, 周棋赢, 柳琳, 段斌, 宋世枝. 水稻香味基因及其在育种中的应用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 797-807. |
| [5] | 徐江民, 姜洪真, 林晗, 黄苗苗, 符巧丽, 曾大力, 饶玉春. 水稻ES1参与生物钟基因表达调控以及逆境胁迫响应[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(6): 743-756. |
| [6] | 王长忠, 李忠, 梁宏伟, 呼光富, 吴勤超, 邹桂伟, 罗相忠. 长江下游地区4个克氏原螯虾群体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(5): 518-523. |
| [7] | 梁宏伟, 李忠, 罗相忠, 王长忠, 呼光富, 邹桂伟, 杨永铨. 基于微卫星标记的5个尼罗罗非鱼品系的遗传多样性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(1): 82-87. |
| [8] | 徐张红, 赵晓刚, 何奕昆. 拟南芥生物钟分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2005, 22(03): 341-349. |
| [9] | 房迈莼 王小菁 李洪清. 光对植物生物钟的调节[J]. 植物学报, 2005, 22(02): 207-214. |
| [10] | 杨江义 李旭锋. 植物雌性单倍体的离体诱导[J]. 植物学报, 2002, 19(05): 552-559. |
| [11] | 吴刚 崔海瑞 夏英武. 原位杂交技术在植物遗传育种上的应用[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(06): 625-630. |
| [12] | 吴敏生 戴景瑞. 扩增片段长度多态性( AFLP) ——一种新的分子标记技术[J]. 植物学报, 1998, 15(04): 68-74. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||