

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 666-676.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20085 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20085
收稿日期:2020-05-15
接受日期:2020-07-29
出版日期:2020-11-01
发布日期:2020-11-11
通讯作者:
卜红梅
作者简介:*E-mail: buhm@igsnrr.ac.cn基金资助:
Rui Zhao1,2, Hongmei Bu1,*( ), Xianfang Song1,2, Rongjin Gao3
), Xianfang Song1,2, Rongjin Gao3
Received:2020-05-15
Accepted:2020-07-29
Online:2020-11-01
Published:2020-11-11
Contact:
Hongmei Bu
摘要: 再生水是城市景观河湖的重要补给水源, 然而再生水中含量较高的氮和磷营养盐会引起水体富营养化, 破坏水生态平衡。以再生水补给的潮白河为研究区, 运用高光谱技术分析了挺水植物芦苇(Phragmites australis)叶片的光谱特征, 并结合水质数据, 通过拟合模型, 探究了芦苇对再生水中氮和磷的响应关系。结果表明, 各采样点水体的总氮(TN)和总磷(TP)含量分别介于1.85-18.16 mg·L-1及0.01-0.36 mg·L-1之间, 叶绿素a (Chl a)和溶解氧(DO)含量的范围分别为0.60-47.45 μg·L-1与4.24-11.4 mg·L-1。水体富营养化较为严重, 但仍处于富氧环境。多重方差分析表明, 不同采样点之间水体的TN、TP和Chl a含量差异显著(P<0.05)。由光谱反射率及反射率一阶导数曲线可知, 水体TN含量越高, 叶片光谱在可见光区的反射率越小, 红边位置也越向波长长的方向移动(即红移)。相关分析表明, 水体TN和TP含量与吸光度值log(1/R)在可见光区的相关性较强, 且TN与log(1/R)的相关系数高于TP。芦苇叶片光谱可在一定程度上区分水体TN含量差异, 但TP对光谱特征的影响模式不明显。光谱指数与水体TN含量之间的拟合模型中, 基于光化学指数(PRI)、修正叶绿素吸收指数(MCARI)和导数叶绿素指数(DCI)的模型能够解释水体TN含量变化的62.4%-70.9% (P<0.05), 可用于再生水氮含量的定量监测。该研究证明了植物光谱技术在水体富营养化监测上的可行性, 为保障再生水修复河道水质和生态安全提供了科学依据。
赵睿, 卜红梅, 宋献方, 高融瑾. 再生水补给河道内芦苇的光谱特征及其对水体氮和磷含量的响应. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 666-676.
Rui Zhao, Hongmei Bu, Xianfang Song, Rongjin Gao. Spectral Characteristics of Phragmites australis and Its Response to Riverine Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents in River Reaches Restored by Reclaimed Water. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 666-676.
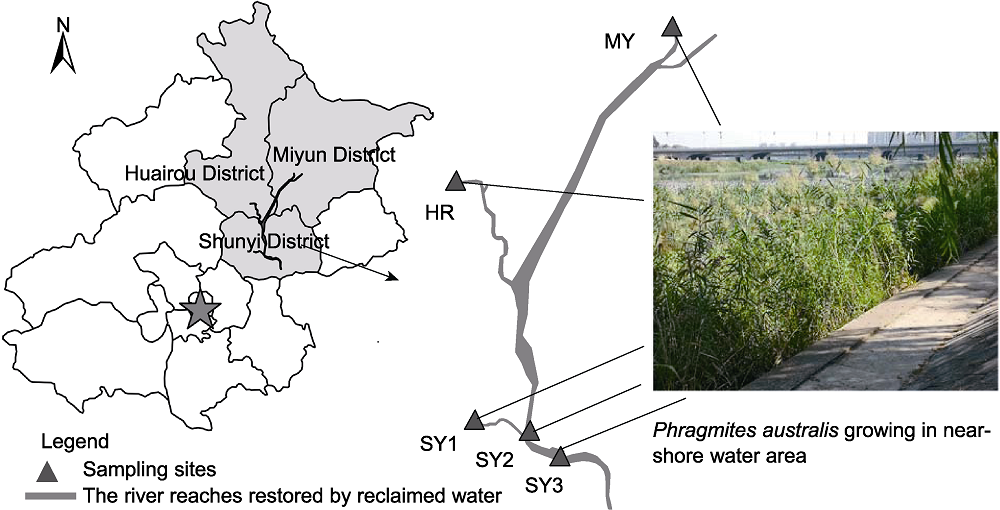
图1 潮白河再生水补给区采样点分布图 审图号: 京s(2020)028号 MY: 密云段再生水出水口附近; HR: 怀柔段再生水出水口附近; SY1: 顺义段再生水出水口附近; SY2: 顺义段减河公园内; SY3: 顺义段河南橡胶坝
Figure 1 The sampling sites in Chaobai River restored by reclaimed water MY: Reclaimed water outlet in Miyun District; HR: Reclaimed water outlet in Huairou District; SY1: Reclaimed water outlet in Shunyi District; SY2: Jian River Park in Shunyi District; SY3: Henan Rubber Dam in Shunyi District
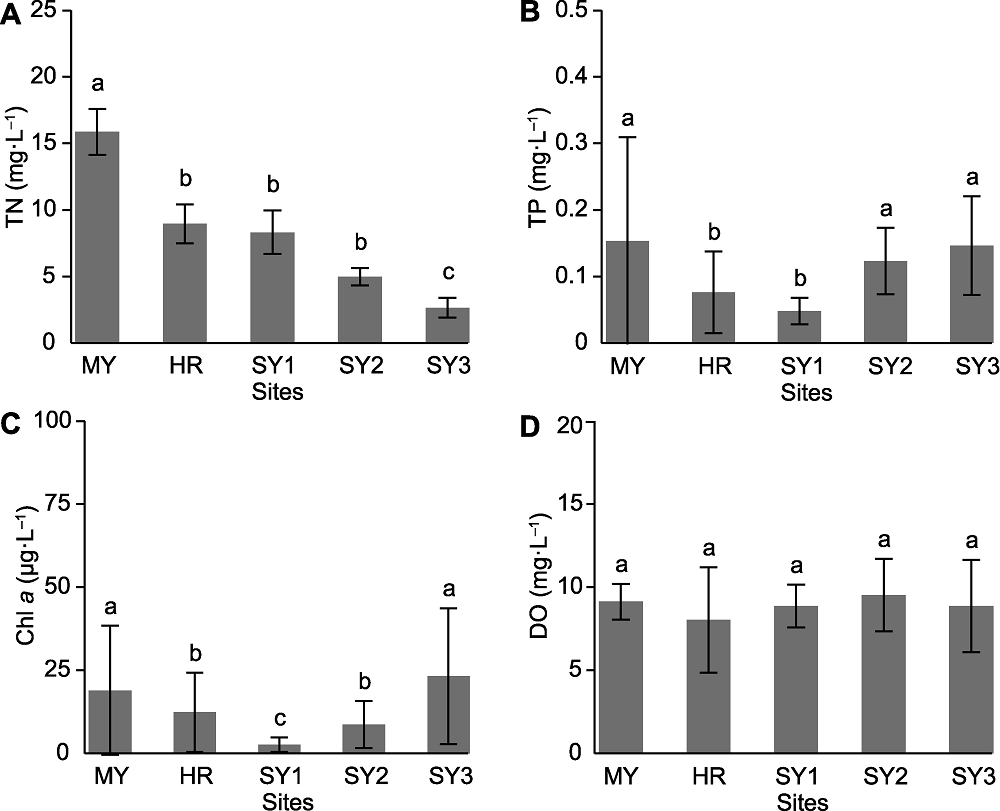
图2 潮白河再生水补给区各采样点水体中TN (A)、TP (B)、Chl a (C)和DO含量(D) TN: 全氮; TP: 全磷; DO: 溶解氧。MY、HR、SY1、SY2和SY3同图1。不同小写字母表示不同采样点之间平均值的显著性差异。
Figure 2 The contents of TN (A), TP (B), Chl a (C) and DO (D) at different sampling sites in Chaobai River restored by reclaimed water TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus; DO: Dissolved oxygen. MY, HR, SY1, SY2 and SY3 see Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between sampling sites.
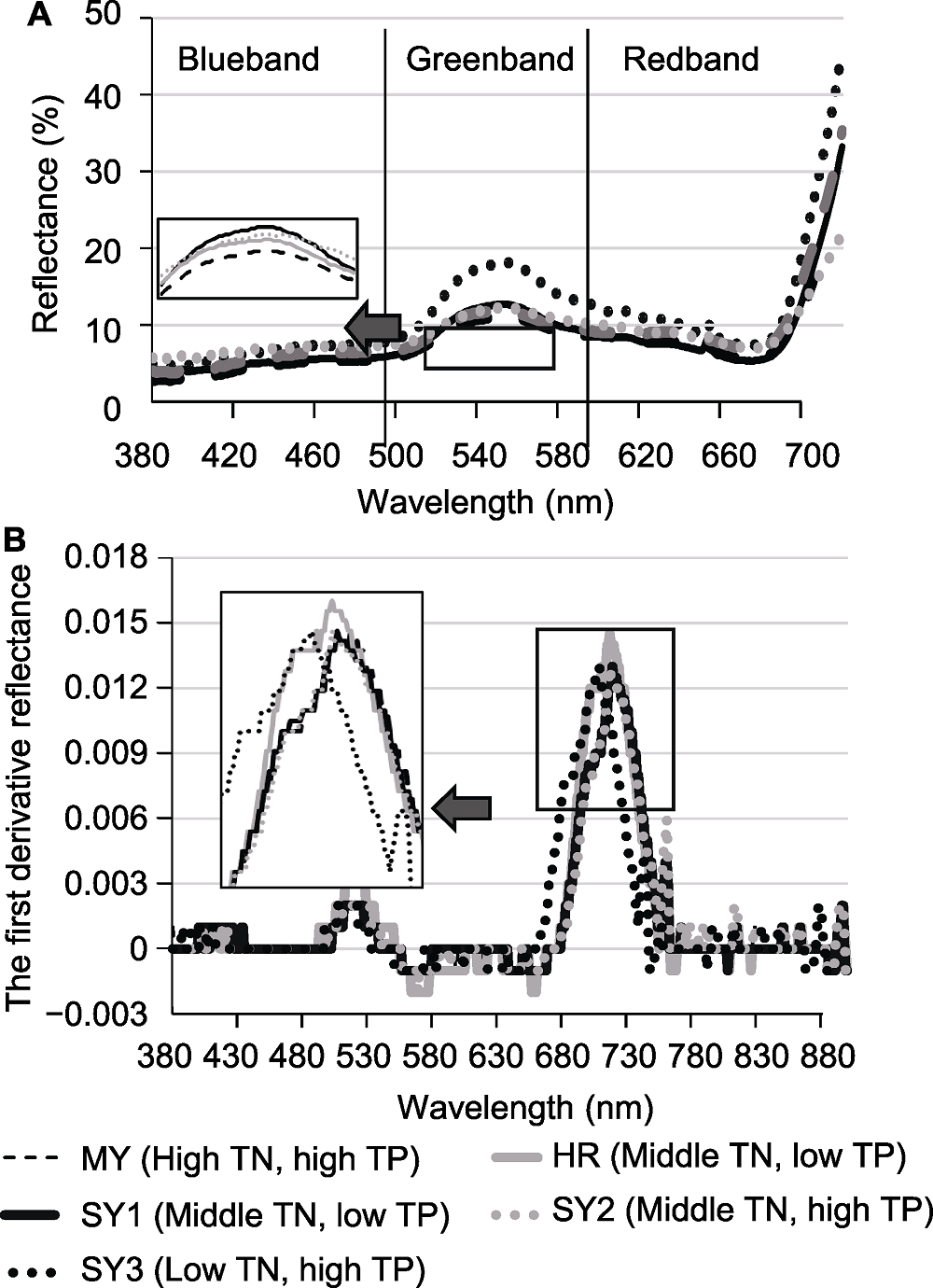
图3 潮白河再生水补给区各采样点芦苇叶片光谱反射率(A)及反射率一阶导数(B) TN和TP同图2。MY、HR、SY1、SY2和SY3同图1。
Figure 3 Spectral reflectance (A) and the first derivative reflectance (B) of Phragmites australis leaves at different sampling sites in the Chaobai River restored by reclaimed water TN and TP see Figure 2. MY, HR, SY1, SY2 and SY3 see Figure 1.
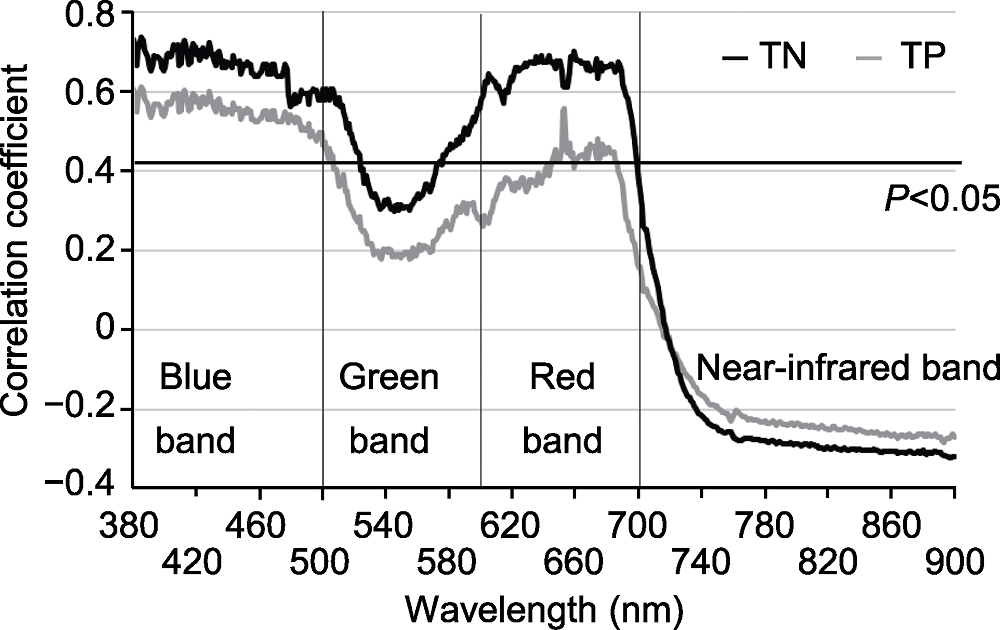
图4 潮白河再生水补给区水体TN和TP含量与芦苇叶片吸光度值log(1/R)的相关系数 TN和TP同图2。
Figure 4 Correlation coefficients between contents of riverine TN and TP and absorbance values of Phragmites australis leaves in Chaobai River restored by reclaimed water TN and TP see Figure 2.
| Spectral indexes and expressions | Model types | Fitting equations | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRI (R531-R570)/(R531+R570) | Linear equation | y=5.243x+5.685 | 0.042 |
| Exponential equation | y=6.914e1.102x | 0.693* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=1.254x2+0.489x-0.156 | 0.219 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=0.492lnx-0.641 | 0.038 | |
| MCARI [(R700-R670)-0.2(R700-R550)] (R700/R670) | Linear equation | y=-3.122x+7.396 | 0.119 |
| Exponential equation | y=8.854e-0.105x | 0.709* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=-0.595x2+1.821x+2.608 | 0.426 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=-0.567lnx+1.614 | 0.092 | |
| NPCI (R680-R430)/(R680+R430) | Linear equation | y=4.915x+7.725 | 0.110 |
| Exponential equation | y=9.940e0.008x | 0.507 | |
| Quadratic equation | y=1.285x2+0.518x-0.087 | 0.209 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=1.043lnx+0.168 | 0.093 | |
| DCI D725/D705 | Linear equation | y=2.485x+3.498 | 0.038 |
| Exponential equation | y=5.197e0.164x | 0.624* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=2.703x2-3.752x+1.854 | 0.478 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=2.07lnx-1.019 | 0.096 | |
表1 芦苇叶片光谱指数与水体总氮(TN)含量的拟合模型
Table 1 Fitting models between spectral indexes of Phragmites australis leaves and riverine total nitrogen (TN) contents
| Spectral indexes and expressions | Model types | Fitting equations | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRI (R531-R570)/(R531+R570) | Linear equation | y=5.243x+5.685 | 0.042 |
| Exponential equation | y=6.914e1.102x | 0.693* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=1.254x2+0.489x-0.156 | 0.219 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=0.492lnx-0.641 | 0.038 | |
| MCARI [(R700-R670)-0.2(R700-R550)] (R700/R670) | Linear equation | y=-3.122x+7.396 | 0.119 |
| Exponential equation | y=8.854e-0.105x | 0.709* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=-0.595x2+1.821x+2.608 | 0.426 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=-0.567lnx+1.614 | 0.092 | |
| NPCI (R680-R430)/(R680+R430) | Linear equation | y=4.915x+7.725 | 0.110 |
| Exponential equation | y=9.940e0.008x | 0.507 | |
| Quadratic equation | y=1.285x2+0.518x-0.087 | 0.209 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=1.043lnx+0.168 | 0.093 | |
| DCI D725/D705 | Linear equation | y=2.485x+3.498 | 0.038 |
| Exponential equation | y=5.197e0.164x | 0.624* | |
| Quadratic equation | y=2.703x2-3.752x+1.854 | 0.478 | |
| Logarithmic equation | y=2.07lnx-1.019 | 0.096 | |
| [1] | 迟光宇, 刘新会, 刘素红, 杨志峰 (2005). 环境污染监测中的植物光谱效应研究. 环境科学与技术 28(S1), 16-19. |
| [2] |
宫兆宁, 范云豹, 刘辉, 赵文吉 (2016). 不同水氮梯度下典型挺水植物叶绿素荧光的响应特性. 植物学报 51, 631-638.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 顾永钢, 吴晓辉, 李兆欣, 赵立新, 刘操 (2017). 潮白河再生水受水区水体水质沿程变化规律研究. 北京水务 (1), 29-35. |
| [4] | 李玲玉, 杨浩萌, 任为波, 吴新宏, 黄芳 (2017). 利用叶绿素荧光评估草原植物羊草缺磷缺氮状况. 植物学报 52, 271-277. |
| [5] | 李哲, 张飞, 陈丽华, 张海威 (2018). 光谱指数的植物叶片叶绿素含量估算模型. 光谱学与光谱分析 38, 1533-1539. |
| [6] | 刘辉, 宫兆宁, 赵文吉 (2014). 基于挺水植物高光谱信息的再生水总氮含量估测——以北京市门城湖湿地公园为例. 应用生态学报 25, 3609-3618. |
| [7] | 刘克, 唐新明, 赵文吉, 雷兵, 郭逍宇, 宫兆宁 (2015). 水体总氮浓度与湿地芦苇叶片高光谱特征关系研究. 地理与地理信息科学 31(2), 24-28. |
| [8] | 刘克, 赵文吉, 郭逍宇, 王翊虹, 孙永华, 苗茜, 王京萌 (2012). 基于湿地植物光谱的水体总氮估测. 生态学报 32, 2410-2419. |
| [9] | 刘瑞斌 (2019). 人工湿地植物群落造景艺术研究——评《人工湿地植物配置与管理》. 植物学报 54, 674. |
| [10] | 任红艳, 庄大方, 潘剑君, 邱冬生, 张佳宝 (2008). 磷营养胁迫对冬小麦冠层光谱的影响. 土壤通报 39, 1326-1330. |
| [11] | 王健, 何江涛, 刘玉梅, 姜烈 (2014). 潮白河再生水受水区水质变化特征多元统计分析. 环境科学与技术 37(6), 171-176. |
| [12] | 薛利红, 曹卫星, 罗卫红, 张宪 (2004). 小麦叶片氮素状况与光谱特性的相关性研究. 植物生态学报 28, 172-177. |
| [13] | 薛利红, 卢萍, 杨林章, 单玉华, 范晓晖, 韩勇 (2006). 利用水稻冠层光谱特征诊断土壤氮素营养状况. 植物生态学报 30, 675-681. |
| [14] | 于一雷 (2013). 河道景观再生水对地下水影响研究——以潮白河北京段为例. 博士论文. 北京: 中国科学院大学. pp. 18-20. |
| [15] | 张丽彬, 王启山, 徐新惠, 丁丽丽, 任洪强 (2008). 乙醇法测定浮游植物叶绿素a含量的讨论. 中国环境监测 24(6), 9-10. |
| [16] | 张璐, 何新华 (2020). C3和C4植物的氮素利用机制. 植物学报 55, 228-239. |
| [17] | 张茜, 裘天航, 王安安, 周华健, 袁敏, 李利, 白素兰, 崔素霞 (2020). 北京地区芦苇资源状态及其多样性. 植物学报 55, 693-704. |
| [18] | Ågren GI (2004). The C:N:P stoichiometry of autotrophs- theory and observations. Ecol Lett 7, 185-191. |
| [19] | Ågren GI (2008). Stoichiometry and nutrition of plant growth in natural communities. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 39, 153-170. |
| [20] | Bricker SB, Ferreira JG, Simas T (2003). An integrated methodology for assessment of estuarine trophic status. Ecol Modell 169, 39-60. |
| [21] | Chang DH, Ma Z (2012). Wastewater reclamation and reuse in Beijing: influence factors and policy implications. Desalination 297, 72-78. |
| [22] | Daughtry CST, Walthall CL, Kim MS, De Colstoun EB, McMurtrey III JE (2000). Estimating corn leaf chlorophyll concentration from leaf and canopy reflectance. Remote Sens Environ 74, 229-239. |
| [23] | Eitel JUH, Long DS, Gessler PE, Hunt ER (2008). Com-bined spectral index to improve ground-based estimates of nitrogen status in dryland wheat. Agron J 100, 1694-1702. |
| [24] |
Eller F, Skálová H, Caplan JS, Bhattarai GP, Burger MK, Cronin JT, Guo WY, Guo X, Hazelton ELG, Kettenring KM, Lambertini C, McCormick MK, Meyerson LA, Mozdzer TJ, Pyšek P, Sorrell BK, Whigham DF, Brix H (2017). Cosmopolitan species as models for ecophysio- logical responses to global change: the common reed Phragmites australis. Front Plant Sci 8, 1833.
URL PMID |
| [25] |
Gamon JA, Serrano L, Surfus JS (1997). The photochemical reflectance index: an optical indicator of photosynthetic radiation use efficiency across species, functional types, and nutrient levels. Oecologia 112, 492-501.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Gitelson AA, Merzlyak MN (1997). Remote estimation of chlorophyll content in higher plant leaves. Int J Remote Sens 18, 2691-2697. |
| [27] | Horler DNH, Dockray M, Barber J (1983). The red edge of plant leaf reflectance. Int J Remote Sens 4, 273-288. |
| [28] | Knipling EB (1970). Physical and physiological basis for the reflectance of visible and near-infrared radiation from vegetation. Remote Sens Environ 1, 155-159. |
| [29] | Kokaly RF (2001). Investigating a physical basis for spectroscopic estimates of leaf nitrogen concentration. Remote Sens Environ 75, 153-161. |
| [30] | Lamb DW, Steyn-Ross M, Schaare P, Hanna MM, Silvester W, Steyn-Ross A (2002). Estimating leaf nitrogen concentration in ryegrass ( Lolium spp.) pasture using the chlorophyll red-edge: theoretical modelling and experimental observations. Int J Remote Sens 23, 3619-3648. |
| [31] | Li F, Miao YX, Hennig SD, Gnyp ML, Chen XP, Jia LL, Bareth G (2010). Evaluating hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimating nitrogen concentration of winter wheat at different growth stages. Precision Agric 11, 335-357. |
| [32] | Lyu S, Chen WP, Zhang WL, Fan YP, Jiao WT (2016). Wastewater reclamation and reuse in China: opportunities and challenges. J Environ Sci 39, 86-96. |
| [33] | Mykleby PM, Awada T, Lenters JD, Bihmidine S, Yarina AJ, Young SL (2015). Responses of common reed (Ph-ragmites australis) to nitrogen and temperature manipulations. Great Plains Research 25, 63-74. |
| [34] | Osborne SL, Schepers JS, Francis DD, Schlemmer MR (2002). Detection of phosphorus and nitrogen deficiencies in corn using spectral radiance measurements. Agron J 94, 1215-1221. |
| [35] |
Shrestha S, Brueck H, Asch F (2012). Chlorophyll index, photochemical reflectance index and chlorophyll fluorescence measurements of rice leaves supplied with different N levels. J Photochem Photobiol B 113, 7-13.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] | Siciliano D, Wasson K, Potts DC, Olsen RC (2008). Evaluating hyperspectral imaging of wetland vegetation as a tool for detecting estuarine nutrient enrichment. Remote Sens Environ 112, 4020-4033. |
| [37] | Tanner CC (1996). Plants for constructed wetland treatment systems—a comparison of the growth and nutrient uptake of eight emergent species. Ecol Eng 7, 59-83. |
| [38] | Tilley DR, Ahmed M, Son JH, Badrinarayanan H (2003). Hyperspectral reflectance of emergent macrophytes as an indicator of water column ammonia in an oligohaline, subtropical marsh. Ecol Eng 21, 153-163. |
| [39] | Wu CY, Niu Z, Tang Q, Huang WJ (2008). Estimating chlorophyll content from hyperspectral vegetation indices: modeling and validation. Agric For Meteorol 148, 1230-1241. |
| [40] | Yang L, He JT, Liu YM, Wang J, Jiang L, Wang GC (2016). Characteristics of change in water quality along reclaimed water intake area of the Chaobai River in Beijing, China. J Environ Sci 50, 93-102. |
| [41] | Yoder BJ, Pettigrew-Crosby RE (1995). Predicting nitrogen and chlorophyll content and concentrations from reflectance spectra (400-2 500 nm) at leaf and canopy scales. Remote Sens Environ 53, 199-211. |
| [42] |
Zarco-Tejada PJ, Miller JR, Mohammed GH, Noland TL, Sampson PH (2002). Vegetation stress detection through chlorophyll a + b estimation and fluorescence effects on hyperspectral imagery. J Environ Qual 31, 1433-1441.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | Zarco-Tejada PJ, Pushnik JC, Dobrowski S, Ustin SL (2003). Steady-state chlorophyll a fluorescence detection from canopy derivative reflectance and double-peak re- dedge effects. Remote Sens Environ 84, 283-294. |
| [1] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [2] | 裘天航, 王安安, 李利, 王迎春, 崔继鹏, 王紫瑶, 王蕊, 崔素霞. 2种生态型芦苇RCA基因特征及表达特异性[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 687-700. |
| [3] | 史欢欢, 雪穷, 于振林, 汪承焕. 密度、物种比例对盐沼植物种子萌发阶段种内、种间相互作用的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(1): 77-87. |
| [4] | 张茜, 裘天航, 王安安, 周华健, 袁敏, 李利, 白素兰, 崔素霞. 北京地区芦苇资源状态及其多样性[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 693-704. |
| [5] | 郭瑞, 周际, 刘琪, 顾峰雪. 松嫩退化草地芦苇不同叶位叶片营养元素代谢特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(7): 734-740. |
| [6] | 李群, 赵成章, 赵连春, 王建良, 张伟涛, 姚文秀. 秦王川盐沼湿地芦苇比叶面积与叶片热耗散的关联性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(9): 985-994. |
| [7] | 刘畅, 孙鹏森, 刘世荣. 水分敏感的反射光谱指数比较研究——以锐齿槲栎为例[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 850-861. |
| [8] | 高林, 王晓菲, 顾行发, 田庆久, 焦俊男, 王培燕, 李丹. 植冠下土壤类型差异对遥感估算冬小麦叶面积指数的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(12): 1273-1288. |
| [9] | 宫兆宁, 范云豹, 刘辉, 赵文吉. 不同水氮梯度下典型挺水植物叶绿素荧光的响应特性[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 631-638. |
| [10] | 刘波, 吕宪国, 姜明, 张文广, 武海涛. 光照、水深交互作用对松嫩湿地芦苇种子萌发的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(6): 616-620. |
| [11] | 陈清, 王义东, 郭长城, 王中良. 天津沼泽湿地芦苇叶片的碳稳定同位素比值分布特征及其环境影响因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(11): 1044-1052. |
| [12] | 胡楚琦, 刘金珂, 王天弘, 王文琳, 卢山, 周长芳. 三种盐胁迫对互花米草和芦苇光合作用的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(1): 92-103. |
| [13] | 刘利丹, 介冬梅, 刘洪妍, 郭梅娥, 李楠楠. 东北地区芦苇植硅体的变化特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(9): 861-871. |
| [14] | 朱敏,张振华,于君宝,吴立新,韩广轩,杨利琼,邢庆会,谢宝华,毛培利,王光美. 氮沉降对黄河三角洲芦苇湿地土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(6): 517-529. |
| [15] | 杨利琼,韩广轩,于君宝,吴立新,朱敏,邢庆会,王光美,毛培利. 开垦对黄河三角洲湿地净生态系统CO2交换的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(6): 503-516. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||