

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 204-217.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24093 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24093
• RESEARCH ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huiling Fan1,3, Yan Lu3, Wenhai Jin1, Hui Wang1, Xiaoxing Peng1, Xuexia Wu1,*( ), Yujiao Liu1,2,*(
), Yujiao Liu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-16
Accepted:2024-10-14
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2024-10-16
Contact:
Xuexia Wu, Yujiao Liu
Huiling Fan, Yan Lu, Wenhai Jin, Hui Wang, Xiaoxing Peng, Xuexia Wu, Yujiao Liu. Identification and Comprehensive Evaluation of Faba Bean Salt-alkali Tolerance Based on Root Phenotypic Traits[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 204-217.
| Traits | Mean (%) | Mode (%) | Skewness | Standard deviation | Variation range | Interquartile range (%) | Variable coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 2.630 | 2.000 | 3.829 | 1.530 | 1.000-17.300 | 1.259 | 58.175 |
| NRT | 3.123 | 3.000 | 4.876 | 1.336 | 1.000-17.700 | 0.990 | 42.779 |
| LR | 1.651 | 1.496 | 3.502 | 0.733 | 0.510-8.721 | 0.693 | 44.397 |
| ADR | 2.008 | 1.757 | 0.187 | 0.351 | 1.903-3.418 | 0.450 | 17.480 |
| TPAR | 34.662 | 9.324 | 2.478 | 15.534 | 9.324-136.722 | 15.591 | 44.816 |
| TSAR | 108.895 | 29.291 | 2.478 | 48.802 | 29.291-429.524 | 48.981 | 44.816 |
| BUR | 60.948 | 11.289 | 2.344 | 32.776 | 11.289-262.196 | 34.705 | 53.777 |
| TNCP | 5.457 | 0.400 | 3.613 | 3.219 | 0.200-35.700 | 2.875 | 58.987 |
| EP | 3.123 | 3.000 | 4.876 | 1.336 | 1.000-17.700 | 0.990 | 42.779 |
| CL | 2.334 | 1.000 | 2.640 | 2.393 | 0.000-19.000 | 2.141 | 102.528 |
| LN | 5.027 | 3.000 | 2.843 | 3.876 | 1.000-35.300 | 3.310 | 77.104 |
| BN | 1.628 | 1.000 | 3.742 | 1.524 | 0.000-16.000 | 1.259 | 93.612 |
| ON | 0.713 | 0.000 | 5.648 | 1.494 | 0.000-19.000 | 0.961 | 209.537 |
| GP | 51.200 | 20.000 | 0.058 | 30.300 | 0.000-100.000 | 51.050 | 59.179 |
| GI | 3.679 | 1.593 | 0.865 | 2.433 | 0.000-11.964 | 3.613 | 66.132 |
| GR | 60.000 | 80.000 | -0.209 | 28.900 | 0.000-100.000 | 49.000 | 48.167 |
Table 1 Parameter value of different traits under saline-alkali stress
| Traits | Mean (%) | Mode (%) | Skewness | Standard deviation | Variation range | Interquartile range (%) | Variable coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 2.630 | 2.000 | 3.829 | 1.530 | 1.000-17.300 | 1.259 | 58.175 |
| NRT | 3.123 | 3.000 | 4.876 | 1.336 | 1.000-17.700 | 0.990 | 42.779 |
| LR | 1.651 | 1.496 | 3.502 | 0.733 | 0.510-8.721 | 0.693 | 44.397 |
| ADR | 2.008 | 1.757 | 0.187 | 0.351 | 1.903-3.418 | 0.450 | 17.480 |
| TPAR | 34.662 | 9.324 | 2.478 | 15.534 | 9.324-136.722 | 15.591 | 44.816 |
| TSAR | 108.895 | 29.291 | 2.478 | 48.802 | 29.291-429.524 | 48.981 | 44.816 |
| BUR | 60.948 | 11.289 | 2.344 | 32.776 | 11.289-262.196 | 34.705 | 53.777 |
| TNCP | 5.457 | 0.400 | 3.613 | 3.219 | 0.200-35.700 | 2.875 | 58.987 |
| EP | 3.123 | 3.000 | 4.876 | 1.336 | 1.000-17.700 | 0.990 | 42.779 |
| CL | 2.334 | 1.000 | 2.640 | 2.393 | 0.000-19.000 | 2.141 | 102.528 |
| LN | 5.027 | 3.000 | 2.843 | 3.876 | 1.000-35.300 | 3.310 | 77.104 |
| BN | 1.628 | 1.000 | 3.742 | 1.524 | 0.000-16.000 | 1.259 | 93.612 |
| ON | 0.713 | 0.000 | 5.648 | 1.494 | 0.000-19.000 | 0.961 | 209.537 |
| GP | 51.200 | 20.000 | 0.058 | 30.300 | 0.000-100.000 | 51.050 | 59.179 |
| GI | 3.679 | 1.593 | 0.865 | 2.433 | 0.000-11.964 | 3.613 | 66.132 |
| GR | 60.000 | 80.000 | -0.209 | 28.900 | 0.000-100.000 | 49.000 | 48.167 |
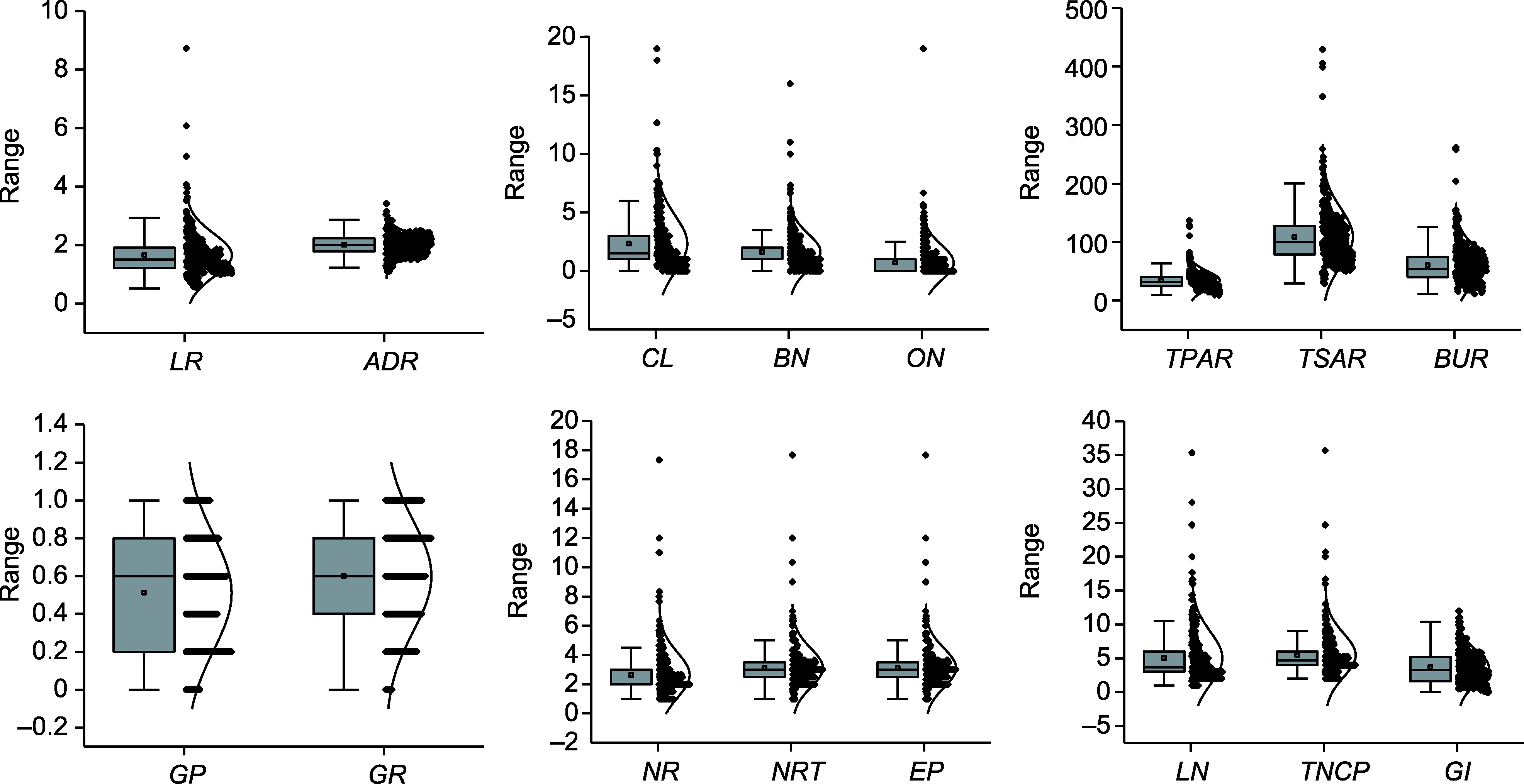
Figure 1 Plots of the distribution of means for phenotypic index in faba bean root LR, ADR, CL, BN, ON, TPAR, TSAR, BUR, GP, GR, NR, NRT, EP, LN, TNCP, and GI are the same as shown in Table 1.
| Index | NR | NRT | LR | ADR | TPAR | TSAR | BUR | EP | CL | LN | BN | ON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRT | 0.837** | |||||||||||
| LR | 0.759** | 0.521** | ||||||||||
| ADR | -0.362** | -0.181** | -0.215** | |||||||||
| TPAR | 0.606** | 0.400** | 0.930** | 0.061 | ||||||||
| TSAR | 0.606** | 0.400** | 0.930** | 0.061 | 1.000** | |||||||
| BUR | 0.485** | 0.302** | 0.819** | 0.228** | 0.968** | 0.968** | ||||||
| EP | 0.837** | 1.000** | 0.521** | -0.181** | 0.400** | 0.400** | 0.302** | |||||
| CL | 0.798** | 0.445** | 0.858** | -0.323** | 0.766** | 0.766** | 0.665** | 0.445** | ||||
| LN | 0.872** | 0.574** | 0.871** | -0.328** | 0.766** | 0.766** | 0.658** | 0.574** | 0.988** | |||
| BN | 1.000** | 0.836** | 0.757** | -0.361** | 0.606** | 0.606** | 0.486** | 0.836** | 0.798** | 0.872** | ||
| ON | 0.281** | -0.124* | 0.615** | -0.162** | 0.621** | 0.621** | 0.581** | -0.124 | 0.800** | 0.707** | 0.282** | |
| TNCP | 0.941** | 0.746** | 0.855** | -0.315** | 0.735** | 0.735** | 0.620** | 0.746** | 0.928** | 0.973** | 0.941** | 0.543** |
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of indexes under salt-alkali stress
| Index | NR | NRT | LR | ADR | TPAR | TSAR | BUR | EP | CL | LN | BN | ON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRT | 0.837** | |||||||||||
| LR | 0.759** | 0.521** | ||||||||||
| ADR | -0.362** | -0.181** | -0.215** | |||||||||
| TPAR | 0.606** | 0.400** | 0.930** | 0.061 | ||||||||
| TSAR | 0.606** | 0.400** | 0.930** | 0.061 | 1.000** | |||||||
| BUR | 0.485** | 0.302** | 0.819** | 0.228** | 0.968** | 0.968** | ||||||
| EP | 0.837** | 1.000** | 0.521** | -0.181** | 0.400** | 0.400** | 0.302** | |||||
| CL | 0.798** | 0.445** | 0.858** | -0.323** | 0.766** | 0.766** | 0.665** | 0.445** | ||||
| LN | 0.872** | 0.574** | 0.871** | -0.328** | 0.766** | 0.766** | 0.658** | 0.574** | 0.988** | |||
| BN | 1.000** | 0.836** | 0.757** | -0.361** | 0.606** | 0.606** | 0.486** | 0.836** | 0.798** | 0.872** | ||
| ON | 0.281** | -0.124* | 0.615** | -0.162** | 0.621** | 0.621** | 0.581** | -0.124 | 0.800** | 0.707** | 0.282** | |
| TNCP | 0.941** | 0.746** | 0.855** | -0.315** | 0.735** | 0.735** | 0.620** | 0.746** | 0.928** | 0.973** | 0.941** | 0.543** |
| Index | Principal components | Total load | Rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| TNCP | 0.959 | 0.049 | -0.206 | -0.096 | 42.666 | 6 |
| LN | 0.957 | 0.040 | -0.015 | -0.213 | 44.003 | 4 |
| LR | 0.950 | 0.013 | 0.130 | 0.025 | 47.112 | 2 |
| CL | 0.929 | 0.033 | 0.113 | -0.282 | 43.698 | 5 |
| TSAR | 0.891 | -0.037 | 0.335 | 0.246 | 48.063 | 1 |
| TPAR | 0.891 | -0.037 | 0.335 | 0.246 | 48.063 | 1 |
| BN | 0.873 | 0.059 | -0.426 | -0.048 | 36.232 | 7 |
| BUR | 0.799 | -0.069 | 0.430 | 0.362 | 45.419 | 3 |
| ON | 0.616 | -0.071 | 0.605 | -0.405 | 33.728 | 8 |
| NR | -0.367 | 0.250 | -0.206 | 0.128 | -15.286 | 10 |
| GP | -0.053 | 0.937 | 0.124 | 0.021 | 13.437 | 13 |
| GI | -0.031 | 0.920 | 0.110 | 0.037 | 14.168 | 11 |
| GR | -0.012 | 0.855 | 0.070 | 0.042 | 13.600 | 12 |
| NRT | 0.644 | 0.058 | -0.700 | 0.275 | 24.383 | 9 |
| EP | 0.644 | 0.058 | -0.700 | 0.275 | 24.383 | 9 |
| ADR | -0.212 | -0.089 | 0.360 | 0.799 | -0.139 | 14 |
| Eigen values | 8.052 | 2.566 | 2.242 | 1.382 | ||
| Contribution rate (%) | 47.366 | 15.092 | 13.189 | 8.132 | ||
| Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 47.366 | 62.458 | 75.648 | 83.779 | ||
| Weight | 0.565 | 0.180 | 0.157 | 0.097 | ||
Table 3 The eigen values of 4 principal components and total load number of each index
| Index | Principal components | Total load | Rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| TNCP | 0.959 | 0.049 | -0.206 | -0.096 | 42.666 | 6 |
| LN | 0.957 | 0.040 | -0.015 | -0.213 | 44.003 | 4 |
| LR | 0.950 | 0.013 | 0.130 | 0.025 | 47.112 | 2 |
| CL | 0.929 | 0.033 | 0.113 | -0.282 | 43.698 | 5 |
| TSAR | 0.891 | -0.037 | 0.335 | 0.246 | 48.063 | 1 |
| TPAR | 0.891 | -0.037 | 0.335 | 0.246 | 48.063 | 1 |
| BN | 0.873 | 0.059 | -0.426 | -0.048 | 36.232 | 7 |
| BUR | 0.799 | -0.069 | 0.430 | 0.362 | 45.419 | 3 |
| ON | 0.616 | -0.071 | 0.605 | -0.405 | 33.728 | 8 |
| NR | -0.367 | 0.250 | -0.206 | 0.128 | -15.286 | 10 |
| GP | -0.053 | 0.937 | 0.124 | 0.021 | 13.437 | 13 |
| GI | -0.031 | 0.920 | 0.110 | 0.037 | 14.168 | 11 |
| GR | -0.012 | 0.855 | 0.070 | 0.042 | 13.600 | 12 |
| NRT | 0.644 | 0.058 | -0.700 | 0.275 | 24.383 | 9 |
| EP | 0.644 | 0.058 | -0.700 | 0.275 | 24.383 | 9 |
| ADR | -0.212 | -0.089 | 0.360 | 0.799 | -0.139 | 14 |
| Eigen values | 8.052 | 2.566 | 2.242 | 1.382 | ||
| Contribution rate (%) | 47.366 | 15.092 | 13.189 | 8.132 | ||
| Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 47.366 | 62.458 | 75.648 | 83.779 | ||
| Weight | 0.565 | 0.180 | 0.157 | 0.097 | ||
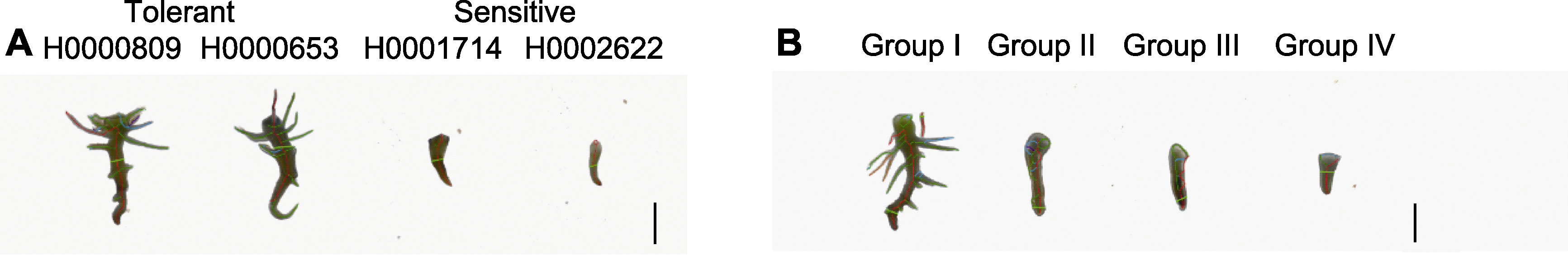
Figure 2 Root phenotype of extremely salt-alkali tolerant and sensitive germplasms (A) and germplasms with different levels of salt-alkali tolerance (B) in faba bean Group I, Group II, Group III, and Group IV showed the representative root phenotypes of salt-alkaline tolerant, moderately salt-alkaline tolerant, weakly salt-alkaline tolerant, and salt-alkaline sensitive faba bean germplasms, respectively. The red and green marking lines indicated the main root and the lateral roots, respectively. Bars=1 cm
| Salt-alkali tolerance | Salt-alkali tolerant faba bean | Salt-alkali sensitive faba bean | Salt-alkali tolerance | Salt-alkali tolerant faba bean | Salt-alkali sensitive faba bean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | H0000809 | H0000653 | H0002622 | H0001714 | Code | H0000809 | H0000653 | H0002622 | H0001714 |
| NR | 17.333 | 12.000 | 1.500 | 2.000 | CL | 18.000 | 12.667 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| NRT | 17.667 | 12.000 | 2.500 | 3.000 | LN | 35.333 | 24.667 | 2.000 | 3.000 |
| LR | 8.721 | 6.078 | 0.510 | 0.653 | BN | 16.000 | 11.000 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| ADR | 1.288 | 1.704 | 1.889 | 1.930 | ON | 2.000 | 1.667 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| TPAR | 136.722 | 127.020 | 9.324 | 11.882 | TNCP | 35.667 | 24.667 | 3.000 | 4.000 |
| TSAR | 429.524 | 399.046 | 29.291 | 37.329 | GP | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| BUR | 204.520 | 262.196 | 13.409 | 17.031 | GI | 5.538 | 7.964 | 0.000 | 0.143 |
| EP | 17.667 | 12.000 | 2.500 | 3.000 | GR | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.600 | 0.200 |
Table 4 Salt-alkali tolerance indexes of 4 materials with extremely tolerant level
| Salt-alkali tolerance | Salt-alkali tolerant faba bean | Salt-alkali sensitive faba bean | Salt-alkali tolerance | Salt-alkali tolerant faba bean | Salt-alkali sensitive faba bean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | H0000809 | H0000653 | H0002622 | H0001714 | Code | H0000809 | H0000653 | H0002622 | H0001714 |
| NR | 17.333 | 12.000 | 1.500 | 2.000 | CL | 18.000 | 12.667 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| NRT | 17.667 | 12.000 | 2.500 | 3.000 | LN | 35.333 | 24.667 | 2.000 | 3.000 |
| LR | 8.721 | 6.078 | 0.510 | 0.653 | BN | 16.000 | 11.000 | 0.500 | 1.000 |
| ADR | 1.288 | 1.704 | 1.889 | 1.930 | ON | 2.000 | 1.667 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| TPAR | 136.722 | 127.020 | 9.324 | 11.882 | TNCP | 35.667 | 24.667 | 3.000 | 4.000 |
| TSAR | 429.524 | 399.046 | 29.291 | 37.329 | GP | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| BUR | 204.520 | 262.196 | 13.409 | 17.031 | GI | 5.538 | 7.964 | 0.000 | 0.143 |
| EP | 17.667 | 12.000 | 2.500 | 3.000 | GR | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.600 | 0.200 |
| [1] | Abdel Latef AA, Hasanuzzaman M, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M (2021). Mitigation of salinity stress by exogenous application of cytokinin in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoca 49, 12192. |
| [2] | Ali A, Raddatz N, Pardo JM, Yun DJ (2021). HKT sodium and potassium transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana and related halophyte species. Physiol Plant 174, 546-558. |
| [3] | An YP, Qiang AL, Zhang YY, Zhang WY, Cao GL, Han LZ (2006). Study on characteristics of germination and drought- resistance index by osmotic stress in rice. J Plant Genet Resour 7, 421-426. (in Chinese) |
| 安永平, 强爱玲, 张媛媛, 张文银, 曹桂兰, 韩龙植 (2006). 渗透胁迫下水稻种子萌发特性及抗旱性鉴定指标研究. 植物遗传资源学报 7, 421-426. | |
| [4] | Ben Dkhil B, Denden M (2010). Salt stress induced changes in germination, sugars, starch and enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism in Abelmoschus esculentus L. (Moench.) seed. Afr J Agric Res 5, 1412-1418. |
| [5] |
Bimurzayev N, Sari H, Kurunc A, Doganay KH, Asmamaw M (2021). Effects of different salt sources and salinity levels on emergence and seedling growth of faba bean genotypes. Sci Rep 11, 18198.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Cai KX, Zhang WD, Cheng HT, Li XP, Zhai DP, Guo Y, Jiang XQ, Wu T (2020). Effects of salt stress on physiological changes of five Adzuki bean sprouts stage in northeast China. J Ningxia Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 41, 80-86. (in Chinese) |
| 蔡可心, 张卫东, 程海涛, 李修平, 翟登攀, 郭勇, 姜雪琪, 邬桐 (2020). 盐胁迫对东北5种红小豆芽期生理变化的影响. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版) 41, 80-86. | |
| [7] | Chen EY, Wang RF, Qin L, Yang YB, Li FF, Zhang HW, Wang HL, Liu B, Kong QH, Guan YA (2020). Comprehensive identification and evaluation of foxtail millet for saline-alkaline tolerance during germination. Acta Agron Sin 46, 1591-1604. (in Chinese) |
|
陈二影, 王润丰, 秦岭, 杨延兵, 黎飞飞, 张华文, 王海莲, 刘宾, 孔清华, 管延安 (2020). 谷子芽期耐盐碱综合鉴定及评价. 作物学报 46, 1591-1604.
DOI |
|
| [8] | Fan YC (2021). Screening of Salt Tolerant Germplasm Resources and Cloning and Expression Analysis of Salt Tolerant Genes in Vicia faba L. Master’s thesis. Xining: Qinghai University. pp. 1. (in Chinese) |
| 樊有存 (2021). 蚕豆耐盐种质资源筛选与抗盐基因的克隆及表达分析. 硕士论文. 西宁: 青海大学. pp. 1. | |
| [9] | Gao ZW (2011). Research on the Salt-alkali Resistance Mechanism of Alfalfa and Oat. PhD dissertation. Changchun: Northeast Normal University. pp. 4-5. (in Chinese) |
| 高占武 (2011). 紫花苜蓿和燕麦抗盐碱机制研究. 博士论文. 长春: 东北师范大学. pp. 4-5. | |
| [10] | Hao SL (2020). Identification and Salt Tolerance Analysis of F-box Genes in Vicia faba L. Master’s thesis. Jingzhou: Yangtze University. pp. 1. (in Chinese) |
| 郝树林 (2020). 蚕豆F-box基因的鉴定及耐盐性分析. 硕士论文. 荆州: 长江大学. pp. 1. | |
| [11] | Hu LL, Wang SH, Wang LX, Cheng XZ, Chen HL (2022). Identification of salt tolerance and screening of salt tolerant germplasm of mungbean (Vigna radiate L.) at seedling stage. Acta Agron Sin 48, 367-379. (in Chinese) |
|
胡亮亮, 王素华, 王丽侠, 程须珍, 陈红霖 (2022). 绿豆种质资源苗期耐盐性鉴定及耐盐种质筛选. 作物学报 48, 367-379.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Jiang XQ (2015). Study on Salt Tolerance of Red Adzuki Bean at Germination Stage. Master’s thesis. Jiamusi: Jiamusi University. pp. 18. (in Chinese) |
| 姜雪琪 (2015). 红小豆发芽期的耐盐性鉴定研究. 硕士论文. 佳木斯: 佳木斯大学. pp. 18. | |
| [13] | Jin HX, Guo DD, Yang QH, Yu XM, Fu XJ, Yuan FJ (2021). Comprehensive evaluation of salt tolerance in soybean germination period by fuzzy subordinate function method. Mol Plant Breed 19, 8265-8271. (in Chinese) |
| 金杭霞, 郭丹丹, 杨清华, 郁晓敏, 傅旭军, 袁凤杰 (2021). 利用模糊隶属函数法综合评价大豆萌发期耐盐性. 分子植物育种 19, 8265-8271. | |
| [14] | Lang BY, Wang WY, Feng RQ, Zhou ZH, Chen Y, Zhao YL, Jin F, Du YL (2024). Comprehensive evaluation on saline-alkali tolerance of 35 mung bean germplasm resources during germination period and analysis of saline-alkali tolerant mechanism. Shandong Agric Sci 56, 69-79. (in Chinese) |
| 郎炳尧, 王伟宇, 冯瑞琦, 周志衡, 陈悦, 赵岩林, 金峰, 杜艳丽 (2024). 35份绿豆种质资源萌发期耐盐碱性综合评价及耐盐碱机制分析. 山东农业科学 56, 69-79. | |
| [15] | Li XX (2022). Comprehensive Evaluation and Physiological Mechanism of Saline-alkali Tolerance of Wild Soybean. Master’s thesis. Qinhuangdao: Hebei Normal University of Science and Technology. pp. 8-25. (in Chinese) |
| 李祥祥 (2022). 野生大豆盐碱耐性综合评价及生理机制研究. 硕士论文. 秦皇岛: 河北科技师范学院. pp. 8-25. | |
| [16] | Liu SX, Lai JY, Li HM, Chen P, Ji YF, Zhang WH, Ma QB, Jia JT, Liu J (2023). Identification of salt tolerance of soybean landraces at germination stage in Guangdong. J Southern Agric 54, 3228-3238. (in Chinese) |
| 刘双幸, 赖剑云, 李红梅, 陈沛, 吉浴芳, 张文虎, 马启彬, 贾俊婷, 刘军 (2023). 广东省大豆农家种芽期耐盐性鉴定. 南方农业学报 54, 3228-3238. | |
| [17] | Liu W, Long ZX, Zhang XM, Gu WY, Chi XN, Wang YP (2024). The physiological mechanism by which exogenous salicylic acid enhances salt tolerance in Vicia faba seedlings. J Gansu Agric Univ 59(2), 36-44, 53. (in Chinese) |
| 刘伟, 龙子轩, 张兴民, 顾文媛, 池小娜, 王玉萍 (2024). 外源水杨酸影响蚕豆幼苗耐盐性的生理机制. 甘肃农业大学学报 59(2), 36-44, 53. | |
| [18] |
Liu XY, Guo XY, Wang XR, Xin DW, Guan RX, Qiu LJ (2024). Establishment of screening method for salt tolerance at germination stage and identification of salt-tolerant germplasms in soybean. Acta Agron Sin 50, 2122-2130. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
刘欣玥, 郭潇阳, 王欣茹, 辛大伟, 关荣霞, 邱丽娟 (2024). 大豆萌发期耐盐性鉴定方法建立及耐盐大豆资源筛选. 作物学报 50, 2122-2130.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Nachshon U (2018). Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: trends, processes and examples. Water 10, 1030. |
| [20] | Ren JH, Gao PP, Qiao YX, Jing SE (1993). Identification of salt tolerance of mung bean variety resources. Crop Variety Resour (3), 14-15. (in Chinese) |
| 任建华, 高平平, 乔燕祥, 荆淑娥 (1993). 绿豆品种资源耐盐性鉴定. 作物品种资源 (3), 14-15. | |
| [21] | Shi HY, Fan BJ, Liu CY, Wang Y, Wang S, Zhang ZX, Su QZ, Tian J (2024). Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance germplasm of mung bean during germination. Crops. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1808.S.20240401.0958.002. (in Chinese) |
| 时会影, 范保杰, 刘长友, 王彦, 王珅, 张志肖, 苏秋竹, 田静 (2024). 绿豆种质资源萌发期耐盐性鉴定与评价. 作物杂志. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1808.S.20240401.0958.002. | |
| [22] |
Shrivastava P, Kumar R (2015). Soil salinity: a serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J Biol Sci 22, 123-131.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Sun XF, Liu YL (2001). Test on criteria of evaluating salt tolerance of cotton cultivars. Acta Agron Sin 27, 794-801. (in Chinese) |
| 孙小芳, 刘友良 (2001). 棉花品种耐盐性鉴定指标可靠性的检验. 作物学报 27, 794-801. | |
| [24] | Wang G, Yang D, Zhang Y, Li Q, Ji J, Jin C, Wu GX, Guan CF (2020). Na+/H+ antiporter (NHX1) positively enhances cadmium (Cd) resistance and decreases Cd accumulation in tobacco plants cultivated in Cd-containing soil. Plant Soil 453, 389-408. |
| [25] | Wang LZ, Gao FJ, Hua FJ, Cao PP (2015). Study on salt tolerance of different mung bean varieties at germination stage. Shandong Agric Sci 47(9), 31-35. (in Chinese) |
| 王乐政, 高凤菊, 华方静, 曹鹏鹏 (2015). 不同绿豆品种萌发期耐盐性研究. 山东农业科学 47(9), 31-35. | |
| [26] | Wu JF, Yang BW, Xiang XC, Xu L, Yan LM (2017). Identification of salt tolerance in different rice germplasm at different growth stages. Chin Bull Bot 52, 77-88. (in Chinese) |
|
吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许亮, 颜李梅 (2017). 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异. 植物学报 52, 77-88.
DOI |
|
| [27] | Ya XX, Yang DX, Zhou GM, Chen J, Liu ZX (2022). Identification and evaluation of salt tolerance of pea resources. J Sichuan Agric Univ 40, 505-511. (in Chinese) |
| 亚秀秀, 杨东旭, 周桂梅, 陈健, 刘振兴 (2022). 豌豆种质资源耐盐性的鉴定与评价. 四川农业大学学报 40, 505-511. | |
| [28] | Yang FW (2020). Transcriptome Profile of Faba Bean During Seed Germination Under Salt Stress and Analysis of LEA Gene Family. Master’s thesis. Jingzhou: Yangtze University. pp. 14. (in Chinese) |
| 杨访问 (2020). 盐胁迫下蚕豆萌发期转录组及LEA基因家族分析. 硕士论文. 荆州: 长江大学. pp. 14. | |
| [29] | Yang J (2012). Molecular Cloning, Functional Analysis and Genetic Transformation of a Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene GmNHX1 from Soybean. Master’s thesis. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei. pp. 1. (in Chinese) |
| 杨郡 (2012). 大豆GmNHX1基因的克隆、功能初探及遗传转化. 硕士论文. 保定: 河北农业大学. pp. 1. | |
| [30] | Yin GX, Zhang L, She MY (2015). Structural characterization and abiotic stress response of soybean TRK-HKT family genes. Acta Agron Sin 41, 259-275. (in Chinese) |
|
殷桂香, 张磊, 佘茂云 (2015). 大豆TRK-HKT家族基因结构及逆境胁迫响应机制. 作物学报 41, 259-275.
DOI |
|
| [31] | Yu S, Guo XX, Liang HY, Fu LH, Shi JJ, Zhang YF, Chuang L (2017). Analysis of saline-alkaline tolerance and screening of identification indicators at the germination stage among different mung bean genotypes. Plant Physiol J 53, 1629-1639. (in Chinese) |
| 于崧, 郭潇潇, 梁海芸, 付鸾鸿, 史京京, 张翼飞, 闯磊 (2017). 不同基因型绿豆萌发期耐盐碱性分析及其鉴定指标的筛选. 植物生理学报 53, 1629-1639. | |
| [32] | Zhang DF, Fan GH, Ma YL (2016). Study on the type of saline-alkaline land and saltion correlation of Qaidam Basin. Sci Technol Qinghai Agric For (3), 1-6. (in Chinese) |
| 张得芳, 樊光辉, 马玉林 (2016). 柴达木盆地盐碱土壤类型及其盐离子相关性研究. 青海农林科技 (3), 1-6. | |
| [33] | Zhang XC, Xue XX, Jiang S, Wang YF, Cao YC (2020). Identification of mixed saline-alkali tolerance and screening of indicators in soybean at germination stage. Acta Agric Boreali-Occident Sin 29, 374-381. (in Chinese) |
| 张新草, 薛项潇, 姜深, 王延峰, 曹永策 (2020). 大豆种质发芽期耐盐碱性鉴定及指标筛选. 西北农业学报 29, 374-381. | |
| [34] | Zhou XW, Zhang XR, Sun HX, Zhao X, Zhang N, Yao XD, Xie FT (2022). Evaluation of salt tolerance of soybean germplasms at germination and seedling Stages. J Shenyang Agric Univ 53, 257-264. (in Chinese) |
| 周秀文, 张晓蕊, 孙贺祥, 赵翔, 张娜, 姚兴东, 谢甫绨 (2022). 大豆种质萌发期和苗期耐盐性评价. 沈阳农业大学学报 53, 257-264. | |
| [35] | Zhu ZH, Wang MZ, Song JZ (1989). Identification of salt tolerance of pea variety resources. Crop Variety Resour (4), 29-30. (in Chinese) |
| 朱志华, 王明珍, 宋景芝 (1989). 豌豆品种资源耐盐性鉴定. 作物品种资源 (4), 29-30. | |
| [36] | Zhu ZH, Wang MZ, Song JZ, Zhang XF (1990). Preliminary report on salt tolerance identification of broad bean and cowpea varieties. Crop Variety Resour (4), 29-30. (in Chinese) |
| 朱志华, 王明珍, 宋景芝, 张晓芳 (1990). 蚕豆和豇豆品种耐盐性鉴定初报. 作物品种资源 (4), 29-30. | |
| [37] | Zong XX, Bao SY, Guan JP (2006). Descriptors and Data Standard for Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). Beijing: China Agriculture Press. pp. 56. (in Chinese) |
| 宗绪晓, 包世英, 关建平 (2006). 蚕豆种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 56. |
| [1] | ZHANG Kun, QIAN Min, WANG Yang, LI Zhi-Hua, KONG Ling-Na, LI Ming-Yang, MA Jin-Yu, YUSUPU Nueraihemaiti, CHEN Yi-Yi, CHENG Yi-Rui, ZHANG Huan-Shi, QIN Feng-Fei, QU Hui. Comprehensive evaluation of shade tolerance of alfalfa and screening of identification indexes [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 773-787. |
| [2] | Feng Zhang, Richard Dormatey, Yindu Liu, Chengju Li, Yunjiao Wang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Zhenzhen Bi, Yuhui Liu, Jiangping Bai, Chao Sun. Screening and Evaluation of Phosphite-tolerant Potatoes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [3] | Yindu Liu, Junkang Tuo, Chengju Li, Feng Zhang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Yunjiao Wang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Chao Sun, Yuhui Liu, Zhen Liu, Zhenzhen Bi, Jiangping Bai. Screening and Evaluation of Low-potassium Tolerance Potato Varieties [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 75-88. |
| [4] | Guo Shuya, Ai Jinxiang, Chen Hongyu, Shao Yeyao, Wang Yan, Wang Qian, Ye Yitong, Zhang Yating, Ding Zhexiao, Wu Haochen, Wu Yuhuan, Zhang Jianxin, Rao Mide, Liu Peng. Establishment of a Comprehensive Evaluation System for Aluminum Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings Based on Principal Component Analysis-Clustering Analysis-Stepwise Regression Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 479-489. |
| [5] | Xun Liu,Jiao Zhang,Yuchen Shen,Debin Xie,Hongli Li,Chunming Li,Xiaoping Yi,Yong Zhao,Daobin Tang,Changwen Lü,Jichun Wang. [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 360-370. |
| [6] | Zhangjian Shan,Lina Zhao,Yuchang Yang,Dan Xie,Haining Qin. An overview on assessment systems for threatened plants in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1352-1363. |
| [7] | LIU Cheng-Gang, XUE Jian-Hui. Basic soil properties and comprehensive evaluation in different plantations in rocky desertification sites of the karst region of Guizhou Province, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2011, 35(10): 1050-1060. |
| [8] | Siqingaowa Bao;Zhanxin Ma*. Correlation Between Crop Seed Growth and Electric Field Condition [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2010, 45(03): 384-391. |
| [9] | LIU Chu-Guang, LU Jun, Yu Yu-Qun, WANG Wei, JI Ming-Zhou, GUO Song-Tao. A comprehensive evaluation on management of three international hunting grounds for argali in Gansu [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2000, 08(4): 441-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||