

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 12-23.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21159 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21159
• INVITED REVIEWS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lei Qin1,2, Zhihong Peng2, Shitou Xia1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-14
Accepted:2022-02-07
Online:2022-01-01
Published:2022-02-07
Contact:
Shitou Xia
Lei Qin, Zhihong Peng, Shitou Xia. Recognition, Immune Activation and Signal Regulation of Plant NLR Immune Receptor[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 12-23.
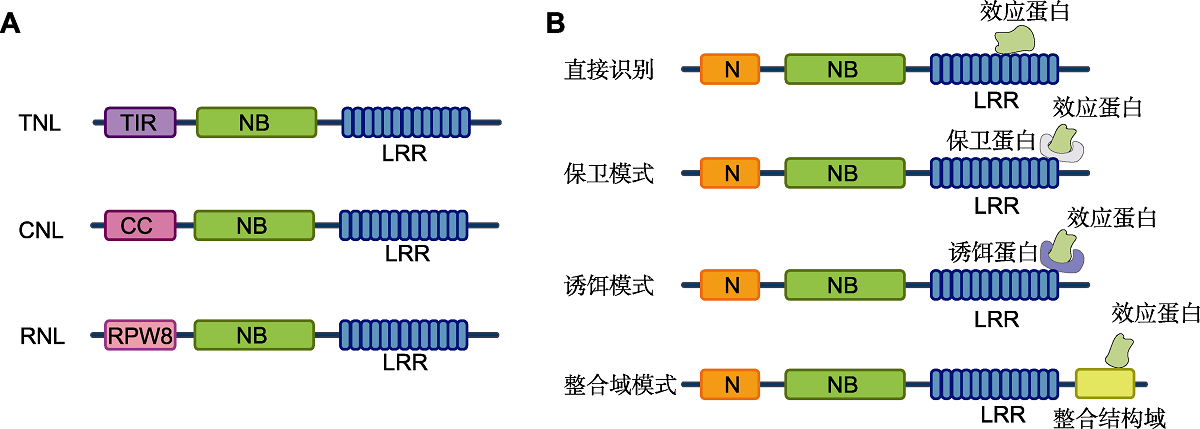
Figure 1 Structural composition of NLRs and its recognition pattern to effector proteins (modified from Duxbury et al., 2021) (A) The domains of plant NLRs are divided into three categories, including a central nucleotide-binding (NB) domain, a C-terminal leucine-rich repeats (LRR) region and N-terminal TIR, CC, or RPW8-like CC domain; (B) Different patterns of effector recognition by plant NLRs: Some plant NLRs directly bind to the corresponding effector proteins or indirectly detect the pathogen effector through the guardee or decoy proteins; Some plant NLRs have special integrated domains (ID) to mediate effector recognition.
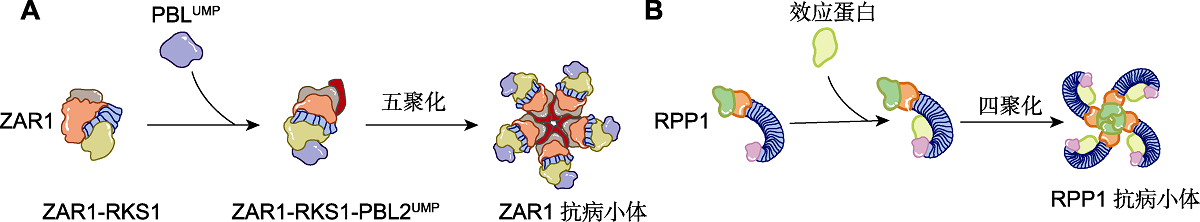
Figure 2 Activation modes of two NLRs (modified from Duxbury et al., 2021) (A) Schematic diagram of CNL (ZAR1) resistosome formation. The Xanthomonas effector AvrAC uridylates the Arabidopsis thaliana kinase PBL2. Uridylated PBL2 (PBL2UMP) associates with the intracellular pre-formed ZAR1-RKS1 dimer. This leads to a conformational change of ZAR1 and replacement of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by adenosine triphosphate or deoxyadenosine triphosphate ((d)ATP) in the nucleotide-binding site of the NBD of ZAR1. Ultimately, this results in the formation of a pentameric wheel-like ZAR1 resistosome, which is composed of five ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMPprotomers. (B) Schematic diagram of TNL (RPP1) resistosome formation. Direct recognition of a pathogen avirulence effector by the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) and carboxy-terminal domains (C-JID) of a canonical Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing intracellular nucleotide- binding domain (NBD)-like receptor (TIR-type NLR) leads to the formation of a tetrameric structure with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase (NADase) activity.
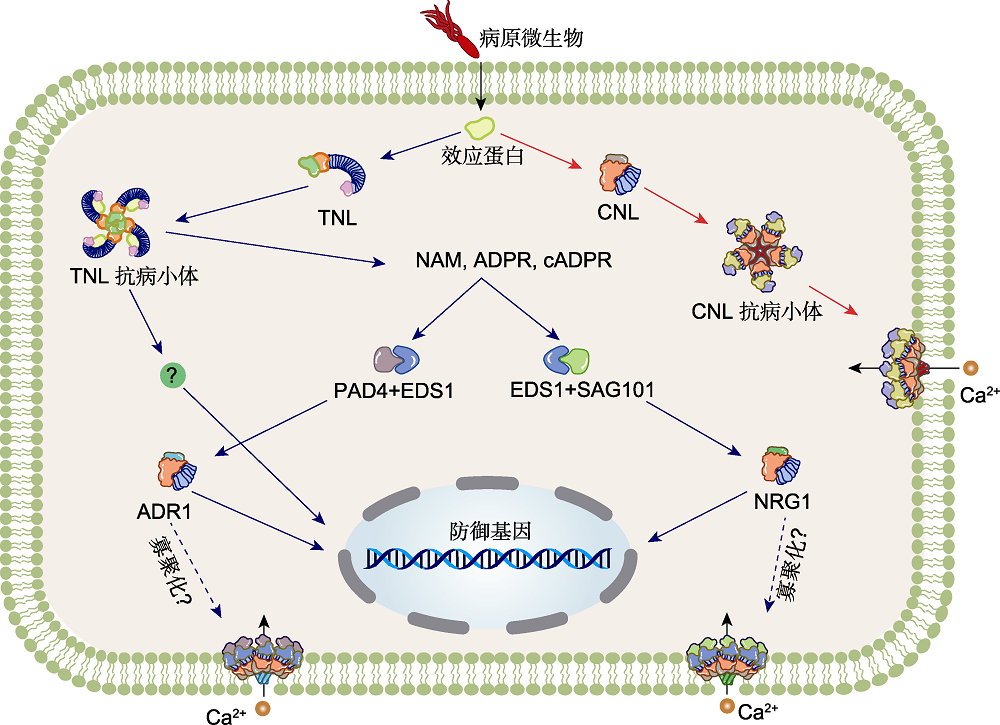
Figure 3 Working models of activation of NLRs-mediated immunity in higher plants (modified from Liu et al., 2021) Upon an infection of a plant cell by a pathogen, some pathogens can secrete effectors to break through the immune defense line of plants. In the process of long-term evolution, plants have evolved many intracellular receptors to recognize these effectors, so as to promote resistance to pathogens. CNLs triggers pentamerization and resistosome formation on the plasma membrane (PM) through sensing effector (The example here depicts a ZAR1 resistosome which indirect recognition effector assembly). The pore formed by the N-terminal CC α1 helices serves as a Ca2+ influx channel, mediating increase of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and turning on cell death and defense responses. TNLs, upon perception of effectors (the model here depicts an example of direct effector-receptor recognition as with RPP1), formation of the TNL resistosome leads to activation of TIR NADase activity, triggering assembly of oligomeric complexes presumably containing EDS1-PAD4-ADR1s or EDS1-SAG101-NRG1s. The oligomerization of the helper NLRs enables a similar pore formation as CNLs, serving as Ca2+ influx channels to mediate downstream immunity and cell death.The red arrows indicate CNL signal, and the blue arrows indicate TNL and RNL signals.
| [1] | 王伟, 唐定中 (2021). 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线. 植物学报 56, 142-146. |
| [2] |
夏石头, 李昕 (2019). 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体. 植物学报 54, 288-292.
DOI |
| [3] |
Ade J, DeYoung BJ, Golstein C, Innes RW (2007). Indirect activation of a plant nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein by a bacterial protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 2531-2536.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Axtell MJ, Staskawicz BJ (2003). Initiation of RPS2-specified disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112, 369-377.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bai SW, Liu J, Chang C, Zhang L, Maekawa T, Wang QY, Xiao WK, Liu YL, Chai JJ, Takken FLW, Schulze-Lefert P, Shen QH (2012). Structure-function analysis of barley NLR immune receptor MLA10 reveals its cell compartment specific activity in cell death and disease resistance. PLoS Pathog 8, e1002752.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bailey PC, Schudoma C, Jackson W, Baggs E, Dagdas G, Haerty W, Moscou M, Krasileva KV (2018). Dominant integration locus drives continuous diversification of plant immune receptors with exogenous domain fusions. Genome Biol 19, 23.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Bartsch M, Gobbato E, Bednarek P, Debey S, Schultze JL, Bautor J, Parker JE (2006). Salicylic acid-independent ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY 1 signaling in Arabidopsis immunity and cell death is regulated by the monooxygenase FMO1 and the Nudix hydrolase NUDT7. Plant Cell 18, 1038-1051.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Bhandari DD, Lapin D, Kracher B, Von Born P, Bautor J, Niefind K, Parker JE (2019). An EDS1 heterodimer signaling surface enforces timely reprogramming of immunity genes in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 10, 772.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Bi GZ, Su M, Li N, Liang Y, Dang S, Xu JC, Hu MJ, Wang JZ, Zou MX, Deng YN, Li QY, Huang SJ, Li JJ, Chai JJ, He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021). The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184, 3528-3541.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bonardi V, Tang SJ, Stallmann A, Roberts M, Cherkis K, Dangl JL (2011). Expanded functions for a family of plant intracellular immune receptors beyond specific recognition of pathogen effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 16463-16468.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Castel B, Ngou PM, Cevik V, Redkar A, Kim DS, Yang Y, Ding P, Jones JDG (2019). Diverse NLR immune receptors activate defence via the RPW8-NLR NRG1. New Phytol 222, 966-980.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Césari S, Kanzaki H, Fujiwara T, Bernoux M, Chalvon V, Kawano Y, Shimamoto K, Dodds P, Terauchi R, Kroj T (2014). The NB-LRR proteins RGA4 and RGA5 interact functionally and physically to confer disease resistance. EMBO J 33, 1941-1959.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Chiang YH, Coaker G (2014). Effector triggered immunity: NLR immune perception and downstream defense responses. The Arabidopsis Book 12, e0183. |
| [14] |
Choi S, Prokchorchik M, Lee H, Gupta R, Lee Y, Chung EH, Cho B, Kim MS, Kim ST, Sohn KH (2021). Direct acetylation of a conserved threonine of RIN4 by the bac-terial effector HopZ5 or AvrBsT activates RPM1-dependent immunity in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14, 1051-1960.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Chung EH, Da Cunha L, Wu AJ, Gao ZY, Cherkis K, Afzal AJ, Mackey D, Dangl JL (2011). Specific threonine phosphorylation of a host target by two unrelated type III effectors activates a host innate immune receptor in plants. Cell Host Microbe 9, 125-136.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Couto D, Zipfel C (2016). Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling in plants. Nat Rev Immunol 16, 537-552.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Cui HT, Tsuda K, Parker JE (2015). Effector-triggered im-munity: from pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 487-511.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001). Plant pathogens and integ-rated defence responses to infection. Nature 411, 826-833.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Davis BK, Wen HT, Ting JPY (2011). The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases. Annu Rev Immunol 29, 707-735.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
De La Concepcion JC, Franceschetti M, MacLean D, Terauchi R, Kamoun S, Banfield MJ (2019). Protein engineering expands the effector recognition profile of a rice NLR immune receptor. eLife 8, e47713.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ding PT, Ngou BPM, Furzer OJ, Sakai T, Shrestha RK, MacLean D, Jones JDG (2020). High-resolution expres-sion profiling of selected gene sets during plant immune activation. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 1610-1619.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Dodds PN, Lawrence GJ, Catanzariti AM, Teh T, Wang CIA, Ayliffe MA, Kobe B, Ellis JG (2006). Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevo-lution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 8888-8893.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Dodds PN, Rathjen JP (2010). Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet 11, 539-548. |
| [24] |
Dong OX, Tong MMZ, Bonardi V, El Kasmi F, Woloshen V, Wünsch LK, Dangl JL, Li X (2016). TNL-mediated immunity in Arabidopsis requires complex regulation of the redundant ADR1 gene family. New Phytol 210, 960-973.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Duxbury Z, Wu CH, Ding PT (2021). A comparative over-view of the intracellular guardians of plants and animals: NLRs in innate immunity and beyond. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 155-184.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Essuman K, Summers DW, Sasaki Y, Mao XR, DiAntonio A, Milbrandt J (2017). The SARM1 Toll/interleukin-1 re-ceptor domain possesses intrinsic NAD+cleavage activity that promotes pathological axonal degeneration. Neuron 93, 1334-1343.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Feng F, Yang F, Rong W, Wu XG, Zhang J, Chen S, He CZ, Zhou JM (2012). A Xanthomonas uridine 5'-monophosphate transferase inhibits plant immune kinases. Na-ture 485, 114-118. |
| [28] |
Gantner J, Ordon J, Kretschmer C, Guerois R, Stuttmann J (2019). An EDS1-SAG101 complex is essential for TNL-mediated immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 31, 2456-2474.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Gao ZY, Chung EH, Eitas TK, Dangl JL (2011). Plant intracellular innate immune receptor resistance to Pseudo-monas syringae pv. maculicola 1 (RPM1) is activated at, and functions on, the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 7619-7624.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Hu M, Qi J, Bi G, Zhou JM (2020). Bacterial effectors in-duce oligomerization of immune receptor ZAR1 in vivo. Mol Plant 13, 793-801.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Jacob F, Kracher B, Mine A, Seyfferth C, Blanvillain- Baufumé S, Parker JE, Tsuda K, Schulze-Lefert P, Maekawa T (2018). A dominant-interfering camta3 muta-tion compromises primary transcriptional outputs mediated by both cell surface and intracellular immune recep-tors in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 217, 1667-1680.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Jacob P, Kim NH, Wu F, El-Kasmi F, Chi Y, Walton WG, Furzer OJ, Lietzan AD, Sunil S, Kempthorn K, Redinbo MR, Pei ZM, Wan L, Dangl JL (2021). Plant ‘helper' im-mune receptors are Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channels. Science 373, 420-425.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Jones JDG, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016). Intracellular in-nate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354, aaf6395. |
| [34] |
Jubic LM, Saile S, Furzer OJ, El Kasmi F, Dangl JL (2019). Help wanted: helper NLRs and plant immune re-sponses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 82-94.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Kourelis J, Van Der Hoorn RAL (2018). Defended to the nines: 25 years of resistance gene cloning identifies nine mechanisms for R protein function. Plant Cell 30, 285-299.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Laflamme B, Dillon MM, Martel A, Almeida RND, Des-veaux D, Guttman DS (2020). The pan-genome effec-tor-triggered immunity landscape of a host-pathogen in-teraction. Science 367, 763-768.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Lapin D, Kovacova V, Sun XH, Dongus JA, Bhandari D, Von Born P, Bautor J, Guarneri N, Rzemieniewski J, Stuttmann J, Beyer A, Parker JE (2019). A coevolved EDS1-SAG101-NRG1 module mediates cell death sig-naling by TIR-domain immune receptors. Plant Cell 31, 2430-2455.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Le Roux C, Huet G, Jauneau A, Camborde L, Trémousaygue D, Kraut A, Zhou BB, Levaillant M, Adachi H, Yoshioka H, Raffaele S, Berthomé R, Couté Y, Parker JE, Deslandes L (2015). A receptor pair with an integrated decoy converts pathogen disabling of transcription factors to immunity. Cell 161, 1074-1088.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Lewis JD, Lee AH, Hassan JA, Wan J, Hurley B, Jhingree JR, Wang PW, Lo T, Youn JY, Guttman DS, Desveaux D (2013). The Arabidopsis ZED1 pseudokinase is required for ZAR1-mediated immunity induced by the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopZ1a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 18722-18727.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Liu J, Elmore JM, Lin ZJD, Coaker G (2011). A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase phosphorylates the host target RIN4, leading to the activation of a plant innate immune receptor. Cell Host Microbe 9, 137-146.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Liu Y, Zeng Z, Zhang YM, Li Q, Jiang XM, Jiang Z, Tang JH, Chen DJ, Wang Q, Chen JQ, Shao ZQ (2021). An angiosperm NLR Atlas reveals that NLR gene reduction is associated with ecological specialization and signal transduction component deletion. Mol Plant 14, 2015-2031.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Ma S, Lapin D, Liu L, Sun Y, Song W, Zhang XX, Logemann E, Yu DL, Wang J, Jirschitzka J, Han ZF, Schulze-Lefert P, Parker JE, Chai JJ (2020). Direct pathogen-induced assembly of an NLR immune receptor complex to form a holoenzyme. Science 370, eabe3069.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Mackey D, Belkhadir Y, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Dangl JL (2003). Arabidopsis RIN4 is a target of the type III virulence effector AvrRpt2 and modulates RPS2-mediated resistance. Cell 112, 379-389.
PMID |
| [44] |
Martin R, Qi TC, Zhang HB, Liu FR, King M, Toth C, Nogales E, Staskawicz BJ (2020). Structure of the activated ROQ1 resistosome directly recognizing the pathogen effector XopQ. Science 370, eabd9993.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Mine A, Seyfferth C, Kracher B, Berens ML, Becker D, Tsuda K (2018). The defense phytohormone signaling network enables rapid, high-amplitude transcriptional reprogramming during effector-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 30, 1199-1219.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Ngou BPM, Ahn HK, Ding PT, Jones JDG (2021). Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 592, 110-115. |
| [47] |
Nimchuk Z, Marois E, Kjemtrup S, Leister RT, Katagiri F, Dangl JL (2000). Eukaryotic fatty acylation drives plasma membrane targeting and enhances function of several type III effector proteins from Pseudomonas syringae. Cell 101, 353-363.
PMID |
| [48] |
Ofir G, Herbst E, Baroz M, Cohen D, Millman A, Doron S, Tal N, Malheiro DBA, Malitsky S, Amitai G, Sorek R (2021). Antiviral activity of bacterial TIR domains via sig-naling molecules that trigger cell death. Nature 600, 116-120.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Peart JR, Mestre P, Lu R, Malcuit I, Baulcombe DC (2005). NRG1, a CC-NB-LRR protein, together with N, a TIR-NB-LRR protein, mediates resistance against tobacco mosaic virus. Curr Biol 15, 968-973.
PMID |
| [50] | Qi TC, Seong K, Thomazella DPT, Kim JR, Pham J, Seo E, Cho MJ, Schultink A, Staskawicz BJ (2018). NRG1 functions downstream of EDS1 to regulate TIR-NLR-mediated plant immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E10979-E10987. |
| [51] |
Rayamajhi M, Zak DE, Chavarria-Smith J, Vance RE, Miao EA (2013). Cutting edge: mouse NAIP1 detects the type III secretion system needle protein. J Immunol 191, 3986-3989.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Redditt TJ, Chung EH, Karimi HZ, Rodibaugh N, Zhang YX, Trinidad JC, Kim JH, Zhou Q, Shen MZ, Dangl JL, Mackey D, Innes RW (2019). AvrRpm1 functions as an ADP-ribosyltransferase to modify NOI domain-containing proteins, including Arabidopsis and soybean RPM1-interacting protein 4. Plant Cell 31, 2664-2681.
DOI |
| [53] |
Rufián JS, Rueda-Blanco J, López-Márquez D, Macho AP, Beuzón CR, Ruiz-Albert J (2021). The bacterial ef-fector HopZ1a acetylates MKK7 to suppress plant immu-nity. New Phytol 231, 1138-1156.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Saile SC, Jacob P, Castel B, Jubic LM, Salas-Gonzáles I, Bäcker M, Jones JDG, Dangl JL, El Kasmi F (2020). Two unequally redundant ‘helper' immune receptor fami-lies mediate Arabidopsis thaliana intracellular 'sensor' immune receptor functions. PLoS Biol 18, e3000783.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Sarris PF, Duxbury Z, Huh SU, Ma Y, Segonzac C, Skle-nar J, Derbyshire P, Cevik V, Rallapalli G, Saucet SB, Wirthmueller L, Menke FLH, Sohn KH, Jones JDG (2015). A plant immune receptor detects pathogen effec-tors that target WRKY transcription factors. Cell 161, 1089-1100.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Saur IM, Bauer S, Kracher B, Lu XL, Franzeskakis L, Müller MC, Sabelleck B, Kümmel F, Panstruga R, Maekawa T, Schulze-Lefert P (2019). Multiple pairs of allelic MLA immune receptor-powdery mildew AVRA ef-fectors argue for a direct recognition mechanism. eLife 8, e44471.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Saur IML, Panstruga R, Schulze-Lefert P (2021). NOD-like receptor-mediated plant immunity: from structure to cell death. Nat Rev Immunol 21, 305-318. |
| [58] |
Schultink A, Qi TC, Bally J, Staskawicz B (2019). Using forward genetics in Nicotiana benthamiana to uncover the immune signaling pathway mediating recognition of the Xanthomonas perforans effector XopJ4. New Phytol 221, 1001-1009.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Seto D, Koulena N, Lo T, Menna A, Guttman DS, Des-veaux D (2017). Expanded type III effector recognition by the ZAR1 NLR protein using ZED1-related kinases. Nat Plants 3, 17027.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Shao F, Golstein C, Ade J, Stoutemyer M, Dixon JE, Innes RW (2003). Cleavage of Arabidopsis PBS1 by a bacterial type III effector. Science 301, 1230-1233.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Shen QH, Saijo Y, Mauch S, Biskup C, Bieri S, Keller B, Seki H, Ülker B, Somssich IE, Schulze-Lefert P (2007). Nuclear activity of MLA immune receptors links isolate- specific and basal disease-resistance responses. Science 315, 1098-1103.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Sun XH, Lapin D, Feehan JM, Stolze SC, Kramer K, Dongus JA, Rzemieniewski J, Blanvillain-Baufumé S, Harzen A, Bautor J, Derbyshire P, Menke FLH, Finkemeier I, Nakagami H, Jones JDG, Parker JE (2021). Pathogen effector recognition-dependent association of NRG1 with EDS1 and SAG101 in TNL receptor immunity. Nat Commun 12, 3335.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Tamborski J, Krasileva KV (2020). Evolution of plant NLRs: from natural history to precise modifications. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71, 355-378.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Thor K, Jiang SS, Michard E, George J, Scherzer S, Huang SG, Dindas J, Derbyshire P, Leitão N, DeFalco TA, Köster P, Hunter K, Kimura S, Gronnier J, Stransfeld L, Kadota Y, Bücherl CA, Charpentier M, Wrzaczek M, MacLean D, Oldroyd GED, Menke FLH, Roelfsema MRG, Hedrich R, Feijó J, Zipfel C (2020). The calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.3 regulates plant stomatal immunity. Nature 585, 569-573.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Tian W, Hou CC, Ren ZJ, Wang C, Zhao FG, Dahlbeck D, Hu SP, Zhang LY, Niu Q, Li LG, Staskawicz BJ, Luan S (2019). A calmodulin-gated calcium channel links patho-gen patterns to plant immunity. Nature 572, 131-135.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Urbach JM, Ausubel FM (2017). The NBS-LRR architect-tures of plant R-proteins and metazoan NLRs evolved in independent events. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 1063-1068.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Van De Weyer AL, Monteiro F, Furzer OJ, Nishimura MT, Cevik V, Witek K, Jones JDG, Dangl JL, Weigel D, Bemm F (2019). A species-wide inventory of NLR genes and alleles in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 178, 1260-1272.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Van Der Burgh AM, Joosten MHAJ (2019). Plant immunity: thinking outside and inside the box. Trends Plant Sci 24, 587-601.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Van Der Hoorn RAL, Kamoun S (2008). From guard to decoy: a new model for perception of plant pathogen effectors. Plant Cell 20, 2009-2017.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Wan L, Essuman K, Anderson RG, Sasaki Y, Monteiro F, Chung EH, Nishimura EO, DiAntonio A, Milbrandt J, Dangl JL, Nishimura MT (2019). TIR domains of plant immune receptors are NAD+-cleaving enzymes that pro-mote cell death. Science 365, 799-803.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Wang GX, Roux B, Feng F, Guy E, Li L, Li NN, Zhang XJ, Lautier M, Jardinaud MF, Chabannes M, Arlat M, Chen S, He CZ, Noël LD, Zhou JM (2015). The decoy substrate of a pathogen effector and a pseudokinase specify pathogen-induced modified-self recognition and immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 18, 285-295.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Wang JZ, Hu MJ, Wang J, Qi JF, Han ZF, Wang GX, Qi YJ, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019). Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring im-munity. Science 364, eaav5870.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Wu ZS, Li M, Dong OX, Xia ST, Liang WW, Bao YK, Wasteneys G, Li X (2019). Differential regulation of TNL-mediated immune signaling by redundant helper CNLs. New Phytol 222, 938-953.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Wu ZS, Tian L, Liu XR, Zhang YL, Li X (2021). TIR signal promotes interactions between lipase-like proteins and ADR1-L1 receptor and ADR1-L1 oligomerization. Plant Physiol 187, 681-686.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Xia BQ, Fang S, Chen XQ, Hu H, Chen PY, Wang HY, Gao ZB (2016). MLKL forms cation channels. Cell Res 26, 517-528.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Xia ST, Liu XR, Zhang YL (2021). Calcium channels at the center of NLR-mediated plant immunity. J Genet Genomics 48, 429-432.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Yin JL, Wang LQ, Jin TT, Nie Y, Liu H, Qiu YL, Yang YH, Li BW, Zhang JJ, Wang DG, Li K, Xu K, Zhi HJ (2021). A cell wall-localized NLR confers resistance to Soybean mosaic virus by recognizing viral-encoded cylindrical in-clusion protein. Mol Plant 14, 1881-1990.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Yoshioka K, Moeder W, Kang HG, Kachroo P, Masmoudi K, Berkowitz G, Klessig DF (2006). The chimeric Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHANNEL11/12 activates multiple pathogen resistance responses. Plant Cell 18, 747-763.
PMID |
| [79] | Yuan MH, Jiang ZY, Bi GZ, Nomura K, Liu MH, Wang YP, Cai BY, Zhou JM, He SY, Xin XF (2021). Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 592, 105-109. |
| [80] |
Zhang J, Li W, Xiang TT, Liu ZX, Laluk K, Ding XJ, Zou Y, Gao MH, Zhang XJ, Chen S, Mengiste T, Zhang YL, Zhou JM (2010). Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell Host Microbe 7, 290-301.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Zhao CH, Tang YH, Wang JL, Zeng YH, Sun HQ, Zheng ZC, Su R, Schneeberger K, Parker JE, Cui HT (2021). A mis-regulated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel mediates cytosolic calcium elevation and activates immunity in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 230, 1078-1094.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2008). Plant pathogenic bacterial type III effectors subdue host responses. Curr Opin Microbiol 11, 179-185.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Zhou JM, Zhang YL (2020). Plant immunity: danger perception and signaling. Cell 181, 978-989.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Jian-Min Zhou. A Ca2+-ROS Signaling Axis in Rice Provides Clues to Rice-pathogen Coevolution and Crop Improvements [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [2] | Wei Wang, Dingzhong Tang. Synergistic Cooperation Between Cell Surface and Intracellular Immune Receptors Potentiates to Activate Robust Plant Defense [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [3] | Chenghuizi Yang,Xianyu Tang,Wei Li,Shitou Xia. NLR and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [4] | Yaning Cui, Hongping Qian, Yanxia Zhao, Xiaojuan Li. Intracellular Trafficking in Pattern Recognition Receptor-triggered Plant Immunity [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [5] | Weitao Li, Min He, Xuewei Chen. Discovery of ZmFBL41 Chang7-2 as A Key Weapon against Banded Leaf and Sheath Blight Resistance in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [6] | Shitou Xia, Xin Li. Open a Door of Defenses: Plant Resistosome [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||