

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 245-154.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18115 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18115
Special Issue: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yajing Wang,Xinying Zhang,Guirong Huang,Xiaoying Liu,Rui Guo,Fengxue Gu,Xiuli Zhong( ),Xurong Mei(
),Xurong Mei( )
)
Received:2018-05-07
Accepted:2018-08-23
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Xiuli Zhong,Xurong Mei
Yajing Wang,Xinying Zhang,Guirong Huang,Xiaoying Liu,Rui Guo,Fengxue Gu,Xiuli Zhong,Xurong Mei. Characteristics of Phosphatidic Acid and the Underlying Mechanisms of ABA-induced Stomatal Movement in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 245-154.
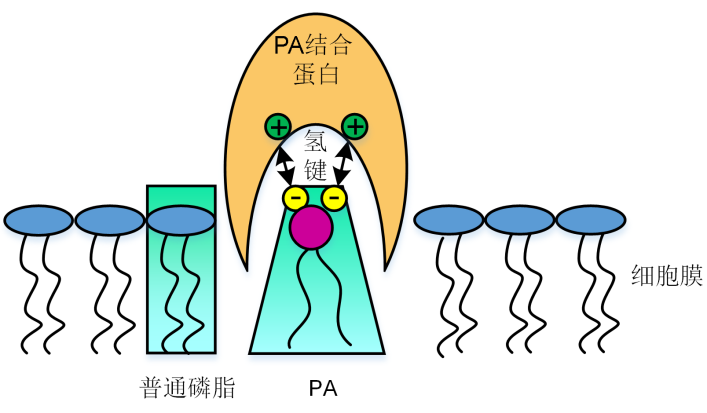
Figure 1 Proposed model for interaction between phosphatidic acid (PA) and proteins The electrostatic and hydrogen bonding switch facilitates PA interaction with basic amino acid residues on PA-binding pro- teins.
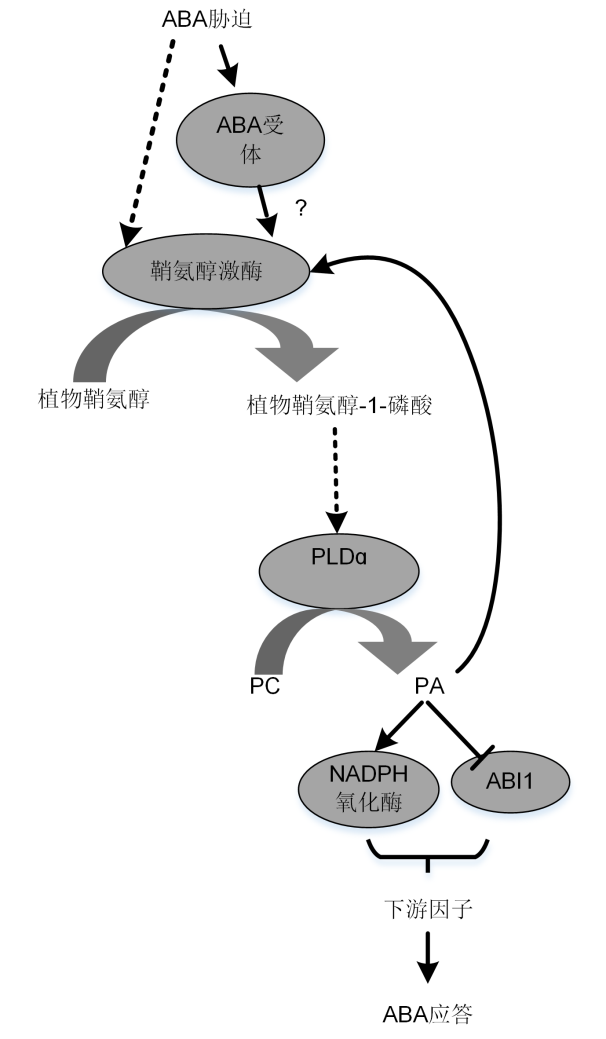
Figure 2 Roles of SPHK/phyto-S1P and PLDɑ1/PA in ABA-induced stomatal closure signaling pathway (Guo et al., 2011)Arrows represent activation, bars mean inhibition, and dotted lines represent unknown mechanisms.
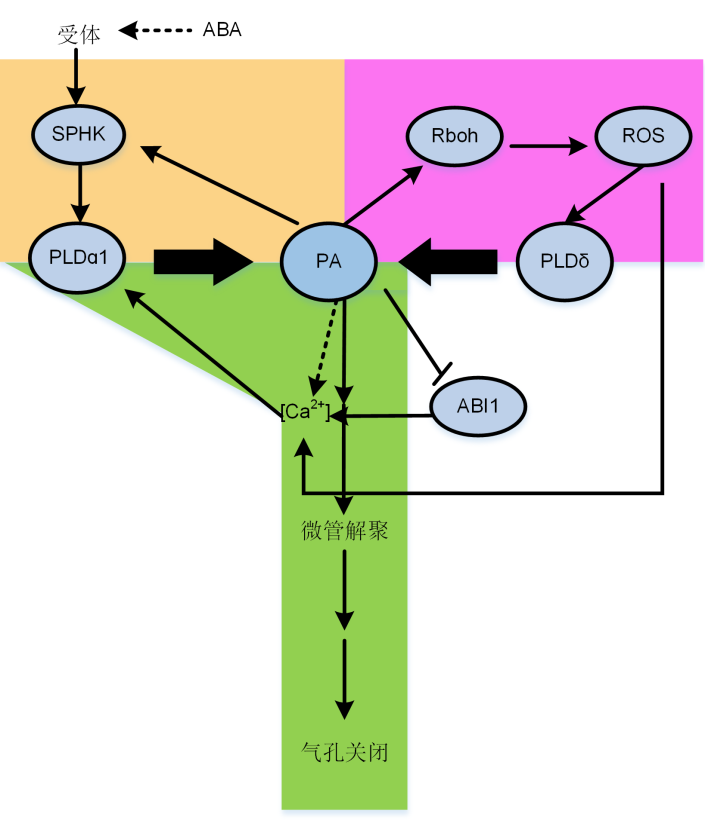
Figure 3 Proposed model of involvements of phosphatidic acid (PA) in regulating stomatal movements The model includes PA involvements in signal transduction pathways as discussed in the review. Arrows represent activation, bold arrows represent that PA production by phospholipids hydrolyzing by PLDs, bars mean inhibition, and dotted lines represent unknown mechanisms. The yellow block is the feedback effect of PA on SPHK in ABA-induced stomatal closure; The purple block represents PA, Rboh and ROS are involved in stomatal closure; The green block shows that PA and [Ca2+] form a feedback loop, which stimulates the depolymerization of microtubules and ultimately promotes stomatal closure.
| 蛋白 | 16:0-16:0 | 16:0-18:1 | 16:0-18:2 | 18:0-18:0 | 18:0-18:1 | 18:0-18:2 | 18:1-18:1 | 18:2-18:2 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RbohD/F | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| ABI1 | (弱) | - (弱) | + (强) | - (弱) | |||||
| MAP65-1 | (弱) | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | |
| MPK6 | (弱) | + | + (强) | - (弱) | + | + | + | ||
| SPHK | - (弱) | + | + | - (弱) | + | - | |||
| ZmCPK11 | + | + |
Table 1 Various interactive proteins bind on specific phosphatidic acid (PA) molecular species
| 蛋白 | 16:0-16:0 | 16:0-18:1 | 16:0-18:2 | 18:0-18:0 | 18:0-18:1 | 18:0-18:2 | 18:1-18:1 | 18:2-18:2 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RbohD/F | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| ABI1 | (弱) | - (弱) | + (强) | - (弱) | |||||
| MAP65-1 | (弱) | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | |
| MPK6 | (弱) | + | + (强) | - (弱) | + | + | + | ||
| SPHK | - (弱) | + | + | - (弱) | + | - | |||
| ZmCPK11 | + | + |
| [1] | 李莉, 井文, 章文华 ( 2015). 植物细胞中磷酸肌醇和磷脂酶C介导的信号转导. 植物生理学报 51, 1590-1596. |
| [2] | 李一路, 张晴晴, 胡卫芹, 屈钢, 洪月云 ( 2017). 磷脂酸磷酸酶在脂质代谢和信号转导中的作用及其调控. 植物生理学报 53, 897-904. |
| [3] | 王涛, 梅旭荣, 钟秀丽, 李玉中, 曾正兵, 王海燕, 孙磊, 夏旭 ( 2010). 磷脂酶Dδ参与植物的低温驯化过程. 植物学报 45, 541-547. |
| [4] |
Barenholz Y, Gibbes D, Litman BJ, Goll J, Thompson TE, Carlson FD ( 1977). A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 16, 2806-2810.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bargmann BOR, Laxalt AM, Riet BT, Schouten E, van Leeuwen W, Dekker HL, de Koster CG, Haring MA, Munnik T ( 2006). LePLDβ1 activation and relocalization in suspension-cultured tomato cells treated with xylanase. Plant J 45, 358-368.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bargmann BOR, Laxalt AM, ter Riet B, van Schooten B, Merquiol E, Testerink C, Haring MA, Bartels D, Munnik T ( 2009). Multiple PLDs required for high salinity and water deficit tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 78-89.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Chalfant CE, Spiegel S ( 2005). Sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide 1-phosphate: expanding roles in cell signaling. J Cell Sci 118, 4605-4612.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cruz-Ramirez A, Oropeza-Aburto A, Razo-Hernández F, Ramírez-Chávez E, Herrera-Estrella L ( 2006). Phospholipase DZ2 plays an important role in extraplastidic galactolipid biosynthesis and phosphate recycling in Ara- bidopsis roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 6765-6770.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Devaiah SP, Pan XQ, Hong YY, Roth M, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2007). Enhancing seed quality and viability by suppres- sing phospholipase D in Arabidopsis. Plant J 50, 950-957.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Distéfano AM, Valiñas MA, Scuffi D, Lamattina L, ten Have A, García-Mata C, Laxalt AM ( 2015). Phospholipase D δ knock-out mutants are tolerant to severe drought stress. Plant Signal Behav 10, e1089371.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Fan L, Zheng SQ, Wang XM ( 1997). Antisense suppression of phospholipase Dα retards abscisic acid- and ethy- lene-promoted senescence of postharvest Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell 9, 2183-2196. |
| [12] |
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD ( 2002). Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14, S15-S45.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Gosti F, Beaudoin N, Serizet C, Webb AAR, Vartanian N, Giraudat J ( 1999). ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 11, 1897-1909.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Guo L, Mishra G, Markham JE, Li MY, Tawfall A, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2012). Connections between sphingosine kinase and phospholipase D in the abscisic acid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 287, 8286-8296.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Guo L, Mishra G, Taylor K, Wang XM ( 2011). Phosphatidic acid binds and stimulates Arabidopsis sphingosine kina- ses. J Biol Chem 286, 13336-13345.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Himmelbach A, Hoffmann T, Leube M, Höhener B, Grill E ( 2002). Homeodomain protein ATHB6 is a target of the protein phosphatase ABI1 and regulates hormone responses in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21, 3029-3038.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Hong YY, Devaiah SP, Bahn SC, Thamasandra BN, Li MY, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2009). Phospholipase Dε and phosphatidic acid enhance Arabidopsis nitrogen signaling and growth. Plant J 58, 376-387.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Hong YY, Pan XQ, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2008a). Phospholipase Dα3 is involved in the hyperosmotic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 803-816.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Hong YY, Zhang WH, Wang XM ( 2010). Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid signaling in plant response to drought and salinity. Plant Cell Environ 33, 627-635.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Hong YY, Zhao J, Guo L, Kim SC, Deng XJ, Wang GL, Zhang GY, Li MY, Wang XM ( 2016). Plant phospholipases D and C and their diverse functions in stress responses. Prog Lipid Res 62, 55-74.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Hong YY, Zheng SQ, Wang XM ( 2008b). Dual functions of phospholipase Dα1 in plant response to drought. Mol Plant 1, 262-269.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Jang JH, Lee CS, Hwang D, Ryu SH ( 2012). Understanding of the roles of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid through their binding partners. Prog Lipid Res 51, 71-81.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Jiang Y, Wu K, Lin F, Qu YN, Liu XX, Zhang Q ( 2014). Phosphatidic acid integrates calcium signaling and microtubule dynamics into regulating ABA-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Planta 239, 565-575.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Kalachova T, Iakovenko O, Kretinin S, Kravets V ( 2013). Involvement of phospholipase D and NADPH-oxidase in salicylic acid signaling cascade. Plant Physiol Biochem 66, 127-133.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Katagiri T, Takahashi S, Shinozaki K ( 2001). Involvement of a novel Arabidopsis phospholipase D, AtPLDδ, in dehydration-inducible accumulation of phosphatidic acid in stress signaling. Plant J 26, 595-605.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Kennedy EP ( 1958). The biosynthesis of phospholipids. Am J Clin Nutr 6, 216-220.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Klimecka M, Szczegielniak J, Godecka L, Lewandowska- Gnatowska E, Dobrowolska G, Muszynska G ( 2011). Regulation of wound-responsive calcium-dependent protein kinase from maize (ZmCPK11) by phosphatidic acid. Acta Biochim Pol 58, 589-595. |
| [28] | Kolesnikov YS, Nokhrina KP, Kretynin SV, Volotovski ID, Martinec J, Romanov GA, Kravets VS ( 2012). Molecular structure of phospholipase D and regulatory mechanisms of its activity in plant and animal cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 77, 1-14. |
| [29] |
Kooijman EE, Chupin V, de Kruijff B, Burger KNJ ( 2003). Modulation of membrane curvature by phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Traffic 4, 162-174.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Kooijman EE, Tieleman DP, Testerink C, Munnik T, Rijkers DTS, Burger KNJ, de Kruijff B ( 2007). An electrostatic/hydrogen bond switch as the basis for the specific interaction of phosphatidic acid with proteins. J Biol Chem 282, 11356-11364.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Lee J, Welti R, Roth M, Schapaugh WT, Li JR, Trick HN ( 2012). Enhanced seed viability and lipid compositional changes during natural ageing by suppressing phospholipase Dα in soybean seed. Plant Biotechnol J 10, 164-173.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Li MY, Hong YY, Wang XM ( 2009). Phospholipase D- and phosphatidic acid-mediated signaling in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791, 927-935.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Li MY, Qin CB, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2006a). Double knockouts of phospholipases Dζ1 and Dζ2 in Arabidopsis affect root elongation during phosphate-limited growth but do not affect root hair patterning. Plant Physiol 140, 761-770.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Li MY, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2006b). Quantitative profiling of Arabidopsis polar glycerolipids in response to phosphorus starvation. Roles of Phospholipases Dζ1 and Dζ2 in phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and digalactosyldiacylgly- cerol accumulation in phosphorus-starved plants. Plant Physiol 142, 750-761.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Lindeboom JJ, Nakamura M, Hibbel A, Shundyak K, Gutierrez R, Ketelaar T, Emons AMC, Mulder BM, Kirik V, Ehrhardt DW ( 2013). A Mechanism for reorientation of cortical microtubule arrays driven by microtubule severing. Science 342, 1245533.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Mishra G, Zhang WH, Deng F, Zhao J, Wang XM ( 2006). A bifurcating pathway directs abscisic acid effects on stoma- tal closure and opening in Arabidopsis. Science 312, 264-266.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Munnik T, Meijer HJG, ter Riet B, Hirt H, Frank W, Bartels D, Musgrave A ( 2000). Hyperosmotic stress stimulates phospholipase D activity and elevates the levels of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant J 22, 147-154.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Nomikos M, Mulgrew-Nesbitt A, Pallavi P, Mihalyne G, Zaitseva I, Swann K, Lai FA, Murray D, McLaughlin S ( 2007). Binding of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-ζ (PLC-ζ) to phospholipid membranes: potential role of an unstructured cluster of basic residues. J Biol Chem 282, 16644-16653.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Ohashi Y, Oka A, Rodrigues-Pousada R, Possenti M, Ruberti I, Morelli G, Aoyama T ( 2003). Modulation of phospholipid signaling by GLABRA2 in root-hair pattern formation. Science 300, 1427-1430.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Ohlrogge J, Browse J ( 1995). Lipid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7, 957-970.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Pinosa F, Buhot N, Kwaaitaal M, Fahlberg P, Thordal- Christensen H, Ellerstrom M, Andersson MX ( 2013). Arabidopsis phospholipase dδ is involved in basal defense and nonhost resistance to powdery mildew fungi. Plant Physiol 163, 896-906.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Pleskot R, Li JJ, Žárský V, Potocký M, Staiger CJ ( 2013). Regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics by phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid. Trends Plant Sci 18, 496-504.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Pleskot R, Pejchar P, Staiger CJ, Potocky M ( 2014). When fat is not bad: the regulation of actin dynamics by phospholipid signaling molecules. Front Plant Sci 5, 5. |
| [44] |
Pleskot R, Potocký M, Pejchar P, Linek J, Bezvoda R, Martinec J, Valentová O, Novotná Z, Žárský V ( 2010). Mutual regulation of plant phospholipase D and the actin cytoskeleton. Plant J 62, 494-507.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Puli MR, Rajsheel P, Aswani V, Agurla S, Kuchitsu K, Raghavendra AS ( 2016). Stomatal closure induced by phytosphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosine-1-phosp- hate depends on nitric oxide and pH of guard cells in Pisum sativum . Planta 244, 831-841. |
| [46] |
Qin CB, Wang CX, Wang XM ( 2002). Kinetic analysis of Arabidopsis phospholipase Dδ. Substrate preference and mechanism of activation by Ca 2+ and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate . J Biol Chem 277, 49685-49690.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Rizzo MA, Shome K, Watkins SC, Romero G ( 2000). The recruitment of Raf-1 to membranes is mediated by direct interaction with phosphatidic acid and is independent of association with Ras. J Biol Chem 275, 23911-23918.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Ryu SB, Wang XM ( 1998). Increase in free linolenic and linoleic acids associated with phospholipase D-mediated hydrolysis of phospholipids in wounded castor bean lea- ves. Biochim Biophys Acta 1393, 193-202.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Shin JJ, Loewen CJ ( 2011). Putting the pH into phosphatidic acid signaling. BMC Biol 9, 85.
DOI |
| [50] |
Testerink C, Larsen PB, van der Does D, van Himbergen JAJ, Munnik T ( 2007). Phosphatidic acid binds to and inhibits the activity of Arabidopsis CTR1. J Exp Bot 58, 3905-3914.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Testerink C, Munnik T ( 2005). Phosphatidic acid: a multifunctional stress signaling lipid in plants. Trends Plant Sci 10, 368-375.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Testerink C, Munnik T ( 2011). Molecular, cellular, and phy- siological responses to phosphatidic acid formation in plants. J Exp Bot 62, 2349-2361.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Torres MA, Dangl JL, Jones JDG ( 2002). Arabidopsis gp91 phox homologues AtrbohD and AtrbohF are required for accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant defense response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 517-522. |
| [54] |
van den Brink-van Der Laan E, Killian JA, de Kruijff B ( 2004). Nonbilayer lipids affect peripheral and integral membrane proteins via changes in the lateral pressure profile. Biochim Biophys Acta 1666, 275-288.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Wang XM, Devaiah SP, Zhang WH, Welti R ( 2006). Signaling functions of phosphatidic acid. Prog Lipid Res 45, 250-278.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Welti R, Li WQ, Li MY, Sang YM, Biesiada H, Zhou HE, Rajashekar CB, Williams TD, Wang XM ( 2002). Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses. Role of phospholipase Dα in freezing-induced lipid changes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277, 31994-32002.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Worrall D, Liang YK, Alvarez S, Holroyd GH, Spiegel S, Panagopulos M, Gray JE, Hetherington AM ( 2008). Involvement of sphingosine kinase in plant cell signaling. Plant J 56, 64-72.
DOI URL |
| [58] | Yamaguchi T, Kuroda M, Yamakawa H, Ashizawa T, Hirayae K, Kurimoto L, Shinya T, Shibuya N ( 2009). Suppression of a phospholipase D gene, OsPLDβ1 , activates defense responses and increases disease resistance in rice. Plant Physiol 150, 308-319. |
| [59] | Yu LJ, Nie JN, Cao CY, Jin YK, Yan M, Wang FZ, Liu J, Xiao Y, Liang YH, Zhang WH ( 2010). Phosphatidic acid mediates salt stress response by regulation of MPK6 in Arabidopsis thaliana . New Phytol 188, 762-773. |
| [60] |
Zhang Q, Lin F, Mao TL, Nie JN, Yan M, Yuan M, Zhang WH ( 2012). Phosphatidic acid regulates microtubule organization by interacting with MAP65-1 in response to salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 4555-4576.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Zhang WH, Qin CB, Zhao J, Wang XM ( 2004). Phospholipase Dα1-derived phosphatidic acid interacts with ABI1 phosphatase 2C and regulates abscisic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 9508-9513.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Zhang YY, Zhu HY, Zhang Q, Li MY, Yan M, Wang R, Wang LL, Welti R, Zhang WH, Wang XM ( 2009). Phospholipase Dα1 and phosphatidic acid regulate NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 2357-2377.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Zhao J, Devaiah SP, Wang CX, Li MY, Welti R, Wang XM ( 2013). Arabidopsis phospholipase Dβ1 modulates defense responses to bacterial and fungal pathogens. New Phytol 199, 228-240.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Zhao J, Wang CX, Bedair M, Welti R, Sumner LW, Baxter I, Wang XM ( 2011). Suppression of phospholipase Dγs confers increased aluminum resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana . PLoS One 6, e28086. |
| [1] | Xiao-Hong YAN Wen-Hai HU. Differences in photoprotective mechanisms during winter in three evergreen broadleaf species in subtropical region [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(预发表): 0-0. |
| [2] | GAO Yu-Xuan, Feng Yu-Cai, Zhang Jun, LIU Ling-Li. Research and conservation status of the rare and endangered relict plant Cathaya argyrophylla Chun & Kuang [J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [3] | MA Fu-Long, WANG Yu-Qing, HAO Yu, DUAN Ji-Chao, LIU Fei-Fei, XI Lin-Qiao, HAN Lu. Effects of altitude gradient on plant and soil microbial community structure and diversity in the middle part of the northern slope of the Kunlun Mountains, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 732-747. |
| [4] | Hongmei Wang, Wei Yuan, Fang Xue, Zhaocong Zhang, Kun Liu, Silong Che. The functions of plant SWEETs and its regulatory mechanisms involved in stress responses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [5] |
Liang Ma, Yongqing Yang, Yan Guo.
“Next-generation Green Revolution” Genes: Toward New “Climate-Smart” Crop Breeding [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [6] | JIANG Xiao-Yu, YU Xin-Miao, LIAO Qin, ZHANG Jin-Wei, WU Xue-Feng, WANG Xu, PAN Jun-Tong, WANG Jun-Feng, MU Chun-Sheng, SHI Yu-Jie. Studies on the emission of nitrous oxide from terrestrial plants [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(4): 513-525. |
| [7] | Zhou Zhihua, Jin Xiaohua, Luo Ying, Li Diqiang, Yue Jianbing, Liu Fang, He Tuo, Li Xi, Dong Hui, Luo Peng. Analyses and suggestions on mechanisms of forestry and grassland administrations in China to achieve targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [8] | TIAN Ao, LI Wei-Jie, CAO Yang, JIA Zhen-Zhen, ZENG Song. Growth response of Rhododendron delavayi seedlings to the soil water stress and its physiological mechanism [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(3): 488-501. |
| [9] | Liu Xupeng, Wang Min, Han Shou'an, Zhu Xuehui, Wang Yanmeng, Pan Mingqi, Zhang Wen. Research Progress on Factors and Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Plant Organ Abscission [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [10] | Xiong Lianglin, Liang Guolu, Guo Qigao, Jing Danlong. Advances in the Regulation of Alternative Splicing of Genes in Plants in Response to Abiotic Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [11] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | Suowei Wu, Xueli An, Xiangyuan Wan. Molecular Mechanisms of Male Sterility and their Applications in Biotechnology-based Male-sterility Hybrid Seed Production in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [13] | Wenjie Zhou, Wenhan Zhang, Wei Jia, Zicheng Xu, Wuxing Huang. Advances in Plant miRNAs Responses to Abiotic Stresses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 810-833. |
| [14] | Yuying Zhou, Hui Chen, Simu Liu. Research Progress on Auxin Responsive Non-canonical Aux/IAA Proteins in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [15] | Lumei He, Bojun Ma, Xifeng Chen. Advances on the Executor Resistance Genes in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 671-680. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||