

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 375-387.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21223 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21223
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu Yan1, Mei Xu1, Yutong Wang1, Weihuai Pan2, Jianwei Pan1, Jianxin Shou2( ), Chao Wang2,*(
), Chao Wang2,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-19
Accepted:2022-02-07
Online:2022-05-01
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
Jianxin Shou,Chao Wang
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Xu Yan, Mei Xu, Yutong Wang, Weihuai Pan, Jianwei Pan, Jianxin Shou, Chao Wang. Coupling Regulation of Endocytosis and Exocytosis in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 375-387.
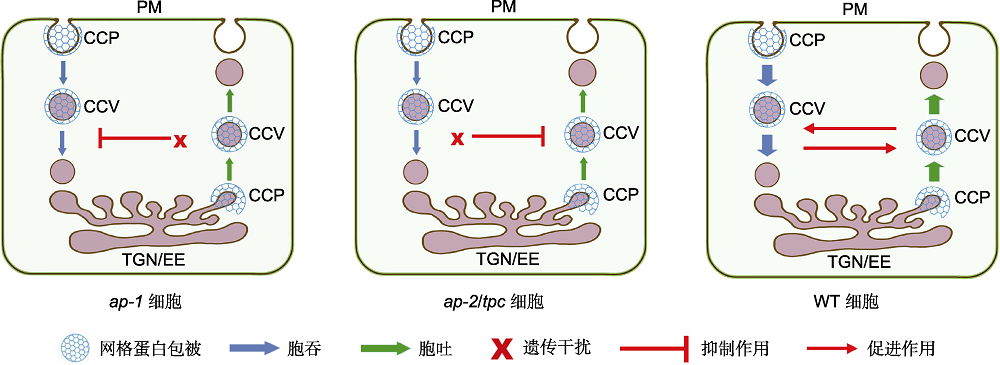
Figure 1 Coupling regulation of clathrin-mediated endocytosis and exocytosis PM: Plasma membrane; TGN/EE: Trans-Golgi network/early endosome; CCP: Clathrin coated pit; CCV: Clathrin coated vesicle; ap-1: AP-1 deficient; ap-2/tpc: AP-2 or TPC deficient; WT: Wildtype
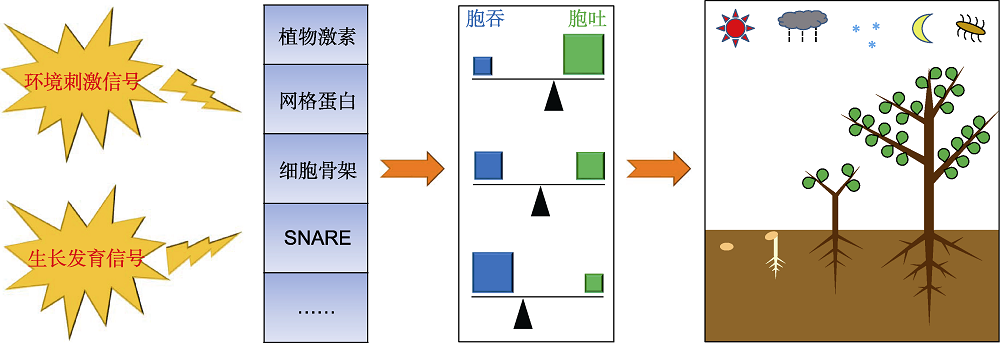
Figure 2 Plants adapt to the environment for growth and reproduction by coupling regulation of endocytosis and exocytosis SNARE: Soluble-N-ethyl-maleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor
| [1] | 鲍永美, 王州飞, 张红生 (2005). 植物SNARE蛋白的结构与功能. 植物学报 22, 715-722. |
| [2] |
崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟 (2020). 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用. 植物学报 55, 329-339.
DOI |
| [3] |
李彤辉, 刘晓楠, 徐静, 李师鹏, 蒋苏 (2019). 胞泌复合体在植物中的功能研究进展. 植物学报 54, 642-651.
DOI |
| [4] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华 (2021). 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展. 植物学报 56, 151-165. |
| [5] |
Abas L, Benjamins R, Malenica N, Paciorek T, Wišniewska J, Moulinier-Anzola JC, Sieberer T, Friml J, Luschnig C (2006). Intracellular trafficking and proteolysis of the Arabidopsis auxin-efflux facilitator PIN2 are involved in root gravitropism. Nat Cell Biol 8, 249-256.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Adamowski M, Narasimhan M, Kania U, Glanc M, De Jaeger G, Friml J (2018). A functional study of AUXILIN- LIKE1 and 2, two putative clathrin uncoating factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30, 700-716.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Aerts N, Pereira Mendes M, Van Wees SCM (2021). Multiple levels of crosstalk in hormone networks regulating plant defense. Plant J 105, 489-504.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Alabi AA, Tsien RW (2013). Perspectives on kiss-and-run: role in exocytosis, endocytosis, and neurotransmission. Annu Rev Physiol 75, 393-422.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
An QL, Hückelhoven R, Kogel KH, van Bel AJ (2006). Multivesicular bodies participate in a cell wall-associated defence response in barley leaves attacked by the pathogenic powdery mildew fungus. Cell Microbiol 8, 1009- 1019.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Baluska F, Samaj J, Hlavacka A, Kendrick-Jones J, Volkmann D (2004). Actin-dependent fluid-phase endocytosis in inner cortex cells of maize root apices. J Exp Bot 55, 463-473.
PMID |
| [11] |
Bashline L, Lei L, Li SD, Gu Y (2014). Cell wall, cytoskeleton, and cell expansion in higher plants. Mol Plant 7, 586- 600.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Bassham DC, Brandizzi F, Otegui MS, Sanderfoot AA (2008). The secretory system of Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis Book 6, e0116.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Beck M, Zhou J, Faulkner C, MacLean D, Robatzek S (2012). Spatio-temporal cellular dynamics of the Arabi-dopsis flagellin receptor reveal activation status-dependent endosomal sorting. Plant Cell 24, 4205-4219.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Bielach A, Hrtyan M, Tognetti VB (2017). Plants under stress: involvement of auxin and cytokinin. Int J Mol Sci 18, 1427.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Blatt MR (2000). Cellular signaling and volume control in stomatal movements in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16, 221-241.
PMID |
| [16] | Bloch D, Pleskot R, Pejchar P, Potocký M, Trpkošová P, Cwiklik L, Vukašinović N, Sternberg H, Yalovsky S, Žárský V (2016). Exocyst SEC3 and phosphoinositides define sites of exocytosis in pollen tube initiation and growth. Plant Physiol 172, 980-1002. |
| [17] |
Boller T, Felix G (2009). A renaissance of elicitors: percep- tion of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 379-406.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Boutté Y, Frescatada-Rosa M, Men S, Chow CM, Ebine K, Gustavsson A, Johansson L, Ueda T, Moore I, Jür-gens G, Grebe M (2010). Endocytosis restricts Arabi-dopsis KNOLLE syntaxin to the cell division plane during late cytokinesis. EMBO J 29, 546-558.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Cai Y, Jia TR, Lam SK, Ding Y, Gao CJ, San MWY, Pimpl P, Jiang LW (2011). Multiple cytosolic and transmembrane determinants are required for the trafficking of SCAMP1 via an ER-Golgi-TGN-PM pathway. Plant J 65, 882- 896.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Cameron C, Geitmann A (2018). Cell mechanics of pollen tube growth. Curr Opin Genet Dev 51, 11-17.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Campanoni P, Blatt MR (2007). Membrane trafficking and polar growth in root hairs and pollen tubes. J Exp Bot 58, 65-74.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Cao WL, Yu Y, Li MY, Luo J, Wang RS, Tang HJ, Huang J, Wang JF, Zhang HS, Bao YM (2019). OsSYP121 ac-cumulates at fungal penetration sites and mediates host resistance to rice blast. Plant Physiol 179,1330-1342.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chandler JW, Werr W (2015). Cytokinin-auxin crosstalk in cell type specification. Trends Plant Sci 20, 291-300.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Cheung AY, Wu HM (2008). Structural and signaling networks for the polar cell growth machinery in pollen tubes. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 547-572.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Crowell EF, Bischoff V, Desprez T, Rolland A, Stierhof YD, Schumacher K, Gonneau M, Höfte H, Vernhettes S (2009). Pausing of Golgi bodies on microtubules regulates secretion of cellulose synthase complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21,1141-1154.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Cui Y, Cao WH, He YL, Zhao Q, Wakazaki M, Zhuang XH, Gao JY, Zeng YL, Gao CJ, Ding Y, Wong HY, Wong WS, Lam HK, Wang PF, Ueda T, Rojas-Pierce M, Toyooka K, Kang BH, Jiang LW (2019). A whole-cell electron tomography model of vacuole biogenesis in Arabidopsis root cells. Nat Plants 5, 95-105.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Cutler JM, Rains DW, Loomis RS (1977). The importance of cell size in the water relations of plants. Physiol Plant 40, 255-260. |
| [28] |
Deng SR, Sun J, Zhao R, Ding MQ, Zhang YN, Sun YL, Wang W, Tan YQ, Liu DD, Ma XJ, Hou PC, Wang MJ, Lu CF, Shen X, Chen SL (2015). Populus euphratica APYRASE2 enhances cold tolerance by modulating vesicular trafficking and extracellular ATP in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol 169, 530-548.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Derksen J, Rutten T, Lichtscheidl IK, de Win AHN, Pierson ES, Rongen G (1995). Quantitative analysis of the distribution of organelles in tobacco pollen tubes: implications for exocytosis and endocytosis. Protoplasma 188, 267-276.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Dhonukshe P, Aniento F, Hwang I, Robinson DG, Mravec J, Stierhof YD, Friml J (2007). Clathrin-mediated constitutive endocytosis of PIN auxin efflux carriers in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 17, 520-527.
PMID |
| [31] |
Dhonukshe P, Baluška F, Schlicht M, Hlavacka A, Šamaj J, Friml J, Gadella TW Jr (2006). Endocytosis of cell surface material mediates cell plate formation during plant cytokinesis. Dev Cell 10, 137-150.
PMID |
| [32] |
Du YL, Tejos R, Beck M, Himschoot E, Li HJ, Robatzek S, Vanneste S, Friml J (2013). Salicylic acid interferes with clathrin-mediated endocytic protein trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 7946-7951.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Eisenach C, Chen ZH, Grefen C, Blatt MR (2012). The trafficking protein SYP121 of Arabidopsis connects programmed stomatal closure and K+ channel activity with vegetative growth. Plant J 69, 241-251.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Ekanayake G, LaMontagne ED, Heese A (2019). Never walk alone: clathrin-coated vesicle (CCV) components in plant immunity. Annu Rev Phytopathol 57, 387-409.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Fowke L, Dibbayawan T, Schwartz O, Harper J, Overall R (1999). Combined immunofluorescence and field emis-sion scanning electron microscope study of plasma mem-brane-associated organelles in highly vacuolated suspensor cells of white spruce somatic embryos. Cell Biol Int 23, 389-397.
PMID |
| [36] |
Fujimoto M, Ebine K, Nishimura K, Tsutsumi N, Ueda T (2020). Longin R-SNARE is retrieved from the plasma membrane by ANTH domain-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 25150-25158.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Gadeyne A, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Vanneste S, Di Rubbo S, Zauber H, Vanneste K, Van Leene J, De Winne N, Eeckhout D, Persiau G, Van De Slijke E, Cannoot B, Vercruysse L, Mayers JR, Adamowski M, Kania U, Ehrlich M, Schweighofer A, Ketelaar T, Maere S, Bednarek SY, Friml J, Gevaert K, Witters E, Russinova E, Persson S, De Jaeger G, Van Damme D (2014). The TPLATE adaptor complex drives clathrin-mediated endocytosis in plants. Cell 156, 691-704.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Galvan-Ampudia CS, Julkowska MM, Darwish E, Gan-dullo J, Korver RA, Brunoud G, Haring MA, Munnik T, Vernoux T, Testerink C (2013). Halotropism is a re-sponse of plant roots to avoid a saline environment. Curr Biol 23, 2044-2050.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Gendre D, McFarlane HE, Johnson E, Mouille G, Sjödin A, Oh J, Levesque-Tremblay G, Watanabe Y, Samuels L, Bhalerao RP (2013). Trans-Golgi network localized ECHIDNA/Ypt interacting protein complex is required for the secretion of cell wall polysaccharides in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 2633-2646.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Gendre D, Oh J, Boutté Y, Best JG, Samuels L, Nilsson R, Uemura T, Marchant A, Bennett MJ, Grebe M, Bhalerao RP (2011). Conserved Arabidopsis ECHIDNA protein mediates trans-Golgi-network trafficking and cell elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 8048-8053.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Gradmann D, Robinson DG (1989). Does turgor prevent endocytosis in plant cells? Plant Cell Environ 12, 151-154.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Grebe M, Xu J, Möbius W, Ueda T, Nakano A, Geuze HJ, Rook MB, Scheres B (2003). Arabidopsis sterol endocytosis involves actin-mediated trafficking via ARA6-positive early endosomes. Curr Biol 13,1378-1387.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Gutkowska M, Wnuk M, Nowakowska J, Lichocka M, Stronkowski MM, Swiezewska E (2015). Rab geranyl-geranyl transferase β subunit is essential for male fertility and tip growth in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 66, 213-224.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Hachez C, Besserer A, Chevalier AS, Chaumont F (2013). Insights into plant plasma membrane aquaporin trafficking. Trends Plant Sci 18, 344-352.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Hao HQ, Fan LS, Chen T, Li RL, Li XJ, He QH, Botella MA, Lin JX (2014). Clathrin and membrane microdomains cooperatively regulate RbohD dynamics and activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 1729-1745.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Hara-Nishimura I, Hatsugai N (2011). The role of vacuole in plant cell death. Cell Death Differ 18, 1298-1304.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Hatsugai N, Iwasaki S, Tamura K, Kondo M, Fuji K, Ogasawara K, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I (2009). A novel membrane fusion-mediated plant immunity against bacterial pathogens. Genes Dev 23, 2496-2506.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
He M, Lan M, Zhang BC, Zhou YH, Wang YQ, Zhu L, Yuan M, Fu Y (2018). Rab-H1b is essential for trafficking of cellulose synthase and for hypocotyl growth in Arabidop-si thaliana. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 1051-1069.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Higashiyama T (2018). Plant reproduction: autocrine machinery for the long journey of the pollen tube. Curr Biol 28, R266-R269.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Higashiyama T, Takeuchi H (2015). The mechanism and key molecules involved in pollen tube guidance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 393-413.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Ichikawa M, Hirano T, Enami K, Fuselier T, Kato N, Kwon C, Voigt B, Schulze-Lefert P, Baluška F, Sato MH (2014). Syntaxin of plant proteins SYP123 and SYP132 mediate root hair tip growth in Arabidopsi. thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 790-800. |
| [52] |
Idilli AI, Morandini P, Onelli E, Rodighiero S, Caccianiga M, Moscatelli A (2013). Microtubule depolymerization affects endocytosis and exocytosis in the tip and influences endosome movement in tobacco pollen tubes. Mol Plant 6, 1109-1130.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Idone V, Tam C, Goss JW, Toomre D, Pypaert M, Andrews NW (2008). Repair of injured plasma membrane by rapid Ca2+-dependent endocytosis. J Cell Biol 180, 905- 914.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Ischebeck T, Werner S, Krishnamoorthy P, Lerche J, Meijón M, Stenzel I, Löfke C, Wiessner T, Im YJ, Perera IY, Iven T, Feussner I, Busch W, Boss WF, Teichmann T, Hause B, Persson S, Heilmann I (2013). Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate influences PIN polarization by controlling clathrin-mediated membrane trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 4894-4911.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Jing HW, Strader LC (2019). Interplay of auxin and cyto-kinin in lateral root development. Int J Mol Sci 20, 486.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Jiroutova P, Oklestkova J, Strnad M (2018). Crosstalk between brassinosteroids and ethylene during plant growth and under abiotic stress conditions. Int J Mol Sci 19, 3283.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Johnson MA, Harper JF, Palanivelu R (2019). A fruitful journey: pollen tube navigation from germination to fertilization. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 809-837.
DOI PMID |
| [58] |
Kakar K, Zhang HT, Scheres B, Dhonukshe P (2013). CLASP-mediated cortical microtubule organization guides PIN polarization axis. Nature 495, 529-533.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Kalde M, Nühse TS, Findlay K, Peck SC (2007). The syntaxin SYP132 contributes to plant resistance against bacteria and secretion of pathogenesis-related protein 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 11850-11855.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Ke MY, Ma ZM, Wang DY, Sun YB, Wen CJ, Huang DQ, Chen ZC, Yang L, Tan ST, Li RX, Friml J, Miao YS, Chen X (2021). Salicylic acid regulates PIN2 auxin transporter hyperclustering and root gravitropic growth via Remorin-dependen lipid nanodomain organisation in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 229, 963-978.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Ketelaar T, Galway ME, Mulder BM, Emons AMC (2008). Rates of exocytosis and endocytosis in Arabidopsis root hairs and pollen tubes. J Microsc 231, 265-273.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Kim H, Kwon H, Kim S, Kim MK, Botella MA, Yun HS, Kwon C (2016). Synaptotagmin 1 negatively controls the two distinct immune secretory pathways to powdery mil-dew fungi in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 1133- 1141.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Larson ER, Domozych DS, Tierney ML (2014). SNARE VTI13 plays a unique role in endosomal trafficking pathways associated with the vacuole and is essential for cell wall organization and root hair growth in Arabidopsis. Ann Bot 114, 1147-1159.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Larson ER, Van Zelm E, Roux C, Marion-Poll A, Blatt MR (2017). Clathrin heavy chain subunits coordinate endo- and exocytic traffic and affect stomatal movement. Plant Physiol 175, 708-720.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Leyman B, Geelen D, Quintero FJ, Blatt MR (1999). A tobacco syntaxin with a role in hormonal control of guard cell ion channels. Science 283, 537-540.
PMID |
| [66] |
Li G, Liang W, Zhang X, Ren H, Hu J, Bennett MJ, Zhang D (2014). Rice actin-binding protein RMD is a key link in the auxin-actin regulatory loop that controls cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111,10377-10382.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Li N, Han X, Feng D, Yuan DY, Huang LJ (2019). Signaling crosstalk between salicylic acid and ethylene/jasmonate in plant defense: do we understand what they are whispering? Int J Mol Sci 20, 671.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Li RL, Liu P, Wan YL, Chen T, Wang QL, Mettbach U, Baluška F, Šamaj J, Fang XH, Lucas WJ, Lin JX (2012). A membrane microdomain-associated protein, Arabidopsis Flot1, is involved in a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway and is required for seedling development. Plant Cell 24, 2105-2122.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Li RX, Rodriguez-Furlan C, Wang JQ, van de Ven W, Gao T, Raikhel NV, Hicks GR (2017). Different endomembrane trafficking pathways establish apical and basal polarities. Plant Cell 29, 90-108.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Lipka V, Kwon C, Panstruga R (2007). SNARE-ware: the role of SNARE-domain proteins in plant biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23, 147-174.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Livanos P, Müller S (2019). Division plane establishment and cytokinesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 239-267.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Lou XL (2018). Sensing exocytosis and triggering endocy-tosis at synapses: synaptic vesicle exocytosis-endocytosis coupling. Front Cell Neurosci 12, 66. |
| [73] |
Ma J, Chen J, Wang M, Ren YL, Wang S, Lei CL, Cheng ZJ, Sodmergen (2018). Disruption of OsSEC3A increases the content of salicylic acid and induces plant defense responses in rice. J Exp Bot 69, 1051-1064.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Marhavý P, Bielach A, Abas L, Abuzeineh A, Duclercq J, Tanaka H, Pařezová M, Petrášek J, Friml J, Kleine- Vehn J, Benková E (2011). Cytokinin modulates endocytic trafficking of PIN1 auxin efflux carrier to control plant organogenesis. Dev Cell 21, 796-804.
DOI PMID |
| [75] |
Maritzen T, Haucke V (2018). Coupling of exocytosis and endocytosis at the presynaptic active zone. Neurosci Res 127, 45-52.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Mayers JR, Hu TW, Wang C, Cárdenas JJ, Tan YQ, Pan JW, Bednarek SY (2017). SCD1 and SCD2 form a complex that functions with the exocyst and RabE1 in exocytosis and cytokinesis. Plant Cell 29, 2610-2625.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
McKenna ST, Kunkel JG, Bosch M, Rounds CM, Vidali L, Winship LJ, Hepler PK (2009). Exocytosis precedes and predicts the increase in growth in oscillating pollen tubes. Plant Cell 21, 3026-3040.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
McMahon HT, Boucrot E (2011). Molecular mechanism and physiological functions of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12, 517-533.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
McMichael CM, Reynolds GD, Koch LM, Wang C, Jiang N, Nadeau J, Sack FD, Gelderman MB, Pan JW, Bednarek SY (2013). Mediation of clathrin-dependent trafficking during cytokinesis and cell expansion by Arabidopsis stomatal cytokinesis defective proteins. Plant Cell 25, 3910-3925.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
McNeil PL, Miyake K, Vogel SS (2003). The endomembrane requirement for cell surface repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 4592-4597.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Meckel T, Gall L, Semrau S, Homann U, Thiel G (2007). Guard cells elongate: relationship of volume and surface area during stomatal movement. Biophys J 92,1072-1080.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Meng JG, Liang L, Jia PF, Wang YC, Li HJ, Yang WC (2020). Integration of ovular signals and exocytosis of a Ca2+ channel by MLOs in pollen tube guidance. Nat Plants 6, 143-153.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Meyer D, Pajonk S, Micali C, O'Connell R, Schulze-Lefert P (2009). Extracellular transport and integration of plant secretory proteins into pathogen-induced cell wall compartments. Plant J 57, 986-999.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Mosesso N, Bläske T, Nagel MK, Laumann M, Isono E (2019). Preparation of clathrin-coated vesicles from Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Front Plant Sci 9,1972.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Mravec J, Petrášek J, Li N, Boeren S, Karlova R, Kitakura S, Pařezová M, Naramoto S, Nodzyński T, Dhonukshe P, Bednarek SY, Zažímalová E, de Vries S, Friml J (2011). Cell plate restricted association of DRP1A and PIN proteins is required for cell polarity establishment in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 21, 1055-1060.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Müller D, Leyser O (2011). Auxin, cytokinin and the control of shoot branching. Ann Bot 107, 1203-1212.
DOI URL |
| [87] | Nagawa S, Xu TD, Lin DS, Dhonukshe P, Zhang XX, Friml J, Scheres B, Fu Y, Yang ZB (2012). ROP GTPase-dependent actin microfilaments promote PIN1 polarization by localized inhibition of clathrin-dependent endocytosis. PLoS Biol 10, e1001299. |
| [88] |
Narasimhan M, Johnson A, Prizak R, Kaufmann WA, Tan ST, Casillas-Pérez B, Friml J (2020). Evolutionarily unique mechanistic framework of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in plants. eLife 9, e52067.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Nielsen ME, Thordal-Christensen H (2013). Transcytosis shuts the door for an unwanted guest. Trends Plant Sci 18, 611-616.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Pacifici E, Polverari L, Sabatini S (2015). Plant hormone cross-talk: the pivot of root growth. J Exp Bot 66, 1113- 1121.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Paez Valencia J, Goodman K, Otegui MS (2016). Endocytosis and endosomal trafficking in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67, 309-335.
DOI PMID |
| [92] |
Pandya-Kumar N, Shema R, Kumar M, Mayzlish-Gati E, Levy D, Zemach H, Belausov E, Wininger S, Abu- Abied M, Kapulnik Y, Koltai H (2014). Strigolactone analog GR24 triggers changes in PIN2 polarity, vesicle trafficking and actin filament architecture. New Phytol 202, 1184-1196.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Preuss ML, Serna J, Falbel TG, Bednarek SY, Nielsen E (2004). The Arabidopsis Rab GTPase RabA4b localizes to the tips of growing root hair cells. Plant Cell 16, 1589- 1603.
PMID |
| [94] | Ravikumar R, Kalbfuß N, Gendre D, Steiner A, Altmann M, Altmann S, Rybak K, Edelmann H, Stephan F, Lampe M, Facher E, Wanner G, Falter-Braun P, Bhalerao RP, Assaad FF (2018). Independent yet overlapping pathways ensure the robustness and responsiveness of trans-Golgi network functions in Arabidopsis. Development 145, dev169201. |
| [95] |
Reynolds GD, Wang C, Pan JW, Bednarek SY (2018). Inroads into internalization: five years of endocytic exploration. Plant Physiol 176, 208-218.
DOI PMID |
| [96] |
Richter S, Kientz M, Brumm S, Nielsen ME, Park M, Gavidia R, Krause C, Voss U, Beckmann H, Mayer U, Stierhof YD, Jürgens G (2014). Delivery of endocytosed proteins to the cell-division plane requires change of pathway from recycling to secretion. eLife 3, e02131.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Robatzek S (2007). Vesicle trafficking in plant immune responses. Cell Microbiol 9, 1-8.
PMID |
| [98] |
Robert S, Kleine-Vehn J, Barbez E, Sauer M, Paciorek T, Baster P, Vanneste S, Zhang J, Simon S, Čovanová M, Hayashi K, Dhonukshe P, Yang ZB, Bednarek SY, Jones AM, Luschnig C, Aniento F, Zažímalová E, Friml J (2010). ABP1 mediates auxin inhibition of clathrin-dependent endocytosis in Arabidopsis. Cell 143, 111-121.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Robinson DG (1996). Clathrin-mediated trafficking. Trends Plant Sci 1, 349-355.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Rounds CM, Hepler PK, Winship LJ (2014). The apical actin fringe contributes to localized cell wall deposition and polarized growth in the lily pollen tube. Plant Physiol 166, 139-151.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Salanenka Y, Verstraeten I, Löfke C, Tabata K, Naramoto S, Glanc M, Friml J (2018). Gibberellin DELLA signaling targets the retromer complex to redirect protein trafficking to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 3716-3721.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Schaller GE, Bishopp A, Kieber JJ (2015). The yin-yang of hormones: cytokinin and auxin interactions in plant development. Plant Cell 27, 44-63.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Schapire AL, Valpuesta V, Botella MA (2009). Plasma membrane repair in plants. Trends Plant Sci 14, 645-652.
DOI PMID |
| [104] |
Shimizu Y, Takagi J, Ito E, Ito Y, Ebine K, Komatsu Y, Goto Y, Sato M, Toyooka K, Ueda T, Kurokawa K, Uemura T, Nakano A (2021). Cargo sorting zones in the trans-Golgi network visualized by super-resolution confocal live imaging microscopy in plants. Nat Commun 12, 1901.
DOI PMID |
| [105] | Shope JC, DeWald DB, Mott KA (2003). Changes in surface area of intact guard cells are correlated with membrane internalization. Plant Physiol 133, 1314-1321. |
| [106] |
Sieberer BJ, Ketelaar T, Esseling JJ, Emons AMC (2005). Microtubules guide root hair tip growth. New Phytol 167, 711-719.
PMID |
| [107] |
Staehelin LA, Hepler PK (1996). Cytokinesis in higher plants. Cell 84, 821-824.
PMID |
| [108] | Stenzel I, Ischebeck T, König S, Hołubowska A, Sporysz M, Hause B, Heilmann I (2008). The type B phosphate-dylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase 3 is essential for root hair formation in Arabidopsi. thaliana. Plant Cell 20, 124- 141. |
| [109] |
Sun JQ, Chen Q, Qi LL, Jiang HL, Li SY, Xu YX, Liu F, Zhou WK, Pan JW, Li XG, Palme K, Li CY (2011). Jasmonate modulates endocytosis and plasma mem-brane accumulation of the Arabidopsis PIN2 protein. New Phytol 191, 360-375.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
Sutter JU, Sieben C, Hartel A, Eisenach C, Thiel G, Blatt MR (2007). Abscisic acid triggers the endocytosis of the Arabidopsis KAT1 K+ channel and its recycling to the plasma membrane. Curr Biol 17,1396-1402.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Tam C, Idone V, Devlin C, Fernandes MC, Flannery A, He XX, Schuchman E, Tabas I, Andrews NW (2010). Exocytosis of acid sphingomyelinase by wounded cells promotes endocytosis and plasma membrane repair. J Cell Biol 189, 1027-1038.
DOI URL |
| [112] |
Togo T, Alderton JM, Bi GQ, Steinhardt RA (1999). The mechanism of facilitated cell membrane resealing. J Cell Sci 112, 719-731.
DOI URL |
| [113] |
Togo T, Krasieva TB, Steinhardt RA (2000). A decrease in membrane tension precedes successful cell-membrane repair. Mol Biol Cell 11, 4339-4346.
PMID |
| [114] |
Uemura T, Ueda T, Ohniwa RL, Nakano A, Takeyasu K, Sato MH (2004). Systematic analysis of SNARE molecules in Arabidopsis: dissection of the post-Golgi network in plant cells. Cell Struct Funct 29, 49-65.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
Wang C, Hu TW, Yan X, Meng TT, Wang YT, Wang QM, Zhang XY, Gu Y, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Gadeyne A, Lin JX, Persson S, Van Damme D, Li CY, Bednarek SY, Pan JW (2016). Differential regulation of clathrin and its adaptor proteins during membrane recruitment for endocytosis. Plant Physiol 171, 215-229.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Wang C, Yan X, Chen Q, Jiang N, Fu W, Ma BJ, Liu JZ, Li CY, Bednarek SY, Pan JW (2013). Clathrin light chains regulate clathrin-mediated trafficking, auxin signaling, and development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 499-516.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
Wang J, Ding Y, Wang JQ, Hillmer S, Miao YS, Lo SW, Wang XF, Robinson DG, Jiang LW (2010). EXPO, an exocyst-positive organelle distinct from multivesicular endosomes and autophagosomes, mediates cytosol to cell wall exocytosis in Arabidopsis and tobacco cells. Plant Cell 22, 4009-4030.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
Wang PW, Pleskot R, Zang JZ, Winkler J, Wang J, Yperman K, Zhang T, Wang K, Gong JL, Guan YJ, Richardson C, Duckney P, Vandorpe M, Mylle E, Fiserova J, Van Damme D, Hussey PJ (2019). Plant AtEH/Pan1 proteins drive autophagosome formation at ER- PM contact sites with actin and endocytic machinery. Nat Commun 10, 5132.
DOI URL |
| [119] |
Webb MS, Steponkus PL (1993). Freeze-induced membrane ultrastructural alterations in rye (Secale cereale) leaves. Plant Physiol 101, 955-963.
PMID |
| [120] |
Yamazaki T, Kawamura Y, Minami A, Uemura M (2008). Calcium-dependent freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis involves membrane resealing via synaptotagmin SYT1. Plant Cell 20, 3389-3404.
DOI URL |
| [121] |
Yan X, Wang YT, Xu M, Dahhan DA, Liu C, Zhang Y, Lin JX, Bednarek SY, Pan JW (2021). Cross-talk between clathrin-dependent post-Golgi trafficking and clathrin-me-diated endocytosis in Arabidopsis root cells. Plant Cell 33, 3057-3075.
DOI URL |
| [122] |
Yu QQ, Zhang Y, Wang J, Yan X, Wang C, Xu J, Pan JW (2016). Clathrin-mediated auxin efflux and maxima regulate hypocotyl hook formation and light-stimulated hook opening in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 9, 101-112.
DOI URL |
| [123] | Zhang CH, Brown MQ, van de Ven W, Zhang ZM, Wu B, Young MC, Synek L, Borchardt D, Harrison R, Pan SQ, Luo N, Huang YMM, Ghang YJ, Ung N, Li RX, Isley J, Morikis D, Song JK, Guo W, Hooley RJ, Chang CEA, Yang ZB, Zarsky V, Muday GK, Hicks GR, Raikhel NV (2016). Endosidin2 targets conserved exocyst complex subunit EXO70 to inhibit exocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E41-E50. |
| [124] |
Zhang L, Ma JW, Liu H, Yi Q, Wang YN, Xing JJ, Zhang PP, Ji SD, Li MJ, Li JY, Shen JB, Lin JX (2021). SNARE proteins VAMP721 and VAMP722 mediate the post-Golgi trafficking required for auxin-mediated development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 108, 426-440.
DOI URL |
| [125] |
Zhang WW, Cai C, Staiger CJ (2019a). Myosins XI are involved in exocytosis of cellulose synthase complexes. Plant Physiol 179, 1537-1555.
DOI URL |
| [126] |
Zhang X, Cui YN, Yu M, Lin JX (2019b). Single-molecule techniques for imaging exo-endocytosis coupling in cells. Trends Plant Sci 24, 879-880.
DOI URL |
| [127] |
Zhang Y, Yu QQ, Jiang N, Yan X, Wang C, Wang QM, Liu JZ, Zhu MY, Bednarek SY, Xu J, Pan JW (2017). Clathrin regulates blue light-triggered lateral auxin distribution and hypocotyl phototropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 40, 165-176.
DOI URL |
| [128] |
Zhao LF, Rehmani MS, Wang H (2020). Exocytosis and endocytosis: yin-yang crosstalk for sculpting a dynamic growing pollen tube tip. Front Plant Sci 11, 572848.
DOI URL |
| [129] |
Zonia L, Munnik T (2007). Life under pressure: hydrostatic pressure in cell growth and function. Trends Plant Sci 12, 90-97.
DOI URL |
| [130] | Zwiewka M, Nodzyński T, Robert S, Vanneste S, Friml J (2015). Osmotic stress modulates the balance between exocytosis and clathrin-mediated endocytosis in Arabidopsi. thaliana. Mol Plant 8, 1175-1187. |
| [1] | WANG Yin, TONG Xiao-Juan, ZHANG Jin-Song, LI Jun, MENG Ping, LIU Pei-Rong, ZHANG Jing-Ru. Impact of drought on carbon and water fluxes and their coupling in a Quercus variabilis plantation [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(9): 1157-1171. |
| [2] | Baican Li, Junguo Zhang, Changchun Zhang, Lifeng Wang, Jiliang Xu, Li Liu. Rare bird recognition method in Beijing based on TC-YOLO model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24056-. |
| [3] | Wu Fan, Shen Jinbo, Hu Shuai. Research Advances of the Plant ESCRT Machinery [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 697-712. |
| [4] | YANG Meng, YU Gui-Rui. Coupling-decoupling of soil CO2 and CH4 fluxes and their responses to temperature in arid and semi-arid regions of China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2022, 46(12): 1497-1507. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhen-Zhen, ZHAO Ping, ZHAO Xiu-Hua, ZHANG Jin-Xiu, ZHU Li-Wei, OUYANG Lei, ZHANG Xiao-Yan. Impact of environmental factors on the decoupling coefficient and the estimation of canopy stomatal conductance for ever-green broad-leaved tree species [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2018, 42(12): 1179-1191. |
| [6] | Jia-Zhi FAN, Dan WANG, Ya-Lin HU, Pan-Pan JING, Peng-Peng WANG, Jiquan CHEN. Optimal stomatal behavior theory for simulating stomatal conductance [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2016, 40(6): 631-642. |
| [7] | Wenjie Cao, Guisheng Li. Plasma Membrane Positioning Mechanism of Auxin Efflux Carrier PIN Proteins [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 265-273. |
| [8] | Peng-Sen SUN, Ning LIU, Shi-Rong LIU, Ge SUN. Trade-offs between water yield and carbon sequestration for sub-alpine catchments in western Sichuan, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2016, 40(10): 1037-1048. |
| [9] | LI Dan-Feng,YU Shun-Li,WANG Guo-Xun,FANG Wei-Wei. Environmental heterogeneity and mechanism of stoichiometry properties of vegetative organs in dominant shrub communities across the Loess Plateau [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(5): 453-465. |
| [10] | Yiqun Xue, Kai Song, Lusheng Fan, Yinglang Wan, Jinxing Lin. pH-sensitive Fluorescent Proteins and Their Applications in Plant Cell Biology [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(3): 394-404. |
| [11] | DU Hu, PENG Wan-Xia, SONG Tong-Qing, WANG Ke-Lin, ZENG Fu-Ping, LU Shi-Yang, SHI Wei-Wei, TANG Cheng, TAN Qiu-Jin. Plant community characteristics and its coupling relationships with soil in depressions between karst hills, North Guangxi, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2013, 37(3): 197-208. |
| [12] | Yijing Zhang;Yongbiao Xue. Molecular Control of S-RNase-based Self-incompatibility [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(03): 372-388. |
| [13] | CHANG Peng-Fei, Li Ping, JALAID Nairsag, Wang Jing, WANG Zhen-Hua, Yang Sen, JIA Zhou, YANG Lu, LIU Ling-Li, Deng Meifeng. Contributions of soil organic carbon and inorganic carbon stocks to total carbon stock and their influencing factors between different types in temperate grasslands of Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, , 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 0-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||