

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 363-376.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24139 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24139
• RESEARCH ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liu Ru1,2, Li Yang2, Tang Zhaocheng2, Hao Tingting2,*( ), Zhang Baolong1,2,*(
), Zhang Baolong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-09
Accepted:2024-12-14
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2024-12-17
Contact:
*E-mail: zhbl2248@hotmail.com;17812067912@126.com
Liu Ru, Li Yang, Tang Zhaocheng, Hao Tingting, Zhang Baolong. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the 5'-nucleotidase Genes Catalyze NMN Degradation to NR in Brassica oleracea var. acephala[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 363-376.
| Primer name | Sequences (5'-3') | Reference gene |
|---|---|---|
| BolN1-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAATCTATGCGCCCATCAG | Bo7g089730 |
| BolN1-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCACATCAG | |
| BolN2-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGCTCCTGTGCGGAGATATG | Bo2g150410 |
| BolN2-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCGCATCAG | |
| BolN3-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGTTAGAGGCTTGGAGCTAGA | Bo6g086480 |
| BolN3-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGGTTTTGAAAAGGCTTGAAGCC | |
| BolN4-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACATCATCTCGCCGTCTT | Bo4g154010 |
| BolN4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATGGCATCCTTGGGCAGC | |
| BolN5-X1.2-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCGAAGAACAACAGCTT | Bo2g079140 |
| BolN5-X3.4-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCGAATCTCCAGGAC | |
| BolN5-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGCATTAAGGGCTT | |
| BolN6-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGCGATTAACGGCGAAGATCG | Bo8g039400 |
| BolN6-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAAGGATGAAGAAATCTTGGG | |
| BolN7-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGCGATTAACGGCGAAGATCG | Bo6g116340 |
| BolN7-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGAGTTAAGGGCTTTGG | |
| BolN8-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCAAAAAACAACGGCTTG | Bo6g089210 |
| BolN8-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGCGTTGAGGTATTTGT | |
| BolN9-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGCTTCTCAACAAGCGTCATTT | Bo6g119360 |
| BolN9-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGAAGGGGGAGAAGGTGGAA | |
| BolN10-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAATCTATGCGCCCATCAG | Bo6g099860 |
| BolN10-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCACATCAG | |
| pET29a-F | TGATGTCGGCGATATAGGCG | - |
| pET29a-R | GCTTAATGCGCCGCTACA | - |
Table 1 Sequence of primers
| Primer name | Sequences (5'-3') | Reference gene |
|---|---|---|
| BolN1-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAATCTATGCGCCCATCAG | Bo7g089730 |
| BolN1-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCACATCAG | |
| BolN2-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGCTCCTGTGCGGAGATATG | Bo2g150410 |
| BolN2-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCGCATCAG | |
| BolN3-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGTTAGAGGCTTGGAGCTAGA | Bo6g086480 |
| BolN3-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGGTTTTGAAAAGGCTTGAAGCC | |
| BolN4-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACATCATCTCGCCGTCTT | Bo4g154010 |
| BolN4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATGGCATCCTTGGGCAGC | |
| BolN5-X1.2-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCGAAGAACAACAGCTT | Bo2g079140 |
| BolN5-X3.4-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCGAATCTCCAGGAC | |
| BolN5-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGCATTAAGGGCTT | |
| BolN6-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGCGATTAACGGCGAAGATCG | Bo8g039400 |
| BolN6-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAAGGATGAAGAAATCTTGGG | |
| BolN7-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGGCGATTAACGGCGAAGATCG | Bo6g116340 |
| BolN7-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGAGTTAAGGGCTTTGG | |
| BolN8-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGACCTCAAAAAACAACGGCTTG | Bo6g089210 |
| BolN8-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTGATCAGCGTTGAGGTATTTGT | |
| BolN9-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGCTTCTCAACAAGCGTCATTT | Bo6g119360 |
| BolN9-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGAAGGGGGAGAAGGTGGAA | |
| BolN10-F | AAGAAGGAGATATACATATGAATCTATGCGCCCATCAG | Bo6g099860 |
| BolN10-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGGTTTTCCATAGCCACATCAG | |
| pET29a-F | TGATGTCGGCGATATAGGCG | - |
| pET29a-R | GCTTAATGCGCCGCTACA | - |
| Strains or plasmids | Characteristics | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | ||
| DH5a | General cloning host | Tsingke |
| BL21 (DE3) | Host strain for protein expression | Tsingke |
| Plasmids | ||
| pET29a | Kanr, protein expression vector | Laboratory preservation |
| pET29a-BolN1-X1 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN1-X1 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN1-X2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN1-X2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN3 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN3 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN4 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN4 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X1 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X1 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X3 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X3 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X4 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X4 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN6 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN6 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN7 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN7 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN8 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN8 gene | This study |
Table 2 Strains and plasmids
| Strains or plasmids | Characteristics | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | ||
| DH5a | General cloning host | Tsingke |
| BL21 (DE3) | Host strain for protein expression | Tsingke |
| Plasmids | ||
| pET29a | Kanr, protein expression vector | Laboratory preservation |
| pET29a-BolN1-X1 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN1-X1 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN1-X2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN1-X2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN3 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN3 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN4 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN4 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X1 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X1 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X2 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X2 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X3 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X3 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN5-X4 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN5-X4 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN6 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN6 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN7 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN7 gene | This study |
| pET29a-BolN8 | Kanr, pET29a derivative for the expression of BolN8 gene | This study |
| Protein name | Amino acid number (aa) | Molecular weight (Da) | Isoelectric point | Acidic amino acid | Basic amino acid | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolN1-X1 | 619 | 70585.80 | 5.95 | 84 | 74 | 44.71 | 83.34 | -0.338 |
| BolN1-X2 | 620 | 70579.90 | 5.91 | 85 | 75 | 44.38 | 85.71 | -0.307 |
| BolN2 | 613 | 69374.34 | 5.73 | 85 | 73 | 43.79 | 85.30 | -0.310 |
| BolN3 | 433 | 50351.39 | 6.48 | 63 | 59 | 39.38 | 82.77 | -0.552 |
| BolN4 | 346 | 40495.22 | 7.71 | 43 | 44 | 34.57 | 74.97 | -0.402 |
| BolN5-X1 | 380 | 40007.05 | 5.23 | 46 | 37 | 42.58 | 84.24 | -0.170 |
| BolN5-X2 | 381 | 40135.18 | 5.23 | 46 | 37 | 42.49 | 84.02 | -0.179 |
| BolN5-X3 | 370 | 39063.98 | 5.15 | 46 | 36 | 41.08 | 83.08 | -0.189 |
| BolN5-X4 | 371 | 39179.07 | 5.09 | 47 | 36 | 41.42 | 82.59 | -0.204 |
| BolN6 | 307 | 33476.79 | 5.11 | 38 | 27 | 37.19 | 90.16 | -0.156 |
| BolN7 | 379 | 40218.03 | 5.01 | 51 | 37 | 47.43 | 81.06 | -0.271 |
| BolN8 | 381 | 40611.46 | 5.04 | 50 | 38 | 39.86 | 85.75 | -0.273 |
Table 3 Basic information of 5'-nucleotidase protein
| Protein name | Amino acid number (aa) | Molecular weight (Da) | Isoelectric point | Acidic amino acid | Basic amino acid | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolN1-X1 | 619 | 70585.80 | 5.95 | 84 | 74 | 44.71 | 83.34 | -0.338 |
| BolN1-X2 | 620 | 70579.90 | 5.91 | 85 | 75 | 44.38 | 85.71 | -0.307 |
| BolN2 | 613 | 69374.34 | 5.73 | 85 | 73 | 43.79 | 85.30 | -0.310 |
| BolN3 | 433 | 50351.39 | 6.48 | 63 | 59 | 39.38 | 82.77 | -0.552 |
| BolN4 | 346 | 40495.22 | 7.71 | 43 | 44 | 34.57 | 74.97 | -0.402 |
| BolN5-X1 | 380 | 40007.05 | 5.23 | 46 | 37 | 42.58 | 84.24 | -0.170 |
| BolN5-X2 | 381 | 40135.18 | 5.23 | 46 | 37 | 42.49 | 84.02 | -0.179 |
| BolN5-X3 | 370 | 39063.98 | 5.15 | 46 | 36 | 41.08 | 83.08 | -0.189 |
| BolN5-X4 | 371 | 39179.07 | 5.09 | 47 | 36 | 41.42 | 82.59 | -0.204 |
| BolN6 | 307 | 33476.79 | 5.11 | 38 | 27 | 37.19 | 90.16 | -0.156 |
| BolN7 | 379 | 40218.03 | 5.01 | 51 | 37 | 47.43 | 81.06 | -0.271 |
| BolN8 | 381 | 40611.46 | 5.04 | 50 | 38 | 39.86 | 85.75 | -0.273 |
| Protein name | Alpha helix (%) | Extended strand (%) | Random coil (%) | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolN1-X1 | 43.62 | 12.12 | 44.26 | Cytoplasm |
| BolN1-X2 | 47.74 | 9.35 | 42.90 | Nucleus |
| BolN2 | 45.35 | 10.11 | 44.54 | Chloroplast |
| BolN3 | 49.19 | 11.09 | 39.72 | Cytoplasm |
| BolN4 | 54.34 | 8.09 | 37.57 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| BolN5-X1 | 29.74 | 16.32 | 53.95 | Chloroplast |
| BolN5-X2 | 28.61 | 14.17 | 57.22 | Chloroplast |
| BolN5-X3 | 31.89 | 15.41 | 52.70 | Nucleus |
| BolN5-X4 | 30.46 | 16.17 | 53.37 | Nucleus |
| BolN6 | 28.99 | 15.31 | 55.70 | Cytoskeleton |
| BolN7 | 28.50 | 14.51 | 56.99 | Chloroplast |
| BolN8 | 28.87 | 15.49 | 55.64 | Chloroplast |
Table 4 The secondary structure analysis of 5'-nucleotidase protein
| Protein name | Alpha helix (%) | Extended strand (%) | Random coil (%) | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolN1-X1 | 43.62 | 12.12 | 44.26 | Cytoplasm |
| BolN1-X2 | 47.74 | 9.35 | 42.90 | Nucleus |
| BolN2 | 45.35 | 10.11 | 44.54 | Chloroplast |
| BolN3 | 49.19 | 11.09 | 39.72 | Cytoplasm |
| BolN4 | 54.34 | 8.09 | 37.57 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| BolN5-X1 | 29.74 | 16.32 | 53.95 | Chloroplast |
| BolN5-X2 | 28.61 | 14.17 | 57.22 | Chloroplast |
| BolN5-X3 | 31.89 | 15.41 | 52.70 | Nucleus |
| BolN5-X4 | 30.46 | 16.17 | 53.37 | Nucleus |
| BolN6 | 28.99 | 15.31 | 55.70 | Cytoskeleton |
| BolN7 | 28.50 | 14.51 | 56.99 | Chloroplast |
| BolN8 | 28.87 | 15.49 | 55.64 | Chloroplast |
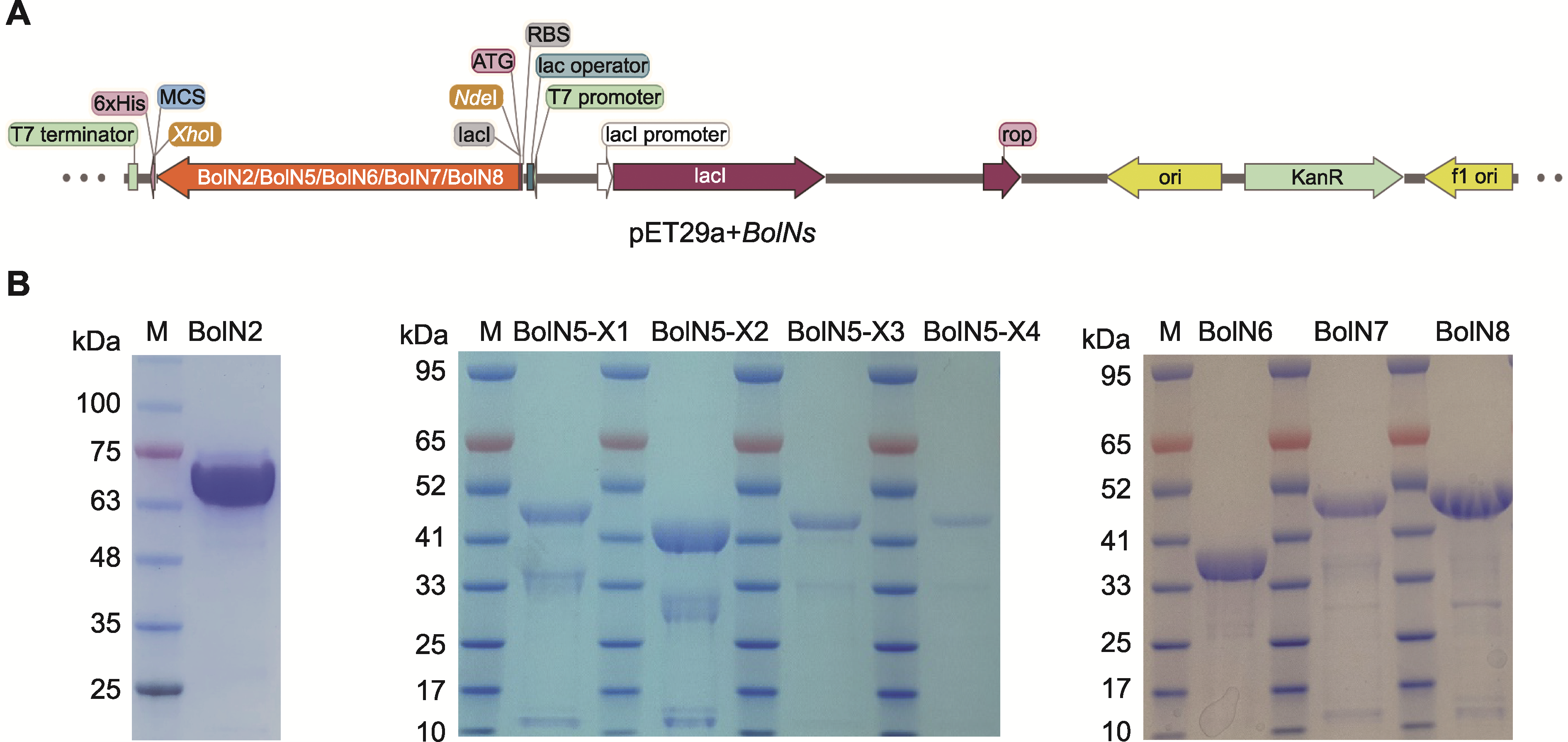
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of construction of recombinant plasmid pET29a+BolNs (A) and 5'-nucleotidase proteins purified by N-His6 tag (B) M: Protein marker. BolN2, BolN5, BolN6, BolN7, and BolN8 are purified proteins bound to N-His6 tag.
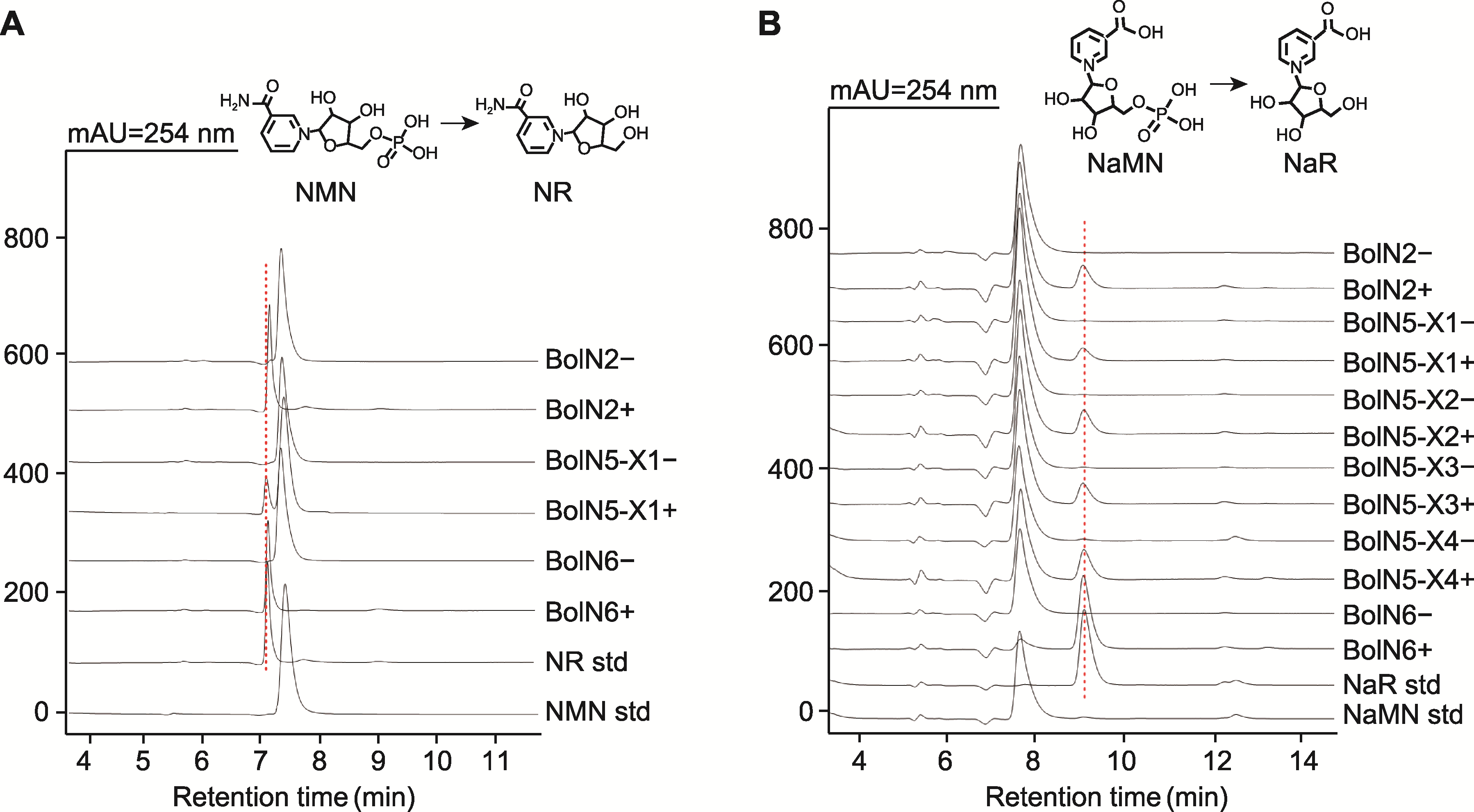
Figure 4 HPLC analysis of the products produced in the BolN2, BolN5, and BolN6 catalyzed reaction (A) Using nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as substrate; (B) Using nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) as substrate. +: Enzyme-catalyzed reaction; -: Negative control; NMN std: NMN standard; NR std: NR standard; NaMN std: NaMN standard; NaR std: NaR standard
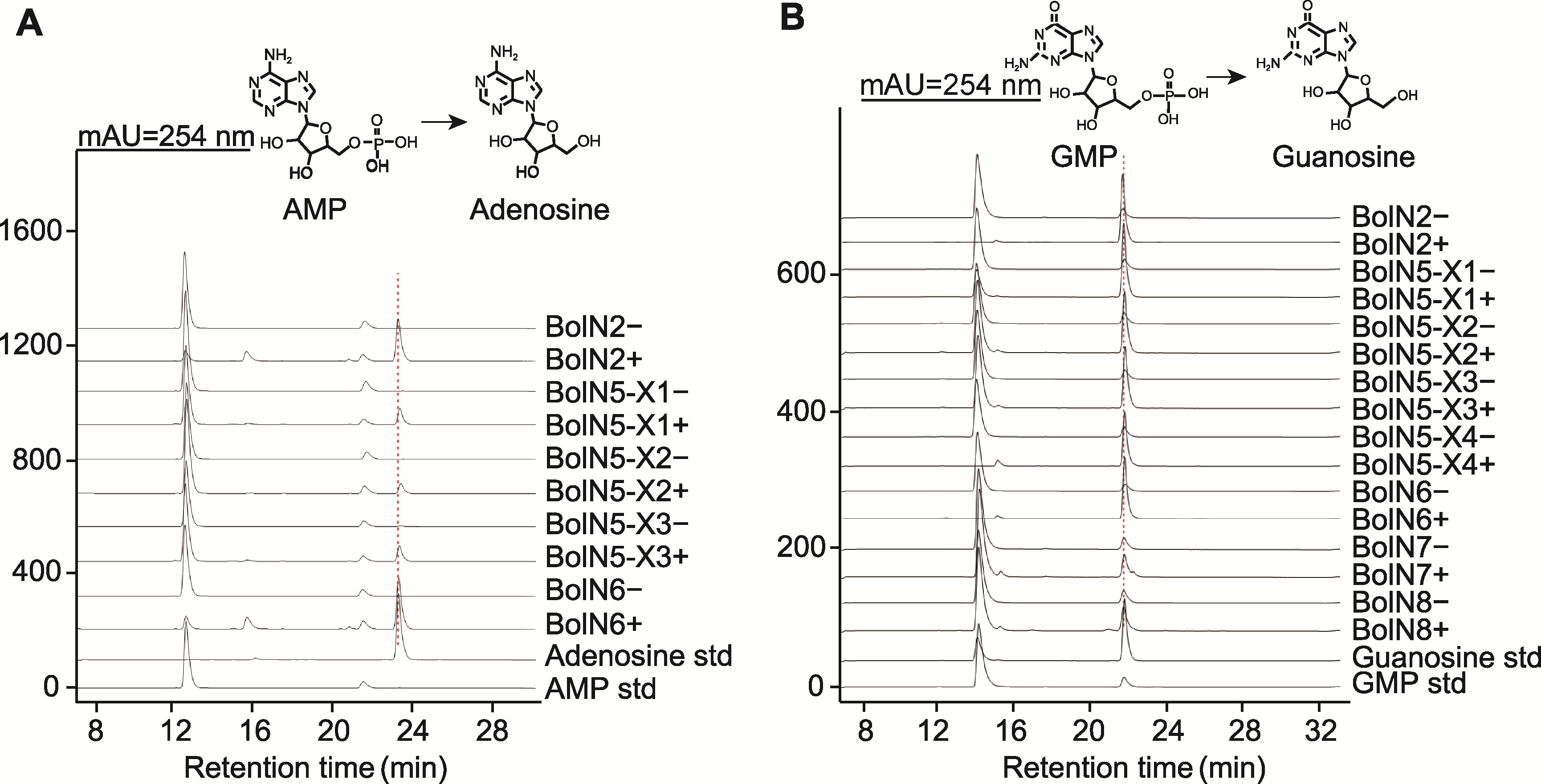
Figure 5 HPLC analysis of the products produced in the BolN2, BolN5, BolN6, BolN7, and BolN8 catalyzed reaction (A) Using adenosine monophosphate (AMP) as substrate; (B) Using guanosine monophosphate (GMP) as substrate. +: Enzyme-catalyzed reaction; -: Negative control; AMP std: AMP standard; Adenosine std: Adenosine standard; GMP std: GMP standard; Guanosine std: Guanosine standard
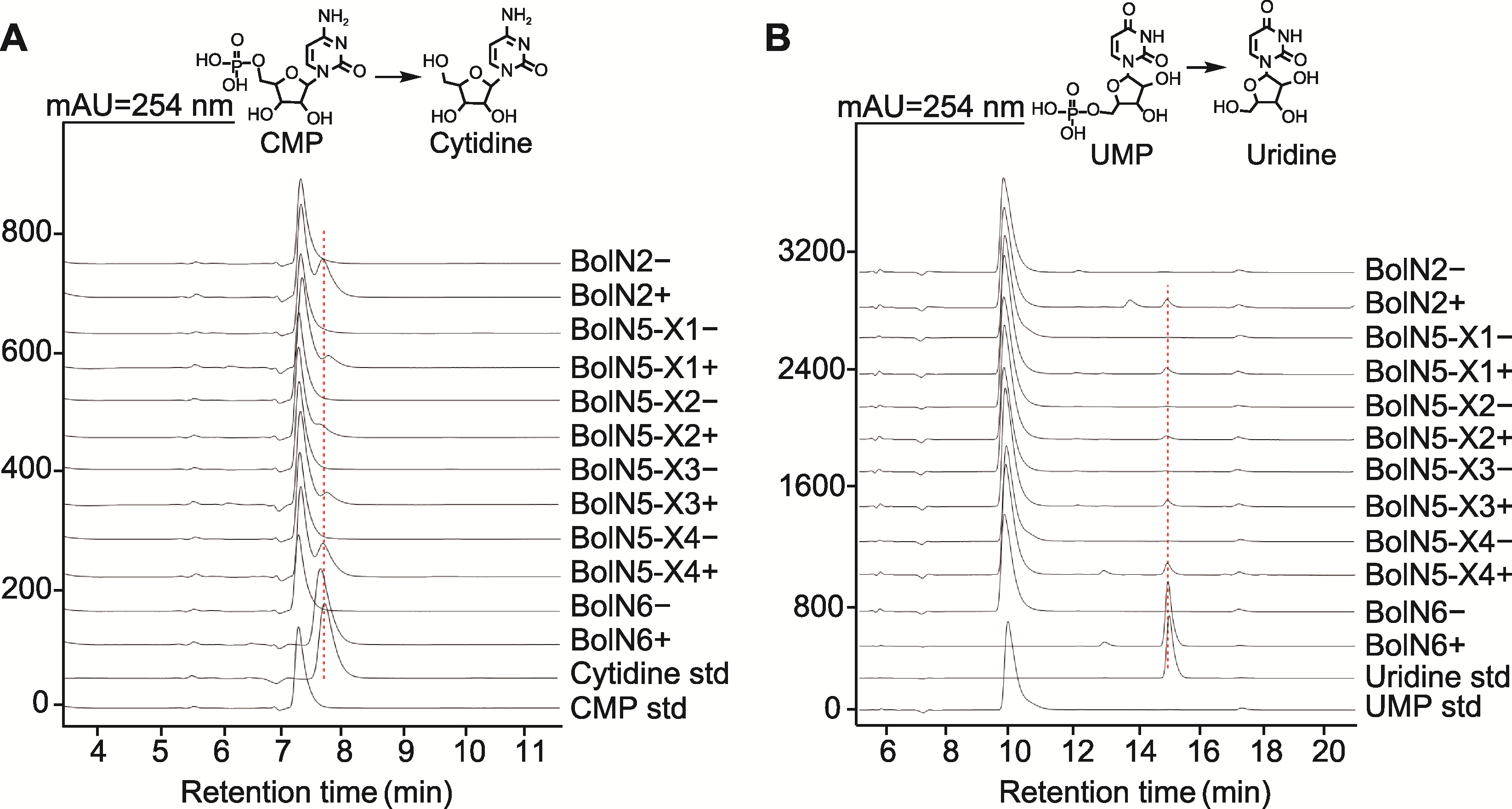
Figure 6 HPLC analysis of the products produced in the BolN2, BolN5, and BolN6 catalyzed reaction (A) Using cytidine monophosphate (CMP) as substrate; (B) Using uridine monophosphate (UMP) as substrate. +: Enzyme-catalyzed reaction; -: Negative control; CMP std: CMP standard; Cytidine std: Cytidine standard; UMP std: UMP standard; Uridine std: Uridine standard
| [1] |
Ashihara H, Deng WW (2012). Pyridine metabolism in tea plants: salvage, conjugate formation and catabolism. J Plant Res 125, 781-791.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Ashihara H, Stasolla C, Yin Y, Loukanina N, Thorpe TA (2005). De novo and salvage biosynthetic pathways of pyridine nucleotides and nicotinic acid conjugates in cultured plant cells. Plant Sci 169, 107-114. |
| [3] |
Bideon GM (1975). Purification and characterization of a cyclic nucleotide-regulated 5'-nucleotidase from potato. Biochim Biophys Acta 384, 443-457.
PMID |
| [4] | Bogan KL, Evans C, Belenky P, Song P, Burant CF, Kennedy R, Brenner C (2009). Identification of Isn1 and Sdt1 as glucose- and vitamin-regulated nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinic acid mononucleotide 5'- nucleotidases responsible for production of nicotinamide riboside and nicotinic acid riboside. J Biol Chem 284, 34861-34869. |
| [5] | Cabello-Díaz JM, Gálvez-Valdivieso G, Caballo C, Lambert R, Quiles FA, Pineda M, Piedras P (2015). Identification and characterization of a gene encoding for a nucleotidase from Phaseolus vulgaris. J Plant Physiol 185, 44-51. |
| [6] | Chen TX, Fu M, Li N, Yang LL, Li LF, Zhong CM (2024). Identification and expression analysis of DNA methyltransferase in Begonia masoniana. Chin Bull Bot 59, 726-737. (in Chinese) |
|
陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅 (2024). 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物学报 59, 726-737.
DOI |
|
| [7] |
Christensen TMIE, Jochimsen BU (1983). Enzymes of ureide synthesis in pea and soybean. Plant Physiol 72, 56-59.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Crozier A, Kamiya Y, Bishop G, Yokota T (2000). Biosynthesis of hormones and elicitor molecules. In: BuchananBB, GruissemW, JonesRL, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants.eds. Rockville: American Society of Plant Physiology. pp. 850-929. |
| [9] | Ding L, Zheng LM, Chang L, Yin XY, Ren TD (2023). Research progress on the nutritional value and processing of kale. Mod Food 29(18), 50-52. (in Chinese) |
| 丁琳, 郑丽敏, 常亮, 尹晓玉, 任腾丹 (2023). 羽衣甘蓝的营养价值与加工研究进展分析. 现代食品 29(18), 50-52. | |
| [10] | Eastwell KC, Stumpf PK (1982). The presence of 5'- nucleotidase in Swiss chard chloroplasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 108, 1690-1694. |
| [11] | Gao HH, Zhang YX, Hu SW, Guo Y (2017). Genome-wide survey and phylogenetic analysis of MADS-box gene family in Brassica napus. Chin Bull Bot 52, 699-712. (in Chinese) |
|
高虎虎, 张云霄, 胡胜武, 郭媛 (2017). 甘蓝型油菜MADS-box基因家族的鉴定与系统进化分析. 植物学报 52, 699-712.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Hashida SN, Takahashi H, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H (2007). Arabidopsis thaliana nicotinate/nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyltransferase (AtNMNAT) is required for pollen tube growth. Plant J 49, 694-703. |
| [13] |
He YL, Kitada N, Yasuhara M, Hori R (2001). Quantitative estimation of renal clearance of N-acetylprocainamide in rats with various experimental acute renal failure. Eur J Pharm Sci 13, 303-308.
PMID |
| [14] |
Herz S, Eberhardt S, Bacher A (2000). Biosynthesis of riboflavin in plants. The ribA gene of Arabidopsis thaliana specifies a bifunctional GTP cyclohydrolase II/3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase. Phytochemistry 53, 723-731.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Hong WQ, Mo F, Zhang ZQ, Huang MY, Wei XW (2020). Nicotinamide mononucleotide: a promising molecule for therapy of diverse diseases by targeting NAD+ metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol 8, 246. |
| [16] |
Hunsucker SA, Mitchell BS, Spychala J (2005). The 5'- nucleotidases as regulators of nucleotide and drug metabolism. Pharmacol Therapeut 107, 1-30.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Jiang YS, Deng YQ, Pang HH, Ma TT, Ye Q, Chen Q, Chen HY, Hu ZP, Qin CF, Xu ZH (2022). Treatment of SARS-CoV-2-induced pneumonia with NAD+ and NMN in two mouse models. Cell Discov 8, 38. |
| [18] |
Katahira R, Ashihara H (2009). Profiles of the biosynthesis and metabolism of pyridine nucleotides in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Planta 231, 35-45.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Lučić D, Pavlović I, Brkljačić L, Bogdanović S, Farkaš V, Cedilak A, Nanić L, Rubelj I, Salopek-Sondi B (2023). Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala DC.) and wild cabbage (Brassica incana Ten.) polyphenolic extracts. Molecules 28, 1840. |
| [20] |
Mills KF, Yoshida S, Stein LR, Grozio A, Kubota S, Sasaki Y, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Apte RS, Uchida K, Yoshino J, Imai SI (2016). Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metab 24, 795-806.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Noctor G, Queval G, Gakière B (2006). NAD(P) synthesis and pyridine nucleotide cycling in plants and their potential importance in stress conditions. J Exp Bot 57, 1603-1620.
PMID |
| [22] | Ogawa T, Ueda Y, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2005). Comprehensive analysis of cytosolic Nudix hydrolases in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 280, 25277-25283. |
| [23] | Sidiq Y, Nakano M, Mori Y, Yaeno T, Kimura M, Nishiuchi T (2021). Nicotinamide effectively suppresses Fusarium head blight in wheat plants. Int J Mol Sci 22, 2968. |
| [24] | Tang ZC, Bao P, Ling XT, Qiu ZY, Zhang BL, Hao TT (2024). In vitro digestion under simulated saliva, gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation of nicotinamide mononucleotide, and its effects on the gut microbiota. Food Res Int 177, 113779. |
| [25] |
Terakawa A, Natsume A, Okada A, Nishihata S, Kuse J, Tanaka K, Takenaka S, Ishikawa S, Yoshida KI (2016). Bacillus subtilis 5'-nucleotidases with various functions and substrate specificities. BMC Microbiol 16, 249.
PMID |
| [26] |
Wagner R, Wagner KG (1985). The pyridine-nucleotide cycle in tobacco. Enzyme activities for the de-novo synthesis of NAD. Planta 165, 532-537.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Wang GD, Pichersky E (2007). Nicotinamidase participates in the salvage pathway of NAD biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 49, 1020-1029. |
| [28] | Yao Q, Shen RD, Shao Y, Tian YF, Han PJ, Zhang XN, Zhu JK, Lu YM (2024). Efficient and multiplex gene upregulation in plants through CRISPR-Cas-mediated knockin of enhancers. Mol Plant 17, 1472-1483. |
| [29] | Yu HX, Zhu MJ, Shi TT, Ding Y, Fang ZH, Xu H, Sun Y (2022). Synthesis and application of nicotinamide mononucleotide. Shandong Chem Ind 51(8), 104-106. (in Chinese) |
| 俞韩啸, 朱梦佳, 石甜甜, 丁阳, 方卓晗, 许衡, 孙燕 (2022). 烟酰胺单核苷酸的合成与应用研究进展. 山东化工 51(8), 104-106. | |
| [30] | Zheng CX, Li YM, Wu X, Gao L, Chen XY (2024). Advances in the synthesis and physiological metabolic regulation of nicotinamide mononucleotide. Nutrients 16, 2354. |
| [31] | Zheng XQ, Matsui A, Ashihara H (2008). Biosynthesis of trigonelline from nicotinate mononucleotide in mungbean seedlings. Phytochemistry 69, 390-395. |
| [32] | Zong ZY, Liu J, Wang N, Yang CM, Wang QT, Zhang WH, Chen YL, Liu XH, Deng HT (2021). Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation to prevent liver fibrosis via promoting PGE2 degradation. Free Radical Biol Med 162, 571-581. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||