

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 812-828.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17179 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17179
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yang Miao1,2,3, Meng Yingying1,3, Chu Yadong1, Xue Song1,*( )
)
Received:2017-09-24
Online:2018-11-01
Published:2018-12-05
Contact:
Xue Song
Yang Miao, Meng Yingying, Chu Yadong, Xue Song. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Polar Glycerolipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii based on LC-MS Techniques[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(6): 812-828.
| Lipids | Classes | Adduct ion | Scanning mode | Mass of characteristic fragment (m/z) | Chemical formula of characteristic fragment | Collision energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolipids | MGDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 179 | [C6H13NO5] | 20 |
| DGDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 341 | [C12H23NO10] | 20 | |
| SQDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 261 | [C6H15NO8S] | 32 | |
| Phospholipids | PE | [M+H]+ | NL | 141 | [C2H8NO4P] | 28 |
| PG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 189 | [C3H12NO6P] | 15 | |
| PI | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 277 | [C6H16NO9P] | 27 | |
| Betaine lipids | DGTS | [M+H]+ | PIS | 236 | [C10H22NO5]+ | 43 |
Table 1 Parameters of neutral loss or precursor ion scanning for the glycerolipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
| Lipids | Classes | Adduct ion | Scanning mode | Mass of characteristic fragment (m/z) | Chemical formula of characteristic fragment | Collision energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolipids | MGDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 179 | [C6H13NO5] | 20 |
| DGDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 341 | [C12H23NO10] | 20 | |
| SQDG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 261 | [C6H15NO8S] | 32 | |
| Phospholipids | PE | [M+H]+ | NL | 141 | [C2H8NO4P] | 28 |
| PG | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 189 | [C3H12NO6P] | 15 | |
| PI | [M+NH4]+ | NL | 277 | [C6H16NO9P] | 27 | |
| Betaine lipids | DGTS | [M+H]+ | PIS | 236 | [C10H22NO5]+ | 43 |
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG 34:7 | 762.5156 | C43H72NO10 | 1 | MGDG 18:3/16:4 | 762.5 | 335.2 |
| MGDG 34:6 | 764.5312 | C43H74NO10 | 2 | MGDG 18:3/16:3 | 764.5 | 335.2 |
| 3 | MGDG 18:2/16:4 | 764.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 4 | MGDG 18:4/16:2 | 764.5 | 309.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:5 | 766.5469 | C43H76NO10 | 5 | MGDG 18:3/16:2 | 766.5 | 335.2 |
| 6 | MGDG 18:2/16:3 | 766.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 7 | MGDG 18:1/16:4 | 766.5 | 339.2 | |||
| 8 | MGDG 18:4/16:1 | 766.5 | 333.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:4 | 768.5625 | C43H78NO10 | 9 | MGDG 18:1/16:3 | 768.5 | 339.2 |
| 10 | MGDG 18:2/16:2 | 768.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 11 | MGDG 18:3/16:1 | 768.5 | 311.2 | |||
| 12 | MGDG 18:4/16:0 | 768.5 | 313.2 | |||
| 13 | MGDG 18:0/16:4 | 768.5 | 341.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:3 | 770.5781 | C43H80NO10 | 14 | MGDG 18:1/16:2 | 770.5 | 339.2 |
| 15 | MGDG 18:2/16:1 | 770.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 16 | MGDG 18:3/16:0 | 770.5 | 335.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:2 | 772.5938 | C43H82NO10 | 17 | MGDG 18:1/16:1 | 772.5 | 339.2 |
| 18 | MGDG 18:0/16:2 | 772.5 | 341.2 | |||
| 19 | MGDG 18:2/16:0 | 772.5 | 313.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:1 | 774.6094 | C43H84NO10 | 20 | MGDG 18:1/16:0 | 774.6 | 339.2 |
| 21 | MGDG 18:0/16:1 | 774.6 | 341.2 | |||
| DGDG 32:3 | 904.5997 | C47H86NO15 | 22 | DGDG 16:0/16:3 | 904.5 | 313.2 |
| 23 | DGDG 16:1/16:2 | 904.5 | 311.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:7 | 924.5684 | C49H82NO15 | 24 | DGDG 18:3/16:4 | 924.5 | 335.2 |
| DGDG 34:6 | 926.5840 | C49H84NO15 | 25 | DGDG 18:3/16:3 | 926.5 | 335.2 |
| 26 | DGDG 18:2/16:4 | 926.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 27 | DGDG 18:4/16:2 | 926.5 | 333.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:5 | 928.5997 | C49H86NO15 | 28 | DGDG 18:2/16:3 | 928.5 | 337.2 |
| 29 | DGDG 18:3/16:2 | 928.5 | 335.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:4 | 930.6153 | C49H88NO15 | 30 | DGDG 18:3/16:1 | 930.6 | 335.2 |
| 31 | DGDG 18:2/16:2 | 930.6 | 337.2 | |||
| 32 | DGDG 18:1/16:3 | 930.6 | 339.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:3 | 932.6309 | C49H90NO15 | 33 | DGDG 18:1/16:2 | 932.6 | 339.2 |
| 34 | DGDG 18:3/16:0 | 932.6 | 313.2 | |||
| 35 | DGDG 18:2/16:1 | 932.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:2 | 934.6466 | C49H92NO15 | 36 | DGDG 18:1/16:1 | 934.6 | 339.2 |
| 37 | DGDG 18:2/16:0 | 934.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:1 | 936.6622 | C49H94NO15 | 38 | DGDG 18:1/16:0 | 936.6 | 339.2 |
| DGDG 34:0 | 938.6779 | C49H96NO15 | 39 | DGDG 18:0/16:0 | 938.6 | 341.2 |
| DGDG 36:4 | 958.6466 | C51H92NO15 | 40 | DGDG 18:1/18:3 | 958.6 | 339.2 |
| 41 | DGDG 18:2/18:2 | 958.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 36:3 | 960.6622 | C51H94NO15 | 42 | DGDG 18:0/18:3 | 960.6 | 341.2 |
| SQDG 32:1 | 810.5400 | C41H80NO12S | 43 | SQDG 16:0/16:1 | 810.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 32:0 | 812.5557 | C41H82NO12S | 44 | SQDG 16:0/16:0 | 812.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:3 | 834.5400 | C43H80NO12S | 45 | SQDG 18:3/16:0 | 834.5 | 313.2 |
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
| SQDG 34:2 | 836.5557 | C43H82NO12S | 46 | SQDG 18:2/16:0 | 836.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:1 | 838.5713 | C43H84NO12S | 47 | SQDG 18:1/16:0 | 838.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:0 | 840.587 | C43H86NO12S | 48 | SQDG 18:0/16:0 | 840.5 | 341.2 |
| PE 32:2 | 688.4916 | C37H71NO8P | 49 | PE 16:1/16:1 | 688.4 | 547.4 |
| PE 32:1 | 690.5073 | C37H73NO8P | 50 | PE 16:0/16:1 | 690.5 | 549.5 |
| PE 32:0 | 692.5229 | C37H75NO8P | 51 | PE 16:0/16:0 | 692.5 | 551.5 |
| PE 34:4 | 712.4916 | C39H71NO8P | 52 | PE 16:0/18:3 | 714.5 | 573.5 |
| PE 34:2 | 716.5229 | C39H75NO8P | 53 | PE 34:2 | 716.5 | 575.5 |
| PE 34:1 | 718.5386 | C39H77NO8P | 54 | PE 16:0/18:1 | 718.5 | 577.5 |
| PE 36:6 | 736.4916 | C41H71NO8P | 55 | PE 18:3/18:3 | 736.4 | 595.4 |
| PE 36:5 | 738.5073 | C41H73NO8P | 56 | PE 18:2/18:3 | 738.5 | 597.5 |
| PE 36:4 | 740.5229 | C41H75NO8P | 57 | PE 36:4 | 740.5 | 599.5 |
| PE 36:3 | 742.5386 | C41H77NO8P | 58 | PE 18:0/18:3 | 742.5 | 601.5 |
| PE 36:2 | 744.5543 | C41H79NO8P | 59 | PE 18:1/18:1 | 744.5 | 603.5 |
| PG 32:2 | 736.5128 | C38H75NO10P | 60 | PG 16:1/16:1 | 736.5 | 547.5 |
| PG 32:1 | 738.5284 | C38H77NO10P | 61 | PG 16:0/16:1 | 738.5 | 549.5 |
| PG 32:0 | 740.5441 | C38H79NO10P | 62 | PG 16:0/16:0 | 740.5 | 551.5 |
| PG 34:4 | 760.5128 | C40H75NO10P | 63 | PG 18:3/16:1 | 760.5 | 571.5 |
| PG 34:3 | 762.5284 | C40H77NO10P | 64 | PG 34:3 | 762.5 | 573.5 |
| PG 34:2 | 764.5441 | C40H79NO10P | 65 | PG 34:2 | 764.5 | 575.5 |
| PG 34:1 | 766.5598 | C40H81NO10P | 66 | PG 18:1/16:0 | 766.5 | 577.5 |
| PG 34:0 | 768.5754 | C40H83NO10P | 67 | PG 18:0/16:0 | 768.5 | 579.5 |
| PI 34:3 | 850.5445 | C43H81NO13P | 68 | PI 18:3/16:0 | 850.5 | 573.5 |
| PI 34:2 | 852.5601 | C43H83NO13P | 69 | PI 34:2 | 852.5 | 575.5 |
| PI 34:1 | 854.5757 | C43H85NO13P | 70 | PI 18:1/16:0 | 854.5 | 577.5 |
| PI 34:0 | 856.5914 | C43H87NO13P | 71 | PI 18:0/16:0 | 856.5 | 579.5 |
| DGTS 32:4 | 704.5464 | C42H74NO7 | 72 | DGTS 16:0/16:4 | 704.5 | 474.4 |
| 73 | DGTS 16:3/16:1 | 704.5 | 472.4 | |||
| 74 | DGTS 16:2/16:2 | 704.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 32:3 | 706.5621 | C42H76NO7 | 75 | DGTS 16:0/16:3 | 706.5 | 474.4 |
| 76 | DGTS 16:2/16:1 | 706.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 32:2 | 708.5778 | C42H78NO7 | 77 | DGTS 16:0/16:2 | 708.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 32:1 | 710.5934 | C42H80NO7 | 78 | DGTS 16:0/16:1 | 710.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 32:0 | 712.6091 | C42H82NO7 | 79 | DGTS 16:0/16:0 | 712.6 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:7 | 726.5308 | C44H72NO7 | 80 | DGTS 16:4/18:3 | 726.5 | 466.4 |
| 81 | DGTS 16:3/18:4 | 726.5 | 468.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:6 | 728.5464 | C44H74NO7 | 82 | DGTS 16:3/18:3 | 728.5 | 468.4 |
| 83 | DGTS 16:4/18:2 | 728.5 | 466.4 | |||
| 84 | DGTS 16:2/18:4 | 728.5 | 494.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:5 | 730.5621 | C44H76NO7 | 85 | DGTS 16:4/18:1 | 730.5 | 500.4 |
| 86 | DGTS 16:1/18:4 | 730.5 | 472.4 | |||
| 87 | DGTS 16:3/18:2 | 730.5 | 498.4 | |||
| 88 | DGTS 16:2/18:3 | 730.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:4 | 732.5778 | C44H78NO7 | 89 | DGTS 16:1/18:3 | 732.5 | 496.4 |
| 90 | DGTS 16:2/18:2 | 732.5 | 498.4 | |||
| 91 | DGTS 16:3/18:1 | 732.5 | 500.4 | |||
| 92 | DGTS 16:0/18:4 | 732.5 | 474.4 | |||
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
| 93 | DGTS 16:4/18:0 | 732.5 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:3 | 734.5934 | C44H80NO7 | 94 | DGTS 16:0/18:3 | 734.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:2 | 736.6091 | C44H82NO7 | 95 | DGTS 16:0/18:2 | 736.6 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:1 | 738.6247 | C44H84NO7 | 96 | DGTS 16:0/18:1 | 738.6 | 474.4 |
| 97 | DGTS 16:1/18:0 | 738.6 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:7 | 754.5621 | C46H76NO7 | 98 | DGTS 18:3/18:4 | 754.5 | 496.4 |
| DGTS 36:6 | 756.5778 | C46H78NO7 | 99 | DGTS 18:3/18:3 | 756.5 | 496.4 |
| 100 | DGTS 18:4/18:2 | 756.5 | 498.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:5 | 758.5934 | C46H80NO7 | 101 | DGTS 18:2/18:3 | 758.5 | 498.4 |
| 102 | DGTS 18:1/18:4 | 758.5 | 500.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:4 | 760.6091 | C46H82NO7 | 103 | DGTS 18:2/18:2 | 760.6 | 498.4 |
| 104 | DGTS 18:1/18:3 | 760.6 | 500.4 | |||
| 105 | DGTS 18:0/18:4 | 760.6 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:3 | 762.6247 | C46H84NO7 | 106 | DGTS 18:0/18:3 | 762.6 | 502.4 |
| 107 | DGTS 18:1/18:2 | 762.6 | 500.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:2 | 764.6404 | C46H86NO7 | 108 | DGTS 18:1/18:1 | 764.6 | 500.4 |
| 109 | DGTS 18:0/18:2 | 764.6 | 502.4 | |||
Table 2 The molecular species of polar glycerolipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii identified by UPLC-Q-Trap/MS and UPLC-Orbitrap/MS2 and the information of 109 ion pairs of polar lipids in MRM mode
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG 34:7 | 762.5156 | C43H72NO10 | 1 | MGDG 18:3/16:4 | 762.5 | 335.2 |
| MGDG 34:6 | 764.5312 | C43H74NO10 | 2 | MGDG 18:3/16:3 | 764.5 | 335.2 |
| 3 | MGDG 18:2/16:4 | 764.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 4 | MGDG 18:4/16:2 | 764.5 | 309.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:5 | 766.5469 | C43H76NO10 | 5 | MGDG 18:3/16:2 | 766.5 | 335.2 |
| 6 | MGDG 18:2/16:3 | 766.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 7 | MGDG 18:1/16:4 | 766.5 | 339.2 | |||
| 8 | MGDG 18:4/16:1 | 766.5 | 333.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:4 | 768.5625 | C43H78NO10 | 9 | MGDG 18:1/16:3 | 768.5 | 339.2 |
| 10 | MGDG 18:2/16:2 | 768.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 11 | MGDG 18:3/16:1 | 768.5 | 311.2 | |||
| 12 | MGDG 18:4/16:0 | 768.5 | 313.2 | |||
| 13 | MGDG 18:0/16:4 | 768.5 | 341.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:3 | 770.5781 | C43H80NO10 | 14 | MGDG 18:1/16:2 | 770.5 | 339.2 |
| 15 | MGDG 18:2/16:1 | 770.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 16 | MGDG 18:3/16:0 | 770.5 | 335.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:2 | 772.5938 | C43H82NO10 | 17 | MGDG 18:1/16:1 | 772.5 | 339.2 |
| 18 | MGDG 18:0/16:2 | 772.5 | 341.2 | |||
| 19 | MGDG 18:2/16:0 | 772.5 | 313.2 | |||
| MGDG 34:1 | 774.6094 | C43H84NO10 | 20 | MGDG 18:1/16:0 | 774.6 | 339.2 |
| 21 | MGDG 18:0/16:1 | 774.6 | 341.2 | |||
| DGDG 32:3 | 904.5997 | C47H86NO15 | 22 | DGDG 16:0/16:3 | 904.5 | 313.2 |
| 23 | DGDG 16:1/16:2 | 904.5 | 311.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:7 | 924.5684 | C49H82NO15 | 24 | DGDG 18:3/16:4 | 924.5 | 335.2 |
| DGDG 34:6 | 926.5840 | C49H84NO15 | 25 | DGDG 18:3/16:3 | 926.5 | 335.2 |
| 26 | DGDG 18:2/16:4 | 926.5 | 337.2 | |||
| 27 | DGDG 18:4/16:2 | 926.5 | 333.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:5 | 928.5997 | C49H86NO15 | 28 | DGDG 18:2/16:3 | 928.5 | 337.2 |
| 29 | DGDG 18:3/16:2 | 928.5 | 335.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:4 | 930.6153 | C49H88NO15 | 30 | DGDG 18:3/16:1 | 930.6 | 335.2 |
| 31 | DGDG 18:2/16:2 | 930.6 | 337.2 | |||
| 32 | DGDG 18:1/16:3 | 930.6 | 339.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:3 | 932.6309 | C49H90NO15 | 33 | DGDG 18:1/16:2 | 932.6 | 339.2 |
| 34 | DGDG 18:3/16:0 | 932.6 | 313.2 | |||
| 35 | DGDG 18:2/16:1 | 932.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:2 | 934.6466 | C49H92NO15 | 36 | DGDG 18:1/16:1 | 934.6 | 339.2 |
| 37 | DGDG 18:2/16:0 | 934.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 34:1 | 936.6622 | C49H94NO15 | 38 | DGDG 18:1/16:0 | 936.6 | 339.2 |
| DGDG 34:0 | 938.6779 | C49H96NO15 | 39 | DGDG 18:0/16:0 | 938.6 | 341.2 |
| DGDG 36:4 | 958.6466 | C51H92NO15 | 40 | DGDG 18:1/18:3 | 958.6 | 339.2 |
| 41 | DGDG 18:2/18:2 | 958.6 | 337.2 | |||
| DGDG 36:3 | 960.6622 | C51H94NO15 | 42 | DGDG 18:0/18:3 | 960.6 | 341.2 |
| SQDG 32:1 | 810.5400 | C41H80NO12S | 43 | SQDG 16:0/16:1 | 810.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 32:0 | 812.5557 | C41H82NO12S | 44 | SQDG 16:0/16:0 | 812.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:3 | 834.5400 | C43H80NO12S | 45 | SQDG 18:3/16:0 | 834.5 | 313.2 |
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
| SQDG 34:2 | 836.5557 | C43H82NO12S | 46 | SQDG 18:2/16:0 | 836.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:1 | 838.5713 | C43H84NO12S | 47 | SQDG 18:1/16:0 | 838.5 | 313.2 |
| SQDG 34:0 | 840.587 | C43H86NO12S | 48 | SQDG 18:0/16:0 | 840.5 | 341.2 |
| PE 32:2 | 688.4916 | C37H71NO8P | 49 | PE 16:1/16:1 | 688.4 | 547.4 |
| PE 32:1 | 690.5073 | C37H73NO8P | 50 | PE 16:0/16:1 | 690.5 | 549.5 |
| PE 32:0 | 692.5229 | C37H75NO8P | 51 | PE 16:0/16:0 | 692.5 | 551.5 |
| PE 34:4 | 712.4916 | C39H71NO8P | 52 | PE 16:0/18:3 | 714.5 | 573.5 |
| PE 34:2 | 716.5229 | C39H75NO8P | 53 | PE 34:2 | 716.5 | 575.5 |
| PE 34:1 | 718.5386 | C39H77NO8P | 54 | PE 16:0/18:1 | 718.5 | 577.5 |
| PE 36:6 | 736.4916 | C41H71NO8P | 55 | PE 18:3/18:3 | 736.4 | 595.4 |
| PE 36:5 | 738.5073 | C41H73NO8P | 56 | PE 18:2/18:3 | 738.5 | 597.5 |
| PE 36:4 | 740.5229 | C41H75NO8P | 57 | PE 36:4 | 740.5 | 599.5 |
| PE 36:3 | 742.5386 | C41H77NO8P | 58 | PE 18:0/18:3 | 742.5 | 601.5 |
| PE 36:2 | 744.5543 | C41H79NO8P | 59 | PE 18:1/18:1 | 744.5 | 603.5 |
| PG 32:2 | 736.5128 | C38H75NO10P | 60 | PG 16:1/16:1 | 736.5 | 547.5 |
| PG 32:1 | 738.5284 | C38H77NO10P | 61 | PG 16:0/16:1 | 738.5 | 549.5 |
| PG 32:0 | 740.5441 | C38H79NO10P | 62 | PG 16:0/16:0 | 740.5 | 551.5 |
| PG 34:4 | 760.5128 | C40H75NO10P | 63 | PG 18:3/16:1 | 760.5 | 571.5 |
| PG 34:3 | 762.5284 | C40H77NO10P | 64 | PG 34:3 | 762.5 | 573.5 |
| PG 34:2 | 764.5441 | C40H79NO10P | 65 | PG 34:2 | 764.5 | 575.5 |
| PG 34:1 | 766.5598 | C40H81NO10P | 66 | PG 18:1/16:0 | 766.5 | 577.5 |
| PG 34:0 | 768.5754 | C40H83NO10P | 67 | PG 18:0/16:0 | 768.5 | 579.5 |
| PI 34:3 | 850.5445 | C43H81NO13P | 68 | PI 18:3/16:0 | 850.5 | 573.5 |
| PI 34:2 | 852.5601 | C43H83NO13P | 69 | PI 34:2 | 852.5 | 575.5 |
| PI 34:1 | 854.5757 | C43H85NO13P | 70 | PI 18:1/16:0 | 854.5 | 577.5 |
| PI 34:0 | 856.5914 | C43H87NO13P | 71 | PI 18:0/16:0 | 856.5 | 579.5 |
| DGTS 32:4 | 704.5464 | C42H74NO7 | 72 | DGTS 16:0/16:4 | 704.5 | 474.4 |
| 73 | DGTS 16:3/16:1 | 704.5 | 472.4 | |||
| 74 | DGTS 16:2/16:2 | 704.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 32:3 | 706.5621 | C42H76NO7 | 75 | DGTS 16:0/16:3 | 706.5 | 474.4 |
| 76 | DGTS 16:2/16:1 | 706.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 32:2 | 708.5778 | C42H78NO7 | 77 | DGTS 16:0/16:2 | 708.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 32:1 | 710.5934 | C42H80NO7 | 78 | DGTS 16:0/16:1 | 710.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 32:0 | 712.6091 | C42H82NO7 | 79 | DGTS 16:0/16:0 | 712.6 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:7 | 726.5308 | C44H72NO7 | 80 | DGTS 16:4/18:3 | 726.5 | 466.4 |
| 81 | DGTS 16:3/18:4 | 726.5 | 468.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:6 | 728.5464 | C44H74NO7 | 82 | DGTS 16:3/18:3 | 728.5 | 468.4 |
| 83 | DGTS 16:4/18:2 | 728.5 | 466.4 | |||
| 84 | DGTS 16:2/18:4 | 728.5 | 494.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:5 | 730.5621 | C44H76NO7 | 85 | DGTS 16:4/18:1 | 730.5 | 500.4 |
| 86 | DGTS 16:1/18:4 | 730.5 | 472.4 | |||
| 87 | DGTS 16:3/18:2 | 730.5 | 498.4 | |||
| 88 | DGTS 16:2/18:3 | 730.5 | 470.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:4 | 732.5778 | C44H78NO7 | 89 | DGTS 16:1/18:3 | 732.5 | 496.4 |
| 90 | DGTS 16:2/18:2 | 732.5 | 498.4 | |||
| 91 | DGTS 16:3/18:1 | 732.5 | 500.4 | |||
| 92 | DGTS 16:0/18:4 | 732.5 | 474.4 | |||
| Lipid species (C:N) | Theoretical mass (m/z) | Chemical formula | No. | Molecular species (sn-1/sn-2) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
| 93 | DGTS 16:4/18:0 | 732.5 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 34:3 | 734.5934 | C44H80NO7 | 94 | DGTS 16:0/18:3 | 734.5 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:2 | 736.6091 | C44H82NO7 | 95 | DGTS 16:0/18:2 | 736.6 | 474.4 |
| DGTS 34:1 | 738.6247 | C44H84NO7 | 96 | DGTS 16:0/18:1 | 738.6 | 474.4 |
| 97 | DGTS 16:1/18:0 | 738.6 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:7 | 754.5621 | C46H76NO7 | 98 | DGTS 18:3/18:4 | 754.5 | 496.4 |
| DGTS 36:6 | 756.5778 | C46H78NO7 | 99 | DGTS 18:3/18:3 | 756.5 | 496.4 |
| 100 | DGTS 18:4/18:2 | 756.5 | 498.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:5 | 758.5934 | C46H80NO7 | 101 | DGTS 18:2/18:3 | 758.5 | 498.4 |
| 102 | DGTS 18:1/18:4 | 758.5 | 500.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:4 | 760.6091 | C46H82NO7 | 103 | DGTS 18:2/18:2 | 760.6 | 498.4 |
| 104 | DGTS 18:1/18:3 | 760.6 | 500.4 | |||
| 105 | DGTS 18:0/18:4 | 760.6 | 502.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:3 | 762.6247 | C46H84NO7 | 106 | DGTS 18:0/18:3 | 762.6 | 502.4 |
| 107 | DGTS 18:1/18:2 | 762.6 | 500.4 | |||
| DGTS 36:2 | 764.6404 | C46H86NO7 | 108 | DGTS 18:1/18:1 | 764.6 | 500.4 |
| 109 | DGTS 18:0/18:2 | 764.6 | 502.4 | |||
| Lipid class | Adduct ion | Ion mode | CE (eV) | CID fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 50 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-179]+, [M+NH4-197]+, [M+NH4-179-RxCOOH]+ |
| DGDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 70 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-180]+, [M+NH4-341]+, [M+NH4- 359]+, [M+NH4-341-RxCOOH]+ |
| SQDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 50 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-261]+, [M+NH4-261-RxCO+H]+ |
| PE | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RxCO+H]- |
| PG | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RxCO+H]-, [PA-H-RxCOOH]- |
| PI | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RCxO+H]-, [M-H-R1COOH-R2- COOH]-, [PA-H-RxCOOH]-, 241 |
| DGTS | [M+H]+ | + | 35 | [M+H-RxCOOH]+, [M+H-RxCO+H]+, 236 |
Table 3 The collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragments of glycerolipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
| Lipid class | Adduct ion | Ion mode | CE (eV) | CID fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 50 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-179]+, [M+NH4-197]+, [M+NH4-179-RxCOOH]+ |
| DGDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 70 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-180]+, [M+NH4-341]+, [M+NH4- 359]+, [M+NH4-341-RxCOOH]+ |
| SQDG | [M+NH4]+ | + | 50 | [M+NH4-17]+, [M+NH4-35]+, [M+NH4-261]+, [M+NH4-261-RxCO+H]+ |
| PE | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RxCO+H]- |
| PG | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RxCO+H]-, [PA-H-RxCOOH]- |
| PI | [M-H]- | - | 35 | [RxCOO]-, [M-H-RxCOOH]-, [M-H-RCxO+H]-, [M-H-R1COOH-R2- COOH]-, [PA-H-RxCOOH]-, 241 |
| DGTS | [M+H]+ | + | 35 | [M+H-RxCOOH]+, [M+H-RxCO+H]+, 236 |
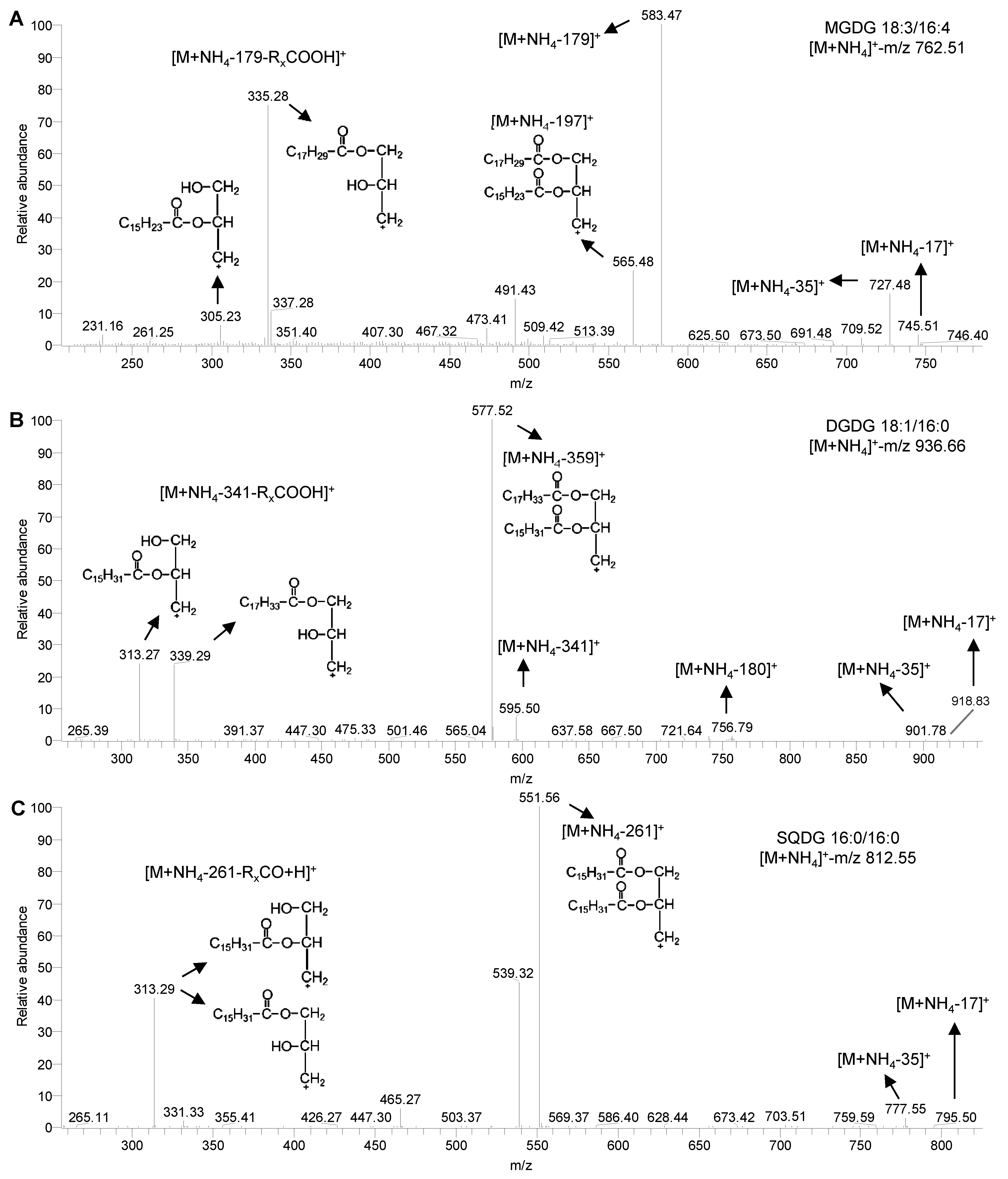
Figure 1 ESI-MS/MS spectra of glycolipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii(A) MS/MS spectra of MGDG 18:3/16:4; (B) MS/MS spectra of DGDG 18:1/16:0; (C) MS/MS spectra of SQDG 16:0/16:0. MGDG, DGDG and SQDG see Table 1.
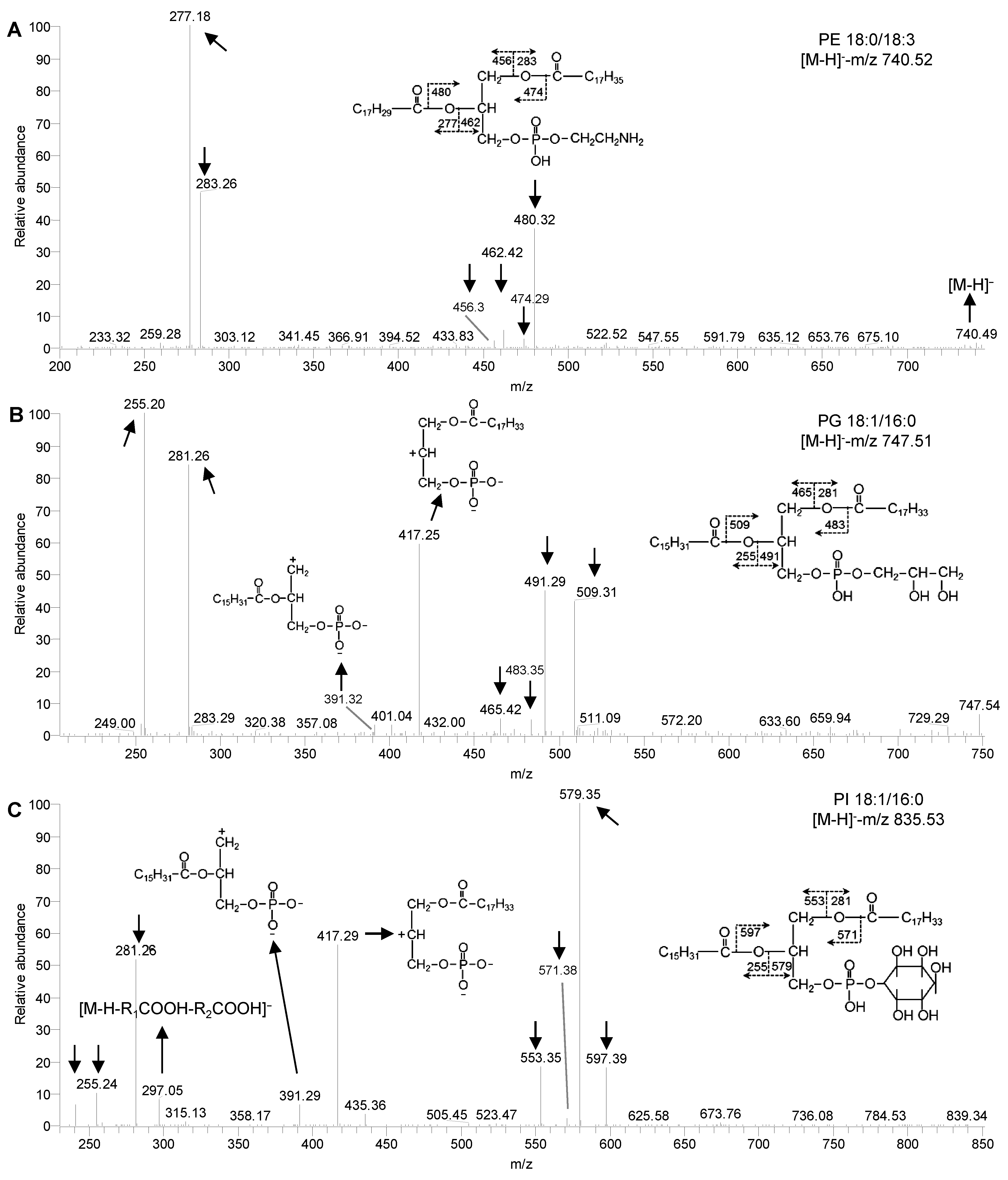
Figure 2 ESI-MS/MS spectra of phospholipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii(A) MS/MS spectra of PE 18:0/18:3; (B) MS/MS spectra of PG 18:1/16:0; (C) MS/MS spectra of PI 18:1/16:0. PE, PG and PI see Table 1.
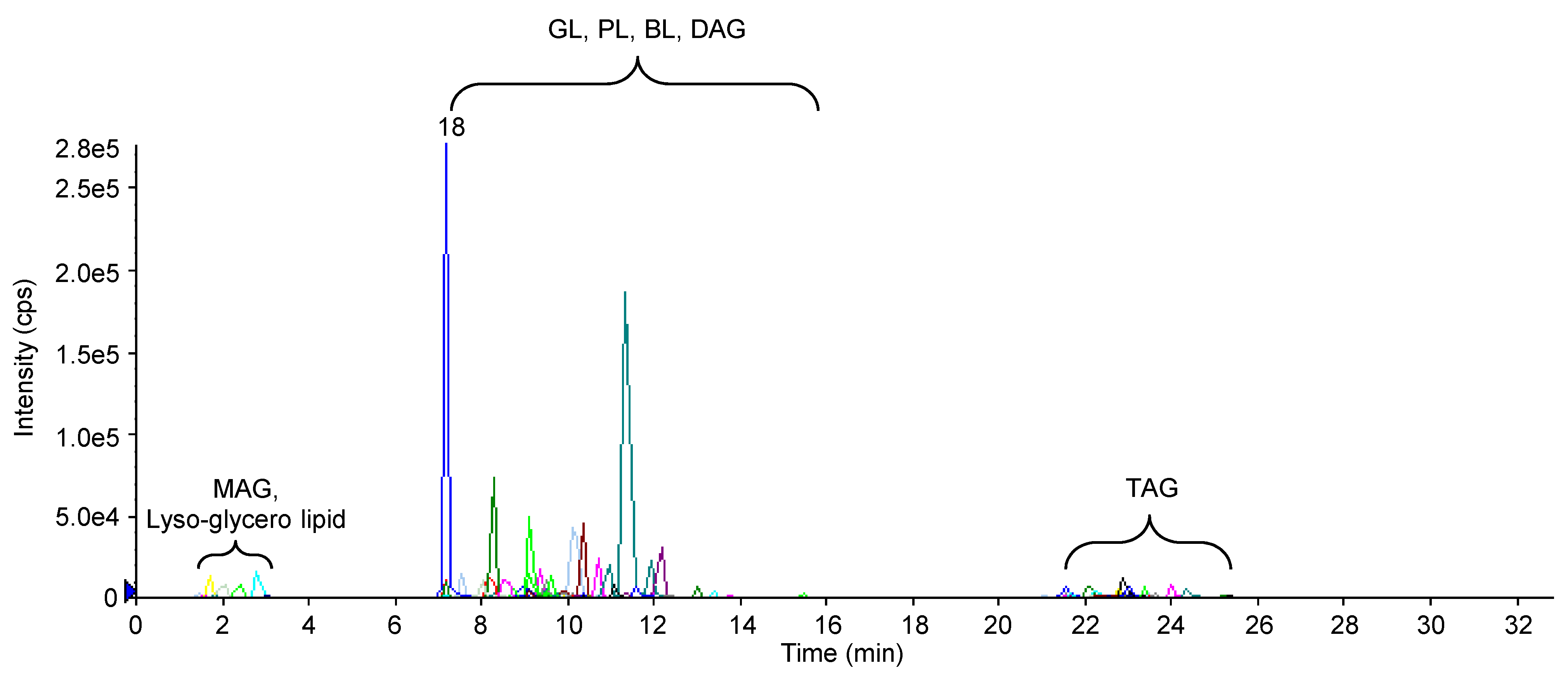
Figure 4 The extracted ion chromatography (XIC) of polar lipids of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in positive and MRM scanning mode MAG: Monoacylglycerol; GL: Glycolipid; PL: Phospholipid; BL: Betaine lipid; DAG: Diacylglycerol; TAG: Triacylglycerol
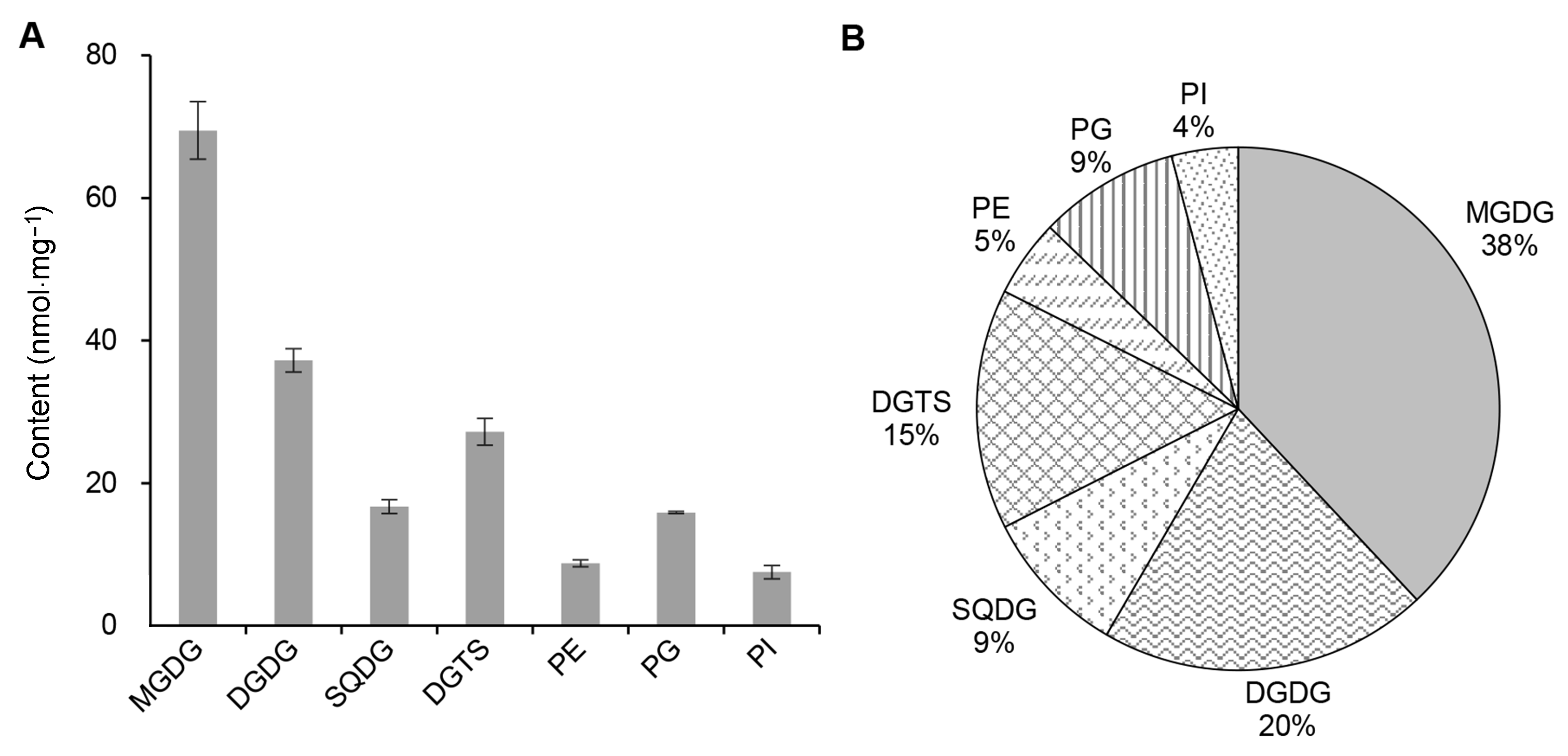
Figure 5 The glycerolipid components of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii(A) The content of the individual polar glycerolipid of C. reinhardtii (nmol·mg-1); (B) The relative abundance (%) of the individual polar glycerolipid of C. reinhardtii. MGDG, DGDG, SQDG, PE, PG, PI and DGTS see Table 1.
| Lipid standard | Linear equation | Correlation coefficient (R2) | Linear range (nmol·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG 18:0/18:0 | y=6.00E-05x+2.50E-01 | 0.9981 | 0.37-39.88 |
| DGDG 18:0/18:0 | y=6.45E-04x+7.98E-01 | 0.9989 | 1.26-41.38 |
| SQDG 18:3/16:0 | y=2.18E-04x-3.30E-01 | 0.9919 | 0.02-35.95 |
| PE 17:0/17:0 | y=2.39E-04x+4.26E-01 | 0.9994 | 1.02-27.76 |
| PG 17:0/17:0 | y=9.25E-05x+6.39E-01 | 0.9971 | 0.68-26.02 |
| PI 16:0/16:0 | y=1.49E-04x+1.65E-01 | 0.9993 | 0.23-22.61 |
| DGTS 16:0/16:0 | y=1.37E-05x+8.63E-02 | 0.9998 | 1.00-28.11 |
Table 4 Linear correlations between the concentrations and the peak areas of lipid standards
| Lipid standard | Linear equation | Correlation coefficient (R2) | Linear range (nmol·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGDG 18:0/18:0 | y=6.00E-05x+2.50E-01 | 0.9981 | 0.37-39.88 |
| DGDG 18:0/18:0 | y=6.45E-04x+7.98E-01 | 0.9989 | 1.26-41.38 |
| SQDG 18:3/16:0 | y=2.18E-04x-3.30E-01 | 0.9919 | 0.02-35.95 |
| PE 17:0/17:0 | y=2.39E-04x+4.26E-01 | 0.9994 | 1.02-27.76 |
| PG 17:0/17:0 | y=9.25E-05x+6.39E-01 | 0.9971 | 0.68-26.02 |
| PI 16:0/16:0 | y=1.49E-04x+1.65E-01 | 0.9993 | 0.23-22.61 |
| DGTS 16:0/16:0 | y=1.37E-05x+8.63E-02 | 0.9998 | 1.00-28.11 |

Figure 6 The constituents and contents of each molecular species of polar lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii(A) The content of the individual molecular species of MGDG; (B) The content of the individual molecular species of SQDG; (C) The content of the individual molecular species of PG; (D) The content of the individual molecular species of DGDG; (E) The content of the individual molecular species of PE; (F) The content of the individual molecular species of DGTS; (G) The content of the individual molecular species of PI. MGDG, DGDG, SQDG, PE, PG, PI and DGTS see Table 1.
| [1] |
王涛, 梅旭荣, 钟秀丽, 李玉中 (2010). 脂质组学研究方法及其应用. 植物学报 45, 249-257.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Abida H, Dolch LJ, Mei C, Villanova V, Conte M, Block MA, Finazzi G, Bastien O, Tirichine L, Bowler C, Rébeillé F, Petroutsos D, Jouhet J, Maréchal E (2015). Membrane glycerolipid remodeling triggered by nitrogen and phosphorus starvation in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Plant Physiol 167, 118-136. |
| [3] |
Allen JW, DiRusso CC, Black PN (2017). Carbon and acyl chain flux during stress-induced triglyceride accumulation by stable isotopic labeling of the polar microalga Coc- comyxa subellipsoidea C169. J Biol Chem 292, 361-374.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Anesi A, Guella G (2015). A fast liquid chromatography- mass spectrometry methodology for membrane lipid pro- filing through hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatog- raphy.J Chromatogr A 1384, 44-52.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Bijttebier SKA, D’Hondt E, Hermans N, Apers S, Voorsp- oels S (2013). Unravelling ionization and fragmentation pathways of carotenoids using orbitrap technology: a first step towards identification of unknowns.J Mass Spectrom 48, 740-754.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification.Can J Biochem Physiol 37, 911-917.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Botella C, Jouhet J, Block MA (2017). Importance of phosphatidylcholine on the chloroplast surface.Prog Lipid Res 65, 12-23.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Brouwers JF (2011). Liquid chromatographic-mass spectro- metric analysis of phospholipids. Chromatography, ionization and quantification.Biochim Biophys Acta 1811, 763-775.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Caprioli G, Cahill M, Logrippo S, James K (2015). Elucida- tion of the mass fragmentation pathways of tomatidine and B1-hydroxytomatine using orbitrap mass spectrometry.Nat Prod Commun 10, 575-576. |
| [10] |
Chen SL, Kong HW, Lu X, Li Y, Yin PY, Zeng ZD, Xu GW (2013). Pseudotargeted metabolomics method and its application in serum biomarker discovery for hepatocel- lular carcinoma based on ultra high-performance liquid chromatography/triple quadrupole mass spectrometry.Anal Chem 85, 8326-8333.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Eliuk S, Makarov A (2015). Evolution of Orbitrap mass spectrometry instrumentation.Rev Anal Chem 8, 61-80.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Geiger T, Cox J, Mann M (2010). Proteomics on an Orbitrap benchtop mass spectrometer using all-ion fragmentation.Mol Cell Proteomics 9, 2252-2261.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Giroud C, Gerber A, Eichenberger W (1988). Lipids of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Analysis of molecular species and intracellular site (s) of biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 29, 587-595. |
| [14] | Han DX, Jia J, Li J, Sommerfeld M, Xu J, Hu Q (2017). Metabolic remodeling of membrane glycerolipids in the microalgaNannochloropsis oceanica under nitrogen depri- vation. Front Mar Sci 4, 242. |
| [15] | Han XL (2016a). Fragmentation patterns of glycerolipids. In: Han XL, ed. Lipidomics: Comprehensive Mass Spectro- metry of Lipids. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporation. pp. 217-228. |
| [16] | Han XL (2016b). Quantification of individual lipid species in lipidomics. In: Han XL, ed. Lipidomics: Comprehensive Mass Spectrometry of Lipids. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporation. pp. 305-334. |
| [17] |
Han XL, Gross RW (2003). Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry: a bridge to lipidomics.J Lipid Res 44, 1071-1079.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Horn PJ, Benning C (2016). The plant lipidome in human and environmental health.Science 353, 1228-1232.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Hu QZ, Noll RJ, Li HY, Makarov A, Hardman M, Cooks RG (2005). The Orbitrap: a new mass spectrometer.J Mass Spectrom 40, 430-443.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Légeret B, Schulz-Raffelt M, Nguyen HM, Auroy P, Beisson F, Peltier G, Blanc G, Li-Beisson Y (2016). Lipidomic and transcriptomic analyses of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under heat stress unveil a direct route for the conversion of membrane lipids into storage lipids. Plant Cell Environ 39, 834-847.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Li J, Han DX, Wang DM, Ning K, Jia J, Wei L, Jing XY, Huang S, Chen J, Li YT, Hu Q, Xu J (2014). Choreo- graphy of transcriptomes and lipidomes of Nannochlo- ropsis reveals the mechanisms of oil synthesis in micro- algae. Plant Cell 26, 1645-1665. |
| [22] |
Li NN, Xu CC, Li-Beisson Y, Philippar K (2016). Fatty acid and lipid transport in plant cells.Trends Plant Sci 21, 145-158.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | Li-Beisson Y, Beisson F, Riekhof W (2015). Metabolism of acyl-lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 82, 504-522. |
| [24] | Li-Beisson Y, Nakamura Y, Harwood J (2016). Lipids: from chemical structures, biosynthesis, and analyses to industrial applications. In: Nakamura Y, Li-Beisson Y, eds. Lipids in Plant and Algae Development. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 1-18. |
| [25] |
Liu BS, Benning C (2013). Lipid metabolism in microalgae distinguishes itself.Curr Opin Biotechnol 24, 300-309.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Martin GJO, Hill DRA, Olmstead ILD, Bergamin A, Shears MJ, Dias DA, Kentish SE, Scales PJ, Botté CY, Callahan DL (2014). Lipid profile remodeling in response to nitrogen deprivation in the microalgae Chlorella sp.(Trebouxiophyceae) and Nannochloropsis sp. 9, e103389. |
| [27] | Meng YY, Cao XP, Yao CH, Xue S, Yang Q (2017). Identi- fication of the role of polar glycerolipids in lipid metabolism and their acyl attribution for TAG accumulation in Nanno- chloropsis oceanica. Algal Res 24, 122-129. |
| [28] |
Murphy RC, Axelsen PH (2011). Mass spectrometric analysis of long-chain lipids.Mass Spectrom Rev 30, 579-599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Overgaard AJ, Weir JM, De Souza DP, Tull D, Haase C, Meikle PJ, Pociot F (2016). Lipidomic and metabolomic characterization of a genetically modified mouse model of the early stages of human type 1 diabetes pathogenesis.Metabolomics 12, 13.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Popko J, Herrfurth C, Feussner K, Ischebeck T, Iven T, Haslam R, Hamilton M, Sayanova O, Napier J, Khozin- Goldberg I, Feussner I (2016). Metabolome analysis reveals betaine lipids as major source for triglyceride formation, and the accumulation of sedoheptulose during nitrogen-starvation of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. PLoS One 11, e0164673.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Rohmer M, Baeumlisberger D, Stahl B, Bahr U, Karas M (2011). Fragmentation of neutral oligosaccharides using the MALDI LTQ Orbitrap.Int J Mass Spectrom 305, 199-208.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Roughan GP, Slack CR (1982). Cellular organization of glycerolipid metabolism.Annu Rev Plant Biol 33, 97-132.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Schlapfer P, Eichenberger W (1983). Evidence for the involvement of diacylglyceryl (N,N,N,-trimethy homoserine) in the desaturation of oleic and linoleic acids in Chlamy- domonas reinhardi(Chlorophyceae). Plant Sci Lett 32, 243-252. |
| [34] |
Schuhmann K, Herzog R, Schwudke D, Metelmann- Strupat W, Bornstein SR, Shevchenko A (2011). Bottom-up shotgun lipidomics by higher energy collisional dissociation on LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometers.Anal Chem 83, 5480-5487.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Slatter DA, Aldrovandi M, O’Connor A, Allen SM, Brasher CJ, Murphy RC, Mecklemann S, Ravi S, Darley-Usmar V, O’Donnell VB (2016). Mapping the human platelet lipidome reveals cytosolic phospholipase A2 as a regulator of mitochondrial bioenergetics during activation.Cell Metab 23, 930-944.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
t’Kindt R, Jorge L, Dumont E, Couturon P, David F, Sandra P, Sandra K (2012). Profiling and characterizing skin ceramides using reversed-phase liquid chromato- graphy-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Anal Chem 84, 403-411.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Taguchi R, Ishikawa M (2010). Precise and global identifica- tion of phospholipid molecular species by an Orbitrap mass spectrometer and automated search engine Lipid Search.J Chromatogr A 1217, 4229-4239.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
Tarazona P, Feussner K, Feussner I (2015). An enhanced plant lipidomics method based on multiplexed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry reveals additional in- sights into cold- and drought-induced membrane remo- deling.Plant J 84, 621-633.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Tenenboim H, Burgos A, Willmitzer L, Brotman Y (2016). Using lipidomics for expanding the knowledge on lipid metabolism in plants.Biochimie 130, 91-96.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Warakanont J, Tsai CH, Michel EJS, Murphy III GR, Hsueh PY, Roston RL, Sears BB, Benning C (2015). Chloro- plast lipid transfer processes inChlamydomonas rein- hardtii involving a TRIGALACTOSYLDIACYLGLYC- EROL 2 (TGD2) orthologue. Plant J 84, 1005-1020. |
| [41] | Yang DW, Song DH, Kind T, Ma Y, Hoefkens J, Fiehn O (2015). Lipidomic analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under nitrogen and sulfur deprivation. PLoS One 10, e013-7948. |
| [42] |
Zhang JJ, Zhao CX, Zeng ZD, Luo P, Zhao YN, Zhao JY, Li LL, Lu X, Xu GW (2016). Sample-directed pseudotargeted method for the metabolic profiling analysis of rice seeds based on liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry.J Sep Sci 39, 247-255.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] | Zienkiewicz K, Du ZY, Ma W, Vollheyde K, Benning C (2016). Stress-induced neutral lipid biosynthesis in micro- algae-molecular, cellular and physiological insights.Bio- chim Biophys Acta 1861, 1269-1281. |
| [44] |
Zubarev RA, Makarov A (2013). Orbitrap mass spectrometry: Orbitrap is the newest addition to the family of high- resolution mass spectrometry analyzers. With its revolutionarily new, miniature design, Orbitrap combines high speed with excellent quantification properties, ranking favorably in many analytical applications.Anal Chem 85, 5288-5296.
DOI URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||