

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 705-723.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15201 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15201
Previous Articles Next Articles
Houqing Zeng, Yaxian Zhang, Shang Wang, Xiajun Zhang, Huizhong Wang, Liqun Du*
Received:2015-11-09
Accepted:2016-03-25
Online:2016-09-01
Published:2016-09-27
Contact:
Du Liqun
About author:# Co-first authors
Houqing Zeng, Yaxian Zhang, Shang Wang, Xiajun Zhang, Huizhong Wang, Liqun Du. Calcium/calmodulin-mediated Signal Transduction System in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 705-723.
| 蛋白种类 | 蛋白名称 | 物种 | 生理功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激酶和磷酸酶 | CBK3 | 拟南芥 | 抗热击 | Liu et al., 2008 | |
| NtCBK1 | 烟草 | 开花调控 | Hua et al., 2004 | ||
| NtCaMK1 | 烟草 | 未知 | Ma et al., 2004 | ||
| CRLK1 | 拟南芥 | 抗冷冻 | Yang et al., 2010 | ||
| CCaMK | 苜蓿、水稻和 玉米 | 共生, 抗氧化防御 | Gleason et al., 2006; Ma et al., 2012; Shi et al., 2012; Routray et al., 2013 | ||
| MPK8 | 拟南芥 | 损伤反应, ROS平衡 | Takahashi et al., 2011 | ||
| PP7 | 拟南芥 | 抗热击 | Kutuzov et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2007 | ||
| MKP1 | 拟南芥 | 抗病、抗紫外、抗盐和 抗基因毒性 | Ulm et al., 2002; Lee et al., 2008; Bartels et al., 2009; Gonzalez Besteiro et al., 2011 | ||
| OsMKP1 | 水稻 | 损伤反应 | Katou et al., 2007 | ||
| NtMKP1 | 烟草 | 抗病虫害和机械损伤 | Yamakawa et al., 2004; Oka et al., 2013 | ||
| PCaMPP | 苔藓 | 未知 | Takezawa, 2003 | ||
| 转录因子和 辅助因子 | CAMTA3 | 拟南芥 | 通用胁迫反应, 抗冷冻和 抗病虫害 | Doherty et al., 2009; Du et al., 2009; Bjornson et al., 2014 | |
| CBP60g | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Wang et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2010 | ||
| WRKY7 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Park et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2006 | ||
| MYB2 | 拟南芥 | ABA信号, 盐胁迫, 叶片衰老, 缺磷反应 | Abe et al., 2003; Yoo et al., 2005; Guo and Gan, 2011; Baek et al., 2013 | ||
| MYB91 | 拟南芥 | 叶片发育 | Han et al., 2012 | ||
| CBNAC | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Kim et al., 2007 | ||
| TGA3 | 拟南芥 | 抗病和抗重金属胁迫 | Szymanski et al., 1996; Choi et al., 2010; Farinati et al., 2010 | ||
| IQD1 | 拟南芥 | 抗虫 | Levy et al., 2005 | ||
| GT2L | 拟南芥 | 抗冷, 抗盐 | Xi et al., 2012 | ||
| BT2 | 拟南芥 | 端粒酶活性, 糖和ABA信号, 配子体发育 | Du and Poovaiah, 2004; Ren et al., 2007; Mandadi et al., 2009; Robert et al., 2009 | ||
| PCBP | 马铃薯 | 未知 | Reddy et al., 2002 | ||
| 离子通道和膜蛋白 | ACA2 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐 | Anil et al., 2008 | |
| ACA4 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐和抗病 | Geisler et al., 2000; Boursiac et al., 2010 | ||
| ACA8 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | dit Frey et al., 2012 | ||
| ACA11 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Boursiac et al., 2010 | ||
| CNGC1 | 拟南芥 | 抗重金属胁迫 | Sunkar et al., 2000 | ||
| CNGC2 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Clough et al., 2000; Ali et al., 2007 | ||
| CNGC3 | 拟南芥 | Na+/K+吸收, 抗盐 | Gobert et al., 2006 | ||
| CNGC4 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Balague et al., 2003 | ||
| CNGC10 | 拟南芥 | K+吸收, 抗盐 | Li et al., 2005; Guo et al., 2008 | ||
| CNGC11 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Yoshioka et al., 2006 | ||
| CNGC12 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Yoshioka et al., 2006 | ||
| NHX1 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐 | Yamaguchi et al., 2005 | ||
| PEN3 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Campe et al., 2015 | ||
| Apyrase1 | 拟南芥 | 花粉萌发, 细胞生长 | Steinebrunner et al., 2000; Wu et al., 2007 | ||
| MLO | 水稻和大麦 | 抗病 | Kim et al., 2002a, 2002b | ||
| CIP111 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Buaboocha et al., 2001 | ||
| AFG1L1 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Bussemer et al., 2009 | ||
| 代谢酶 | CAT3 | 拟南芥 | ROS清除 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2002b | |
| ELP | 常绿大戟 | ROS平衡 | Medda et al., 2003; Mura et al., 2005 | ||
| NtGAD | 烟草 | 氨基丁酸合成 | Baum et al., 1996 | ||
| 蛋白种类 | 蛋白名称 | 物种 | 生理功能 | 参考文献 | |
| NADK | 烟草和拟南芥 | NADP(H)合成, ROS产生 | Harding et al., 1997; Turner et al., 2004 | ||
| DWF1 | 拟南芥 | 油菜素内酯合成 | Du and Poovaiah, 2005 | ||
| LeCBDGK | 番茄 | 磷脂酸合成 | Snedden and Blumwald, 2000 | ||
| PsTic32 | 豌豆 | 叶绿体蛋白移动 | Chigri et al., 2006 | ||
| 其它CBPs | MPCBP | 玉米 | 花粉萌发 | Safadi et al., 2000 | |
| ZmSAUR1 | 玉米 | 生长素信号 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2000a; Knauss et al., 2003 | ||
| Ch-CPN10 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2000b | ||
| NPG1 | 拟南芥 | 花粉萌发 | Golovkin and Reddy, 2003 | ||
| KCBP | 拟南芥 | 细胞分裂, 表皮毛形成 | Reddy et al., 1996; Reddy et al., 2004 | ||
| DRL1 | 拟南芥 | 分裂组织活性, 器官生长 | Nelissen et al., 2003 | ||
| UBP6 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Moon et al., 2005 | ||
| IQM1 | 拟南芥 | 气孔运动 | Zhou et al., 2012 | ||
Table 1 Calmodulin-binding proteins (CBPs) and their physiological functions in plants
| 蛋白种类 | 蛋白名称 | 物种 | 生理功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激酶和磷酸酶 | CBK3 | 拟南芥 | 抗热击 | Liu et al., 2008 | |
| NtCBK1 | 烟草 | 开花调控 | Hua et al., 2004 | ||
| NtCaMK1 | 烟草 | 未知 | Ma et al., 2004 | ||
| CRLK1 | 拟南芥 | 抗冷冻 | Yang et al., 2010 | ||
| CCaMK | 苜蓿、水稻和 玉米 | 共生, 抗氧化防御 | Gleason et al., 2006; Ma et al., 2012; Shi et al., 2012; Routray et al., 2013 | ||
| MPK8 | 拟南芥 | 损伤反应, ROS平衡 | Takahashi et al., 2011 | ||
| PP7 | 拟南芥 | 抗热击 | Kutuzov et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2007 | ||
| MKP1 | 拟南芥 | 抗病、抗紫外、抗盐和 抗基因毒性 | Ulm et al., 2002; Lee et al., 2008; Bartels et al., 2009; Gonzalez Besteiro et al., 2011 | ||
| OsMKP1 | 水稻 | 损伤反应 | Katou et al., 2007 | ||
| NtMKP1 | 烟草 | 抗病虫害和机械损伤 | Yamakawa et al., 2004; Oka et al., 2013 | ||
| PCaMPP | 苔藓 | 未知 | Takezawa, 2003 | ||
| 转录因子和 辅助因子 | CAMTA3 | 拟南芥 | 通用胁迫反应, 抗冷冻和 抗病虫害 | Doherty et al., 2009; Du et al., 2009; Bjornson et al., 2014 | |
| CBP60g | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Wang et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2010 | ||
| WRKY7 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Park et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2006 | ||
| MYB2 | 拟南芥 | ABA信号, 盐胁迫, 叶片衰老, 缺磷反应 | Abe et al., 2003; Yoo et al., 2005; Guo and Gan, 2011; Baek et al., 2013 | ||
| MYB91 | 拟南芥 | 叶片发育 | Han et al., 2012 | ||
| CBNAC | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Kim et al., 2007 | ||
| TGA3 | 拟南芥 | 抗病和抗重金属胁迫 | Szymanski et al., 1996; Choi et al., 2010; Farinati et al., 2010 | ||
| IQD1 | 拟南芥 | 抗虫 | Levy et al., 2005 | ||
| GT2L | 拟南芥 | 抗冷, 抗盐 | Xi et al., 2012 | ||
| BT2 | 拟南芥 | 端粒酶活性, 糖和ABA信号, 配子体发育 | Du and Poovaiah, 2004; Ren et al., 2007; Mandadi et al., 2009; Robert et al., 2009 | ||
| PCBP | 马铃薯 | 未知 | Reddy et al., 2002 | ||
| 离子通道和膜蛋白 | ACA2 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐 | Anil et al., 2008 | |
| ACA4 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐和抗病 | Geisler et al., 2000; Boursiac et al., 2010 | ||
| ACA8 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | dit Frey et al., 2012 | ||
| ACA11 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Boursiac et al., 2010 | ||
| CNGC1 | 拟南芥 | 抗重金属胁迫 | Sunkar et al., 2000 | ||
| CNGC2 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Clough et al., 2000; Ali et al., 2007 | ||
| CNGC3 | 拟南芥 | Na+/K+吸收, 抗盐 | Gobert et al., 2006 | ||
| CNGC4 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Balague et al., 2003 | ||
| CNGC10 | 拟南芥 | K+吸收, 抗盐 | Li et al., 2005; Guo et al., 2008 | ||
| CNGC11 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Yoshioka et al., 2006 | ||
| CNGC12 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Yoshioka et al., 2006 | ||
| NHX1 | 拟南芥 | 抗盐 | Yamaguchi et al., 2005 | ||
| PEN3 | 拟南芥 | 抗病 | Campe et al., 2015 | ||
| Apyrase1 | 拟南芥 | 花粉萌发, 细胞生长 | Steinebrunner et al., 2000; Wu et al., 2007 | ||
| MLO | 水稻和大麦 | 抗病 | Kim et al., 2002a, 2002b | ||
| CIP111 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Buaboocha et al., 2001 | ||
| AFG1L1 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Bussemer et al., 2009 | ||
| 代谢酶 | CAT3 | 拟南芥 | ROS清除 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2002b | |
| ELP | 常绿大戟 | ROS平衡 | Medda et al., 2003; Mura et al., 2005 | ||
| NtGAD | 烟草 | 氨基丁酸合成 | Baum et al., 1996 | ||
| 蛋白种类 | 蛋白名称 | 物种 | 生理功能 | 参考文献 | |
| NADK | 烟草和拟南芥 | NADP(H)合成, ROS产生 | Harding et al., 1997; Turner et al., 2004 | ||
| DWF1 | 拟南芥 | 油菜素内酯合成 | Du and Poovaiah, 2005 | ||
| LeCBDGK | 番茄 | 磷脂酸合成 | Snedden and Blumwald, 2000 | ||
| PsTic32 | 豌豆 | 叶绿体蛋白移动 | Chigri et al., 2006 | ||
| 其它CBPs | MPCBP | 玉米 | 花粉萌发 | Safadi et al., 2000 | |
| ZmSAUR1 | 玉米 | 生长素信号 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2000a; Knauss et al., 2003 | ||
| Ch-CPN10 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Yang and Poovaiah, 2000b | ||
| NPG1 | 拟南芥 | 花粉萌发 | Golovkin and Reddy, 2003 | ||
| KCBP | 拟南芥 | 细胞分裂, 表皮毛形成 | Reddy et al., 1996; Reddy et al., 2004 | ||
| DRL1 | 拟南芥 | 分裂组织活性, 器官生长 | Nelissen et al., 2003 | ||
| UBP6 | 拟南芥 | 未知 | Moon et al., 2005 | ||
| IQM1 | 拟南芥 | 气孔运动 | Zhou et al., 2012 | ||
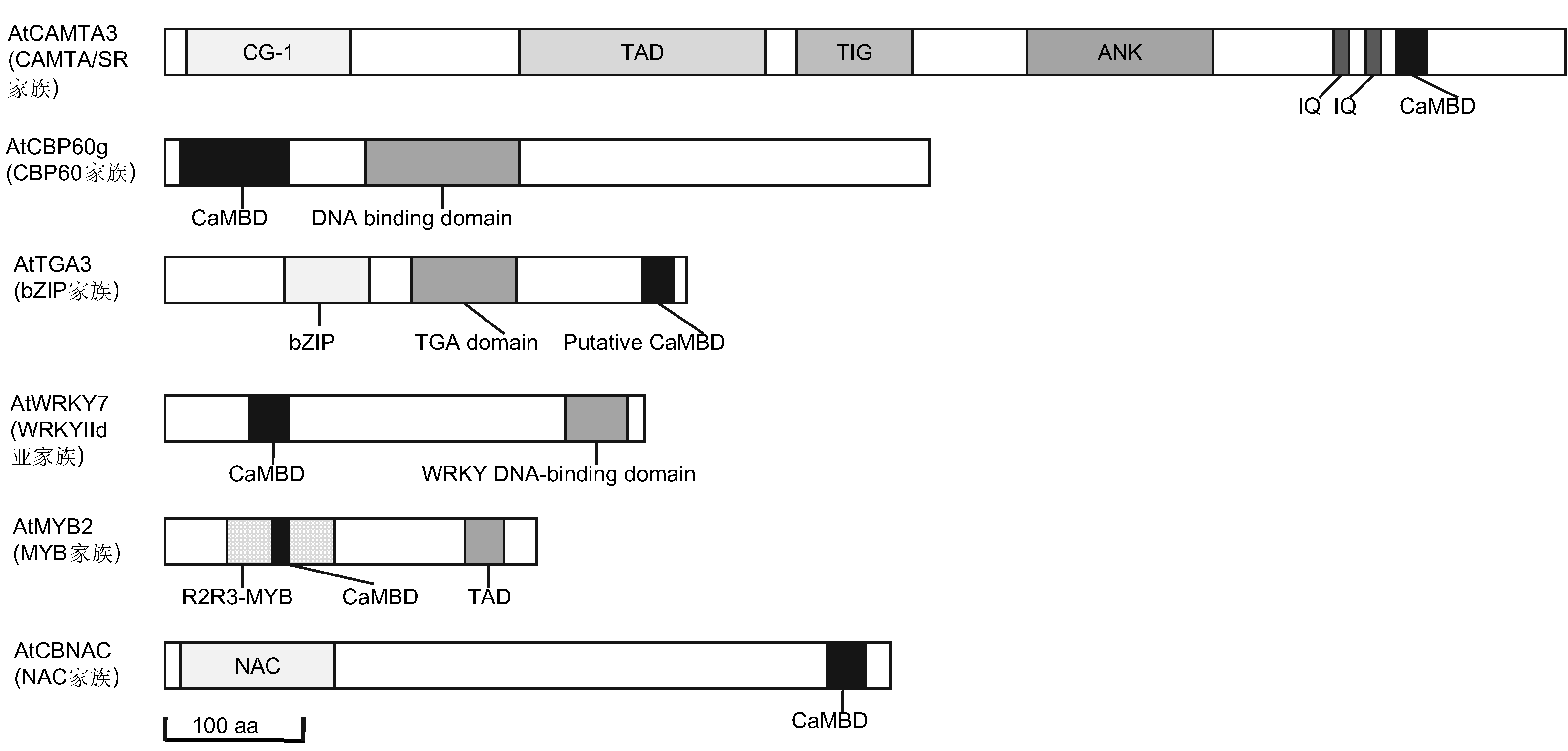
Figure 1 Six typical CaM-binding transcription factors and their functional domains in Arabidopsis CaMBD: CaM binding domain; TAD: Transcription activation domain; TIG: Transcription factor immunoglobulin domain; ANK: Ankyrin repeat domain
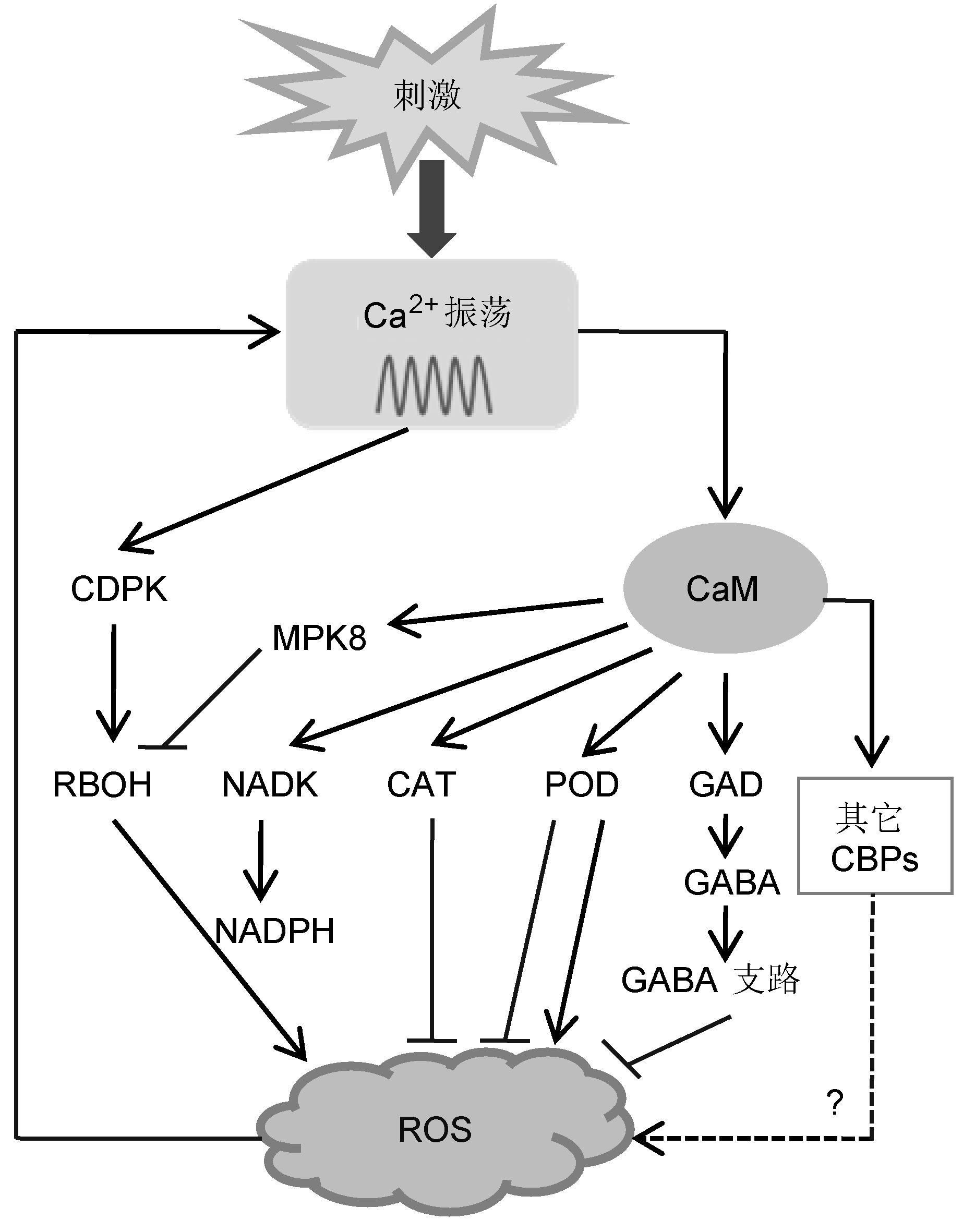
Figure 2 Regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism by Ca2+/CaM signaling CDPK: Calcium-dependent protein kinase; RBOH: Respiratory burst oxidase homologues; NADK: NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) kinase; CAT: Catalase; POD: Peroxidase; GAD: Glutamate decarboxylase; GABA: γ-aminobuty- rate; CBPs: CaM-binding proteins. Solid arrows indicate positive regulation, blunted arrows indicate negative regulation, and dashed lines designate putative regulation.
| 1 | 刘海娇, 李瑞丽, 杜立群, 林金星 (2015). 植物环核苷酸门控离子通道及其功能的研究进展. 植物学报 50, 779-789. |
| 2 | 毛国红, 宋林霞, 孙大业 (2004). 植物钙调素结合蛋白研究进展. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 30, 481-488. |
| 3 | 田长恩, 周玉萍 (2013). 植物具IQ基序的钙调素结合蛋白的研究进展. 植物学报 48, 447-460. |
| 4 | 曾后清, 王国平, 王慧中, 林金星, 杜立群 (2015). 植物钙调素结合转录因子CAMTA/SR功能的研究进展. 植物生理学报 51, 633-641. |
| 5 | 曾后清, 张夏俊, 张亚仙, 汪尚, 皮二旭, 王慧中, 杜立群 (2016). 植物类钙凋素生理功能的研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 6, 705-715. |
| 6 | 郑仲仲, 沈金秋, 潘伟槐, 潘建伟 (2013). 植物钙感受器及其介导的逆境信号途径. 遗传 35, 875-884. |
| 7 | 周卫, 汪洪 (2007). 植物钙吸收、转运及代谢的生理和分子机制. 植物学通报 24, 762-778. |
| 8 | 左建儒, 陈凡 (2015). 中国科学家在植物应答低温信号研究中取得突破性进展. 植物学报 50, 145-147. |
| 9 | Abbas N, Maurya JP, Senapati D, Gangappa SN, Chattopadhyay S (2014). Arabidopsis CAM7 and HY5 physically interact and directly bind to the HY5 promoter to regulate its expression and thereby promote photomor- phogenesis.Plant Cell 26, 1036-1052. |
| 10 | Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi- Shinozaki K (2003). Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling.Plant Cell 15, 63-78. |
| 11 | Ali R, Ma W, Lemtiri-Chlieh F, Tsaltas D, Leng Q, von Bodman S, Berkowitz GA (2007). Death don't have no mercy and neither does calcium: Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE GATED CHANNEL2 and innate immunity.Plant Cell 19, 1081-1095. |
| 12 | Ali R, Zielinski RE, Berkowitz GA (2006). Expression of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in yeast. J Exp Bot 57, 125-138. |
| 13 | Anderson JC, Bartels S, Besteiro MAG, Shahollari B, Ulm R, Peck SC (2011). Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) negatively regulates MPK6- mediated PAMP responses and resistance against bac- teria.Plant J 67, 258-268. |
| 14 | Anil VS, Rajkumar P, Kumar P, Mathew M (2008). A plant Ca2+ pump, ACA2, relieves salt hypersensitivity in yeast: modulation of cytosolic calcium signature and activation of adaptive Na+ homeostasis.J Biol Chem 283, 3497-3506. |
| 15 | Arazi T, Kaplan B, Fromm H (2000). A high-affinity calmodulin-binding site in a tobacco plasma-membrane channel protein coincides with a characteristic element of cyclic nucleotide-binding domains.Plant Mol Biol 42, 591-601. |
| 16 | Arazi T, Sunkar R, Kaplan B, Fromm H (1999). A tobacco plasma membrane calmodulin-binding transporter confers Ni2+ tolerance and Pb2+ hypersensitivity in transgenic plants.Plant J 20, 171-182. |
| 17 | Askerlund P (1997). Calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+-ATPases in the vacuolar and plasma membranes in cauliflower.Plant Physiol 114, 999-1007. |
| 18 | Askerlund P, Evans DE (1992). Reconstitution and char- acter ization of a calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+-pumping ATPase purified from Brassica oleracea L.Plant Physiol 100, 1670-1681. |
| 19 | Bækgaard L, Luoni L, De Michelis MI, Palmgren MG (2006). The plant plasma membrane Ca2+ pump ACA8 contains overlapping as well as physically separated autoinhibitory and calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem 281, 1058-1065. |
| 20 | Baek D, Kim MC, Chun HJ, Kang S, Park HC, Shin G, Park J, Shen M, Hong H, Kim WY, Kim DH, Lee SY, Bressan RA, Bohnert HJ, Yun DJ (2013). Regulation of miR399f transcription by AtMYB2 affects phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 161, 362-373. |
| 21 | Balague C, Lin B, Alcon C, Flottes G, Malmstrom S, Kohler C, Neuhaus G, Pelletier G, Gaymard F, Roby D (2003). HLM1, an essential signaling component in the hypersensitive response, is a member of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel ion channel family.Plant Cell 15, 365-379. |
| 22 | Bartels S, Anderson JC, Gonzalez Besteiro MA, Carreri A, Hirt H, Buchala A, Metraux JP, Peck SC, Ulm R (2009). MAP kinase phosphatase1 and protein tyrosine phosphatase1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and SNC1-mediated responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 2884-2897. |
| 23 | Baum G, Lev-Yadun S, Fridmann Y, Arazi T, Katsnelson H, Zik M, Fromm H (1996). Calmodulin binding to gluta- mate decarboxylase is required for regulation of gluta- mate and GABA metabolism and normal development in plants.EMBO J 15, 2988. |
| 24 | Bender KW, Snedden WA (2013). Calmodulin-related proteins step out from the shadow of their namesake.Plant Physiol 163, 486-495. |
| 25 | Bjornson M, Benn G, Song X, Comai L, Franz AK, Dandekar AM, Drakakaki G, Dehesh K (2014). Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVAT- OR3 in regulating the peak time and amplitude of the plant general stress response. Plant Physiol 166, 988-996. |
| 26 | Bonza MC, De Michelis MI (2011). The plant Ca2+-ATPase repertoire: biochemical features and physiological func- tions.Plant Biol 13, 421-430. |
| 27 | Bonza MC, Morandini P, Luoni L, Geisler M, Palmgren MG, De Michelis MI (2000). At-ACA8 encodes a plasma membrane-localized calcium-ATPase of Arabidopsis with a calmodulin-binding domain at the N terminus.Plant Physiol 123, 1495-1506. |
| 28 | Boonburapong B, Buaboocha T (2007). Genome-wide identification and analyses of the rice calmodulin and related potential calcium sensor proteins.BMC Plant Biol 7, 4. |
| 29 | Bouche N, Fait A, Bouchez D, Moller SG, Fromm H (2003). Mitochondrial succinic-semialdehyde dehydrog- enase of the gamma-aminobutyrate shunt is required to restrict levels of reactive oxygen intermediates in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 6843-6848. |
| 30 | Bouche N, Yellin A, Snedden WA, Fromm H (2005). Plant-specific calmodulin-binding proteins.Annu Rev Plant Biol 56, 435-466. |
| 31 | Boursiac Y, Harper J (2007). The origin and function of calmodulin regulated Ca2+ pumps in plants. J Bioenerg Biomembr 39, 409-414. |
| 32 | Boursiac Y, Lee SM, Romanowsky S, Blank R, Sladek C, Chung WS, Harper JF (2010). Disruption of the vacuolar calcium-ATPases in Arabidopsis results in the activation of a salicylic acid-dependent programmed cell death pathway.Plant Physiol 154, 1158-1171. |
| 33 | Buaboocha T, Liao B, Zielinski RE (2001). Isolation of cDNA and genomic DNA clones encoding a calmodulin- binding protein related to a family of ATPases involved in cell division and vesicle fusion. Planta 212, 774-781. |
| 34 | Bussemer J, Chigri F, Vothknecht UC (2009). Arabidopsis ATPase family gene 1-like protein 1 is a calmodulin- binding AAA+-ATPase with a dual localization in chloro- plasts and mitochondria.FEBS J 276, 3870-3880. |
| 35 | Campe R, Langenbach C, Leissing F, Popescu GV, Popescu SC, Goellner K, Beckers GJM, Conrath U (2016). ABC transporter PEN3/PDR8/ABCG36 interacts with calmodulin that, like PEN3, is required for Arabid- opsis nonhost resistance.New Phytol 209, 294-306. |
| 36 | Charpenteau M, Jaworski K, Ramirez BC, Tretyn A, Ranjeva R, Ranty B (2004). A receptor-like kinase from Arabidopsis thaliana is a calmodulin-binding protein.Biochem J 379, 841-848. |
| 37 | Cheval C, Aldon D, Galaud JP, Ranty B (2013). Calcium/ calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833, 1766-1771. |
| 38 | Chigri F, Hörmann F, Stamp A, Stammers DK, Bölter B, Soll J, Vothknecht UC (2006). Calcium regulation of chloroplast protein translocation is mediated by calm- odulin binding to Tic32.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 16051-16056. |
| 39 | Choe S, Dilkes BP, Gregory BD, Ross AS, Yuan H, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tanaka A, Yoshida S (1999). The Arabidopsis dwarf1 mutant is defective in the conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol in brassinosteroid biosynthesis.Plant Physiol 119, 897-908. |
| 40 | Choi J, Huh SU, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Paek KH, Hwang I (2010). The cytokinin-activated transcription factor ARR2 promotes plant immunity via TGA3/NPR1- dependent salicylic acid signaling in Arabidopsis.Dev Cell 19, 284-295. |
| 41 | Choudhary SP, Yu JQ, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shin- ozaki K, Tran LSP (2012). Benefits of brassinosteroid crosstalk.Trends Plant Sci 17, 594-605. |
| 42 | Chung WS, Lee SH, Kim JC, Heo WD, Kim MC, Park CY, Park HC, Lim CO, Kim WB, Harper JF, Cho MJ (2000). Identification of a calmodulin-regulated soybean Ca2+- ATPase (SCA1) that is located in the plasma membrane. Plant Cell 12, 1393-1407. |
| 43 | Clough SJ, Fengler KA, Yu IC, Lippok B, Smith RKJr, Bent AF (2000). The Arabidopsis dnd1 "defense, no death" gene encodes a mutated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 9323-9328. |
| 44 | Day IS, Reddy VS, Shad Ali G, Reddy AS (2002). Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 3, research0056.1-0056.24. |
| 45 | DeFalco TA, Bender KW, Snedden WA (2010a). Breaking the code: Ca2+ sensors in plant signaling.Biochem J 425, 27-40. |
| 46 | DeFalco TA, Chiasson D, Munro K, Kaiser BN, Snedden WA (2010b). Characterization of GmCaMK1, a member of a soybean calmodulin-binding receptor-like kinase family.FEBS Lett 584, 4717-4724. |
| 47 | Dieter P, Marmé D (1981). A calmodulin-dependent, micro- somal ATPase from corn (Zea mays L.).FEBS Lett 125, 245-248. |
| 48 | Ding X, Richter T, Chen M, Fujii H, Seo YS, Xie M, Zheng X, Kanrar S, Stevenson RA, Dardick C, Li Y, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Yu F, Bartley LE, Chern M, Bart R, Chen X, Zhu L, Farmerie WG, Gribskov M, Zhu JK, Fromm ME, Ronald PC, Song WY (2009). A rice kinase-protein interaction map.Plant Physiol 149, 1478-1492. |
| 49 | dit Frey NF, Mbengue M, Kwaaitaal M, Nitsch L, Altenbach D, Häweker H, Lozano-Duran R, Njo MF, Beeckman T, Huettel B (2012). Plasma membrane calcium ATPases are important components of receptor- mediated signaling in plant immune responses and development.Plant Physiol 159, 798-809. |
| 50 | Dobney S, Chiasson D, Lam P, Smith SP, Snedden WA (2009). The calmodulin-related calcium sensor CML42 plays a role in trichome branching. J Biol Chem 284, 31647-31657. |
| 51 | Dodd AN, Kudla J, Sanders D (2010). The language of calcium signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 593-620. |
| 52 | Doherty CJ, Van Buskirk HA, Myers SJ, Thomashow MF (2009). Roles for Arabidopsis CAMTA transcription fac- tors in cold-regulated gene expression and freezing tolerance.Plant Cell 21, 972-984. |
| 53 | Drum CL, Yan SZ, Bard J, Shen YQ, Lu D, Soelaiman S, Grabarek Z, Bohm A, Tang WJ (2002). Structural basis for the activation of anthrax adenylyl cyclase exotoxin by calmodulin.Nature 415, 396-402. |
| 54 | Du L, Poovaiah BW (2004). A novel family of Ca2+/calmo- dulin-binding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation: interaction with fsh/Ring3 class transcription activators.Plant Mol Biol 54, 549-569. |
| 55 | Du L, Poovaiah BW (2005). Ca2+/calmodulin is critical for brassinosteroid biosynthesis and plant growth. Nature 437, 741-745. |
| 56 | Du L, Yang T, Puthanveettil SV, Poovaiah BW, Luan S (2011). Decoding of calcium signal through calmodulin: calmodulin binding proteins in plants coding and decoding of calcium signals in plants. In: Luan S, ed, Coding and Decoding of Calcium Signals in Plants, Vol. 10. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 177-233. |
| 57 | Du LQ, Ali GS, Simons KA, Hou JG, Yang TB, Reddy ASN, Poovaiah BW (2009). Ca2+/calmodulin regulates salicylic-acid-mediated plant immunity.Nature 457, 1154-1158. |
| 58 | Farinati S, DalCorso G, Varotto S, Furini A (2010). The Brassica juncea BjCdR15, an ortholog of Arabidopsis TGA3, is a regulator of cadmium uptake, transport and accumulation in shoots and confers cadmium tolerance in transgenic plants. New Phytol 185, 964-978. |
| 59 | Fromm H, Chua NH (1992). Cloning of plant cDNAs encoding calmodulin-binding proteins using 35S-labeled recombinant calmodulin as a probe.Plant Mol Biol Rep 10, 199-206. |
| 60 | Geisler M, Frangne N, Gomes E, Martinoia E, Palmgren MG (2000). The ACA4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a vacuolar membrane calcium pump that improves salt tolerance in yeast.Plant Physiol 124, 1814-1827. |
| 61 | Gifford JL, Walsh MP, Vogel HJ (2007). Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix- loop-helix EF-hand motifs.Biochem J 405, 199-221. |
| 62 | Gleason C, Chaudhuri S, Yang T, Munoz A, Poovaiah BW, Oldroyd GE (2006). Nodulation independent of rhizobia induced by a calcium-activated kinase lacking autoinhibition.Nature 441, 1149-1152. |
| 63 | Gobert A, Park G, Amtmann A, Sanders D, Maathuis FJ (2006). Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J Exp Bot 57, 791-800. |
| 64 | Godfroy O, Debellé F, Timmers T, Rosenberg C (2006). A rice calcium-and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase restores nodulation to a legume mutant.Mol Plant Mic- robe In 19, 495-501. |
| 65 | Golovkin M, Reddy AS (2003). A calmodulin-binding protein from Arabidopsis has an essential role in pollen germination.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 10558-10563. |
| 66 | Gong M, Chen SN, Song YQ, Li ZG (1997). Effect of calcium and calmodulin on intrinsic heat tolerance in relation to antioxidant systems in maize seedlings.Funct Plant Biol 24, 371-379. |
| 67 | Gonzalez Besteiro MA, Bartels S, Albert A, Ulm R (2011). Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1 and its target MAP kinases 3 and 6 antagonistically determine UV-B stress tolerance, independent of the UVR8 photoreceptor pathway. Plant J 68, 727-737. |
| 68 | Guo KM, Babourina O, Christopher DA, Borsics T, Rengel Z (2008). The cyclic nucleotide-gated channel, AtCNGC10, influences salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.Phy- siol Plantarum 134, 499-507. |
| 69 | Guo Y, Gan S (2011). AtMYB2 regulates whole plant senescence by inhibiting cytokinin-mediated branching at late stages of development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156, 1612-1619. |
| 70 | Gut H, Dominici P, Pilati S, Astegno A, Petoukhov MV, Svergun DI, Grütter MG, Capitani G (2009). A common structural basis for pH- and calmodulin-mediated regu- lation in plant glutamate decarboxylase. J Mol Biol 392, 334-351. |
| 71 | Han HJ, Park HC, Byun HJ, Lee SM, Kim HS, Yun DJ, Cho MJ, Chung WS (2012). The transcriptional repressor activity of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 is inhibited by direct interaction with calmodulin in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Environ 35, 1969-1982. |
| 72 | Harding SA, Oh SH, Roberts DM (1997). Transgenic tobacco expressing a foreign calmodulin gene shows an enhanced production of active oxygen species.EMBO J 16, 1137-1144. |
| 73 | Harper JF, Hong B, Hwang I, Guo HQ, Stoddard R, Huang JF, Palmgren MG, Sze H (1998). A novel calmodulin-regulated Ca2+-ATPase (ACA2) from Arabid- opsis with an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. J Biol Chem 273, 1099-1106. |
| 74 | Hoeflich KP, Ikura M (2002). Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms.Cell 108, 739-742. |
| 75 | Hong B, Ichida A, Wang Y, Gens JS, Pickard BG, Harper JF (1999). Identification of a calmodulin-regulated Ca2+- ATPase in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Physiol 119, 1165-1176. |
| 76 | Hua BG, Mercier RW, Zielinski RE, Berkowitz GA (2003a). Functional interaction of calmodulin with a plant cyclic nucleotide gated cation channel.Plant Physiol Bioch 41, 945-954. |
| 77 | Hua W, Liang S, Lu YT (2003b). A tobacco (Nicotiana tabaccum) calmodulin-binding protein kinase, NtCBK2, is regulated differentially by calmodulin isoforms.Biochem J 376, 291-302. |
| 78 | Hua W, Zhang L, Liang S, Jones RL, Lu YT (2004). A tobacco calcium/calmodulin-binding protein kinase func- tions as a negative regulator of flowering.J Biol Chem 279, 31483-31494. |
| 79 | Ikura M, Ames JB (2006). Genetic polymorphism and protein conformational plasticity in the calmodulin super- family: two ways to promote multifunctionality.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 1159-1164. |
| 80 | Ishida H, Rainaldi M, Vogel HJ (2009). Structural studies of soybean calmodulin isoform 4 bound to the calmodulin- binding domain of tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 provide insights into a sequential target binding mode. J Biol Chem 284, 28292-28305. |
| 81 | Jammes F, Hu HC, Villiers F, Bouten R, Kwak JM (2011). Calcium-permeable channels in plant cells.FEBS J 278, 4262-4276. |
| 82 | Journot-Catalinoa N, Somssichb IE, Robya D, Kroja T (2006). The transcription factors WRKY11 and WRKY17 act as negative regulators of basal resistance in Arabi- dopsis thaliana.Plant Cell 18, 3289-3302. |
| 83 | Kaplan B, Sherman T, Fromm H (2007). Cyclic nucleotide- gated channels in plants. FEBS Lett 581, 2237-2246. |
| 84 | Katou S, Kuroda K, Seo S, Yanagawa Y, Tsuge T, Yamazaki M, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Ohashi Y (2007). A calmodulin-binding mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase is induced by wounding and regulates the activities of stress-related mitogen-activated protein kinases in rice.Plant Cell Physiol 48, 332-344. |
| 85 | Kim HS, Jung MS, Lee K, Kim KE, Yoo JH, Kim MC, Kim DH, Cho MJ, Chung WS (2009a). An S-locus receptor- like kinase in plasma membrane interacts with calmodulin in Arabidopsis.FEBS Lett 583, 36-42. |
| 86 | Kim HS, Park BO, Yoo JH, Jung MS, Lee SM, Han HJ, Kim KE, Kim SH, Lim CO, Yun DJ, Lee SY, Chung WS (2007). Identification of a calmodulin-binding NAC protein as a transcriptional repressor in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 282, 36292-36302. |
| 87 | Kim J, Kim HY (2006). Functional analysis of a calcium- binding transcription factor involved in plant salt stress signaling.FEBS Lett 580, 5251-5256. |
| 88 | Kim KC, Fan B, Chen Z (2006). Pathogen-induced Arabid- opsis WRKY7 is a transcriptional repressor and enhances plant susceptibility to Pseudomonas syringae.Plant Phy- siol 142, 1180-1192. |
| 89 | Kim MC, Chung WS, Yun DJ, Cho MJ (2009b). Calcium and calmodulin-mediated regulation of gene expression in plants.Mol Plant 2, 13-21. |
| 90 | Kim MC, Lee SH, Kim JK, Chun HJ, Choi MS, Chung WS, Moon BC, Kang CH, Park CY, Yoo JH, Kang YH, Koo SC, Koo YD, Jung JC, Kim ST, Schulze-Lefert P, Lee SY, Cho MJ (2002a). Mlo, a modulator of plant defense and cell death, is a novel calmodulin-binding protein. J Biol Chem 277, 19304-19314. |
| 91 | Kim MC, Panstruga R, Elliott C, Muller J, Devoto A, Yoon HW, Park HC, Cho MJ, Schulze-Lefert P (2002b). Calmodulin interacts with MLO protein to regulate defence against mildew in barley.Nature 416, 447-451. |
| 92 | Knauss S, Rohrmeier T, Lehle L (2003). The auxin-induced maize gene ZmSAUR2 encodes a short-lived nuclear protein expressed in elongating tissues.J Biol Chem 278, 23936-23943. |
| 93 | Kohler C, Merkle T, Neuhaus G (1999). Characterisation of a novel gene family of putative cyclic nucleotide- and calmodulin-regulated ion channels in Arabidopsis thalia- na.Plant J 18, 97-104. |
| 94 | Kudla J, Batistic O, Hashimoto K (2010). Calcium signals: the lead currency of plant information processing.Plant Cell 22, 541-563. |
| 95 | Kushwaha R, Singh A, Chattopadhyay S (2008). Calmo- dulin7 plays an important role as transcriptional regulator in Arabidopsis seedling development.Plant Cell 20, 1747-1759. |
| 96 | Kutuzov MA, Bennett N, Andreeva AV (2001). Interaction of plant protein Ser/Thr phosphatase PP7 with calmo- dulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289, 634-640. |
| 97 | Larkindale J, Knight MR (2002). Protection against heat stress-induced oxidative damage in Arabidopsis involves calcium, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid. Plant Physiol 128, 682-695. |
| 98 | Lee K, Song EH, Kim HS, Yoo JH, Han HJ, Jung MS, Lee SM, Kim KE, Kim MC, Cho MJ, Chung WS (2008). Regulation of MAPK phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) by calmo- dulin in Arabidopsis.J Biol Chem 283, 23581-23588. |
| 99 | Lee SH, Johnson JD, Walsh MP, Van Lierop JE, Sutherland C, Xu AD, Snedden WA, Kosk-Kosicka D, Fromm H, Narayanan N, Cho MJ (2000). Differential regulation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent enzymes by plant calmodulin isoforms and free Ca2+ concentration.Biochem J 350, 299-306. |
| 100 | Lee SM, Kim HS, Han HJ, Moon BC, Kim CY, Harper JF, Chung WS (2007). Identification of a calmodulin- regulated autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase (ACA11) that is localized to vacuole membranes in Arabidopsis.FEBS Lett 581, 3943-3949. |
| 101 | Levy M, Wang Q, Kaspi R, Parrella MP, Abel S (2005). Arabidopsis IQD1, a novel calmodulin-binding nuclear protein, stimulates glucosinolate accumulation and plant defense.Plant J 43, 79-96. |
| 102 | Li JH, Liu YQ, Lu P, Lin HF, Bai Y, Wang XC, Chen YL (2009). A signaling pathway linking nitric oxide production to heterotrimeric G protein and hydrogen peroxide re- gulates extracellular calmodulin induction of stomatal closure in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 150, 114-124. |
| 103 | Li X, Borsics T, Harrington HM, Christopher DA (2005). Arabidopsis AtCNGC10 rescues potassium channel mutants of E. coli, yeast and Arabidopsis and is regulated by calcium/calmodulin and cyclic GMP in E. coli.Funct Plant Biol 32, 643-653. |
| 104 | Lin TW, Hsieh PJ, Lin CL, Fang YY, Yang JX, Tsai CC, Chiang PL, Pan CY, Chen YT (2010). Label-free detection of protein-protein interactions using a calmodu- lin-modified nanowire transistor.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 1047-1052. |
| 105 | Liu HT, Gao F, Li GL, Han JL, Liu DL, Sun DY, Zhou RG (2008). The calmodulin-binding protein kinase 3 is part of heat-shock signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J 55, 760-773. |
| 106 | Liu HT, Li GL, Chang H, Sun DY, Zhou RG, Li B (2007). Calmodulin-binding protein phosphatase PP7 is involved in thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 30, 156-164. |
| 107 | Luan S (2009). The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling.Trends Plant Sci 14, 37-42. |
| 108 | Ma FF, Lu R, Liu HY, Shi B, Zhang JH, Tan MP, Zhang A, Jiang MY (2012). Nitric oxide-activated calcium/ calmo- dulin-dependent protein kinase regulates the abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence in maize.J Exp Bot 63, 4835-4847. |
| 109 | Ma L, Liang S, Jones RL, Lu YT (2004). Characterization of a novel calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase from tobacco. Plant Physiol 135, 1280-1293. |
| 110 | Ma L, Xu X, Cui S, Sun D (1999). The presence of a heterotrimeric G protein and its role in signal transduction of extracellular calmodulin in pollen germination and tube growth.Plant Cell 11, 1351-1363. |
| 111 | Ma W, Berkowitz GA (2011). Ca2+ conduction by plant cyclic nucleotide gated channels and associated signaling com- ponents in pathogen defense signal transduction cas- cades.New Phytol 190, 566-572. |
| 112 | Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D, Xiao J, Guo X, Xu S, Niu Y, Jin J, Zhang H, Xu X, Li L, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K (2015). COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice.Cell 160, 1209-1221. |
| 113 | Malmström S, Åkerlund HE, Askerlund P (2000). Regu- latory role of the N terminus of the vacuolar calcium- ATPase in cauliflower. Plant Physiol 122, 517-526. |
| 114 | Malmström S, Askerlund P, Palmgren MG (1997). A calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+-ATPase from plant vacuolar membranes with a putative regulatory domain at its N-terminus1.FEBS Lett 400, 324-328. |
| 115 | Mandadi KK, Misra A, Ren S, McKnight TD (2009). BT2, a BTB protein, mediates multiple responses to nutrients, stresses, and hormones in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 150, 1930-1939. |
| 116 | McAinsh MR, Pittman JK (2009). Shaping the calcium signature.New Phytol 181, 275-294. |
| 117 | McCormack E, Braam J (2003). Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of Arabidopsis.New Phytol 159, 585-598. |
| 118 | Medda R, Padiglia A, Longu S, Bellelli A, Arcovito A, Cavallo S, Pedersen JZ, Floris G (2003). Critical role of Ca2+ ions in the reaction mechanism of Euphorbia cha- racias peroxidase.Biochemistry 42, 8909-8918. |
| 119 | Meijer HJ, Munnik T (2003). Phospholipid-based signaling in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol 54, 265-306. |
| 120 | Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Suzuki N, Miller G, Tognetti VB, Vandepoele K, Gollery M, Shulaev V, Van Breusegem F (2011). ROS signaling: the new wave? Trends Plant Sci 16, 300-309. |
| 121 | Moon BC, Choi MS, Kang YH, Kim MC, Cheong MS, Park CY, Yoo JH, Koo SC, Lee SM, Lim CO (2005). Arabidopsis ubiquitin-specific protease 6 (AtUBP6) inter- acts with calmodulin.FEBS Lett 579, 3885-3890. |
| 122 | Mura A, Medda R, Longu S, Floris G, Rinaldi AC, Padiglia A (2005). A Ca2+/calmodulin-binding peroxidase from Euphorbia latex: novel aspects of calcium-hydrogen peroxide cross-talk in the regulation of plant defenses. Biochemistry 44, 14120-14130. |
| 123 | Nelissen H, Clarke JH, De Block M, De Block S, Vanderhaeghen R, Zielinski RE, Dyer T, Lust S, Inzé D, Van Lijsebettens M (2003). DRL1, a homolog of the yeast TOT4/KTI12 protein, has a function in meristem activity and organ growth in plants.Plant Cell 15, 639-654. |
| 124 | Nie H, Zhao C, Wu G, Wu Y, Chen Y, Tang D (2012). SR1, a calmodulin-binding transcription factor, modulates plant defense and ethylene-induced senescence by directly regulating NDR1 and EIN3.Plant Physiol 158, 1847-1859. |
| 125 | Ogasawara Y, Kaya H, Hiraoka G, Yumoto F, Kimura S, Kadota Y, Hishinuma H, Senzaki E, Yamagoe S, Nagata K (2008). Synergistic activation of the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtrbohD by Ca2+ and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 283, 8885-8892. |
| 126 | Oh MH, Kim HS, Wu X, Clouse SD, Zielinski RE, Huber SC (2012). Calcium/calmodulin inhibition of the Arabi- dopsis BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1 receptor kinase provides a possible link between calcium and brassinosteroid signaling.Biochem J 443, 515-523. |
| 127 | Oka K, Amano Y, Katou S, Seo S, Kawazu K, Mochizuki A, Kuchitsu K, Mitsuhara I (2013). Tobacco MAP kinase phosphatase (NtMKP1) negatively regulates wound response and induced resistance against necrotrophic pathogens and lepidopteran herbivores.Mol Plant Micro- be In 26, 668-675. |
| 128 | Paliyath G, Thompson JE (1987). Calcium-and calmodulin- regulated breakdown of phospholipid by microsomal membranes from bean cotyledons.Plant Physiol 83, 63-68. |
| 129 | Pappan K, Wang X (1999). Molecular and biochemical properties and physiological roles of plant phospholipase D. BBA-Mol Cell Biol 1439, 151-166. |
| 130 | Park CY, Lee JH, Yoo JH, Moon BC, Choi MS, Kang YH, Lee SM, Kim HS, Kang KY, Chung WS, Lim CO, Cho MJ (2005). WRKY group IId transcription factors interact with calmodulin.FEBS Lett 579, 1545-1550. |
| 131 | Perochon A, Aldon D, Galaud JP, Ranty B (2011). Calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant calcium signaling.Biochimie 93, 2048-2053. |
| 132 | Poovaiah BW, Du L, Wang H, Yang T (2013). Recent advances in calcium/calmodulin-mediated signaling with an emphasis on plant-microbe interactions.Plant Physiol 163, 531-542. |
| 133 | Popescu SC, Popescu GV, Bachan S, Zhang ZM, Seay M, Gerstein M, Snyder M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2007). Differential binding of calmodulin-related proteins to their targets revealed through high-density Arabidopsis protein microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 4730-4735. |
| 134 | Price AH, Taylor A, Ripley SJ, Griffiths A, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1994). Oxidative signals in tobacco increase cytosolic calcium. Plant Cell 6, 1301-1310. |
| 135 | Reddy A, Safadi F, Narasimhulu SB, Golovkin M, Hu X (1996). A novel plant calmodulin-binding protein with a kinesin heavy chain motor domain. J Biol Chem 271, 7052-7060. |
| 136 | Reddy AS, Ali GS, Celesnik H, Day IS (2011a). Coping with stresses: roles of calcium- and calcium/calmodulin- regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 23, 2010-2032. |
| 137 | Reddy AS, Ben-Hur A, Day IS (2011b). Experimental and computational approaches for the study of calmodulin interactions.Phytochemistry 72, 1007-1019. |
| 138 | Reddy AS, Day IS, Narasimhulu SB, Safadi F, Reddy VS, Golovkin M, Harnly MJ (2002). Isolation and charac- terization of a novel calmodulin-binding protein from potato.J Biol Chem 277, 4206-4214. |
| 139 | Reddy ASN, Takezawa D, Fromm H, Poovaiah BW (1993). Isolation and characterization of two cDNAs that encode for calmodulin-binding proteins from corn root tips.Plant Sci 94, 109-117. |
| 140 | Reddy VS, Ali GS, Reddy AS (2002). Genes encoding calmodulin-binding proteins in the Arabidopsis genome. J Biol Chem 277, 9840-9852. |
| 141 | Reddy VS, Day IS, Thomas T, Reddy AS (2004). KIC, a novel Ca2+ binding protein with one EF-hand motif, interacts with a microtubule motor protein and regulates trichome morphogenesis.Plant Cell 16, 185-200. |
| 142 | Ren H, William MG (2015). SAUR proteins as effectors of hormonal and environmental signals in plant growth.Mol Plant 8, 1153-1164. |
| 143 | Ren S, Mandadi KK, Boedeker AL, Rathore KS, McKnight TD (2007). Regulation of telomerase in Arabidopsis by BT2, an apparent target of TELOMERASE ACTIVATOR1. Plant Cell 19, 23-31. |
| 144 | Rentel MC, Knight MR (2004). Oxidative stress-induced calcium signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 135, 1471-1479. |
| 145 | Robert HS, Quint A, Brand D, Vivian-Smith A, Offringa R (2009). BTB and TAZ domain scaffold proteins perform a crucial function in Arabidopsis development.Plant J 58, 109-121. |
| 146 | Routray P, Miller JB, Du L, Oldroyd G, Poovaiah BW (2013). Phosphorylation of S344 in the calmodulin-binding domain negatively affects CCaMK function during bac- terial and fungal symbioses. Plant J 76, 287-296. |
| 147 | Safadi F, Reddy VS, Reddy AS (2000). A pollen-specific novel calmodulin-binding protein with tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem 275, 35457-35470. |
| 148 | Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002). Calcium at the crossroads of signaling.Plant Cell 14, S401-S417. |
| 149 | Schulz P, Herde M, Romeis T (2013). Calcium-dependent protein kinases: hubs in plant stress signaling and de- velopment.Plant Physiol 163, 523-530. |
| 150 | Schumacher MA, Rivard AF, Bachinger HP, Adelman JP (2001). Structure of the gating domain of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel complexed with Ca2+/calmodulin.Nature 410, 1120-1124. |
| 151 | Schuurink RC, Shartzer SF, Fath A, Jones RL (1998). Characterization of a calmodulin-binding transporter from the plasma membrane of barley aleurone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 1944-1949. |
| 152 | Shen X, Valencia CA, Szostak JW, Dong B, Liu R (2005). Scanning the human proteome for calmodulin-binding proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 5969-5974. |
| 153 | Shi B, Ni L, Zhang A, Cao J, Zhang H, Qin T, Tan M, Zhang J, Jiang M (2012). OsDMI3 is a novel component of abscisic acid signaling in the induction of antioxidant defense in leaves of rice.Mol Plant 5, 1359-1374. |
| 154 | Snedden WA, Blumwald E (2000). Alternative splicing of a novel diacylglycerol kinase in tomato leads to a cal- modulin-binding isoform. Plant J 24, 317-326. |
| 155 | Snedden WA, Fromm H (2001). Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants.New Phytol 151, 35-66. |
| 156 | Snedden WA, Koutsia N, Baum G, Fromm H (1996). Activation of a recombinant petunia glutamate decar- boxylase by calcium/calmodulin or by a monoclonal anti- body which recognizes the calmodulin binding domain.J Biol Chem 271, 4148-4153. |
| 157 | Steinebrunner I, Jeter C, Song C, Roux SJ (2000). Molecular and biochemical comparison of two different apyrases from Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Physiol Bioch 38, 913-922. |
| 158 | Sunkar R, Kaplan B, Bouche N, Arazi T, Dolev D, Talke IN, Maathuis FJ, Sanders D, Bouchez D, Fromm H (2000). Expression of a truncated tobacco NtCBP4 channel in transgenic plants and disruption of the homologous Arabidopsis CNGC1 gene confer Pb2+ tole- rance.Plant J 24, 533-542. |
| 159 | Suzuki N, Miller G, Morales J, Shulaev V, Torres MA, Mittler R (2011). Respiratory burst oxidases: the engines of ROS signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 691-699. |
| 160 | Szymanski DB, Liao B, Zielinski RE (1996). Calmodulin isoforms differentially enhance the binding of cauliflower nuclear proteins and recombinant TGA3 to a region derived from the Arabidopsis Cam-3 promoter.Plant Cell 8, 1069-1077. |
| 161 | Takahashi F, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K (2011). Calmodulin-dependent activation of MAP kinase for ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis.Mol Cell 41, 649-660. |
| 162 | Takezawa D (2003). Characterization of a novel plant PP2C- like protein Ser/Thr phosphatase as a calmodulin-binding protein. J Biol Chem 278, 38076-38083. |
| 163 | Tang W, Tu L, Yang X, Tan J, Deng F, Hao J, Guo K, Lindsey K, Zhang X (2014). The calcium sensor GhCaM7 promotes cotton fiber elongation by modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.New Phytol 202, 509-520. |
| 164 | Turner WL, Waller JC, Vanderbeld B, Snedden WA (2004). Cloning and characterization of two NAD kinases from Arabidopsis. identification of a calmodulin binding isoform.Plant Physiol 135, 1243-1255. |
| 165 | Ulm R, Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Peck SC, Zhu T, Wang X, Shinozaki K, Paszkowski J (2002). Distinct regulation of salinity and genotoxic stress responses by Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1.EMBO J 21, 6483-6493. |
| 166 | Vanderbeld B, Snedden WA (2007). Developmental and stimulus-induced expression patterns of Arabidopsis calmodulin-like genes CML37, CML38 and CML39.Plant Mol Biol 64, 683-697. |
| 167 | Vanoosthuyse V, Tichtinsky G, Dumas C, Gaude T, Cock JM (2003). Interaction of calmodulin, a sorting nexin and kinase-associated protein phosphatase with the Brassica oleracea S locus receptor kinase.Plant Physiol 133, 919-929. |
| 168 | Veluthambi K, Poovaiah BW (1984). Calcium-promoted protein phosphorylation in plants. Science 223, 167-169. |
| 169 | Vinogradova MV, Reddy VS, Reddy AS, Sablin EP, Fletterick RJ (2004). Crystal structure of kinesin regulated by Ca2+-calmodulin.J Biol Chem 279, 23504-23509. |
| 170 | Virdi AS, Singh S, Singh P (2015). Abiotic stress responses in plants: roles of calmodulin-regulated proteins.Front Plant Sci 6, 809. |
| 171 | Wang G, Zeng H, Hu X, Zhu Y, Chen Y, Shen C, Wang H, Poovaiah BW, Du L (2015). Identification and expression analyses of calmodulin-binding transcription activator genes in soybean.Plant Soil 386, 205-221. |
| 172 | Wang L, Tsuda K, Sato M, Cohen JD, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J (2009). Arabidopsis CaM binding protein CBP60g contributes to MAMP-induced SA accumulation and is involved in disease resistance against Pseudo- monas syringae.PLoS Pathog 5, e1000301. |
| 173 | Wang Y, Liang S, Xie QG, Lu YT (2004). Characterization of a calmodulin-regulated Ca2+-dependent-protein-kinase- related protein kinase, AtCRK1, from Arabidopsis.Bio- chem J 383, 73-81. |
| 174 | Watillon B, Kettmann R, Boxus P, Burny A (1993). A calcium/calmodulin-binding serine/threonine protein kin- ase homologous to the mammalian type II calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase is expressed in plant cells.Plant Physiol 101, 1381-1384. |
| 175 | Wu J, Steinebrunner I, Sun Y, Butterfield T, Torres J, Arnold D, Gonzalez A, Jacob F, Reichler S, Roux SJ (2007). Apyrases (nucleoside triphosphate-diphosphohy- drolases) play a key role in growth control in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 144, 961-975. |
| 176 | Xi J, Qiu Y, Du L, Poovaiah BW (2012). Plant-specific trihelix transcription factor AtGT2L interacts with cal- cium/calmodulin and responds to cold and salt stresses. Plant Sci 185-186, 274-280. |
| 177 | Xue H, Chen X, Li G (2007). Involvement of phospholipid signaling in plant growth and hormone effects.Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 483-489. |
| 178 | Yamaguchi T, Aharon GS, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2005). Vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter cation selectivity is regulated by calmodulin from within the vacuole in a Ca2+- and pH-dependent manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 16107-16112. |
| 179 | Yamakawa H, Katou S, Seo S, Mitsuhara I, Kamada H, Ohashi Y (2004). Plant MAPK phosphatase interacts with calmodulins. J Biol Chem 279, 928-936. |
| 180 | Yamniuk AP, Vogel HJ (2004). Calmodulin's flexibility allows for promiscuity in its interactions with target proteins and peptides.Mol Biotechnol 27, 33-57. |
| 181 | Yamniuk AP, Vogel HJ (2005). Structural investigation into the differential target enzyme regulation displayed by plant calmodulin isoforms.Biochemistry 44, 3101-3111. |
| 182 | Yang T, Chaudhuri S, Yang L, Chen Y, Poovaiah BW (2004). Calcium/calmodulin up-regulates a cytoplasmic receptor-like kinase in plants. J Biol Chem 279, 42552-42559. |
| 183 | Yang T, Chaudhuri S, Yang L, Du L, Poovaiah BW (2010). A calcium/calmodulin-regulated member of the receptor- like kinase family confers cold tolerance in plants. J Biol Chem 285, 7119-7126. |
| 184 | Yang T, Poovaiah B (2007). Concept of redesigning pro- teins by manipulating calcium/calmodulin-binding do- mains to engineer plants with altered traits.Funct Plant Biol 34, 343-352. |
| 185 | Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2000a). Molecular and biochemical evidence for the involvement of calcium/calmodulin in auxin action.J Biol Chem 275, 3137-3143. |
| 186 | Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2000b). Arabidopsis chloroplast chaperonin 10 is a calmodulin-binding protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275, 601-607. |
| 187 | Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2002a). A calmodulin-binding/ CGCG box DNA-binding protein family involved in mul- tiple signaling pathways in plants.J Biol Chem 277, 45049-45058. |
| 188 | Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2002b). Hydrogen peroxide home- ostasis: activation of plant catalase by calcium/calmo- dulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 4097-4102. |
| 189 | Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2003). Calcium/calmodulin-media- ted signal network in plants.Trends Plant Sci 8, 505-512. |
| 190 | Yap KL, Yuan T, Mal TK, Vogel HJ, Ikura M (2003). Structural basis for simultaneous binding of two carboxy- terminal peptides of plant glutamate decarboxylase to calmodulin.J Mol Biol 328, 193-204. |
| 191 | Yoo JH, Cheong MS, Park CY, Moon BC, Kim MC, Kang YH, Park HC, Choi MS, Lee JH, Jung WY (2004). Regulation of the dual specificity protein phosphatase, DsPTP1, through interactions with calmodulin. J Biol Chem 279, 848-858. |
| 192 | Yoo JH, Park CY, Kim JC, Do Heo W, Cheong MS, Park HC, Kim MC, Moon BC, Choi MS, Kang YH, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee SM, Yoon HW, Lim CO, Yun DJ, Lee SY, Chung WS, Cho MJ (2005). Direct interaction of a divergent CaM isoform and the transcription factor, MYB2, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 280, 3697-3706. |
| 193 | Yoshioka K, Moeder W, Kang HG, Kachroo P, Masmoudi K, Berkowitz G, Klessig DF (2006). The chimeric Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHA- NNEL11/12 activates multiple pathogen resistance res- ponses.Plant Cell 18, 747-763. |
| 194 | Zelman AK, Dawe A, Gehring C, Berkowitz GA (2012). Evolutionary and structural perspectives of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels. Front Plant Sci 3, 95. |
| 195 | Zeng H, Xu L, Singh A, Wang H, Du L, Poovaiah BW (2015). Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant responses to abiotic stresses.Front Plant Sci 6, 600. |
| 196 | Zhang L, Du L, Shen C, Yang Y, Poovaiah B (2014). Regulation of plant immunity through ubiquitin-mediated modulation of Ca2+-calmodulin-AtSR1/CAMTA3 signaling.Plant J 78, 269-281. |
| 197 | Zhang L, Liu BF, Liang S, Jones RL, Lu YT (2002). Molecular and biochemical characterization of a calcium/ calmodulin-binding protein kinase from rice.Biochem J 368, 145-157. |
| 198 | Zhang L, Lu YT (2003). Calmodulin-binding protein kinases in plants.Trends Plant Sci 8, 123-127. |
| 199 | Zhang Y, Xu S, Ding P, Wang D, Cheng YT, He J, Gao M, Xu F, Li Y, Zhu Z, Li X, Zhang Y (2010). Control of salicylic acid synthesis and systemic acquired resistance by two members of a plant-specific family of transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 18220-18225. |
| 200 | Zhao B, Li J (2012). Regulation of brassinosteroid biosyn- thesis and inactivation.J Integr Plant Biol 54, 746-759. |
| 201 | Zhou YP, Duan J, Fujibe T, Yamamoto KT, Tian CE (2012). AtIQM1, a novel calmodulin-binding protein, is involved in stomatal movement in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol 79, 333-346. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||