

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 560-572.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22123 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22123
陈昌婕, 苗玉焕, 罗丹丹, 王梓欣, 郭璐娟, 赵婷婷( ), 刘大会(
), 刘大会( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-17
接受日期:2022-11-15
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-11-15
通讯作者:
*E-mail: datingsdau@126.com;liudahui@hbtcm.edu.cn
基金资助:
Changjie Chen, Yuhuan Miao, Dandan Luo, Zixin Wang, Lujuan Guo, Tingting Zhao( ), Dahui Liu(
), Dahui Liu( )
)
Received:2022-06-17
Accepted:2022-11-15
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-11-15
Contact:
*E-mail: datingsdau@126.com;liudahui@hbtcm.edu.cn
摘要: 龙脑是艾(Artemisia argyi)叶中最重要的药效成分之一, 具有抗菌、消炎及镇痛等药理活性。其生物合成和代谢受多种酶的影响, 其中龙脑脱氢酶是将龙脑氧化为樟脑的关键酶之一。利用气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)技术测定了35份艾种质叶片中龙脑和樟脑的含量。结果表明, 不同品种艾叶片中龙脑和樟脑含量差异较大, 在部分种质中樟脑含量甚至超过了龙脑, 说明大量的龙脑被氧化为樟脑后严重降低了艾叶中龙脑的含量。基于全长转录组和同源性比较分析, 在艾叶中克隆到1个艾龙脑脱氢酶编码基因AArBDH1。AArBDH1基因含有2个外显子和1个内含子, 编码包含289个氨基酸残基的蛋白。qRT-PCR分析表明, 在艾不同组织和不同发育时期的叶片中AArBDH1呈差异表达, 在茎和30天叶龄的叶片中高表达。以龙脑为底物、NAD+为辅酶的酶促反应表明, AArBDH1能催化龙脑脱氢生成樟脑。该研究为进一步揭示艾叶片中龙脑积累的调控和改进机制提供了理论依据和基因资源。
陈昌婕, 苗玉焕, 罗丹丹, 王梓欣, 郭璐娟, 赵婷婷, 刘大会. 艾龙脑脱氢酶基因AArBDH1的克隆及功能鉴定. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 560-572.
Changjie Chen, Yuhuan Miao, Dandan Luo, Zixin Wang, Lujuan Guo, Tingting Zhao, Dahui Liu. Cloning and Functional Verification of the Borneol Dehydrogenase Encoding Gene AArBDH1 in Artemisia argyi. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 560-572.
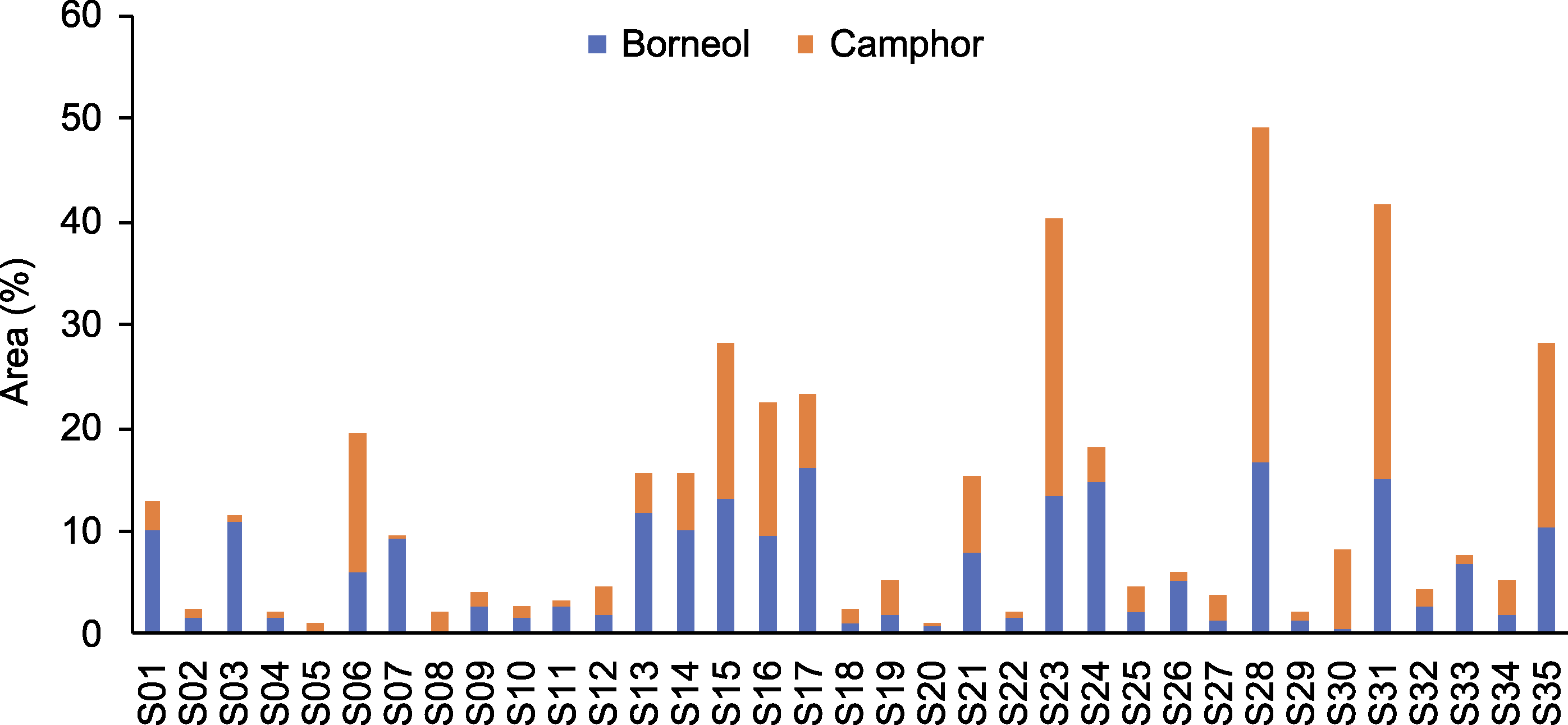
图2 35份艾种质叶片中龙脑和樟脑的相对含量 S01-S35为35份艾叶样品编号。
Figure 2 Relative contents of borneol and camphor in the leaves of 35 Artemisia argyi varieties S01-S35 is the number of 35 Artemisia argyi varieties.
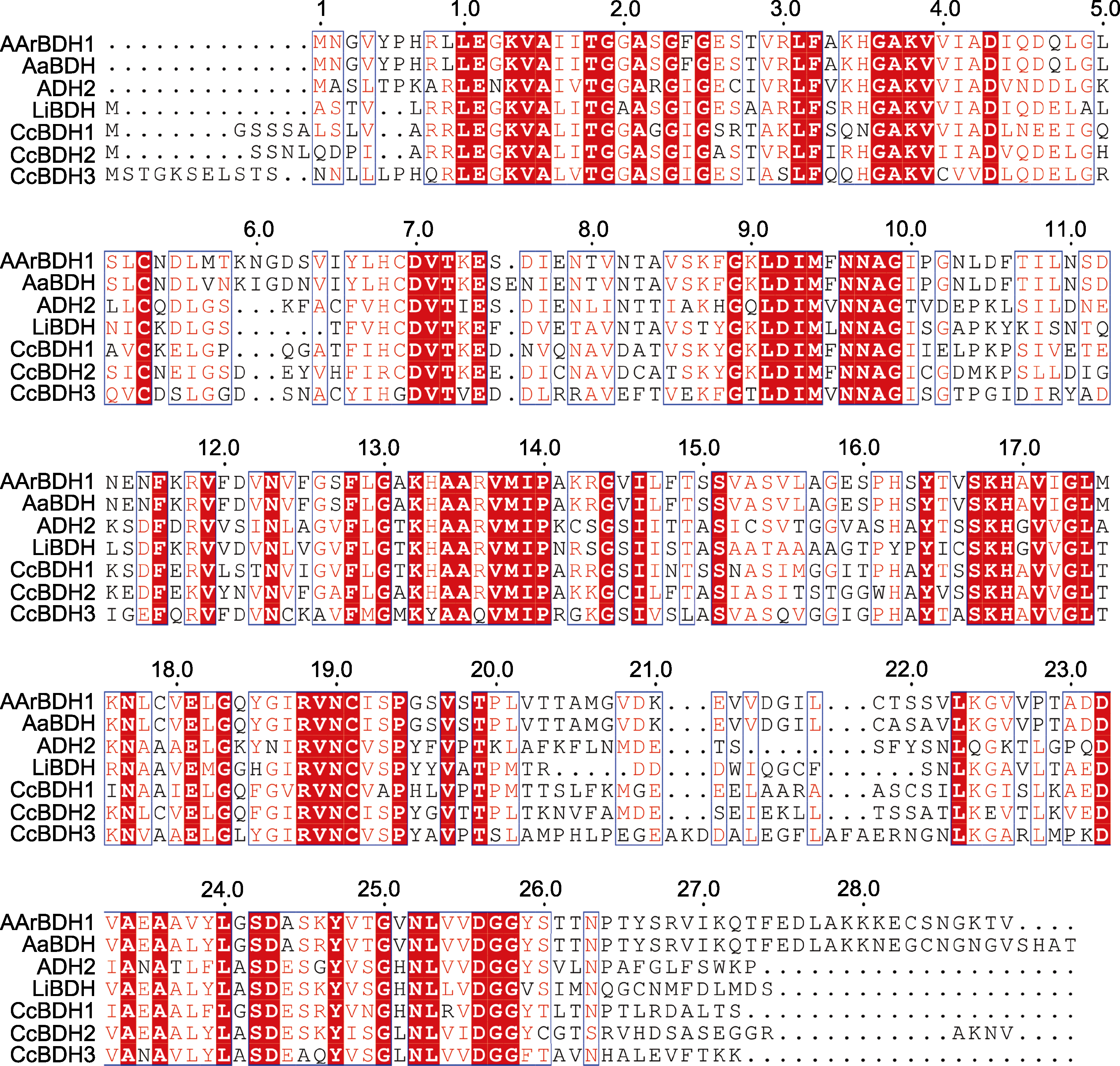
图3 AArBDH1与AaBDH、ADH2、LiBDH、CcBDH1、CcBDH2和CcBDH3的多序列比对
Figure 3 Multiple sequence alignment of AArBDH1 with AaBDH, ADH2, LiBDH, CcBDH1, CcBDH2, and CcBDH3
| No. | Gene | Species | GenBank accession | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AaBDH | Artemisia annua | KT070864 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Tian et al., |
| 2 | ADH2 | A. annua | GU253890 | Alcohol dehydrogenase | Polichuk et al., |
| 3 | ALDH | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | WP_028626884 | Dehydrogenase | Tsang et al., |
| 4 | CcBDH1 | Cinnamomum camphora | MW012431 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 5 | CcBDH2 | C. camphora | MW012432 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 6 | CcBDH3 | C. camphora | MN551096 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 7 | CHCR | Cricetulus griseus | AB020238 | Carbonyl reductase | Terada et al., |
| 8 | DlSDR | Digitalis lanata | Q93Y47 | 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | Finsterbusch et al., |
| 9 | FiSDR | Forsythia intermedia | AF352735 | Secoisolariciresinol dehydrogenase | Xia et al., |
| 10 | ISPD | Mentha × piperita | AAU20370 | (-)-isopiperitenol dehydrogenase | Ringer et al., |
| 11 | HSCR | Homo sapiens | J04056 | Carbonyl reductase | Wermuths et al., |
| 12 | LiBDH | Lavandula × intermedia | AFV30207 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Sarker et al., |
| 13 | MIR | Mentha × piperita | AY300162 | (-)-isopiperitenone reductase | Ringer et al., |
| 14 | MNR | Mentha × piperita | ABC88670 | (+)-neomenthol reductase | Davis et al., |
| 15 | MMR | Mentha × piperita | AAQ55960 | Menthol dehydrogenase | Davis et al., |
| 16 | NEPS | Nepeta mussinii | 6F9Q_D | Nepetalactol-related short-chain dehydrogenase | Lichman et al., |
| 17 | PsSDR | Pisum sativum | AAF04253 | Short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase | Brosché and Strid, |
| 18 | PTCR | Sus scrofa | M80709 | 20-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | Tanaka et al., |
| 19 | RED1 | A. annua | GU167953 | Reductase/dehydrogenase | Rydén et al., |
| 20 | SalR | Papaver bracteatum | EF184229 | Salutaridine reductase | Geissle et al., |
| 21 | ZSD1 | Zingiber zerumbet | AB480831 | Short-chain dehydrogenase | Okamoto et al., |
表1 从NCBI下载的SDR蛋白质编码基因信息
Table 1 Information of SDR encoding genes downloaded from NCBI
| No. | Gene | Species | GenBank accession | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AaBDH | Artemisia annua | KT070864 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Tian et al., |
| 2 | ADH2 | A. annua | GU253890 | Alcohol dehydrogenase | Polichuk et al., |
| 3 | ALDH | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | WP_028626884 | Dehydrogenase | Tsang et al., |
| 4 | CcBDH1 | Cinnamomum camphora | MW012431 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 5 | CcBDH2 | C. camphora | MW012432 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 6 | CcBDH3 | C. camphora | MN551096 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Ma et al., |
| 7 | CHCR | Cricetulus griseus | AB020238 | Carbonyl reductase | Terada et al., |
| 8 | DlSDR | Digitalis lanata | Q93Y47 | 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | Finsterbusch et al., |
| 9 | FiSDR | Forsythia intermedia | AF352735 | Secoisolariciresinol dehydrogenase | Xia et al., |
| 10 | ISPD | Mentha × piperita | AAU20370 | (-)-isopiperitenol dehydrogenase | Ringer et al., |
| 11 | HSCR | Homo sapiens | J04056 | Carbonyl reductase | Wermuths et al., |
| 12 | LiBDH | Lavandula × intermedia | AFV30207 | Borneol dehydrogenase | Sarker et al., |
| 13 | MIR | Mentha × piperita | AY300162 | (-)-isopiperitenone reductase | Ringer et al., |
| 14 | MNR | Mentha × piperita | ABC88670 | (+)-neomenthol reductase | Davis et al., |
| 15 | MMR | Mentha × piperita | AAQ55960 | Menthol dehydrogenase | Davis et al., |
| 16 | NEPS | Nepeta mussinii | 6F9Q_D | Nepetalactol-related short-chain dehydrogenase | Lichman et al., |
| 17 | PsSDR | Pisum sativum | AAF04253 | Short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase | Brosché and Strid, |
| 18 | PTCR | Sus scrofa | M80709 | 20-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | Tanaka et al., |
| 19 | RED1 | A. annua | GU167953 | Reductase/dehydrogenase | Rydén et al., |
| 20 | SalR | Papaver bracteatum | EF184229 | Salutaridine reductase | Geissle et al., |
| 21 | ZSD1 | Zingiber zerumbet | AB480831 | Short-chain dehydrogenase | Okamoto et al., |
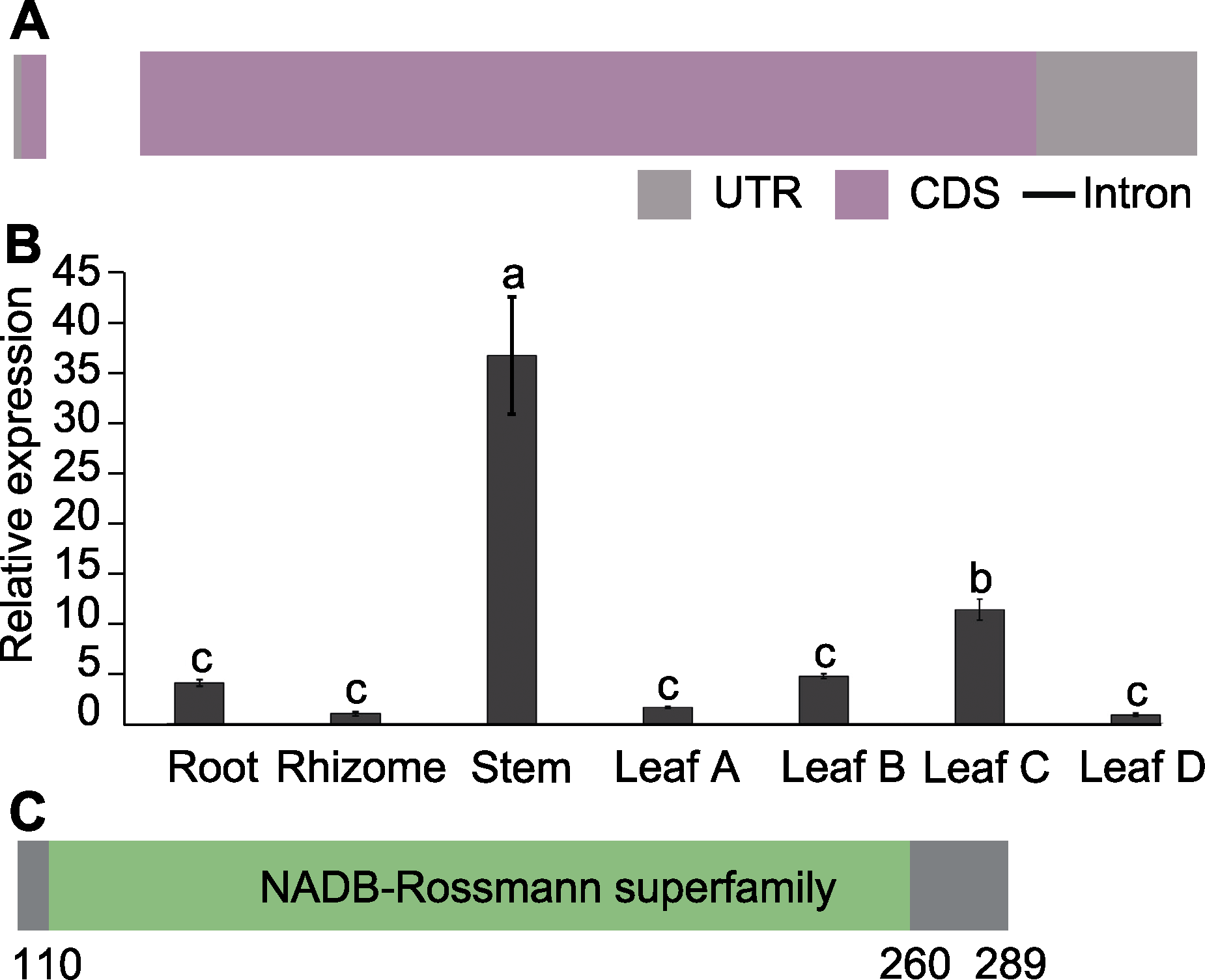
图5 AArBDH1基因的结构(A)、在不同组织中的表达丰度(B)和AArBDH1蛋白质结构分析(C) UTR: 非翻译区; CDS: 编码区。Leaf A、Leaf B、Leaf C、Leaf D分别为叶芽及叶龄为15天、30天和45天的叶片。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5 Gene structure (A), expression profiles in different organizations of AArBDH1 (B) and protein structure analysis of AArBDH1 (C) UTR: Untranslated region; CDS: Coding sequence. Leaf A, Leaf B, Leaf C and Leaf D represent leaf buds, 15 days, 30 days and 45 days old leaves, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
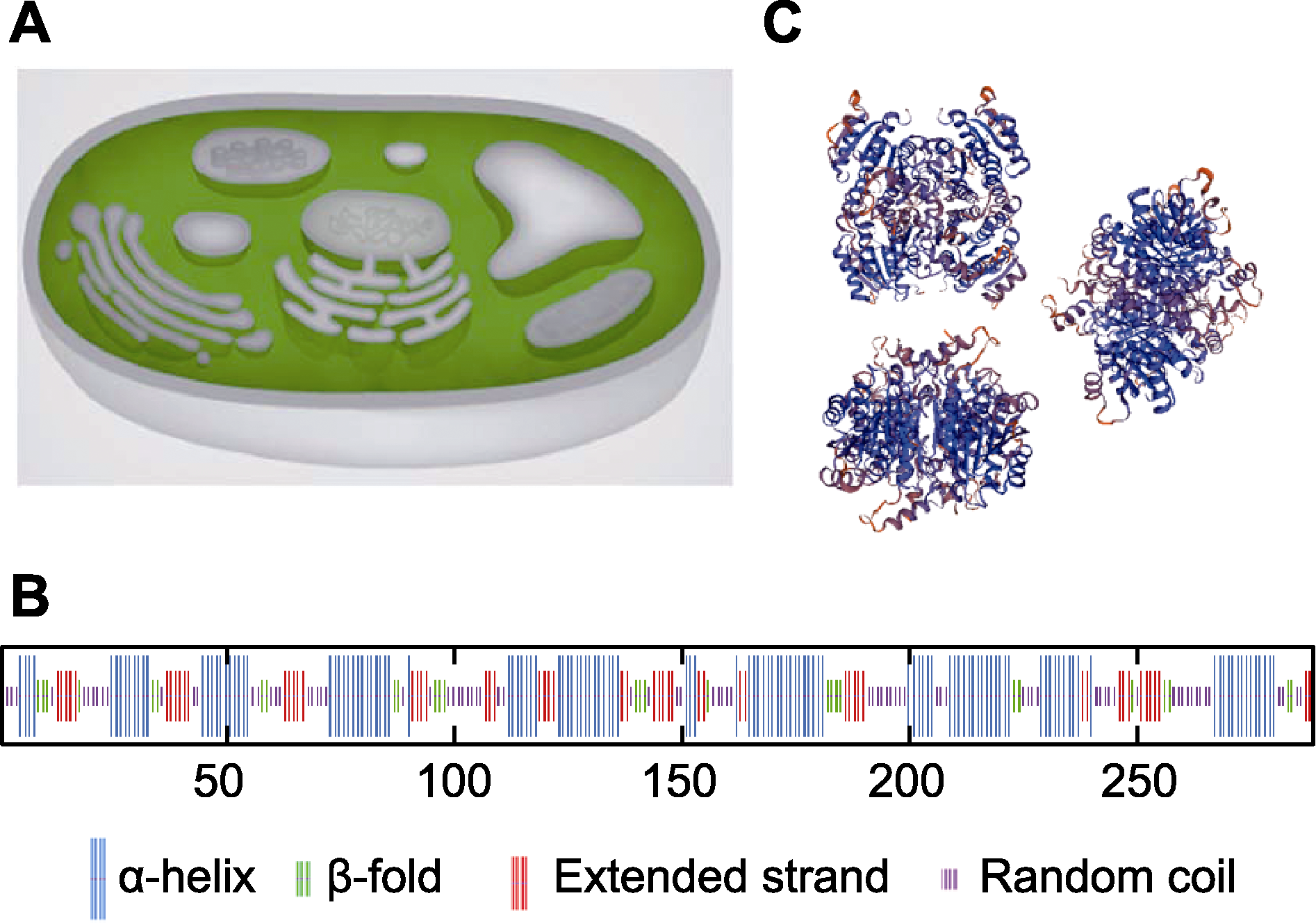
图6 AArBDH1蛋白质结构预测 (A) AArBDH1的亚细胞定位预测; (B) AArBDH1蛋白质二级结构预测; (C) AArBDH1蛋白质三级结构预测
Figure 6 Protein structure prediction of AArBDH1 (A) The subcellular localization prediction of AArBDH1; (B) The secondary structure prediction of AArBDH1; (C) The tertiary structure prediction of AArBDH1
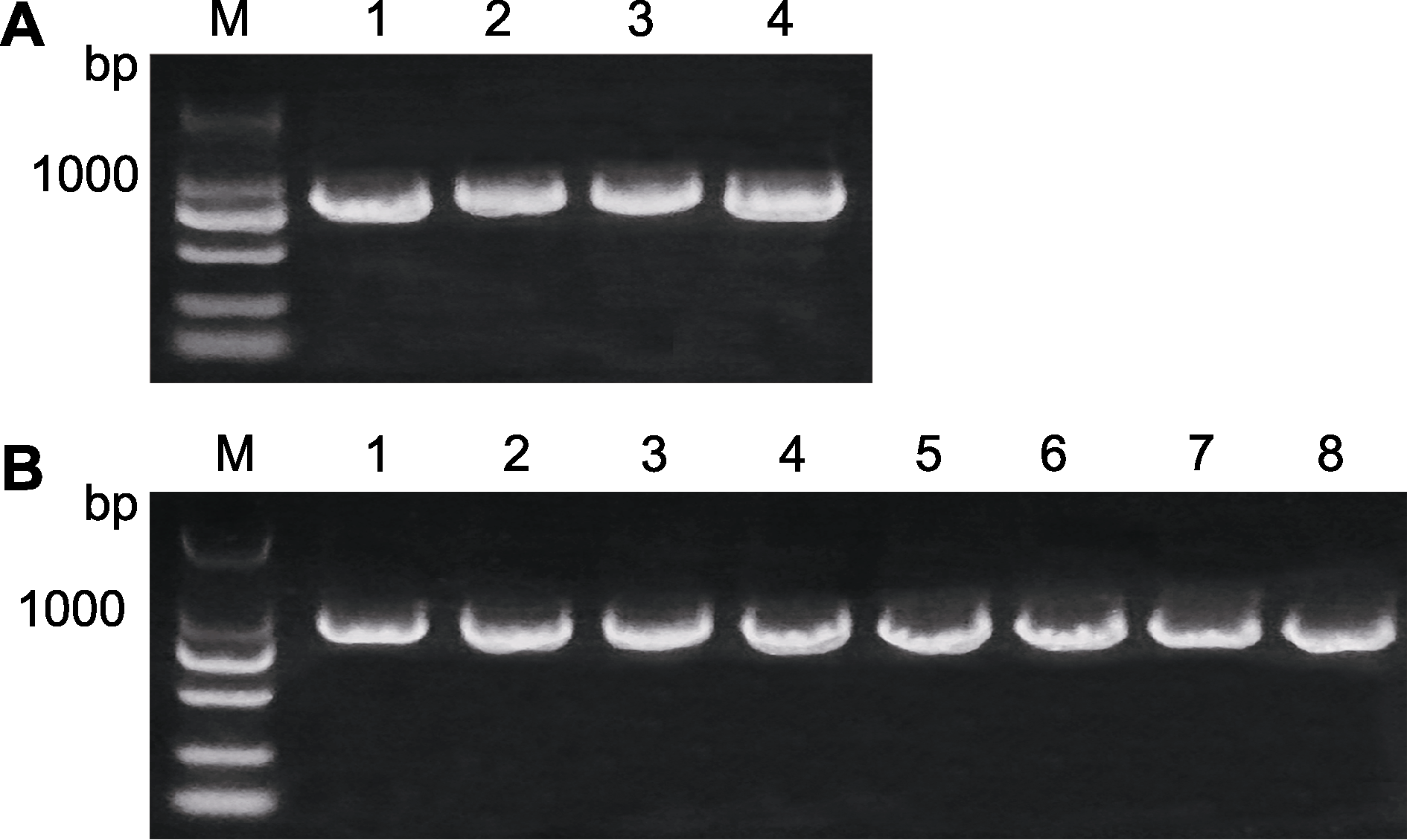
图7 AArBDH1的克隆(A)和阳性克隆鉴定(B) M: 分子标记; 编号为待检测样品的序号。
Figure 7 Cloning of AArBDH1 (A) and the identification of positive clones (B) M: Markers; Numbers: The number of the samples tested.
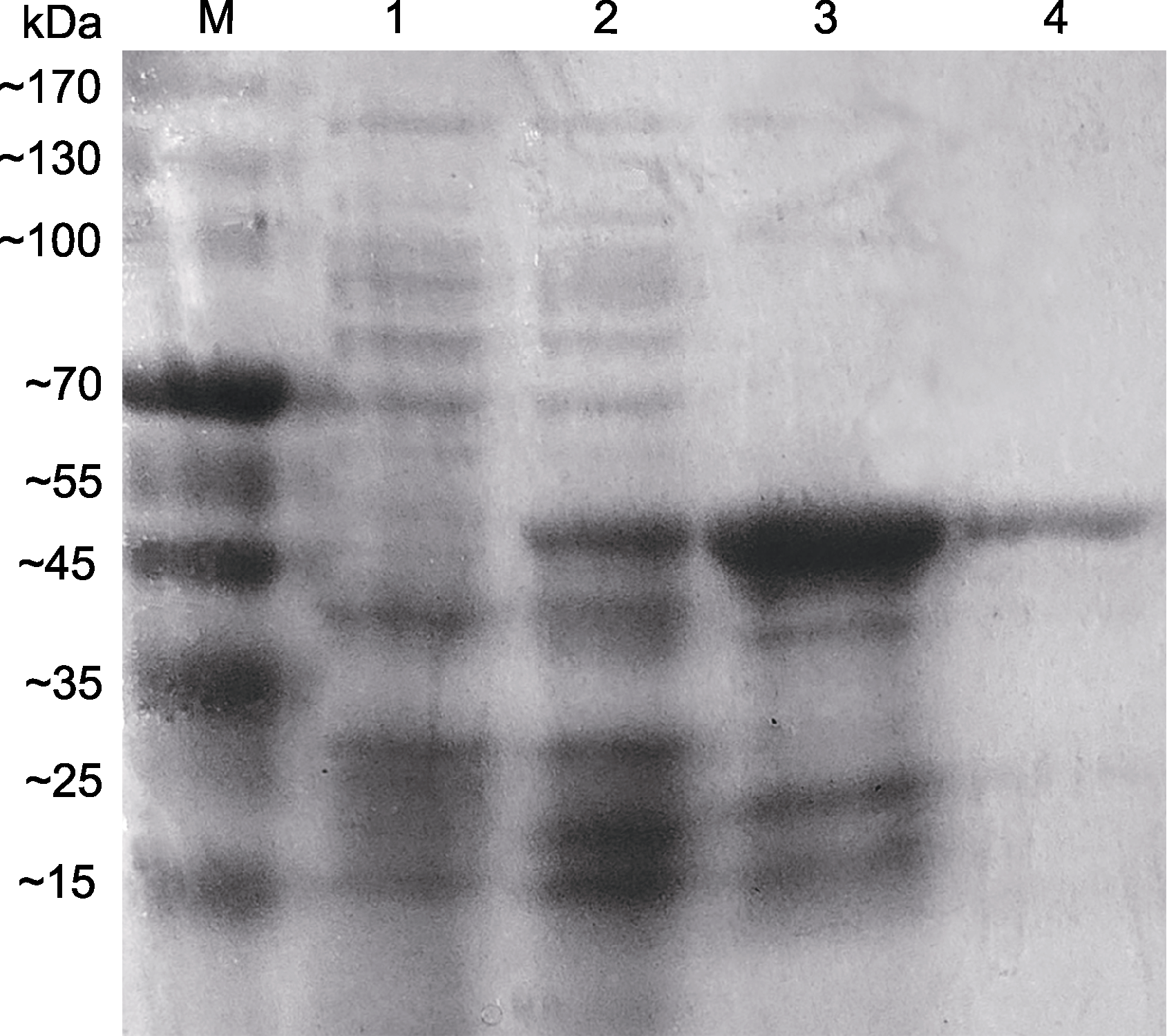
图8 AArBDH1的诱导表达产物和纯化 1: 未经诱导的菌体蛋白; 2: IPTG诱导表达的菌体蛋白; 3: 1次纯化后的菌体蛋白; 4: 2次纯化后的菌体蛋白
Figure 8 Induced expression product and purification of AA- rBDH1 1: Expression products without IPTG; 2: Induced expression by IPTG; 3: Primary purified protein; 4: Secondary purified protein
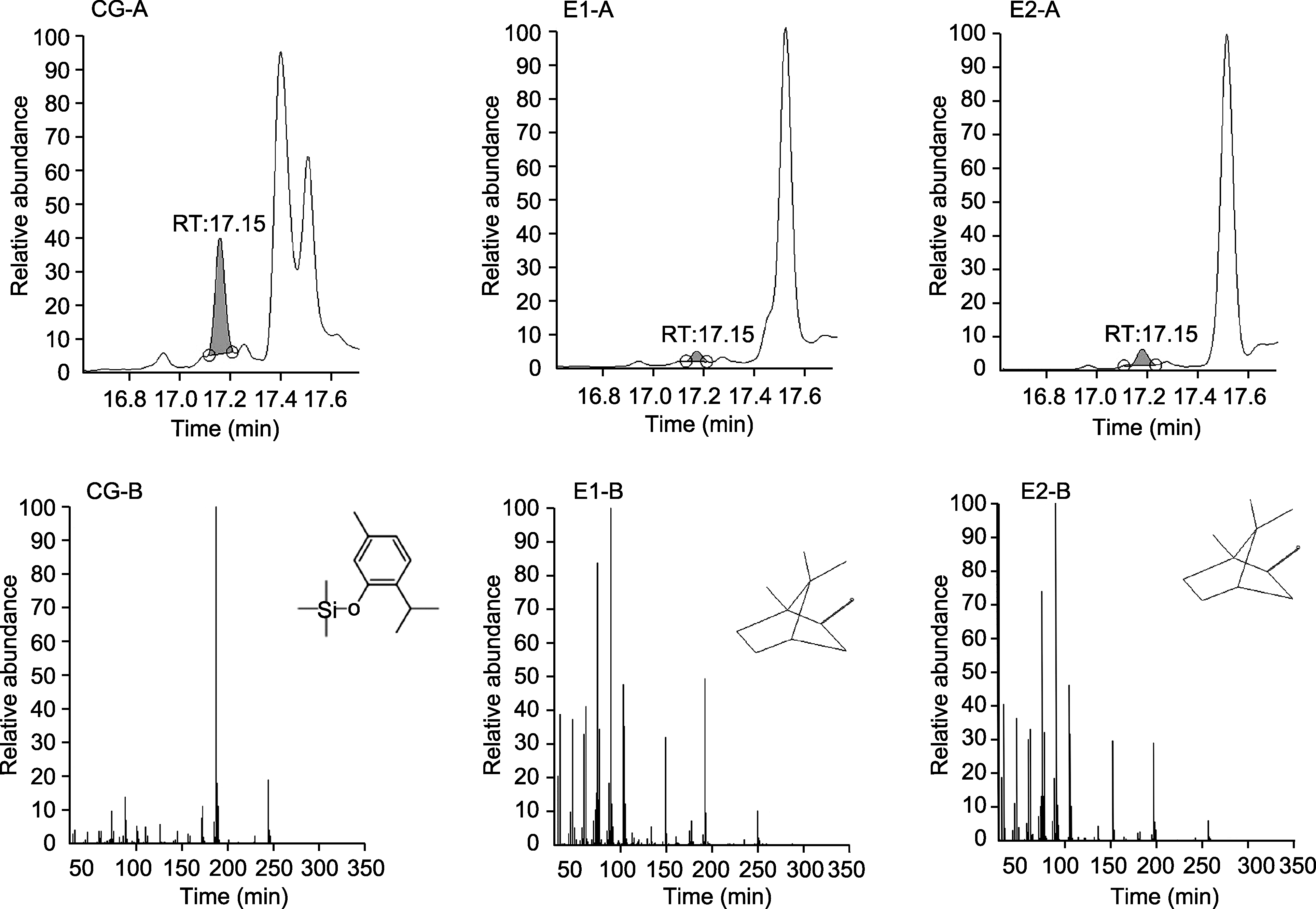
图10 AArBDH1催化产物的GC-MS分析 CG: 对照组; E1, E2: 实验组; A: 色谱峰; B: 碎片离子峰
Figure 10 GC-MS analysis of products catalyzed by AArBDH1 CG: Control group; E1, E2: Experimental groups; A: Chromatographic peak; B: Fragment ion peak
| [1] | 陈昌婕, 罗丹丹, 苗玉焕, 康利平, 郭兰萍, 刘大会, 黄璐琦 (2021). 艾种质资源挥发性成分分析与评价. 中国中药杂志 46, 3814-3823. |
| [2] | 陈昌婕, 马琳, 康利平, 苗玉焕, 陈中文, 郭兰萍, 刘大会, 黄璐琦 (2020). 不同种植时期和垄作模式对蕲艾生长和品质的影响. 中国中药杂志 45, 4041-4050. |
| [3] | 丁贤华, 张丽萍, 费璇, 朱强, 张金华, 任仙樱, 吴志刚, 姜程曦 (2021). 温郁金法呢基焦磷酸合酶(CwFPPS)基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析. 中草药 52, 6968-6974. |
| [4] | 国家药典委员会 (2020). 中华人民共和国药典. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社. pp. 92. |
| [5] | 兰晓燕, 张元, 朱龙波, 刘大会, 黄显章, 周利, 康利平 (2020). 艾叶化学成分、药理作用及质量研究进展. 中国中药杂志 45, 4017-4030. |
| [6] |
刘星星, 张茜, 郭夏丽, 龚上佶, 江香梅, 付宇新, 罗丽萍 (2014). 不同化学型樟树叶挥发性成分组成的多变量分析. 植物学报 49, 161-166.
DOI |
| [7] | 马琳, 陈昌婕, 康利平, 苗玉焕, 方艳, 郭兰萍, 刘大会, 黄璐琦 (2020). 不同种植密度、叶位与叶龄对蕲艾产量和品质的影响. 中国中药杂志 45, 4031-4040. |
| [8] | 马青, 马蕊, 靳保龙, 崔光红 (2021). 天然冰片资源研究进展. 中国中药杂志 46, 57-61. |
| [9] | 田梅, 陈灵丽, 靳保龙, 郭娟, 葛慧, 赵鑫, 崔光红 (2021). 铁棒锤转录组分析及乌头碱生物合成相关基因的挖掘. 药学学报 56, 3353-3361. |
| [10] | 王文然, 张文颖, 管乐, 汤崴, 房经贵, 王晨 (2017). 石榴木质素相关蛋白PgCAD蛋白的生物信息学分析. 果树学报 34, 67-75. |
| [11] | 徐应文, 吕季娟, 吴卫, 郑有良 (2009). 植物单萜合酶研究进展. 生态学报 29, 3188-3197. |
| [12] | 张雪琳, 陈新旺, 吴毅明 (2021). 近10年来艾叶挥发油的化学成分及药理活性研究进展. 中华中医药学刊 39(5), 111-118. |
| [13] | 赵圆圆, 孙叶雯, 郑诗敏, 李萌, 马东明, 杨锦芬 (2022). 阳春砂龙脑基二磷酸合酶关键氨基酸位点筛选及突变体的构建. 中草药 53, 529-537. |
| [14] | 郑昆, 钟肖飞, 张华 (2020). 艾叶挥发油类成分及其药理作用的研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志 26(18), 224-234. |
| [15] |
Amstutz CL, Fristedt R, Schultink A, Merchant SS, Niyogi KK, Malnoë A (2020). An atypical short-chain dehydrogenase-reductase functions in the relaxation of photo- protective qH in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 6, 154-166.
DOI |
| [16] |
Brosché M, Strid Ǻ (1999). Cloning, expression, and molecular characterization of a small pea gene family regulated by low levels of ultraviolet B radiation and other stresses. Plant Physiol 121, 479-488.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Davis EM, Ringer KL, McConkey ME, Croteau R (2005). Monoterpene metabolism. Cloning, expression, and characterization of menthone reductases from peppermint. Plant Physiol 137, 873-881.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Dong TW, Chen N, Ma X, Wang J, Wen J, Xie Q, Ma R (2018). The protective roles of L-borneolum, D-borneolum and synthetic borneol in cerebral ischaemia via modulation of the neurovascular unit. Biomed Pharmacother 102, 874-883.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Finsterbusch A, Lindemann P, Grimm R, Eckerskorn C, Luckner M (1999). Δ5-3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Digitalis lanata Ehrh. — a multifunctional enzyme in steroid metabolism? Planta 209, 478-486.
PMID |
| [20] |
Geissler R, Brandt W, Ziegler J (2007). Molecular modeling and site-directed mutagenesis reveal the benzylisoquinoline binding site of the short-chain dehydrogenase/ reductase salutaridine reductase. Plant Physiol 143, 1493-1503.
PMID |
| [21] |
Ho TJ, Hung CC, Shih TL, Yiin LM, Chen HP (2018). Investigation of borneols sold in Taiwan by chiral gas chromatography. J Food Drug Anal 26, 348-352.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Hurd MC, Kwon M, Ro DK (2017). Functional identification of a Lippia dulcis bornyl diphosphate synthase that contains a duplicated, inhibitory arginine-rich motif. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490, 963-968.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Khine AA, Lu PC, Ko TP, Huang KF, Chen HP (2020). Cloning, expression, identification and characterization of borneol dehydrogenase isozymes in Pseudomonas sp. TCU-HL1. Protein Expression Purif 175, 105715.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Lichman BR, Kamileen MO, Titchiner GR, Saalbach G, Stevenson CEM, Lawson DM, O’Connor SE (2019). Uncoupled activation and cyclization in catmint reductive terpenoid biosynthesis. Nat Chem Biol 15, 71-79.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Lu DD, Tan ZW, Li L, Yu YL, Xu LJ, Yang HQ, Dong W, Liang HZ (2022). Cloning and expression analysis of anthocyanidin reductase gene ANR in Carthamus tinctorius L. J Nucl Agric Sci 36, 517-526. |
| [26] |
Ma R, Su P, Guo J, Jin BL, Ma Q, Zhang HY, Chen LL, Mao LY, Tian M, Lai CJS, Tang JF, Cui GH, Huang LQ (2021a). Bornyl diphosphate synthase from Cinnamomum burmanni and its application for (+)-borneol biosynthesis in yeast. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9, 631863.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Ma R, Su P, Jin BL, Guo J, Tian M, Mao LY, Tang JF, Chen T, Lai CJS, Zeng W, Cui GH, Huang LQ (2021b). Molecular cloning and functional identification of a high- efficiency (+)-borneol dehydrogenase from Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl. Plant Physiol Biochem 158, 363-371.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Miao YH, Luo DD, Zhao TT, Du HZ, Liu ZH, Xu ZP, Guo LP, Chen CJ, Peng SN, Li JX, Ma L, Ning GG, Liu DH, Huang LQ (2022). Genome sequencing reveals chromosome fusion and extensive expansion of genes related to secondary metabolism in Artemisia argyi. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 1902-1915.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Okamoto S, Yu FN, Harada H, Okajima T, Hattan JI, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2011). A short-chain dehydrogenase involved in terpene metabolism from Zingiber zerumbet. FEBS J 278, 2892-2900.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Polichuk DR, Zhang YS, Reed DW, Schmidt JF, Covello PS (2010). A glandular trichome-specific monoterpene alcohol dehydrogenase from Artemisia annua. Phytochemistry 71, 1264-1269.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Ringer KL, Davis EM, Croteau R (2005). Monoterpene metabolism. Cloning, expression, and characterization of (-)-isopiperitenol/(-)-carveol dehydrogenase of peppermint and spearmint. Plant Physiol 137, 863-872.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Ringer KL, McConkey ME, Davis EM, Rushing GW, Croteau R (2003). Monoterpene double-bond reductases of the (-)-menthol biosynthetic pathway: isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding (-)-isopiperitenone reductase and (+)-pulegone reductase of peppermint. Arch Biochem Biophys 418, 80-92.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Rydén AM, Ruyter-Spira C, Litjens R, Takahashi S, Quax W, Osada H, Bouwmeester H, Kayser O (2010). Molecular cloning and characterization of a broad substrate terpenoid oxidoreductase from Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1219-1228.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Sarker LS, Galata M, Demissie ZA, Mahmoud SS (2012). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of borneol dehydrogenase from the glandular trichomes of Lavandula × intermedia. Arch Biochem Biophys 528, 163-170.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Tanaka M, Ohno S, Adachi S, Nakajin S, Shinoda M, Nagahama Y (1992). Pig testicular 20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase exhibits carbonyl reductase-like structure and activity. cDNA cloning of pig testicular 20 beta- hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 267, 13451-13455.
PMID |
| [36] |
Terada T, Sugihara Y, Nakamura K, Sato R, Inazu N, Maeda M (2000). Cloning and bacterial expression of monomeric short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (carbonyl reductase) from CHO-K1 cells. Eur J Biochem 267, 6849-6857.
PMID |
| [37] |
Tian N, Tang YW, Xiong S, Tian DM, Chen YH, Wu DC, Liu ZH, Liu SQ (2015). Molecular cloning and functional identification of a novel borneol dehydrogenase from Artemisia annua L. Ind Crops Prod 77, 190-195.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Tsang HL, Huang JL, Lin YH, Huang KF, Lu PL, Lin GH, Khine AA, Hu A, Chen HP (2016). Borneol dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain TCU-HL1 catalyzes the oxidation of (+)-borneol and its isomers to camphor. Appl Environ Microbiol 82, 6378-6385.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Wang H, Ma DM, Yang JF, Deng K, Li M, Ji XY, Zhong LT, Zhao HY (2018). An integrative volatile terpenoid profiling and transcriptomics analysis for gene mining and functional characterization of AvBPPS and AvPS involved in the monoterpenoid biosynthesis in Amomum villosum. Front Plant Sci 9, 846.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wermuth B, Bohren KM, Heinemann G, von Wartburg JP, Gabbay KH (1988). Human carbonyl reductase. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a cDNA and amino acid sequence of the encoded protein. J Biol Chem 263, 16185-16188.
PMID |
| [41] |
Xia ZQ, Costa MA, Pélissier HC, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2001). Secoisolariciresinol dehydrogenase purification, cloning, and functional expression. Implications for human health protection. J Biol Chem 276, 12614-12623.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Youn B, Moinuddin SGA, Davin LB, Lewis NG, Kang C (2005). Crystal structures of Apo-form and binary/ternary complexes of Podophyllum secoisolariciresinol dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in formation of health-protecting and plant defense lignans. J Biol Chem 280, 12917-12926.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Yu CS, Lin CJ, Hwang JK (2004). Predicting subcellular localization of proteins for Gram-negative bacteria by sup- port vector machines based on n-peptide compositions. Protein Sci 13, 1402-1406.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 姚宝辉, 王蓉, 谈昭贤, 张妍, 王义弘, 王苏芹, 周华坤, 曲家鹏. 艾美耳球虫投放对高原鼠兔及高寒草地植物群落特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 199-210. |
| [2] | 胡宜峰, 余文华, 岳阳, 黄正澜懿, 李玉春, 吴毅. 海南岛翼手目物种多样性现状与分布预测[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 400-408. |
| [3] | 胡建霖,刘志芳,慈秀芹,李捷. DNA条形码在热带龙脑香科树种鉴定中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 350-359. |
| [4] | 杨晓东, 吕光辉. 新疆艾比湖湿地自然保护区胡杨根系水分再分配的估算[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(8): 816-824. |
| [5] | 孟令曾, 张教林, 曹坤芳, 许再富. 迁地保护的4种龙脑香冠层叶光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数的日变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(6): 976-984. |
| [6] | 石兆勇, 陈应龙, 刘润进, 王维华. 西双版纳地区龙脑香科植物AM真菌的初步研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2003, 27(3): 360-365. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||