

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 320-326.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22043 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22043
收稿日期:2022-03-10
接受日期:2022-05-11
出版日期:2022-05-01
发布日期:2022-05-18
通讯作者:
杨玲
作者简介:* E-mail: yangl@zjnu.cn基金资助:
Haitao Hu, Tingting Qian, Ling Yang( )
)
Received:2022-03-10
Accepted:2022-05-11
Online:2022-05-01
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
Ling Yang
摘要: 活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)是植物体内的一把“双刃剑”。ROS作为信号分子在植物生命活动中发挥关键作用, 但ROS过量积累会对生物大分子造成氧化损伤。准确测定ROS含量对于评估植物细胞内的氧化还原状态至关重要。由于植物体内ROS各组分半衰期短且反应活性强, 定性定量检测较为困难。因此, 选择合适的检测方法以提高检测的时空准确性非常重要。目前, 荧光分析法因其具有灵敏度高、选择性好、检出限低和直观性强等优点, 受到研究人员的广泛关注。该文详细描述基于流式细胞仪和激光共聚焦显微镜, 利用2′,7′-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(H2DCFDA)荧光探针检测水稻(Oryza sativa)体内ROS水平和时空分布的操作流程及注意事项。该技术也可用于直接检测拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)、玉米(Zea mays)和大豆(Glycine max)等模式植物组织中ROS的水平和分布。
胡海涛, 钱婷婷, 杨玲. 基于H2DCFDA荧光探针的植物活性氧检测方法. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 320-326.
Haitao Hu, Tingting Qian, Ling Yang. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species Using H2DCFDA Probe in Plant. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 320-326.
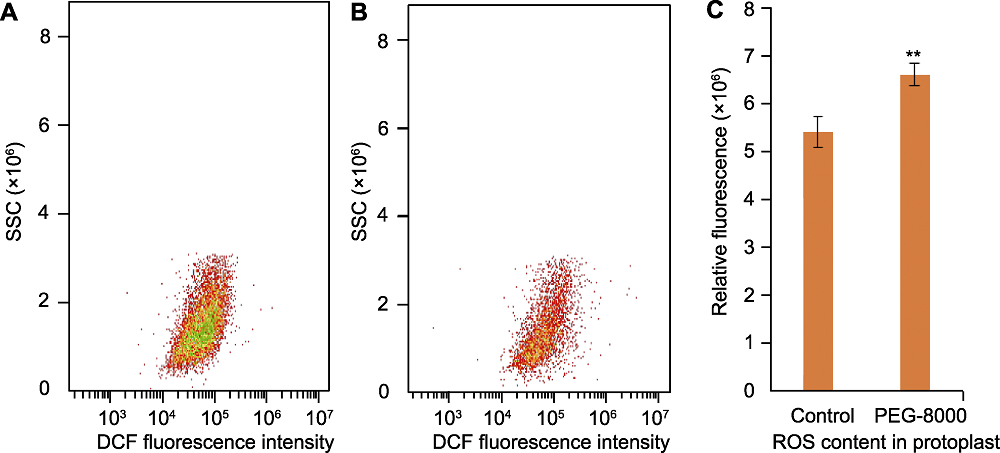
图1 基于2′,7′-二氯荧光素(DCF)的流式细胞仪检测水稻叶片原生质体活性氧含量 (A) 正常生长水稻叶片中的活性氧(ROS)荧光强度; (B) PEG-8000处理组水稻叶片中的ROS荧光强度; (C) 对照和处理组水稻叶片中的ROS相对荧光强度, 其值用于评估ROS含量。n=3; **表示经Student’s t检验在P<0.01水平差异显著。SSC: 侧向散射光
Figure 1 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) evaluation in rice protoplasts using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF)-based flow cytometry (A) ROS fluorescence intensity in rice leaves under normal growth conditions; (B) ROS fluorescence intensity in rice leaves under PEG-8000 treatment conditions; (C) The relative fluorescence intensity in treatment and control groups was determined to assess the ROS content. n=3; ** indicates significant difference at P<0.01 level by Student’s t test. SSC: Side scatter
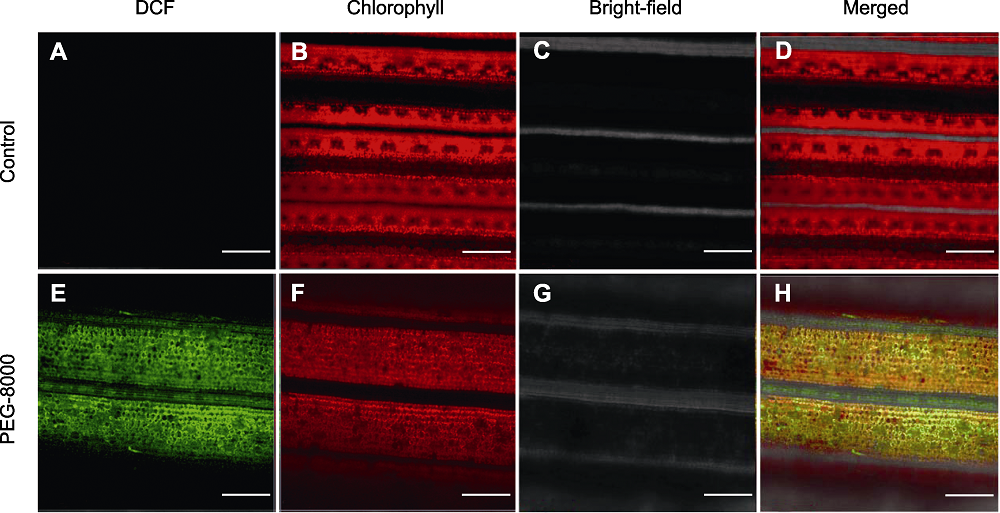
图2 正常生长(A)-(D)和PEG-8000处理(E)-(H)的水稻叶片共聚焦荧光成像图 红色为叶绿素的自发荧光, 绿色为2′,7′-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(H2DCFDA)氧化产生的2′,7′-二氯荧光素(DCF)荧光。Bars=100 µm
Figure 2 Confocal imaging analysis of rice leaves under normal growth (A)-(D) and PEG-8000 treatment (E)-(H) Red is the spontaneous fluorescence of chlorophyll, and green is the fluorescence of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) generated by 2′,7′-dichlorodi-hydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA) oxidation. Bars=100 µm
| [1] |
Akter S, Khan MS, Smith EN, Flashman E (2021). Measuring ROS and redox markers in plant cells. RSC Chem Biol 2, 1384-1401.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Anjum NA, Amreen N, Tantray AY, Khan NA, Ahmad A (2020). Reactive oxygen species detection-approaches in plants: insights into genetically encoded FRET-based sen- sors. J Biotechnol 308, 108-117.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Apel K, Hirt H (2004). REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55, 373-399.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Castro B, Citterico M, Kimura S, Stevens DM, Wrzaczek M, Coaker G (2021). Stress-induced reactive oxygen species compartmentalization, perception and signaling. Nat Plants 7, 403-412.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chan ZL, Yokawa K, Kim WY, Song CP (2016). Editorial: ROS regulation during plant abiotic stress responses. Front Plant Sci 7, 1536. |
| [6] |
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017). Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90, 856-867.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Considine MJ, Foyer CH (2021a). Oxygen and reactive oxygen species-dependent regulation of plant growth and development. Plant Physiol 186, 79-92.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Considine MJ, Foyer CH (2021b). Stress effects on the reactive oxygen species-dependent regulation of plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 72, 5795-5806.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Duanghathaipornsuk S, Farrell EJ, Alba-Rubio AC, Zelenay P, Kim DS (2021). Detection technologies for reactive oxygen species: fluorescence and electrochemical methods and their applications. Biosensors 11, 30.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Eruslanov E, Kusmartsev S (2010). Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry. Methods Mol Biol 594, 57-72.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Fichman Y, Miller G, Mittler R (2019). Whole-plant live imaging of reactive oxygen species. Mol Plant 12, 1203- 1210.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Gomes A, Fernandes E, Lima JLFC (2005). Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J Biochem Biophys Methods 65, 45-80.
PMID |
| [13] |
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHMB, Zulfiqar F, Raza A, Mohsin SM, Mahmud JA, Fujita M, Fotopoulos V (2020). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 9, 681.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Hu HT, Ren DY, Hu J, Jiang HZ, Chen P, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Guo LB (2021). WHITE AND LESION-MIMIC LEAF1, encoding a lumazine synthase, affects reactive oxygen species balance and chloroplast development in rice. Plant J 108, 1690-1703.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kristiansen KA, Jensen PE, Møller IM, Schulz A (2009). Monitoring reactive oxygen species formation and localisation in living cells by use of the fluorescent probe CM- H2DCFDA and confocal laser microscopy. Physiol Plant 136, 369-383.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Li HX, Liu Y, Qin HH, Lin XL, Tang D, Wu ZJ, Luo W, Shen Y, Dong FQ, Wang YL, Feng TT, Wang LL, Li LY, Chen DD, Zhang Y, Murray JD, Chao DY, Chong K, Cheng ZK, Meng Z (2020). A rice chloroplast-localized ABC transporter ARG1 modulates cobalt and nickel homeostasis and contributes to photosynthetic capacity. New Phytol 228, 163-178.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Liu XY, Zhang ZG (2022). A double-edged sword: reactive oxygen species (ROS) during the rice blast fungus and host interaction. FEBS J doi:10.1111/febs.16171
DOI |
| [18] |
Maulucci G, Bačić G, Bridal L, Schmidt HH, Tavitian B, Viel T, Utsumi H, Yalçın AS, De Spirito M (2016). Imaging reactive oxygen species-induced modifications in living systems. Antioxid Redox Signal 24, 939-958.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Mhamdi A, van Breusegem F (2018). Reactive oxygen species in plant development. Development 145, dev164376. |
| [20] |
Oparka M, Walczak J, Malinska D, van Oppen LMPE, Szczepanowska J, Koopman WJH, Wieckowski MR (2016). Quantifying ROS levels using CM-H2DCFDA and HyPer. Methods 109, 3-11.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ortega-Villasante C, Burén S, Barón-Sola Á, Martínez F, Hernández LE (2016). In vivo ROS and redox potential fluorescent detection in plants: present approaches and future perspectives. Methods 109, 92-104.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Ortega-Villasante C, Burén S, Blázquez-Castro A, Barón- Sola Á, Hernández LE (2018). Fluorescent in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen species and redox potential in plants. Free Radic Biol Med 122, 202-220.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Qi JS, Song CP, Wang BS, Zhou JM, Kangasjärvi J, Zhu JK, Gong ZZ (2018). Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement in plant responses to drought stress and pathogen attack. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 805- 826.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Rajneesh, Pathak J, Chatterjee A, Singh SP, Sinha RP (2017). Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cyanobacteria using the oxidant-sensing probe 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). Bio Protoc 7, e2545.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Robles V, Riesco MF, Martínez-Vázquez JM, Valcarce DG (2021). Flow cytometry and confocal microscopy for ROS evaluation in fish and human spermatozoa. Methods Mol Biol 2202, 93-102. |
| [26] |
Tripathy BC, Oelmüller R (2012). Reactive oxygen species generation and signaling in plants. Plant Signal Behav 7, 1621-1633.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Waszczak C, Carmody M, Kangasjärvi J (2018). Reactive oxygen species in plant signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 209-236.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Xia SS, Liu H, Cui YJ, Yu HP, Rao YC, Yan YP, Zeng DL, Hu J, Zhang GH, Gao ZY, Zhu L, Shen L, Zhang Q, Li Q, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Qian Q, Ren DY (2022). UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase enhances rice survival at high temperature. New Phytol 233, 344- 359.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Xiong HY, Yu JP, Miao JL, Li JJ, Zhang HL, Wang X, Liu PL, Zhao Y, Jiang CH, Yin ZG, Li Y, Guo Y, Fu BY, Wang WS, Li ZK, Ali J, Li ZC (2018). Natural variation in OsLG3 increases drought tolerance in rice by inducing ROS scavenging. Plant Physiol 178, 451-467.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 惠城阳, 章巧依, 刘腾腾, 刘维勇, 周丽娜, 金鑫杰, 张永华, 刘金亮. 温州大罗山主要植被类型及物种组成特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [2] | 曹毅 张松林 王旭峰 杨安昌 任敏慧 杨浩 韩超. 兰州市南北两山植物群落数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [3] | 陈龙 郭柯 勾晓华 赵秀海 马泓若. 祁连圆柏林群落组成及特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 0-0. |
| [4] | 童金莲, 张博纳, 汤璐瑶, 叶琳峰, 李姝雯, 谢江波, 李彦, 王忠媛. C4植物狗尾草功能性状网络沿降水梯度带的区域分异规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [5] | 闫小红 胡文海. 亚热带地区3种常绿阔叶植物冬季光保护机制的差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 0-0. |
| [6] | 赵常明 熊高明 申国珍 葛结林 徐文婷 徐凯 武元帅 谢宗强. 神农架常绿落叶阔叶混交林和亚高山针叶林植物群落特征数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(典型生态系统数据集): 0-0. |
| [7] | 赵珮杉 高广磊 丁国栋 张英. 林龄和生态位对樟子松人工林地下真菌群落构建的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 1-0. |
| [8] | 黄承玲, 黎荣瀚, 覃红玲, 杨胜雄, 田晓玲, 夏国威, 陈正仁, 周玮. 基于SNP分子标记的极小种群野生植物荔波杜鹃保护遗传学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [9] | 周鑫宇, 刘会良, 高贝, 卢妤婷, 陶玲庆, 文晓虎, 张岚, 张元明. 新疆特有濒危植物雪白睡莲繁殖生物学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [10] | 高雨轩, 苏艳军, 冯育才, 张军, 汪小全, 刘玲莉. 珍稀濒危孑遗植物银杉的研究与保护现状[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [11] | 张子睿, 周静, 胡艳萍, 梁爽, 马永鹏, 陈伟乐. 极度濒危植物巧家五针松的根内和根际真菌群落特征[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [12] | 逯子佳, 王天瑞, 郑斯斯, 孟宏虎, 曹建国, Gregor Kozlowski, 宋以刚. 孑遗植物湖北枫杨的环境适应性遗传变异与遗传脆弱性[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [13] | 朱润铖, 蔡锡安, 黄娟. 植物防御相关挥发性有机物排放及对氮沉降的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 681-696. |
| [14] | 平晓燕, 杜毅倩, 赖仕蓉, 孔梦桥, 余国杰. 植物应对食草动物采食的化学防御策略研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 667-680. |
| [15] | 贾妍妍, 柳华清, 解欣然, 王博, 张维, 杨允菲. 珍稀濒危植物天山梣林龄结构及种群动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 760-772. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||