

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 733-742.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16218 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16218
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fu Qingqing, Sun Lulong, Zhai Heng, Du Yuanpeng*( )
)
Received:2016-11-14
Accepted:2016-12-11
Online:2017-11-01
Published:2018-02-22
Contact:
Du Yuanpeng
Fu Qingqing, Sun Lulong, Zhai Heng, Du Yuanpeng. Salt Tolerant Evaluation of F1-generation Hybrids in Grape[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 733-742.
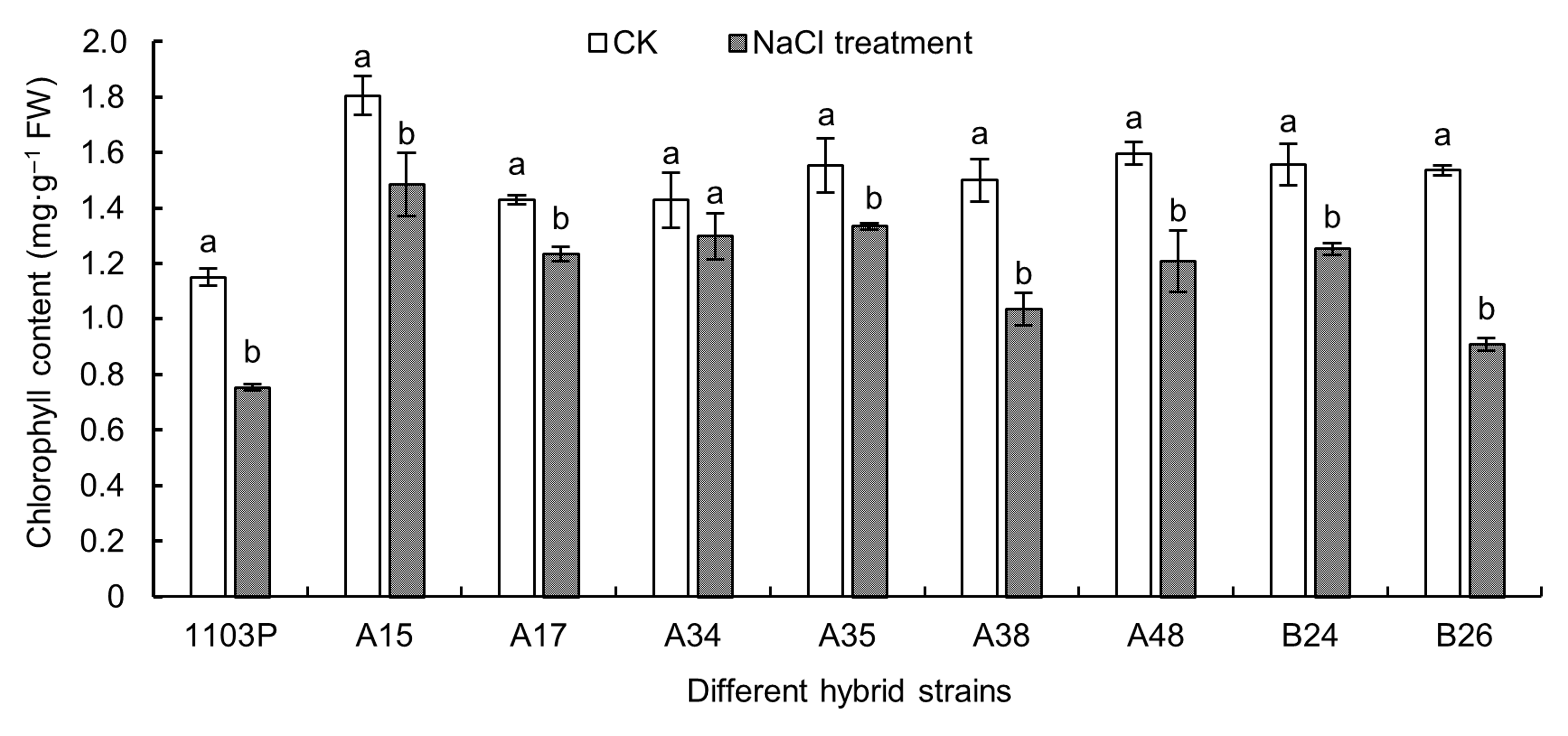
Figure 2 Effects of NaCl stress on chlorophyll content in different grape hybrid strainsDifferent lowercase letters indicate significant differences under different treatments of the same strain (P<0.05).
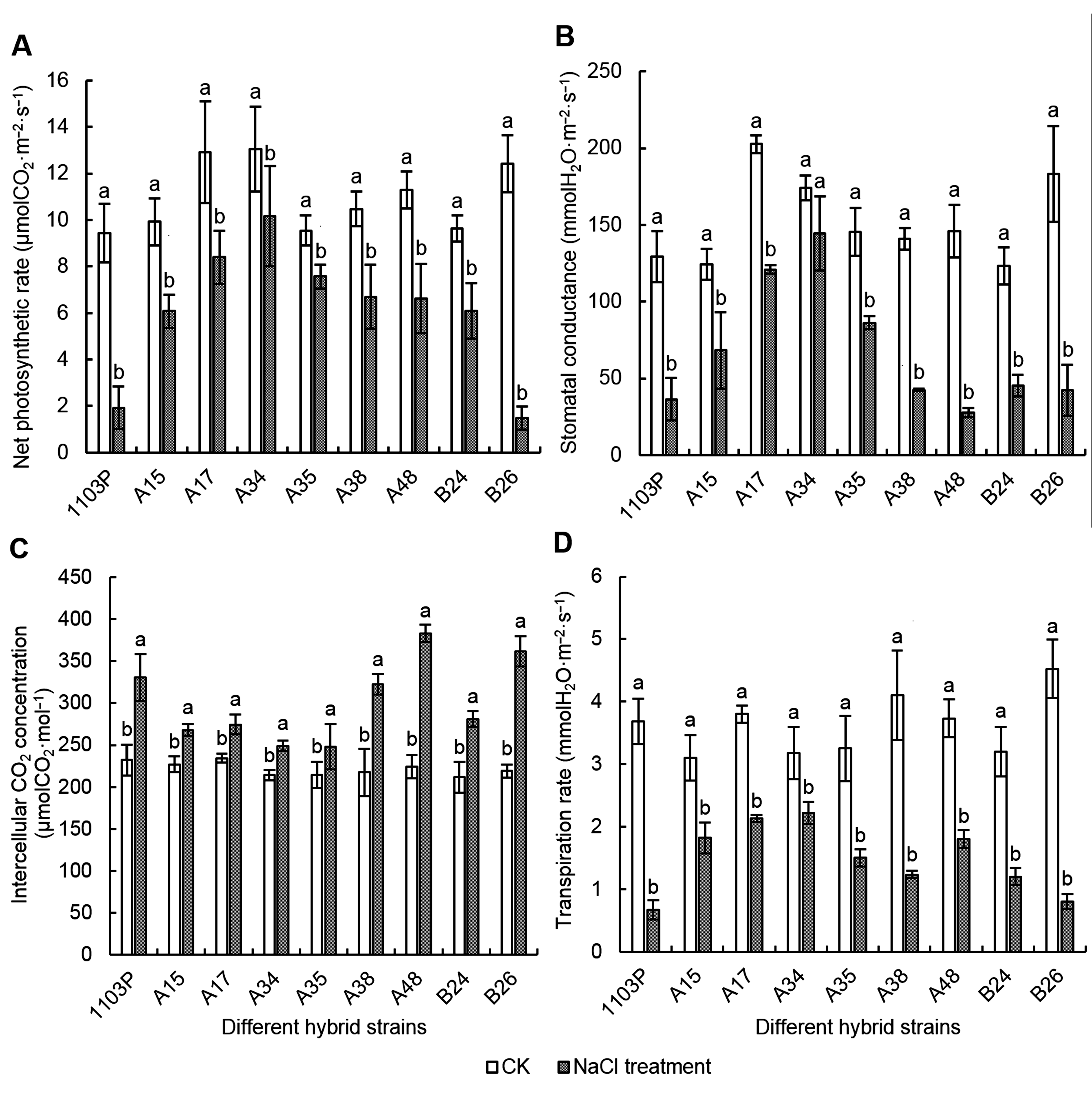
Figure 3 Effects of NaCl stress on Pn, Gs, Ci and Tr of different grape hybrid strainsPn: Net photosynthetic rate; Gs: Stomatal conductance; Ci: Intercellular CO2 concentration; Tr: Transpiration rate. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences under different treatments of the same strain (P<0.05).
| Strains | NaCl concentration (mmol·L-1) | Fv/Fm | ΦPSII | Wk | RC/CSm | Ψ0 | qP | NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103p | 0 | 0.811±0.007 a | 0.612±0.053 a | 0.387±0.009 ef | 776.5±34.8 abc | 0.545±0.065 a | 0.856±0.026 ab | 0.703±0.139 g |
| 100 | 0.285±0.150 f | 0.153±0.062 e | 0.536±0.072 b | 111.7±94.21 h | 0.21±0.079 e | 0.322±0.131 f | 4.608±0.81 bc | |
| A15 | 0 | 0.827±0.018 a | 0.61±0.027 a | 0.385±0.025 ef | 793±51.51 ab | 0.539±0.040 a | 0.857±0.012 ab | 1.256±0.04 fg |
| 100 | 0.68±0.024 cde | 0.35±0.071 cd | 0.515±0.045 bc | 621.1±73.95 cd | 0.383±0.062 cd | 0.662±0.051 e | 3.017±0.46 de | |
| A17 | 0 | 0.818±0.023 a | 0.601±0.057 a | 0.402±0.016 ef | 643.2±55.1 bcd | 0.507±0.08 abc | 0.863±0.028 a | 0.908±0.049 g |
| 100 | 0.70±0.016 bcde | 0.425±0.01 cd | 0.475±0.037 cd | 514.9±76.19 de | 0.347±0.059 d | 0.76±0.020 bcd | 1.62±0.146 fg | |
| A34 | 0 | 0.818±0.009 a | 0.609±0.033 a | 0.401±0.016 ef | 668.1±33.3 bcd | 0.52±0.044 ab | 0.875±0.009 a | 1.137±0.07 fg |
| 100 | 0.768±0.023 abc | 0.463±0.03 bc | 0.436±0.014 de | 568.7±19.40 de | 0.491±0.02 abc | 0.712±0.019 de | 2.057±0.403 ef | |
| A35 | 0 | 0.824±0.008 a | 0.543±0.04 ab | 0.397±0.022 ef | 631.3±74.80 cd | 0.517±0.018 ab | 0.82±0.014 abc | 2.235±0.251 ef |
| 100 | 0.75±0.006 abcd | 0.39±0.035 cd | 0.415±0.03 def | 528±25.68 de | 0.395±0.07 bcd | 0.76±0.027 bcd | 2.982±1.11 de | |
| A38 | 0 | 0.813±0.007 a | 0.607±0.023 a | 0.352±0.014 f | 773.3±37.2 abc | 0.563±0.078 a | 0.887±0.018 a | 0.856±0.103 g |
| 100 | 0.629±0.059 e | 0.324±0.065 d | 0.528±0.035 bc | 280.7±130.3 fg | 0.302±0.042 de | 0.682±0.048 de | 5.53±0.287 ab | |
| A48 | 0 | 0.816±0.012 a | 0.607±0.079 a | 0.39±0.022 ef | 748.5±49.6 abc | 0.53±0.042 a | 0.873±0.011 a | 1.076±0.085 g |
| 100 | 0.633±0.077 de | 0.368±0.03 cd | 0.58±0.051 ab | 418.6±51.03 ef | 0.275±0.054 de | 0.675±0.076 de | 3.396±0.391 d | |
| B24 | 0 | 0.806±0.003 ab | 0.576±0.098 a | 0.388±0.011 ef | 901.3±65.99 a | 0.534±0.034 a | 0.861±0.015 a | 1.335±0.26 fg |
| 100 | 0.646±0.030 de | 0.344±0.036 d | 0.548±0.028 ab | 653.5±44.5 bcd | 0.35±0.048 d | 0.715±0.051 de | 3.614±0.07 cd | |
| B26 | 0 | 0.818±0.012 a | 0.57±0.039 ab | 0.369±0.004 f | 875.6±38.21 a | 0.55±0.038 a | 0.851±0.018 ab | 1.27±0.114 fg |
| 100 | 0.256±0.108 f | 0.093±0.079 e | 0.616±0.062 a | 151.3±128.4 gh | 0.188±0.047 e | 0.307±0.307 f | 6.42±1.076 a |
Table 1 Effects of NaCl stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaves of grape
| Strains | NaCl concentration (mmol·L-1) | Fv/Fm | ΦPSII | Wk | RC/CSm | Ψ0 | qP | NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103p | 0 | 0.811±0.007 a | 0.612±0.053 a | 0.387±0.009 ef | 776.5±34.8 abc | 0.545±0.065 a | 0.856±0.026 ab | 0.703±0.139 g |
| 100 | 0.285±0.150 f | 0.153±0.062 e | 0.536±0.072 b | 111.7±94.21 h | 0.21±0.079 e | 0.322±0.131 f | 4.608±0.81 bc | |
| A15 | 0 | 0.827±0.018 a | 0.61±0.027 a | 0.385±0.025 ef | 793±51.51 ab | 0.539±0.040 a | 0.857±0.012 ab | 1.256±0.04 fg |
| 100 | 0.68±0.024 cde | 0.35±0.071 cd | 0.515±0.045 bc | 621.1±73.95 cd | 0.383±0.062 cd | 0.662±0.051 e | 3.017±0.46 de | |
| A17 | 0 | 0.818±0.023 a | 0.601±0.057 a | 0.402±0.016 ef | 643.2±55.1 bcd | 0.507±0.08 abc | 0.863±0.028 a | 0.908±0.049 g |
| 100 | 0.70±0.016 bcde | 0.425±0.01 cd | 0.475±0.037 cd | 514.9±76.19 de | 0.347±0.059 d | 0.76±0.020 bcd | 1.62±0.146 fg | |
| A34 | 0 | 0.818±0.009 a | 0.609±0.033 a | 0.401±0.016 ef | 668.1±33.3 bcd | 0.52±0.044 ab | 0.875±0.009 a | 1.137±0.07 fg |
| 100 | 0.768±0.023 abc | 0.463±0.03 bc | 0.436±0.014 de | 568.7±19.40 de | 0.491±0.02 abc | 0.712±0.019 de | 2.057±0.403 ef | |
| A35 | 0 | 0.824±0.008 a | 0.543±0.04 ab | 0.397±0.022 ef | 631.3±74.80 cd | 0.517±0.018 ab | 0.82±0.014 abc | 2.235±0.251 ef |
| 100 | 0.75±0.006 abcd | 0.39±0.035 cd | 0.415±0.03 def | 528±25.68 de | 0.395±0.07 bcd | 0.76±0.027 bcd | 2.982±1.11 de | |
| A38 | 0 | 0.813±0.007 a | 0.607±0.023 a | 0.352±0.014 f | 773.3±37.2 abc | 0.563±0.078 a | 0.887±0.018 a | 0.856±0.103 g |
| 100 | 0.629±0.059 e | 0.324±0.065 d | 0.528±0.035 bc | 280.7±130.3 fg | 0.302±0.042 de | 0.682±0.048 de | 5.53±0.287 ab | |
| A48 | 0 | 0.816±0.012 a | 0.607±0.079 a | 0.39±0.022 ef | 748.5±49.6 abc | 0.53±0.042 a | 0.873±0.011 a | 1.076±0.085 g |
| 100 | 0.633±0.077 de | 0.368±0.03 cd | 0.58±0.051 ab | 418.6±51.03 ef | 0.275±0.054 de | 0.675±0.076 de | 3.396±0.391 d | |
| B24 | 0 | 0.806±0.003 ab | 0.576±0.098 a | 0.388±0.011 ef | 901.3±65.99 a | 0.534±0.034 a | 0.861±0.015 a | 1.335±0.26 fg |
| 100 | 0.646±0.030 de | 0.344±0.036 d | 0.548±0.028 ab | 653.5±44.5 bcd | 0.35±0.048 d | 0.715±0.051 de | 3.614±0.07 cd | |
| B26 | 0 | 0.818±0.012 a | 0.57±0.039 ab | 0.369±0.004 f | 875.6±38.21 a | 0.55±0.038 a | 0.851±0.018 ab | 1.27±0.114 fg |
| 100 | 0.256±0.108 f | 0.093±0.079 e | 0.616±0.062 a | 151.3±128.4 gh | 0.188±0.047 e | 0.307±0.307 f | 6.42±1.076 a |
| Strains | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| A15 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| A17 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| A34 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| A35 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| A38 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| A48 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| B24 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.91 |
| B26 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 1.29 | 0.85 |
Table 2 Salt tolerant coefficient of every single index of each grape strains under NaCl stress
| Strains | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| A15 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| A17 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| A34 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| A35 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| A38 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| A48 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| B24 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.91 |
| B26 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 1.29 | 0.85 |
| Growth parameters | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| X2 | 0.881** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| X3 | 0.437 | 0.523 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X4 | 0.111 | 0.278 | 0.592 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X5 | 0.266 | 0.431 | 0.893** | 0.711* | 1.000 | |||||||
| X6 | 0.516 | 0.678* | 0.271 | 0.522 | 0.284 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X7 | 0.458 | 0.525 | 0.852** | 0.309 | 0.576 | 0.275 | 1.000 | |||||
| X8 | -0.358 | -0.321 | 0.378 | 0.628 | 0.495 | -0.317 | 0.116 | 1.000 | ||||
| X9 | 0.373 | 0.473 | 0.984** | 0.702* | 0.898** | 0.347 | 0.821** | 0.436 | 1.000 | |||
| X10 | 0.376 | 0.588 | 0.833** | 0.770* | 0.909** | 0.644 | 0.605 | 0.245 | 0.874** | 1.000 | ||
| X11 | 0.301 | 0.297 | -0.501 | -0.137 | -0.564 | 0.615 | -0.273 | 0.678* | -0.456 | -0.203 | 1.000 | |
| X12 | 0.324 | 0.363 | 0.926** | 0.608 | 0.763* | 0.196 | 0.890** | 0.519 | 0.935** | 0.720* | -0.483 | 1.000 |
Table 3 Correlation matrix of every single index under NaCl stress
| Growth parameters | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| X2 | 0.881** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| X3 | 0.437 | 0.523 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X4 | 0.111 | 0.278 | 0.592 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X5 | 0.266 | 0.431 | 0.893** | 0.711* | 1.000 | |||||||
| X6 | 0.516 | 0.678* | 0.271 | 0.522 | 0.284 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X7 | 0.458 | 0.525 | 0.852** | 0.309 | 0.576 | 0.275 | 1.000 | |||||
| X8 | -0.358 | -0.321 | 0.378 | 0.628 | 0.495 | -0.317 | 0.116 | 1.000 | ||||
| X9 | 0.373 | 0.473 | 0.984** | 0.702* | 0.898** | 0.347 | 0.821** | 0.436 | 1.000 | |||
| X10 | 0.376 | 0.588 | 0.833** | 0.770* | 0.909** | 0.644 | 0.605 | 0.245 | 0.874** | 1.000 | ||
| X11 | 0.301 | 0.297 | -0.501 | -0.137 | -0.564 | 0.615 | -0.273 | 0.678* | -0.456 | -0.203 | 1.000 | |
| X12 | 0.324 | 0.363 | 0.926** | 0.608 | 0.763* | 0.196 | 0.890** | 0.519 | 0.935** | 0.720* | -0.483 | 1.000 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.24 | -0.24 | 0.35 | 0.554 |
| CI2 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.44 | 0.14 | -0.42 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.42 | -0.03 | 0.252 |
| CI3 | -0.04 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.105 |
Table 4 Correlation of comprehensive indexes and their contribution rates under NaCl stress
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.24 | -0.24 | 0.35 | 0.554 |
| CI2 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.44 | 0.14 | -0.42 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.42 | -0.03 | 0.252 |
| CI3 | -0.04 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.105 |
| Strains | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | Value D | Salt tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 1.39 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.252 | Weaker |
| A15 | 1.68 | 0.82 | 3.19 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.761 | Strong |
| A17 | 1.76 | 0.69 | 3.15 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.758 | Strong |
| A34 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.907 | Strong |
| A35 | 1.85 | 0.67 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.826 | Strong |
| A38 | 1.48 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.499 | Medium |
| A48 | 1.61 | 0.46 | 2.94 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.418 | Medium |
| B24 | 1.49 | 0.64 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.353 | Medium |
| B26 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 2.67 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.066 | Weaker |
| Index weight | 0.608 | 0.277 | 0.115 |
Table 5 Each strain’s comprehensive index, index weight, membership function value, value D and comprehensive evaluation under NaCl stress
| Strains | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | Value D | Salt tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 1.39 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.252 | Weaker |
| A15 | 1.68 | 0.82 | 3.19 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.761 | Strong |
| A17 | 1.76 | 0.69 | 3.15 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.758 | Strong |
| A34 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.907 | Strong |
| A35 | 1.85 | 0.67 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.826 | Strong |
| A38 | 1.48 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.499 | Medium |
| A48 | 1.61 | 0.46 | 2.94 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.418 | Medium |
| B24 | 1.49 | 0.64 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.353 | Medium |
| B26 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 2.67 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.066 | Weaker |
| Index weight | 0.608 | 0.277 | 0.115 |
| [1] | 高建明, 夏卜贤, 袁庆华, 罗峰, 韩芸, 桂枝, 裴忠有, 孙守钧 (2012). 高粱种质材料幼苗期耐盐碱性评价. 应用生态学报 23,1303-1310. |
| [2] | 贺普超 (1999). 葡萄学(第1版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 23. |
| [3] | 何伟, 艾军, 范书田, 杨义明, 王振兴, 赵滢, 乔永在, 张亚凤, 李晓燕 (2015). 葡萄品种及砧木抗寒性评价方法研究. 果树学报 32, 1135-1142. |
| [4] | 黄毅, 张玉龙 (2004). 保护地生产条件下的土壤退化问题及其防治对策. 土壤通报 35, 212-216. |
| [5] | 金立桥, 车兴凯, 张子山, 高辉远 (2015). 高温、强光下黄瓜叶片PSII供体侧和受体侧的伤害程度与快速荧光参数Wk变化的关系. 植物生理学报 51, 969-976. |
| [6] | 李丰先, 周宇飞, 王艺陶, 孙璐, 白薇, 闫彤, 许文娟, 黄瑞冬 (2013). 高粱品种萌发期耐碱性筛选与综合鉴定. 中国农业科学 46, 1762-1771. |
| [7] |
李鹏民, 高辉远, Strasser RJ (2005). 快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学分析在光合作用研究中的应用. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 31, 559-566.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
李晓芬, 尚庆茂, 张志刚, 王立浩, 张宝玺 (2008). 多元统计分析方法在辣椒品种耐盐性评价中的应用. 园艺学报 35, 351-356.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 廖祥儒, 贺普超, 万怡震, 朱新产 (1996). 盐胁迫对葡萄离体新梢叶片的伤害作用. 果树科学 13(4), 211-214. |
| [10] |
刘家尧, 衣艳君, 张其德 (1998). 盐胁迫对不同抗盐性小麦叶片荧光诱导动力学的影响. 植物学通报 15(2), 47-50.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 罗海波, 马苓, 段伟, 李绍华, 王利军 (2010). 高温胁迫对‘赤霞珠’葡萄光合作用的影响. 中国农业科学 43, 2744-2750. |
| [12] | 莫伟平, 周琳耀, 张静逸, 黄俊波, 贝学文, 付欣雨, 王惠聪, 黄旭明 (2013). 遮阴和环剥对荔枝枝梢生长和光合生理的影响. 园艺学报 40, 117-124. |
| [13] | 钮福祥, 华希新, 郭小丁, 邬景禹, 李洪民, 丁成伟 (1996). 甘薯品种抗旱性生理指标及其综合评价初探. 作物学报 22, 392-398. |
| [14] | 秦红艳 (2010). 山葡萄种质资源耐盐性评价研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 33-40. |
| [15] |
孙璐, 周宇飞, 李丰先, 肖木辑, 陶冶, 许文娟, 黄瑞冬 (2012). 盐胁迫对高粱幼苗光合作用和荧光特性的影响. 中国农业科学 45, 3265-3272.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 王邦锡, 何军贤, 黄久常 (1992). 水分胁迫导致小麦叶片光合作用下降的非气孔因素. 植物生理学报 18, 77-84. |
| [17] |
王军, 周美学, 许如根, 吕超, 黄祖六 (2007). 大麦耐湿性鉴定指标和评价方法研究. 中国农业科学 40, 2145-2152.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 王业遴, 马凯, 姜卫兵, 凌志奋, 顾平, 吴兵, 陈炳泉, 应宝清 (1990). 五种果树耐盐力试验初报. 中国果树 (3), 8-12. |
| [19] | 薛忠财, 高辉远, 柳洁 (2011). 野生大豆和栽培大豆光合机构对NaCl胁迫的不同响应. 生态学报 31, 3101-3109. |
| [20] |
杨升, 张华新, 杨秀艳, 陈秋夏, 武海雯 (2015). NaCl胁迫下不同种源沙枣的生长表现差异. 林业科学 51(9), 51-58.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 杨淑萍, 危常州, 梁永超 (2013). 新疆主要棉花品种耐盐性筛选与鉴定. 干旱区研究 30, 1129-1135. |
| [22] | 张菂, 陈昌盛, 李鹏民, 马锋旺 (2013). 利用快速荧光、延迟荧光和820 nm光反射同步测量技术探讨干旱对平邑甜茶叶片光合机构的伤害机制. 植物生理学报 49, 551-560. |
| [23] |
赵俊香, 任翠梅, 吴凤芝, 刘守伟, 王殿奎 (2015). 16份菊芋种质苗期耐盐碱性筛选与综合鉴定. 中国生态农业学报 23, 620-627.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯 (2002). 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社. pp. 55-57. |
| [25] | 赵昕, 吴雨霞, 赵敏桂, 何建新 (2007). NaCl胁迫对盐芥和拟南芥光合作用的影响. 植物学通报 24, 154-160. |
| [26] |
Appenroth KJ, St?ckel J, Srivastava A, Strasser RJ (2001). Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environ Pollut 115, 49-64.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Chartzoulakis K, Klapaki G (2000). Response of two greenhouse pepper hybrids to NaCl salinity during different growth stages.Sci Hortic 86, 247-260.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2000). Oxygen processing in photosynthesis: a molecular approach.New Phytol 146, 359-388.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Galet P (1991). Precis de Pathologie Viticole (6th Edn). pp. 285. |
| [30] |
Gilmore AM (1997). Mechanistic aspects of xanthophyll cycle-dependent photoprotection in higher plant chloroplasts and leaves.Physiol Plant 99, 197-209.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Grotkopp E, Rejmánek M, Rost TL (2002). Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine ( Pinus) species. Am Nat 159, 396-419.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Hernández JA, Olmos E, Corpas FJ, Sevilla F, Del Río LA (1995). Salt-induced oxidative stress in chloroplasts of pea plants.Plant Sci 105, 151-167.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Hoshida H, Tanaka Y, Hibino T, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A, Takabe T, Takabe T (2000). Enhanced tolerance to salt stress in transgenic rice that over expresses chloroplast glutamine synthetase.Plant Mol Biol 43, 103-111.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Lu CM, Zhang JH (1999). Effects of water stress on photosystem II photochemistry and its thermo stability in wheat plants.J Exp Bot 50, 1199-1206.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Munns R, Tester M (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance.Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 651-681.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Samra JS (1985). Sodicity tolerance of grapes with reference to the uptake of nutrients.Indian J Hortic 42, 12-17. |
| [37] |
Strasser BJ (1997). Donor side capacity of photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients.Photosynth Res 52, 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Troncoso A, Matte C, Cantos M, Lavee S (1999). Evaluation of salt tolerance of in vitro-grown grapevine rootstock varieties. Vitis 38, 55-60. |
| [39] |
Walker RR, T?r?kfalvy E, Scott NS, Kriedemann PE (1981). An analysis of photosynthetic response to salt treatment in Vitis vinifera. Aust J Plant Physiol 8, 359-374.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Xu CC, Li DQ, Zou Q, Zhang JH (1999). Effect of drought on chlorophyll fluorescence and xanthophyll cycle components in winter wheat leaves with different ages.Acta Phytophys Sin 25, 29-37. |
| [43] |
Zhu JK (2002). Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol 53, 247-273.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Yamasaki T, Yamakawa T, Yamane Y, Koike H, Satoh K, Katoh S (2002). Temperature acclimation of photosynthesis and related changes in photosystem II electron tran- sport in winter wheat.Plant Physiol 128, 1087-1097.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Yang XH, Chen XY, Ge QY, Li B, Tong YP, Zhang AM, Li ZS, Kuang TY, Lu CM (2006). Tolerance of photosynthesis to photoinhibition, high temperature and drought stress in flag leaves of wheat: a comparison between a hybridization line and its parents grown under field conditions.Plant Sci 171, 389-397.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | ZHANG Kun, QIAN Min, WANG Yang, LI Zhi-Hua, KONG Ling-Na, LI Ming-Yang, MA Jin-Yu, YUSUPU Nueraihemaiti, CHEN Yi-Yi, CHENG Yi-Rui, ZHANG Huan-Shi, QIN Feng-Fei, QU Hui. Comprehensive evaluation of shade tolerance of alfalfa and screening of identification indexes [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 773-787. |
| [2] | Jie Cao, Qiulian Lu, Jianping Zhai, Baohui Liu, Chao Fang, Shichen Li, Tong Su. Changes in the Expression of the Soybean TPS Gene Family Under Salt Stress and Haplotype Selection Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [3] | Huiling Fan, Yan Lu, Wenhai Jin, Hui Wang, Xiaoxing Peng, Xuexia Wu, Yujiao Liu. Identification and Comprehensive Evaluation of Faba Bean Salt-alkali Tolerance Based on Root Phenotypic Traits [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 204-217. |
| [4] | Zhang Shuxin, Jia Zixuan, Fang Tao, Liu Yifan, Zhao Wei, Wang Rong, Chang Haichao, Luo Fangli, Zhu Yaojun, Yu Feihai. Methods to evaluate plant tolerance to environmental stresses [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24168-. |
| [5] | Feng Zhang, Richard Dormatey, Yindu Liu, Chengju Li, Yunjiao Wang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Zhenzhen Bi, Yuhui Liu, Jiangping Bai, Chao Sun. Screening and Evaluation of Phosphite-tolerant Potatoes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [6] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | Yindu Liu, Junkang Tuo, Chengju Li, Feng Zhang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Yunjiao Wang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Chao Sun, Yuhui Liu, Zhen Liu, Zhenzhen Bi, Jiangping Bai. Screening and Evaluation of Low-potassium Tolerance Potato Varieties [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 75-88. |
| [8] | LI Bo-Xin, JIANG Chao, SUN Osbert Jianxin. Comprehensive assessment of vegetation carbon use efficiency in southwestern China simulated by CMIP6 models [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2023, 47(9): 1211-1224. |
| [9] | Shiyu Li, Yiqi Zhang, Pu Zou, Zulin Ning, Jingping Liao. Ex situ conservation of plant diversity status and suggestions for the development of botanical gardens in Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [10] | Lei Zhang, Pengfei Jiang, Yiming Wang, Ting Lan, Yanjing Liu, Qingyin Zeng. Comparative Study on the Drought Resistance of Young Seedling from Populus laurifolia × P. simonii F1 Progeny [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 519-534. |
| [11] | Zhaocheng Li, Yanxuedan Zhang. Applying a new valuation method for endangered species based on extinction risk evaluation and population growth to wildlife related judicial practice [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22319-. |
| [12] | Xiaohu Shen, Xiangyu Zhu, Hongfei Shi, Chuanzhi Wang. Research progress of birdsong recognition algorithms based on machine learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23272-. |
| [13] | Guo Shuya, Ai Jinxiang, Chen Hongyu, Shao Yeyao, Wang Yan, Wang Qian, Ye Yitong, Zhang Yating, Ding Zhexiao, Wu Haochen, Wu Yuhuan, Zhang Jianxin, Rao Mide, Liu Peng. Establishment of a Comprehensive Evaluation System for Aluminum Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings Based on Principal Component Analysis-Clustering Analysis-Stepwise Regression Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 479-489. |
| [14] | Jinshui Qiu, Yanan Wang, Huifu Zhuang. Construction of the Chinese biodiversity online data processing platform [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22356-. |
| [15] | Conglin Zhang, Mengzhen Chu, Huizhi Zhang, Haijuan Qiao, Baorong Huang. Evaluation indicator system for the recreational sustainability management of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau national park cluster [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 780-789. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||