

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 82-93.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17010 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17010
收稿日期:2017-01-14
接受日期:2017-08-01
出版日期:2018-01-01
发布日期:2018-08-10
通讯作者:
曹永强
基金资助:
Yongqiang Cao*( ), Liangliang Zhang, Liting Yuan
), Liangliang Zhang, Liting Yuan
Received:2017-01-14
Accepted:2017-08-01
Online:2018-01-01
Published:2018-08-10
Contact:
Yongqiang Cao
摘要: 基于2000-2010年辽宁省内的37个气象站及周边5个气象站的基础数据, 结合MODIS NDVI的遥感影像资料, 运用趋势分析、相关分析和空间分析等方法研究植被生长与气候的关系, 探讨不同气候因子对植被生长的影响与主导作用。结果表明: (1) 辽宁省植被在研究时段内的7-8月生长最为旺盛, 生长季植被NDVI呈显著升高趋势, 2007年后维持在0.73- 0.74之间; (2) 在研究时段内, 整个生长季植被NDVI与降水量和日照时数主要呈正相关, 与气温主要呈负相关, 且在6-8月相关性较为显著, 植被生长对气温的变化最敏感, 对日照的响应最缓慢; (3) 5月辽宁省东部植被生长的主要气候影响因子为气温和日照, 西部为降水, 6-8月东部植被主要气候影响因子则转为降水和日照, 9月再度转为气温和日照; (4) 气温和日照对植被影响的滞后时间由东北向西南逐渐延长, 降水则与之相反。
曹永强, 张亮亮, 袁立婷. 辽宁省植被生长季NDVI对气候因子的响应. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 82-93.
Yongqiang Cao, Liangliang Zhang, Liting Yuan. Correlation Analysis of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Climatic Factors in the Vegetative Growing Season in Liaoning Province. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 82-93.
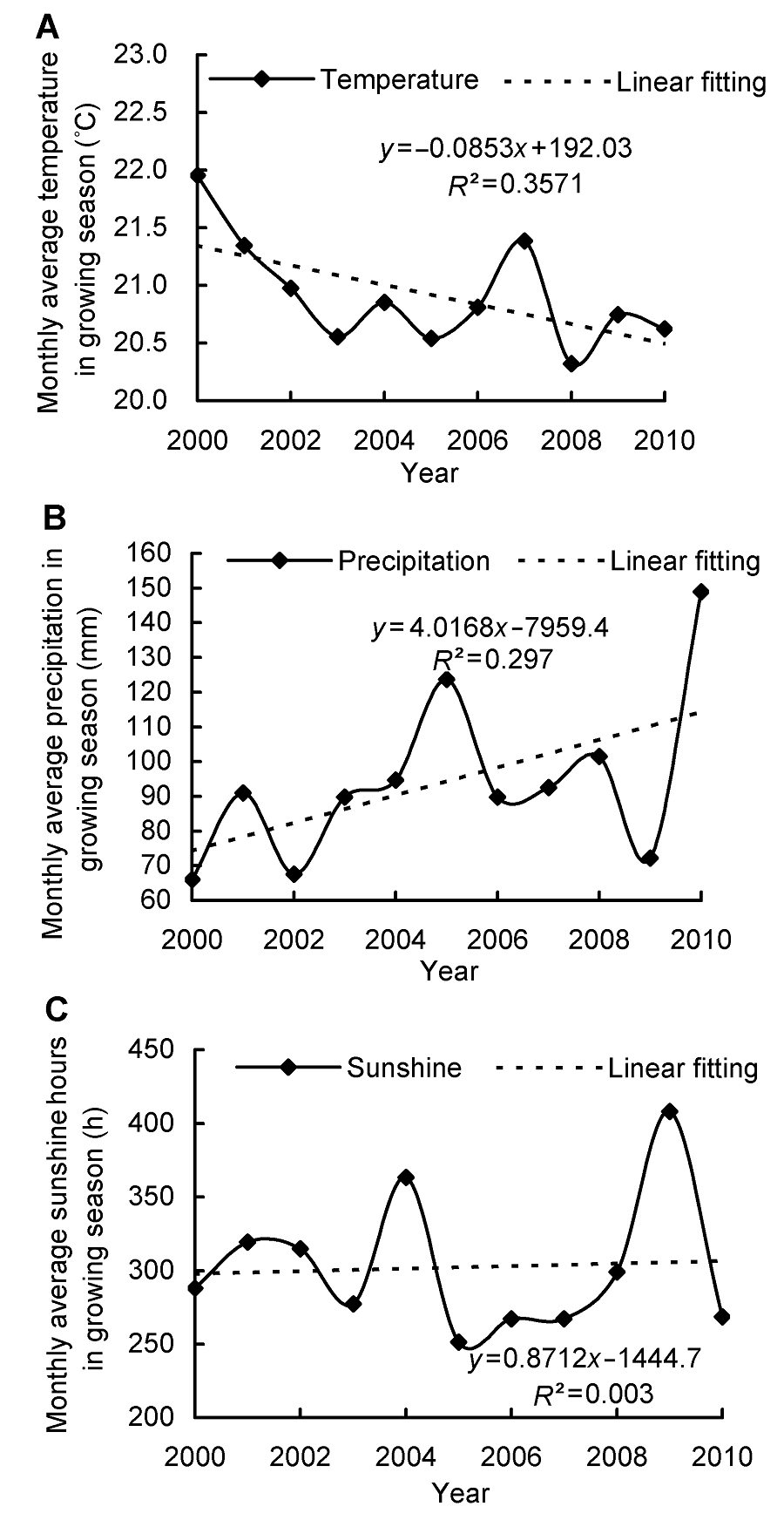
图3 气候因子的趋势变化(A) 植被生长季的月平均温度; (B) 植被生长季的月平均降雨量; (C) 植被生长季的月平均日照时数
Figure 3 Trend change of climatic factors(A) Monthly average temperature in growing season; (B) Mon- thly average precipitation in growing season; (C) Monthly ave- rage sunshine hours in growing season
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 83.93 | 14.93 | 0.52 | 52.04 | 47.96 |
| 6 | 0.15 | 8.83 | 91.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.23 | 0.77 |
| 7 | 10.65 | 11.12 | 78.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 96.02 | 3.98 |
| 8 | 6.00 | 47.38 | 46.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.68 | 0.32 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 2.10 | 97.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 69.06 | 30.94 |
表1 气温与植被NDVI的相关系数分级和面积占比
Table 1 The correlation coefficient grade of temperature and NDVI and its area proportion
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 83.93 | 14.93 | 0.52 | 52.04 | 47.96 |
| 6 | 0.15 | 8.83 | 91.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.23 | 0.77 |
| 7 | 10.65 | 11.12 | 78.23 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 96.02 | 3.98 |
| 8 | 6.00 | 47.38 | 46.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.68 | 0.32 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 2.10 | 97.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 69.06 | 30.94 |
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 1.29 | 9.47 | 87.70 | 1.54 | 0.00 | 37.08 | 62.92 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 99.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 72.72 | 27.28 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 92.92 | 6.12 | 0.15 | 31.15 | 68.85 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.52 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 34.24 | 65.76 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 84.54 | 13.99 | 1.47 | 1.83 | 98.17 |
表2 降水量与植被NDVI的相关系数分级和面积占比
Table 2 The correlation coefficient grade of precipitation and NDVI and its area proportion
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 1.29 | 9.47 | 87.70 | 1.54 | 0.00 | 37.08 | 62.92 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 99.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 72.72 | 27.28 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 92.92 | 6.12 | 0.15 | 31.15 | 68.85 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.52 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 34.24 | 65.76 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 84.54 | 13.99 | 1.47 | 1.83 | 98.17 |
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 96.51 | 3.04 | 0.33 | 39.51 | 60.49 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.99 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 27.95 | 72.05 |
| 7 | 0.05 | 1.17 | 97.90 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 60.99 | 39.01 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 99.67 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 21.30 | 78.70 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 99.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 73.82 | 26.18 |
表3 日照时数与植被NDVI的相关系数分级和面积占比
Table 3 The correlation coefficient grade of sunshine hours and NDVI and its area proportion
| Month | The correlation coefficient grade | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.68 (%) | -0.68- -0.50 (%) | -0.50-0.50 (%) | 0.50-0.68 (%) | >0.68 (%) | <0 (%) | >0 (%) | |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 96.51 | 3.04 | 0.33 | 39.51 | 60.49 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.99 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 27.95 | 72.05 |
| 7 | 0.05 | 1.17 | 97.90 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 60.99 | 39.01 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 99.67 | 0.32 | 0.00 | 21.30 | 78.70 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.85 | 99.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 73.82 | 26.18 |
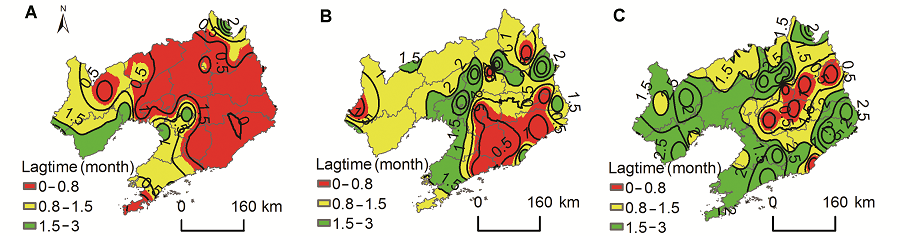
图7 植被NDVI对气候因子响应滞后期的空间分布(A) 气温; (B) 降水量; (C) 日照时数
Figure 7 The spatial distribution of lag time for NDVI response to climatic factors(A) Temperature; (B) Precipitation; (C) Sunshine hours
| [1] | 安佑志 (2014). 基于遥感的中国北部植被NDVI和物候变化研究. 博士论文. 上海: 华东师范大学. pp. 33-36. |
| [2] | 白云俊, 魏雪苹, 秦锋, 李亚蒙, 李金锋, Ranhotra PS, 王宇飞 (2016). 华北上新世-更新世过渡期植被、气候与大气CO2研究进展. 植物学报 51, 257-264. |
| [3] | 崔林丽, 史军, 杨引明, 范文义 (2009). 中国东部植被NDVI对气温和降水的旬响应特征. 地理学报 64, 850-860. |
| [4] | 崔耀平, 刘纪远, 胡云锋, 邴龙飞, 陶福禄, 王军邦 (2012). 中国植被生长的最适温度估算与分析. 自然资源学报 27, 281-292. |
| [5] | 郭敏杰 (2014). 基于NDVI的黄土高原地区植被覆盖度对气候变化响应及定量分析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 中国科学院研究生院(教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心). pp. 8. |
| [6] | 何慧娟, 卓静, 王娟, 董金芳, 权文婷 (2016). 陕西省退耕还林植被覆盖度与湿润指数的变化关系. 生态学报 36, 439-447. |
| [7] | 孔云峰, 仝文伟 (2008). 降雨量地面观测数据空间探索与插值方法探讨. 地理研究 27, 1097-1108. |
| [8] | 李辉霞, 刘国华, 傅伯杰 (2011). 基于NDVI的三江源地区植被生长对气候变化和人类活动的响应研究. 生态学报 31, 5495-5504. |
| [9] | 刘玲玲, 刘良云, 胡勇 (2012). 1982-2006年欧亚大陆植被生长季开始时间遥感监测分析. 地理科学进展 31, 1433-1442. |
| [10] | 刘宪锋, 潘耀忠, 朱秀芳, 李双双 (2015a). 2000-2014年秦巴山区植被覆盖时空变化特征及其归因. 地理学报 70, 705-716. |
| [11] | 刘宪锋, 朱秀芳, 潘耀忠, 李宜展, 赵安周 (2015b). 1982- 2012年中国植被覆盖时空变化特征. 生态学报 35, 5331-5342. |
| [12] | 刘正佳, 刘纪远, 邵全琴 (2014). 不同土地覆盖类型上植被生长的最适温度. 地球信息科学学报 16, 1-7. |
| [13] | 毛德华, 王宗明, 罗玲, 宋开山, 刘殿玮, 张柏, 宋长春 (2010). 1982-2008年东北冻土区植被生长季NDVI对气候变化和CO2体积分数增加的响应. 环境科学学报 30, 2332-2343. |
| [14] | 穆少杰, 李建龙, 陈奕兆, 刚成诚, 周伟, 居为民 (2012). 2001-2010年内蒙古植被覆盖度时空变化特征. 地理学报 67, 1255-1268. |
| [15] | 齐述华, 王长耀, 牛铮, 刘正军 (2004). 利用NDVI时间序列数据分析植被长势对气候因子的响应. 地理科学进展 23(3), 91-99. |
| [16] | 魏凤英 (2007).现代气候统计诊断与预测技术(第2版). 北京: 气象出版社. pp. 36-41. |
| [17] | 吴喜芳, 李改欣, 潘学鹏, 王彦芳, 张莎, 刘峰贵, 沈彦俊 (2015). 黄河源区植被覆盖度对气温和降水的响应研究. 资源科学 37, 512-521. |
| [18] | 谢淦, 白加德, 徐景先, 郝慧, 李金锋, 姚轶锋, 张林源, 李承森, 杨健, 王宇飞 (2016). 北京地区全新世植被和气候变化研究进展. 植物学报 51, 872-881. |
| [19] | 薛薇 (2014).基于SPSS的数据分析(第3版). 北京: 中国人民大学出版社. pp. 270-276. |
| [20] | 杨尚武, 张勃 (2014). 基于SPOT NDVI的甘肃河东植被覆盖变化及其对气候因子的响应. 生态学杂志 33, 455-461. |
| [21] | 张景华, 封志明, 姜鲁光, 杨艳昭 (2015). 澜沧江流域植被NDVI与气候因子的相关性分析. 自然资源学报 30, 1425-1435. |
| [22] | 赵舒怡, 宫兆宁, 刘旭颖 (2015). 2001-2013年华北地区植被覆盖度与干旱条件的相关分析. 地理学报 70, 717-729. |
| [23] | Badeck FW, Bondeau A, Böttcher K, Doktor D, Lucht W, Schaber J, Sitch S (2004). Responses of spring phe- nology to climate change.New Phytol 162, 295-309. |
| [24] | Blazkova S, Beven K (2004). Flood frequency estimation by continuous simulation of subcatchment rainfalls and discharges with the aim of improving dam safety assessment in a large basin in the Czech Republic.J Hydrol 292, 153-172. |
| [25] | Pettorelli N, Vik JO, Mysterud A, Gaillard JM, Tucker CJ, Stenseth NC (2005). Using the satellite-derived NDVI to assess ecological responses to environmental change.Trends Ecol Evol 20, 503-510. |
| [26] | Reed BC, Brown JF (2005). Trend analysis of time-series phenology derived from satellite data. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on the analysis of multi- temporal remote sensing images. Biloxi: IEEE. pp. 166-168. |
| [27] | White MA, De Beurs KM, Didan K, Inouye DW, Richardson AD, Jensen OP, O’Keefe J, Zhang G, Nemani RR, Van Leeuwen WJD, Brown JF, De Wit A, Schaepman M, Lin XM, Dettinger M, Bailey AS, Kimball J, Sch- wartz MD, Baldocchi DD, Lee JT, Lauenroth WK (2009). Intercomparison, interpretation, and assessment of spring phenology in North America estimated from remote sensing for 1982-2006.Glob Chang Biol 15, 2335-2359. |
| [1] | 冯珊珊, 黄春晖, 唐梦云, 蒋维昕, 白天道. 细叶云南松针叶形态和显微性状地理变异及其环境解释[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(8): 1116-1130. |
| [2] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [3] | 牟文博, 徐当会, 王谢军, 敬文茂, 张瑞英, 顾玉玲, 姚广前, 祁世华, 张龙, 苟亚飞. 排露沟流域不同海拔灌丛土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(11): 1422-1431. |
| [4] | 秦乐, 朱彦鹏, 任月恒, 李博炎, 付梦娣, 李俊生. 青藏高原国家级自然保护区管理能力差异及其对保护成效的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22419-. |
| [5] | 刘宁, 彭守璋, 陈云明. 气候因子对青藏高原植被生长的时间效应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(1): 18-26. |
| [6] | 张央, 安明态, 武建勇, 刘锋, 汪伟. 中国兜兰属宽瓣亚属植物地理分布格局及其主导气候因子[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(1): 40-50. |
| [7] | 许祖昌, 罗亚皇, 秦声远, 朱光福, 李德铢. 中国竹类植物馆藏标本现状与地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 897-909. |
| [8] | 倪铭, 张曦月, 姜超, 王鹤松. 中国西南部地区植被对极端气候事件的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(6): 626-640. |
| [9] | 吴建波, 王小丹. 高寒草原优势种紫花针茅叶片解剖结构对青藏高原高寒干旱环境适应性分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(3): 265-273. |
| [10] | 徐光来, 李爱娟, 徐晓华, 杨先成, 杨强强. 中国生态功能保护区归一化植被指数动态及气候因子驱动[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(3): 213-223. |
| [11] | 王兆鹏, 张同文, 袁玉江, 张瑞波, 喻树龙, 刘蕊, 石仁娜•加汗, 郭冬, 王勇辉. 罗霄山南部4个针叶树种生长特征及其气候响应对比分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(12): 1303-1313. |
| [12] | 赵佳宁, 梁韵, 柳莹, 王玉珏, 杨倩茹, 肖春旺. 森林生态系统细根周转规律及影响因素[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 308-317. |
| [13] | 艾则孜提约麦尔·麦麦提, 玉素甫江·如素力, 何辉, 拜合提尼沙·阿不都克日木. 2000-2017年新疆天山植被水分利用效率时空特征及其与气候因子关系分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(6): 490-500. |
| [14] | 董雪蕊, 张红, 张明罡. 基于系统发育的黄土高原地区木本植物多样性及特有性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(12): 1269-1278. |
| [15] | 杨继鸿, 李亚楠, 卜海燕, 张世挺, 齐威. 青藏高原东缘常见阔叶木本植物叶片性状对环境因子的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(10): 863-876. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||