

Dynamics and Interaction of Ca2+ and Nitric Oxide in Wheat Suspension Cells in the Hypersensitive Response
? These authors contributed equally to this paper
Received date: 2013-10-30
Accepted date: 2014-02-23
Online published: 2015-04-09
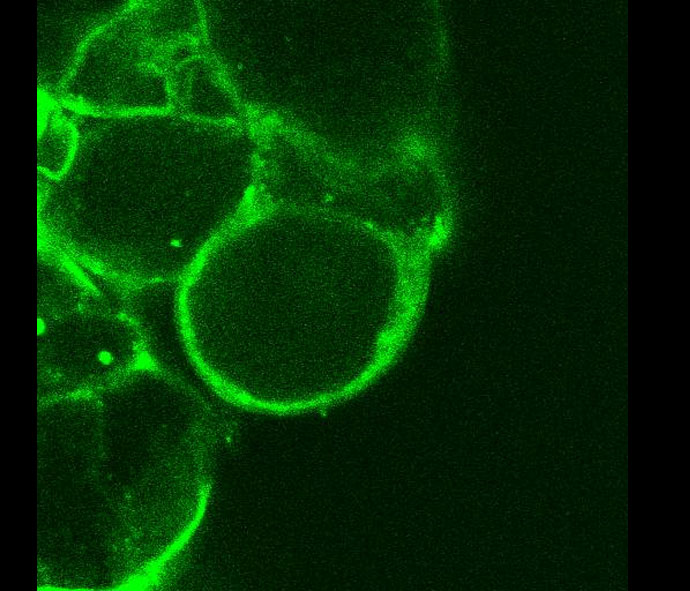
Suspension cells of wheat varieties Lovrin 10 and Zhengzhou 5389 were stimulated with IWF-260, a leaf intercellular washing fluid induced by leaf rust. The dynamics and interaction of Ca2+ and nitric oxide (NO) in the hypersensitive response induced by IWF-260 were analysed. The fluorescence molecular probe Fluo-3AM and DAF-FM DA were used to mark Ca2+ and NO, respectively. The two kinds of suspension cells showed differences in the concentration of Ca2+. Lovrin 10, a disease-resistant variety, showed two peaks of [Ca2+]cyt, at 330 and 700 s, on stimulation, whereas Zhengzhou 5389, a susceptible variety, showed no obvious change in [Ca2+]cyt with stimulation. The increased [Ca2+]cyt depended on Ca2+ flowing into cells, which suggests that Ca2+ may be involved in the hypersensitive response. Like Ca2+, NO showed a similar pattern after elicitor stimulation. For Lovrin 10, NO showed a peak, with no change for Zhengzhou 5389. Thus, NO production and extracellular calcium influx are closely related to wheat suspension cells’ response to stimulation; NO may play a role downstream of calcium.
Mei Qiao , Yan Chen , Chunyan Hou , Gang Liu , Jiawei Sun , Shengfang Han , Dongmei Wang . Dynamics and Interaction of Ca2+ and Nitric Oxide in Wheat Suspension Cells in the Hypersensitive Response[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015 , 50(1) : 1 -11 . DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2015.00001
| 1 | 陈晓波, 王冬梅, 刘娟, 王智炘 (2001). 植物细胞微丝骨架对真菌侵染的反应. 河北农业大学学报 24, 100-104. |
| 2 | 陈晓波, 王冬梅, 刘娟, 王智炘 (2002). 接种叶锈菌的小麦叶片胞间洗脱液对叶肉细胞原生质体微丝骨架的影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 28, 344-350. |
| 3 | 陈琰, 张洁, 王冬梅 (2005). 建立小麦洛夫林10悬浮系初探. 河北农业大学学报 28(4), 68-70. |
| 4 | 陈阳辉, 刘静, 陈琰, 侯春燕, 王冬梅 (2011). IWF诱导小麦悬浮细胞产生NO及其与Ca2+的关系. 中国农业科学 44, 2061-2067. |
| 5 | 高海波, 沈应柏 (2011). 激发子诱导下合作杨细胞钙、氢离子流的振荡. 西北农业学报 20(9), 155-159. |
| 6 | 关春蕾, 侯春燕, 王冬梅 (2006). 影响Ca2+代谢和钙通道的药物对小麦受叶锈菌侵染后诱发的HR的作用. 河北农业大学学报 29(6), 4-8. |
| 7 | 韩胜芳, 王智炘, 王冬梅, 刘娟 (2000). 感染叶锈菌后小麦叶片细胞间隙液中激发子的分离纯化. 植物病理学报 30, 370. |
| 8 | 侯春燕, 王智炘, 王冬梅 (2007). 钙与叶锈菌侵染诱导小麦防卫反应的关系. 华北农学报 22, 145-147. |
| 9 | 胡向阳, 方建颖, 蔡伟明, 汤章城 (2002). 激发子诱导拟南芥悬浮细胞的脱敏性反应. 自然科学通报 12, 1268-1273. |
| 10 | 柯学, 李忠光, 刘娴, 龚明 (2011). 机械刺激诱导的烟草悬浮细胞一氧化氮产生途径及其与Ca2+和钙调素的关系. 植物生理学报 47, 85-90. |
| 11 | 刘刚 (2004). 小麦-叶锈菌互作过程中[Ca2+]cyt的动态变化研究. 硕士论文. 保定: 河北农业大学. pp. 3-17. |
| 12 | 刘刚, 党磊, 王冬梅 (2007). 激发子诱发小麦叶肉细胞原生质体微管骨架排列格局与[Ca2+]cyt的变化. 分子生物学报 40, 205-213. |
| 13 | 刘国华, 刘菁, 侯丽霞, 唐静, 刘新 (2009). NO可能作为Ca2+的下游信号介导乙烯诱导的蚕豆气孔关闭. 分子细胞生物学报 42, 145-155. |
| 14 | 刘刚, 刘娜, 侯春燕, 韩胜芳, 张洁, 赵军峰, 王冬梅 (2004). 荧光指示剂孵育法测定小麦叶肉细胞原生质体胞质游离Ca2+的变化. 河北农业大学学报 27(3), 25-28. |
| 15 | 刘刚, 王冬梅 (2006). 细胞信号转导中Ca2+和微管骨架的关系. 植物生理学通讯 42, 331-336. |
| 16 | 马云鹏, 陈琰, 韩胜芳, 侯春燕, 王冬梅 (2005). 感染叶锈菌的小麦细胞间隙液对小麦悬浮细胞程序性死亡的诱导. 河北农业大学学报 28(3), 12-16. |
| 17 | 齐放军, 高世强, 吴茂森, 何晨阳 (2006). 一氧化氮和过氧化氢诱导水稻细胞过敏反应的协同作用分析. 中国农业科学 39, 61-65. |
| 18 | 乔妹, 陈琰, 张洁, 王冬梅 (2010). 小麦“5389”悬浮细胞系建立的条件摸索. 河北农业大学学报 33(6), 79-83. |
| 19 | 任丽梅, 陈琰, 王冬梅 (2010). IWF诱导小麦悬浮细胞H2O2迸发及其产生机制初探. 中国农业科学 43, 1577-1584. |
| 20 | 王冬梅, 王智炘, 刘娟 (1997). 小麦-叶锈菌互作的细胞间隙液对细胞过敏性坏死的诱导效应. 植物病理学报 27, 376. |
| 21 | 王海波, 黄雪梅, 张昭其 (2010). 植物逆境胁迫中活性氧和钙信号的关系. 北方园艺 (22), 189-194. |
| 22 | 王庆梅, 王智炘, 刘娟, 王冬梅, 陈珈 (2000). 感染叶锈菌的小麦细胞间隙液中激发子的定性及初步分离. 植物生理学报 26, 427-431. |
| 23 | 王文莉, 王秀峰, 郑成淑, 朱翠英, 林桂玉 (2010). A23187和EGTA对光周期诱导菊花成花及其过程中叶片Ca2+分布和碳水化合物的影响. 应用生态学报 21, 675-682. |
| 24 | 徐茂军, 董菊芳, 朱睦元 (2004). NO参与真菌诱导子对红豆杉悬浮细胞中PAL活化和紫杉醇生物合成的促进作用. 科学通报 49, 667-672. |
| 25 | 张蓓, 阎爱华, 刘刚, 刘猛, 侯春燕, 王冬梅 (2010). 胞内钙库对小麦叶锈菌侵染之过敏反应的影响. 作物学报 36, 833-839. |
| 26 | 张国增, 白玲, 宋纯鹏 (2009). 低温胁迫下拟南芥CBF1超表达突变体胞质中Ca2+浓度的变化. 植物学报 44, 283-289. |
| 27 | 赵晓刚, 徐张红, 何奕昆, 张飞雄, 裴真明 (2004). NO在植物中的调控作用. 植物学通报 21, 44-51. |
| 28 | Aboul-Soud MA, Aboul-Enein AM, Loake GJ (2009). Nitric oxide triggers specific and dose-dependent cytosolic calcium transients in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav 4, 191-196. |
| 29 | Ali R, Ma W, Lemtiri-Chlieh F, Tsaltas D, Leng Q, von Bodman S, Berkowitz GA (2007). Death don't have no mercy and neither does calcium: Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE GATED CHANNEL2 and innate immunity.Plant Cell 19, 1081-1095. |
| 30 | Besson-Bard A, Courtois C, Gauthier A, Dahan J, Dobrowolska G, Jeandroz S, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2008). Nitric oxide in plants: production and cross-talk with Ca2+ signaling.Mol Plant 1, 218-228. |
| 31 | Cheval C, Aldon D, Galaud JP, Ranty B (2013). Calcium/calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity.Biochim Biophys Acta 1833, 1766-1771. |
| 32 | Courtois C, Besson A, Dahan J, Bourque S, Dobrowolska G, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2008). Nitric oxide signaling in plants: interplays with Ca2+ and protein kinases.J Exp Bot 59, 155-163. |
| 33 | Furch ACU, van Bel AJE, Fricker MD, Felle HH, Fuchs M, Hafkea JB (2009). Sieve element Ca2+ channels as relay stations between remote stimuli and sieve tube occlusion in Vicia faba.Plant Cell 21, 2118-2132. |
| 34 | Garcia-Mata C, Gay R, Sokolovski S, Hills A, Lamattina L, Blatt MR (2003). Nitric oxide regulates K+ and Cl- channels in guard cells through a subset of abscisic acid-evoked signaling pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 11116-11121. |
| 35 | Jeandroz S, Lamotte O, Astier J, Rasul S, Trapet P, Besson-Bard A, Bourque S, Nicolas-Francès V, Ma W, Berkowitz GA, Wendehenne D (2013). There's more to the picture than meets the eye: nitric oxide cross talk with Ca2+ signaling.Plant Physiol 163, 459-470. |
| 36 | Kenton P, Mur LAJ, Draper J (1999). A requirement for calcium and protein phosphatase in the jasmonate- induced increase in tobacco leaf acid phosphatase specific activity.J Exp Bot 50, 1331-1341. |
| 37 | Kudla J, Batistič O, Hashimoto K (2010). Calcium signals: the lead currency of plant information processing.Plant Cell 22, 541-563. |
| 38 | Lamotte O, Courtois C, Dobrowolska G, Besson A, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2006). Mechanisms of nitric-oxide- induced increase of free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells.Free Radic Biol Med 40, 1369-1376. |
| 39 | Lamotte O, Gould K, Lecourieux D, Sequeira-Legrand A, Lebrun-Garcia A, Durner J, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2004). Analysis of nitric oxide signaling functions in tobacco cells challenged by the elicitor cryptogein. Plant Physiol 135, 516-529. Hou CY, Wang DM (2010). Calcium influx is required for the initiation of the hypersensitive response of Triticum aestivum to Puccinia recondita f.sp. tritici.Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 74, 267-273. |
| 40 | Ma W, Berkowitz GA (2007). The grateful dead: calcium and cell death in plant innate immunity.Cell Microbiol 9, 2571-2585. |
| 41 | Ma W, Berkowitz GA (2011). Ca2+ conduction by plant cyclic nucleotide gated channels and associated signaling components in pathogen defense signal transduction cascades.New Phytol 190, 566-572. |
| 42 | Ma Y, Zhao YC, Walker RK, Berkowitz GA (2013). Molecular steps in the immune signaling pathway evoked by plant elicitor peptides: Ca2+-dependent protein kinases, nitric oxide, and reactive oxygen species are downstream from the early Ca2+ signal.Plant Physiol 163, 1459-1471. |
| 43 | Park JH, Lee S, Cho DH, Park YM, Kang DH, Jo I (2013). Far-infrared radiation acutely increases nitric oxide production by increasing Ca2+ mobilization and Ca2+/calmo- dulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated phos-phory- lation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase at serine 1179.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 436, 601-606. |
| 44 | Vandelle E, Poinssot B, Wendehenne D, Bentéjac M, Pugin A (2006). Integrated signaling network involving calcium, nitric oxide, and active oxygen species but not mitogen-activated protein kinases in BcPG1-elicited gra- pevine defenses.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19, 429-440. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |