

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 90-100.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24040 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24040
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiuxiu Chen1,2,3, Ling Tang1,2,3, Wenjia Hu1,2,3, Zhaolin Yang1,2,3, Xin Deng1,2, Xiaohua Wang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-11
Accepted:2024-05-27
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-05-30
Contact:
* E-mail: Xiuxiu Chen, Ling Tang, Wenjia Hu, Zhaolin Yang, Xin Deng, Xiaohua Wang. Quantitative Analysis of Plasma Membrane Order in Live Plant Cells[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 90-100.
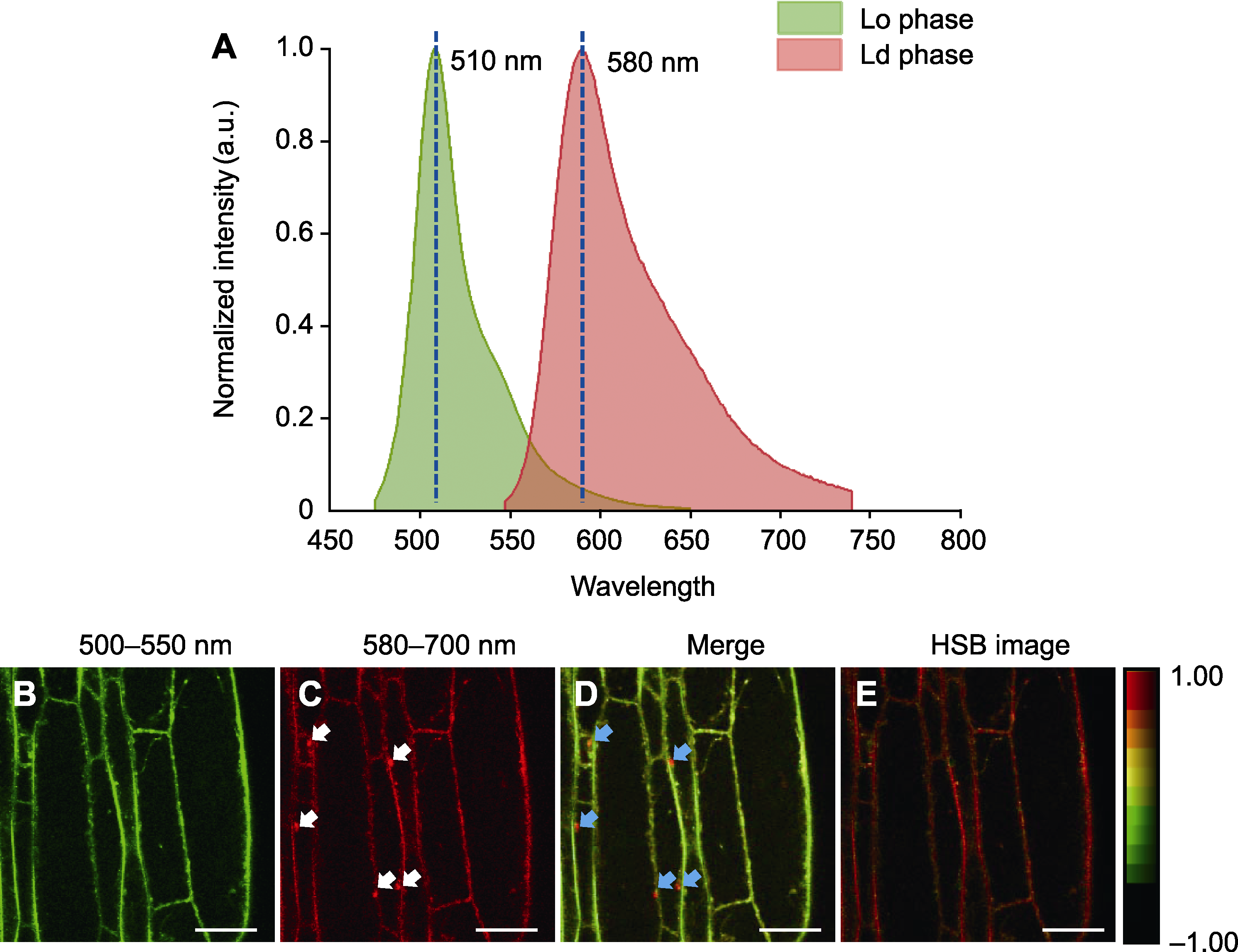
Figure 1 Emission spectrum analysis of the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis root cells labeled with PA (A) Fluorescence spectra of PA in Arabidopsis root cells (Lo phase: Liquid ordered phase; Ld phase: Liquid disordered phase); (B) Green channel (500-550 nm) imaging of PA-labeled Arabidopsis root cells (liquid ordered phase, Lo); (C) Red channel (580-700 nm) imaging of PA-labeled Arabidopsis root cells (liquid disordered phase, Ld) (white arrows indicate the presence of endosomes); (D) The merged image of green (B) and red (C) channels (blue arrows indicate the presence of endosomes); (E) Hue-Saturation-Brightness (HSB) image corresponding to the two-channel image. Bars=10 μm
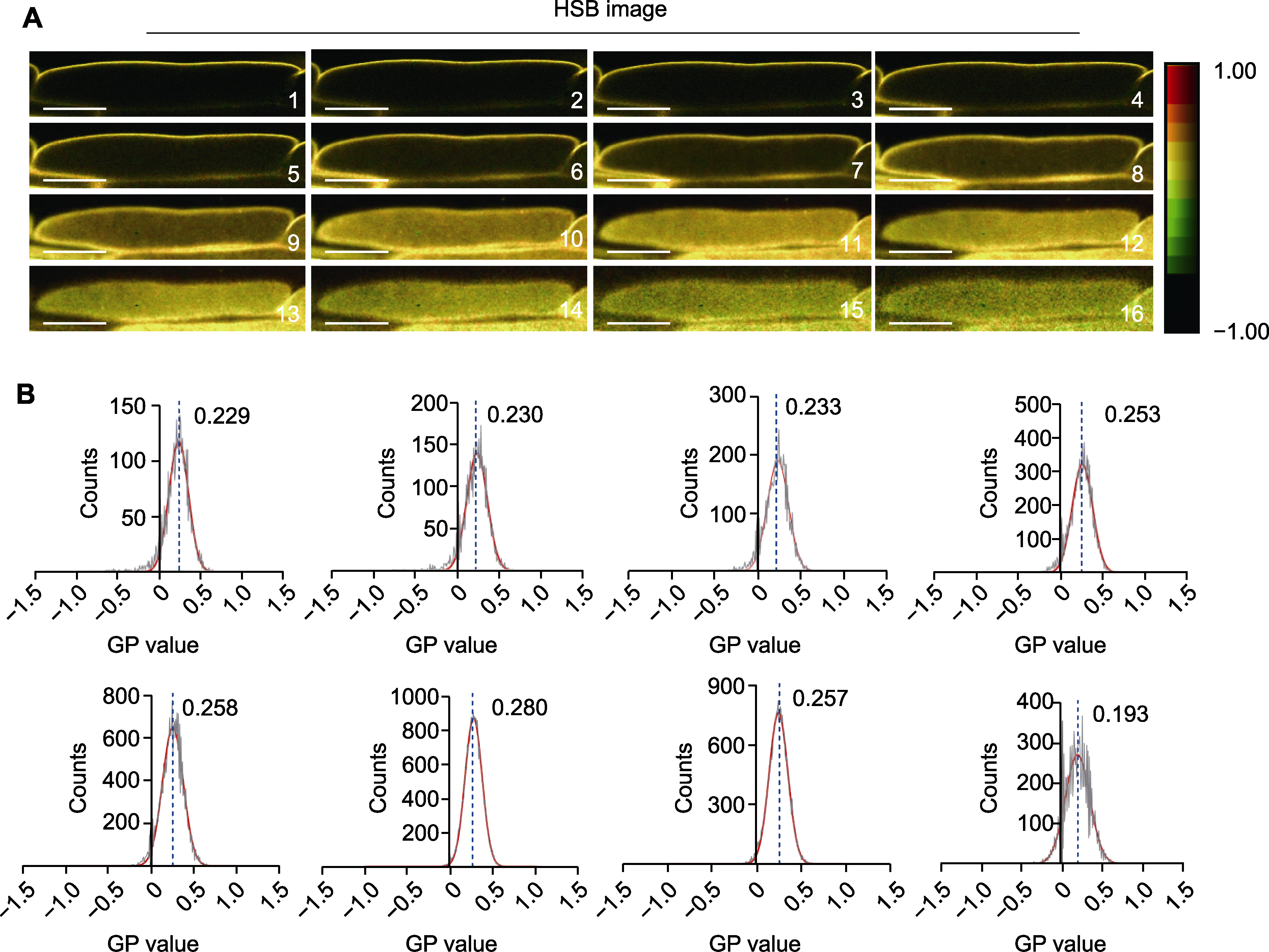
Figure 2 Analysis of membrane degree of different planes (Z-stack) in individual Arabidopsis root cells (A) HSB image of different planes (Z-stack) within individual cells of Arabidopsis roots, the images shown in 1-16 represent HSB fluorescence images of individual cell layers (bars=20 μm); (B) Distribution of GP values of different planes (Z-stack) within individual cells of Arabidopsis roots, more than 3000 pixels were analyzed for each group.
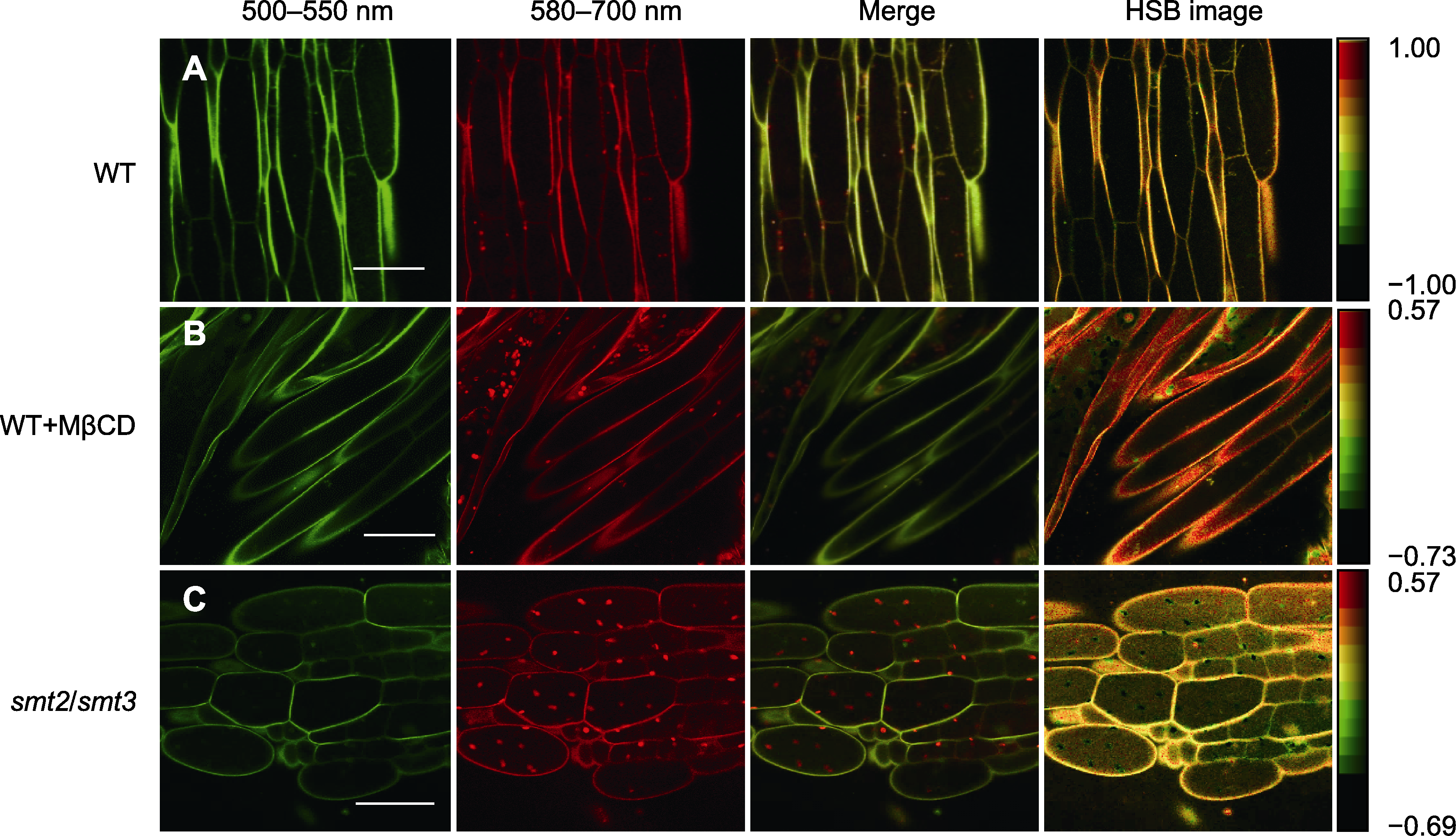
Figure 3 Fluorescence images of Arabidopsis root cells labeled with the PA probe after MβCD treatment and in the smt2/smt3 mutant (A) Fluorescence image of wild type (WT) root cells labeled with PA; (B) Fluorescence image of WT root cells labeled with PA probe after treatment with MβCD; (C) Fluorescence image of root cells in the smt2/smt3 mutant labeled with PA probe. Bars=20 μm
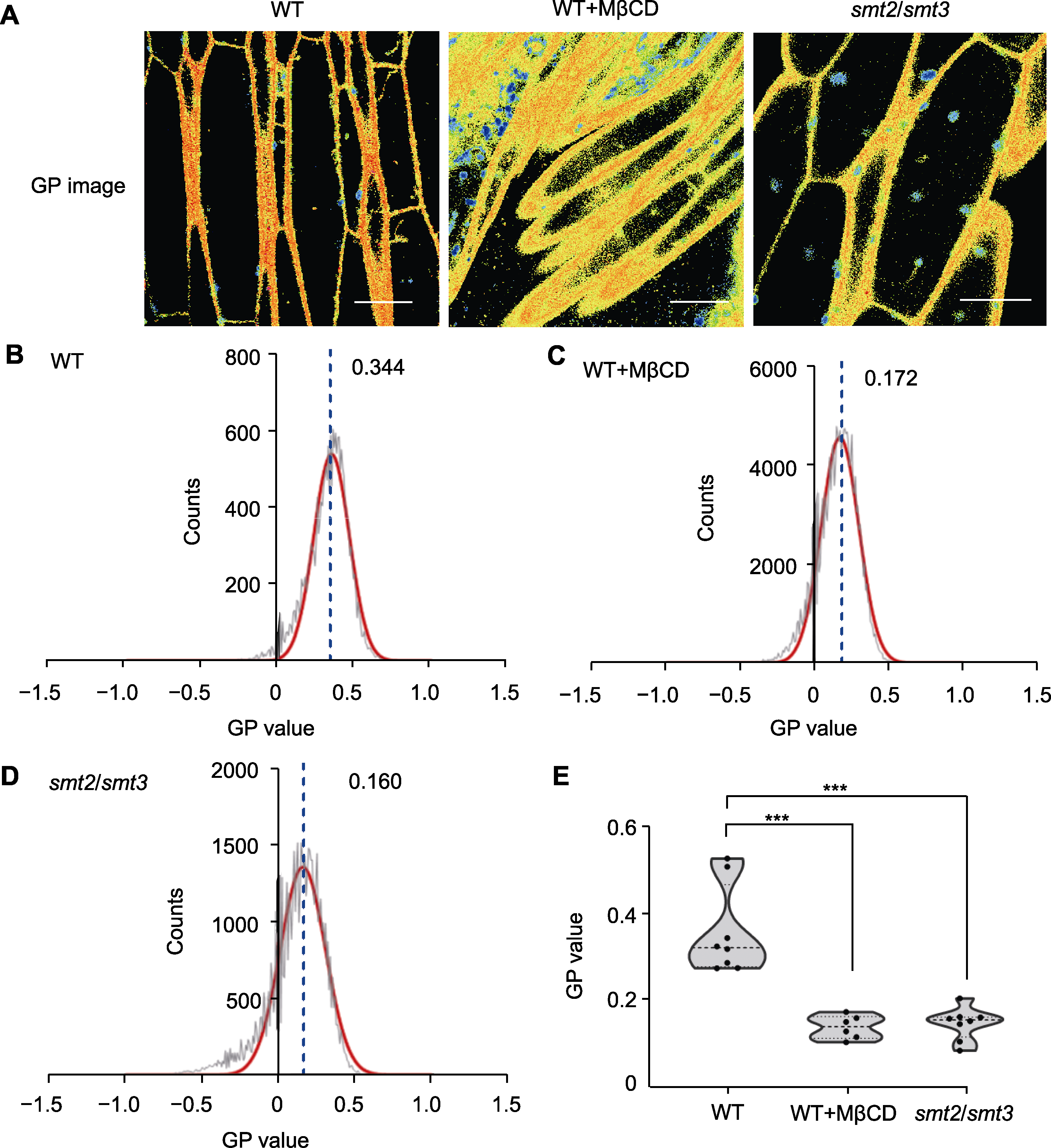
Figure 4 Quantitative analysis and comparison of generalized polarization values of membrane microdomains in Arabidopsis root cells after sterol depletion (A) GP image of the wild type (WT), WT treated with MβCD, and smt2/smt3 double mutant using PA probe (bars=10 μm); (B) GP distribution curve for the WT membrane; (C) GP distribution curve for the WT membrane treated with MβCD; (D) GP distribution curve for the membrane of smt2/smt3 double mutant (the red curves in (B) to (D) represent the Gaussian fitting curves for the distributions of the GP values; The black curves represent the distributions of the membrane GP values; The GP peak values are shown at the top right of each curve; The blue dotted lines indicate the locations of the GP peaks); (E) GP peak values for the WT, WT treated with MβCD, and smt2/smt3 double mutant (each group was analyzed in 6 biological repetitions; *** P<0.001, Student’s t-test).
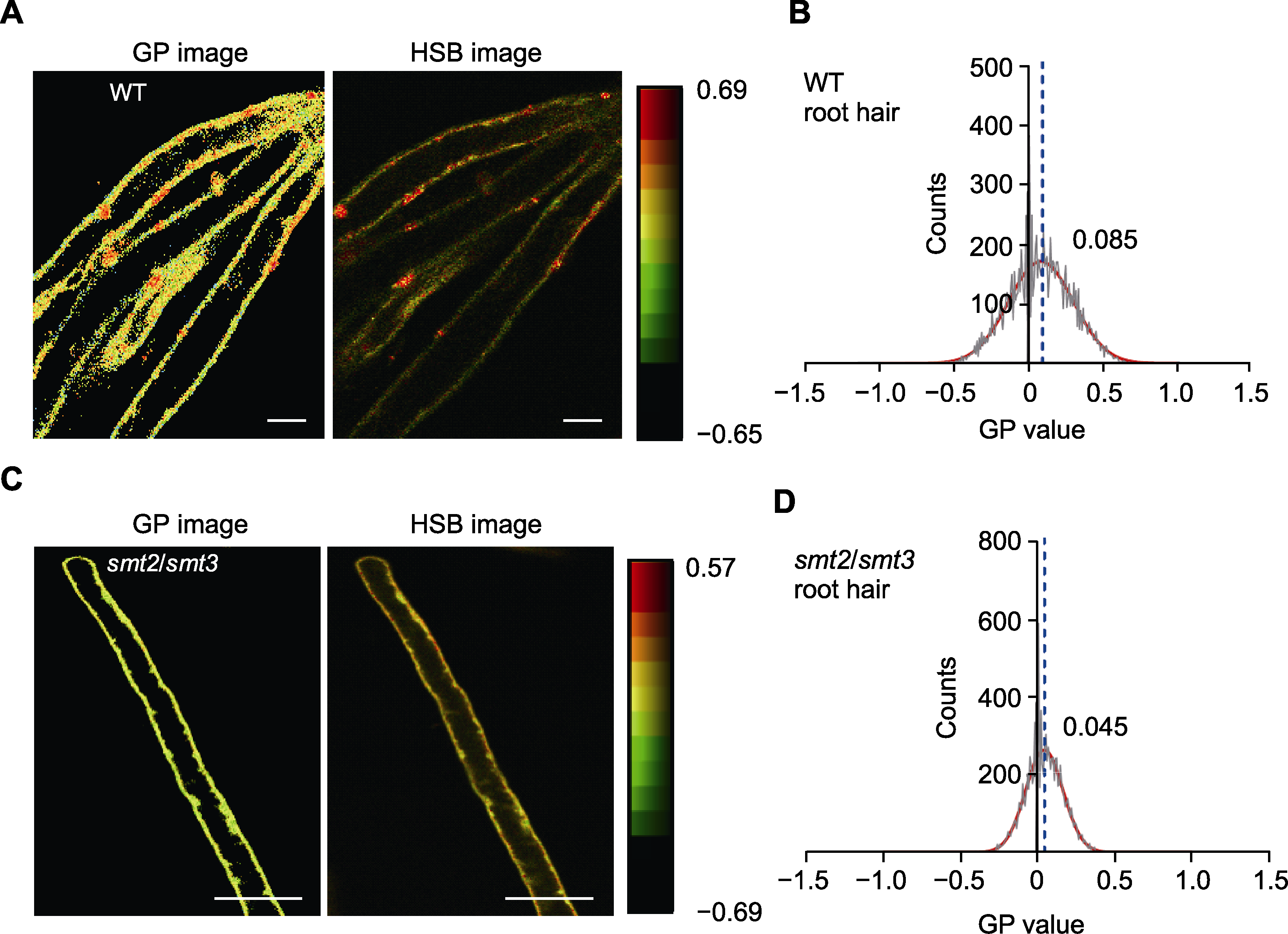
Figure 5 Quantitative analysis of the membrane order of root hair cells in wild type (WT) Arabidopsis and smt2/smt3 double mutant (A) The GP and HSB images of root hair cells in WT Arabidopsis (bars=20 μm); (B) Distribution of the GP values of the root hair cell membranes in WT Arabidopsis, more than 3000 pixels were counted for each group; (C) The GP and HSB images of root hair cells in the smt2/smt3 double mutant (bars=15 μm); (D) Distribution of the GP values of the root hair cell membranes in the smt2/smt3 double mutant. The red curves in (B) and (D) represent the Gaussian fitting curves for the distributions of the GP values; The black curves represent the distributions of the membrane GP values; The numbers indicate the GP peak values at the top right of each curve; The blue dotted lines indicate the locations of the GP peaks.
| [1] |
Brown DA (1992). Interactions between GPI-anchored proteins and membrane lipids. Trends Cell Biol 2, 338-343.
PMID |
| [2] |
Brown DA, London E (2000). Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem 275, 17221-17224.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Carland F, Fujioka S, Nelson T (2010). The sterol methyltransferases SMT1, SMT2, and SMT3 influence Arabidopsis development through nonbrassinosteroid products. Plant Physiol 153, 741-756. |
| [4] |
Carland FM, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Nelson T (2002). The identification of CVP1 reveals a role for sterols in vascular patterning. Plant Cell 14, 2045-2058.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chiantia S, Ries J, Kahya N, Schwille P (2006). Combined AFM and two-focus SFCS study of raft-exhibiting model membranes. Chem Phys Chem 7, 2409-2418. |
| [6] | Dong ZY, Song CW, Cui YN, Yu M, Li RL, Lin JX (2019). Structural models of membrane microdomains and sterol imaging technology. J Chin Electron Microsc Soc 38, 542-549. (in Chinese) |
| 董紫怡, 宋程威, 崔亚宁, 玉猛, 李瑞丽, 林金星 (2019). 膜微区相关结构模型及甾醇成像技术的研究进展. 电子显微学报 38, 542-549. | |
| [7] |
Filippov A, Orädd G, Lindblom G (2003). The effect of cholesterol on the lateral diffusion of phospholipids in oriented bilayers. Biophys J 84, 3079-3086.
PMID |
| [8] | Gerke V, Gavins FNE, Geisow M, Grewal T, Jaiswal JK, Nylandsted J, Rescher U (2024). Annexins—a family of proteins with distinctive tastes for cell signaling and mem-brane dynamics. Nat Commun 15, 1574. |
| [9] |
Goksu EI, Vanegas JM, Blanchette CD, Lin WC, Longo ML (2009). AFM for structure and dynamics of biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1788,254-266.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Hoppe T, Rape M, Jentsch S (2001). Membrane-bound transcription factors: regulated release by RIP or RUP. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13, 344-348.
PMID |
| [11] | Huang XH, Liu W, Tian SP, Chen T (2023). Advances in the regulation of protein liquid-liquid phase separation on development and stress responses in plants. Chin Bull Bot 58, 946-955. (in Chinese) |
|
黄鑫华, 刘伟, 田世平, 陈彤 (2023). 蛋白液-液相分离调控植物发育及胁迫应答研究进展. 植物学报 58, 946-955.
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Ivanov S, Harrison MJ (2024). Receptor-associated kinases control the lipid provisioning program in plant-fungal symbiosis. Science 383, 443-448.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Jin L, Millard AC, Wuskell JP, Clark HA, Loew LM (2005). Cholesterol-enriched lipid domains can be visualized by di-4-ANEPPDHQ with linear and nonlinear optics. Biophys J 89, L04-L06.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Kusumi A, Fujiwara TK, Chadda R, Xie M, Tsunoyama TA, Kalay Z, Kasai RS, Suzuki KGN (2012). Dynamic organizing principles of the plasma membrane that regulate signal transduction: commemorating the fortieth anniversary of singer and nicolson's fluid-mosaic model. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28, 215-250.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Lingwood D, Simons K (2010). Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327, 46-50.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Luo PY, Qian HP, Liu Y, Xu CW, Cui YN (2023). Regulation of plasma membrane protein dynamics and its research methods. Chin Bull Bot 58, 590-601. (in Chinese) |
|
罗鹏云, 钱虹萍, 刘艳, 徐昌文, 崔亚宁 (2023). 质膜蛋白动力学的调控及其研究方法. 植物学报 58, 590-601.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Lv XQ, Jin K, Liu JH, Cui SX, Li JH, Du GC, Liu L (2021). Quantitative analysis of membrane ordering of living industrial model microorganisms. China Biotechnol 41, 20-29. (in Chinese) |
| 吕雪芹, 金柯, 刘家恒, 崔世修, 李江华, 堵国成, 刘龙 (2021). 工业模式微生物膜有序性的活细胞定量分析. 中国生物工程杂志 41, 20-29. | |
| [18] |
Mesmin B, Bigay J, Polidori J, Jamecna D, Lacas-Gervais S, Antonny B (2017). Sterol transfer, PI4P consumption, and control of membrane lipid order by endogenous OS- BP. EMBO J 36, 3156-3174.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Misteli T (2001). Protein dynamics: implications for nuclear architecture and gene expression. Science 291, 843-847.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Munro S (2003). Lipid rafts: elusive or illusive? Cell 115, 377-388.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Niko Y, Didier P, Mely Y, Konishi GI, Klymchenko AS (2016). Bright and photostable push-pull pyrene dye visualizes lipid order variation between plasma and intracellular membranes. Sci Rep 6, 18870.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Niko Y, Kawauchi S, Konishi GI (2013). Solvatochromic pyrene analogues of prodan exhibiting extremely high fluorescence quantum yields in apolar and polar solvents. Chem Eur J 19, 9760-9765. |
| [23] |
Parasassi T, Gratton E, Yu WM, Wilson P, Levi M (1997). Two-photon fluorescence microscopy of laurdan generalized polarization domains in model and natural membranes. Biophys J 72, 2413-2429.
PMID |
| [24] |
Roche Y, Gerbeau-Pissot P, Buhot B, Thomas D, Bonneau L, Gresti J, Mongrand S, Perrier-Cornet JM, Simon-Plas F (2008). Depletion of phytosterols from the plant plasma membrane provides evidence for disruption of lipid rafts. FASEB J 22, 3980-3991.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Sezgin E, Sadowski T, Simons K (2014). Measuring lipid packing of model and cellular membranes with environment sensitive probes. Langmuir 30, 8160-8166.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Shaw JE, Epand RF, Epand RM, Li ZG, Bittman R, Yip CM (2006). Correlated fluorescence-atomic force microscopy of membrane domains: structure of fluorescence probes determines lipid localization. Biophys J 90, 2170-2178.
PMID |
| [27] | Simons K, Ikonen E (1997). Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 387, 569-572. |
| [28] | Simons K, Toomre D (2000). Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1, 31-39. |
| [29] |
Singer SJ, Nicolson GL (1972). The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science 175, 720-731.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Tang L, Li Y, Zhong C, Deng X, Wang XH (2021). Plant sterol clustering correlates with membrane microdomains as revealed by optical and computational microscopy. Mem- branes 11, 747. |
| [31] | Yan X, Xu M, Wang YT, Pan WH, Pan JW, Shou JX, Wang C (2022). Coupling regulation of endocytosis and exocytosis in plants. Chin Bull Bot 57, 375-387. (in Chinese) |
|
严旭, 徐梅, 王玉同, 潘伟槐, 潘建伟, 寿建昕, 王超 (2022). 植物胞吞和胞吐的耦合调控. 植物学报 57, 375-387.
DOI |
|
| [32] |
Zhang L, Xing JJ, Lin JX (2019). At the intersection of exocytosis and endocytosis in plants. New Phytol 224, 1479-1489.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Zhao XY (2014). Application of di-4-ANEPPDHQ as a Novel Fluorescent Probe for Visualization and Detection of Membrane Microdomains in Living Cells in Arabidopsis thaliana. Master’s thesis. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. pp. 1-82. (in Chinese) |
| [34] | 赵晓玉 (2014). 新型荧光探针di-4-ANEPPDHQ在拟南芥质膜微区显微成像和定量检测中的应用. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 1-82. |
| [35] | Zuo CS, Liu DY, Xu QJ, Shi WZ, Niu J, Chass GC (2013). Research progress on structure and function of phytosterols. J Henan Sci Technol 32, 211-213. (in Chinese) |
| 左春山, 刘大勇, 徐启杰, 时文中, 牛静, Chass GC (2013). 植物甾醇的结构与功能的研究进展. 河南科技 32, 211-213. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||