

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (2): 261-273.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22224 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22224
• INVITED PROTOCOLS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huanwen Peng1,2,3, Wei Wang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-19
Accepted:2022-11-12
Online:2023-03-01
Published:2023-03-15
Contact:
*E-mail: Huanwen Peng, Wei Wang. Phylogenetic Tree Reconstruction Based on Molecular Data[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 261-273.
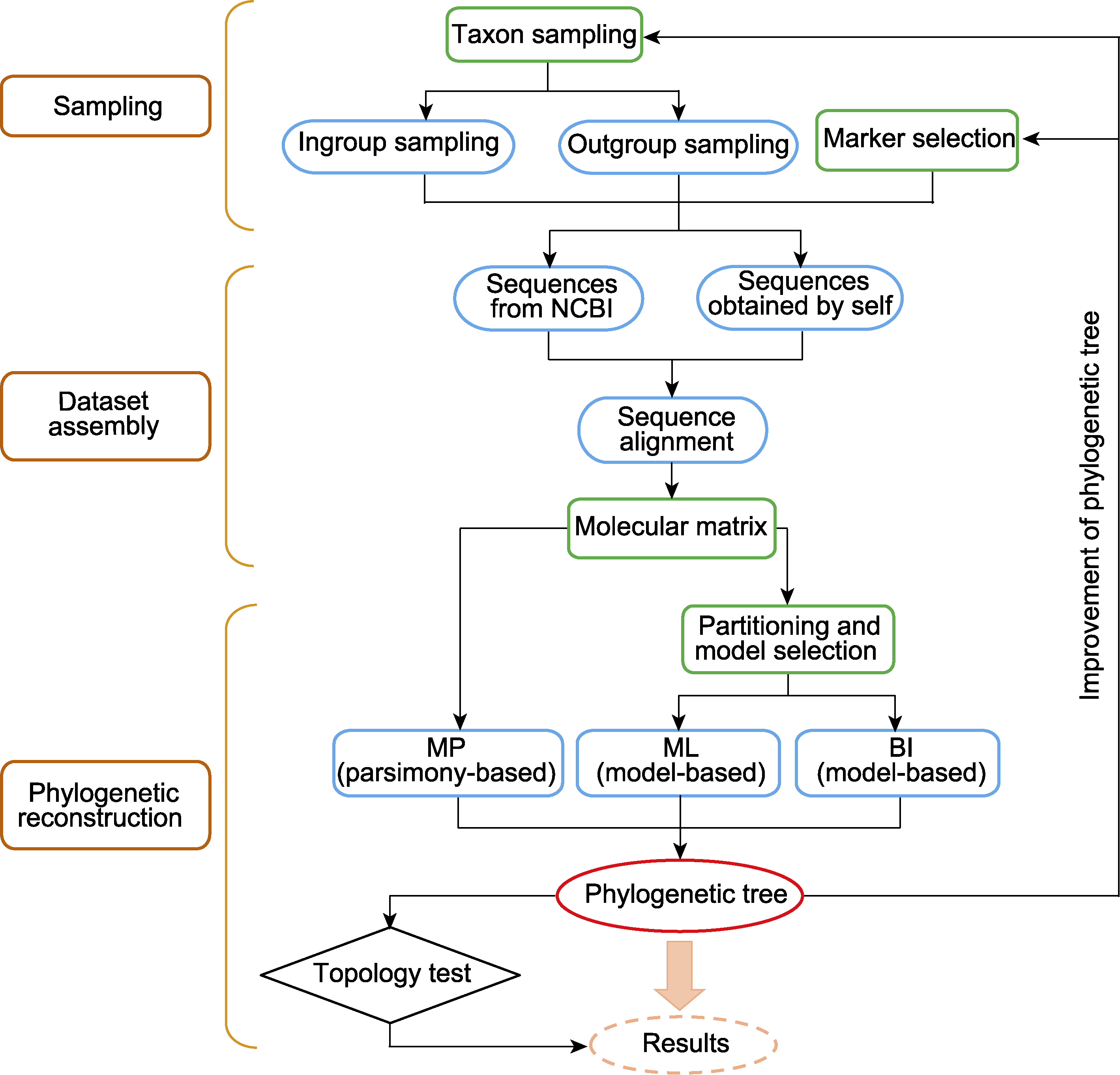
Figure 1 The pipeline of phylogenetic tree reconstruction based on molecular data MP: Maximum parsimony; ML: Maximum likelihood; BI: Bayesian inference
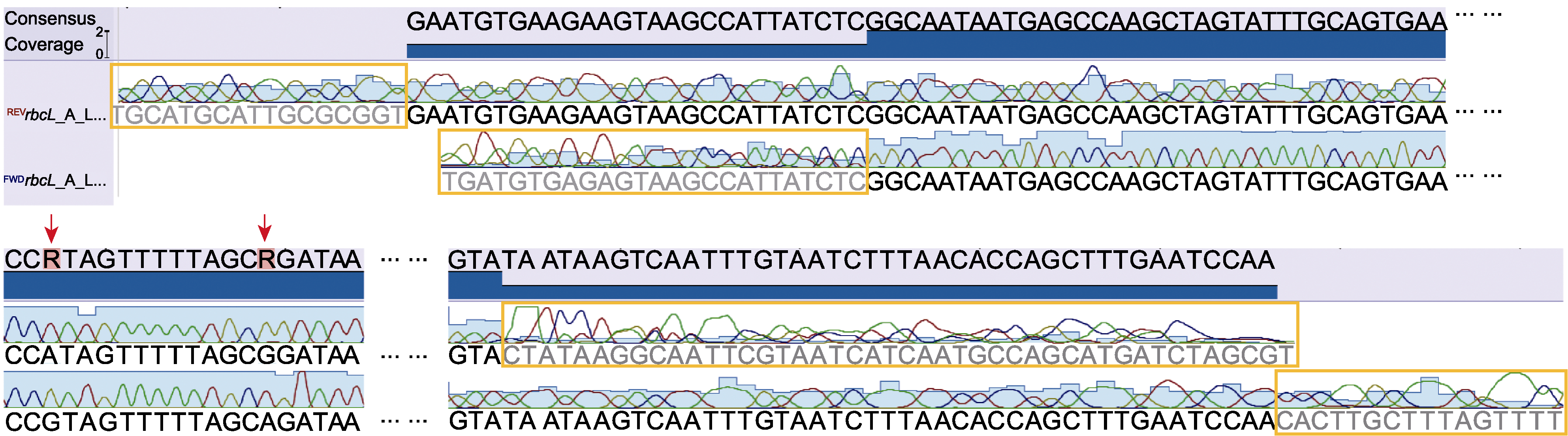
Figure 2 DNA sequence chromatograms obtained through Sanger sequencing using both forward and reverse primers Orange boxes show the ambiguous bases in both ends of the sequences, and red arrows show the conflicting base calls between two chromatograms.
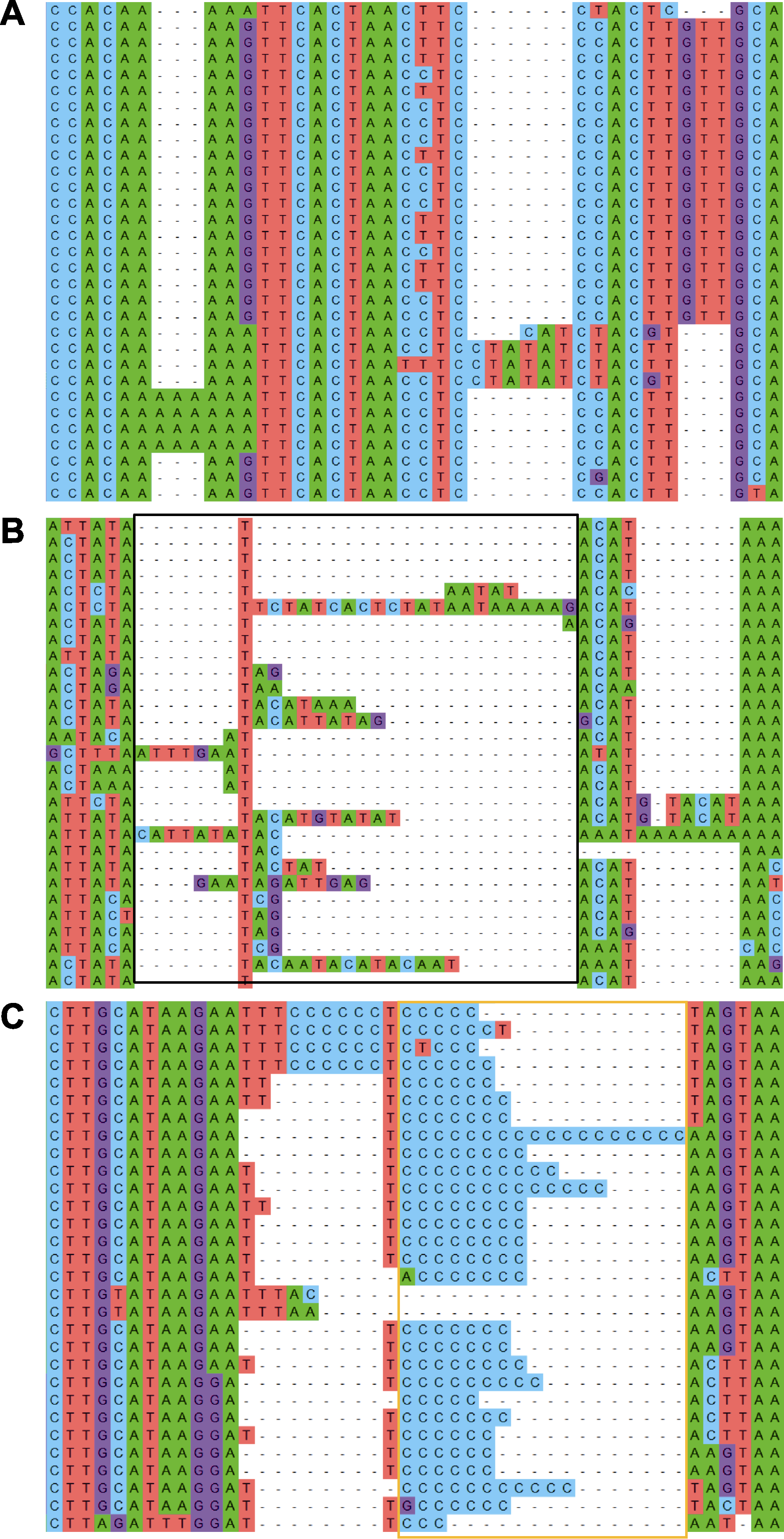
Figure 3 Examples for sequence alignment (A) Alignment for protein-coding sequences; (B) Alignment for non-coding sequences with a difficult-to-align region (indicated by black box); (C) Alignment for non-coding sequences with a poly-base region (indicated by orange box)
| [1] | 范凯, 叶方婷, 毛志君, 潘鑫峰, 李兆伟, 林文雄 (2021). 被子植物小热激蛋白家族的比较基因组学分析. 植物学报 56, 245-261. |
| [2] |
葛颂 (2022). 中国植物系统和进化生物学研究进展. 生物多样性 30, 22385.
DOI |
| [3] | 康凯程, 牛西强, 黄先忠, 胡能兵, 隋益虎, 张开京, 艾昊(2021). 辣椒R2R3-MYB转录因子家族的全基因组鉴定与比较进化分析. 植物学报 56, 315-329. |
| [4] | 王伟, 刘阳 (2020). 植物生命之树重建的现状、问题和对策建议. 生物多样性 28, 176-188. |
| [5] |
向小果, 王伟 (2015). 植物DNA条形码在系统发育研究中的应用. 生物多样性 23, 281-282.
DOI |
| [6] |
Benton MJ, Ayala FJ (2003). Dating the tree of life. Science 300, 1698-1700.
PMID |
| [7] |
Borsch T, Hilu KW, Quandt D, Wilde V, Neinhuis C, Barthlott W (2003). Noncoding plastid trnT-trnF sequences reveal a well resolved phylogeny of basal angiosperms. J Evol Biol 16, 558-576.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T (2009). trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 25, 1972-1973.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Castresana J (2000). Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17, 540-552.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Chase MW, Soltis DE, Olmstead RG, Morgan D, Les DH, Mishler BD, Duvall MR, Price RA, Hills HG, Qiu YL, Kron KA, Rettig JH, Conti E, Palmer JD, Manhart JR, Sytsma KJ, Michaels HJ, Kress WJ, Karol KG, Clark WD, Hedren M, Gaut BS, Jansen RK, Kim KJ, Wimpee CF, Smith JF, Furnier GR, Strauss SH, Xiang QY, Plunkett GM, Soltis PS, Swensen SM, Williams SE, Gadek PA, Quinn CJ, Eguiarte LE, Golenberg E, Learn Jr GH, Graham SW, Barrett SCH, Dayanandan S, Albert VA (1993). Phylogenetics of seed plants: an analysis of nucleotide sequences from the plastid gene rbcL. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 80, 528-580.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Edgar RC (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32, 1792-1797.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Fan CZ, Xiang QY (2003). Phylogenetic analyses of Cornales based on 26S rRNA and combined 26S rDNA-matK- rbcL sequence data. Am J Bot 90, 1357-1372.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Folk RA, Stubbs RL, Mort ME, Cellinese N, Allen JM, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Guralnick RP (2019). Rates of niche and phenotype evolution lag behind diversification in a temperate radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 10874-10882.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Goldman N, Anderson JP, Rodrigo AG (2000). Likelihood- based tests of topologies in phylogenetics. Syst Biol 49, 652-670.
PMID |
| [15] |
Goremykin VV, Nikiforova SV, Biggs PJ, Zhong BJ, Delange P, Martin W, Woetzel S, Atherton RA, Mclenachan PA, Lockhart PJ (2013). The evolutionary root of flowering plants. Syst Biol 62, 50-61.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Hall TA (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/ 98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41, 95-98. |
| [17] |
Jian SG, Soltis PS, Gitzendanner MA, Moore MJ, Li RQ, Hendry TA, Qiu YL, Dhingra A, Bell CD, Soltis DE (2008). Resolving an ancient, rapid radiation in Saxifragales. Syst Biol 57, 38-57.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Joly S, McLenachan PA, Lockhart PJ (2009). A statistical approach for distinguishing hybridization and incomplete lineage sorting. Am Nat 174, E54-E70. |
| [19] |
Kass RE, Raftery AE (1995). Bayes factors. J Am Stat Ass 90, 773-795.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30, 772-780.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C, Thierer T, Ashton B, Meintjes P, Drummond A (2012). Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28, 1647-1649.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Kishino H, Hasegawa M (1989). Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J Mol Evol 29, 170-179.
PMID |
| [23] |
Lanfear R, Frandsen PB, Wright AM, Senfeld T, Calcott B (2017). PartitionFinder 2: new methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol Biol Evol 34, 772-773.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Lian L, Ortiz RDC, Jabbour F, Chen ZD, Wang W (2019). Re-delimitation of Tinospora (Menispermaceae): implications for character evolution and historical biogeography. Taxon 68, 905-917.
DOI |
| [25] |
Liu GQ, Lian L, Wang W (2022). The molecular phylogeny of land plants: progress and future prospects. Diversity 14, 782.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Liu L, Wu SY, Yu LL (2015). Coalescent methods for estimating species trees from phylogenomic data. J Syst Evol 53, 380-390.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Lozano-Fernandez J (2022). A practical guide to design and assess a phylogenomic study. Genome Biol Evol 14, evac129. |
| [28] |
Lu LM, Cox JC, Mathews S, Wang W, Wen J, Chen ZD (2018). Optimal data partitioning, multispecies coalescent and Bayesian concordance analyses resolve early divergences of the grape family (Vitaceae). Cladistics 34, 57-77.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Mirarab S, Nakhleh L, Warnow T (2021). Multispecies coalescent: theory and applications in phylogenetics. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 52, 247-268.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Nandi OI, Chase MW, Endress PK (1998). A combined cladistic analysis of angiosperms using rbcL and non-molecular data sets. Ann Missouri Bot Gard 85, 137-214.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Nei M (1996). Phylogenetic analysis in molecular evolutio-a) nary genetics. Annu Rev Genet 30, 371-403.
PMID |
| [32] |
Owen CL, Marshall DC, Wade EJ, Meister R, Goemans G, Kunte K, Moulds M, Hill K, Villet M, Pham TH, Kortyna M, Lemmon EM, Lemmon AR, Simon C (2022). Detecting and removing sample contamination in phylogenomic data: an example and its implications for Cicadidae phylogeny (Insecta: Hemiptera). Syst Biol 71, 1504-1523.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Pelser PB, Kennedy AH, Tepe EJ, Shidler JB, Nordenstam B, Kadereit JW, Watson LE (2010). Patterns and causes of incongruence between plastid and nuclear Senecioneae (Asteraceae) phylogenies. Am J Bot 97, 856-873.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Xie D, Baele G, Suchard MA (2018). Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst Biol 67, 901-904.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012). MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61, 539-542.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, von Haeseler A (2002). TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18, 502-504.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Shimodaira H (2002). An approximately unbiased test of phylogenetic tree selection. Syst Biol 51, 492-508.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Shimodaira H, Hasegawa M (1999). Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 16, 1114.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Shimodaira H, Hasegawa M (2001). CONSEL: for assessing the confidence of phylogenetic tree selection. Bioinformatics 17, 1246-1247.
PMID |
| [40] |
Smith MR (2013). Likelihood and parsimony diverge at high taxonomic levels. Cladistics 29, 463.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Soltis DE, Moore MJ, Burleigh G, Soltis PS (2009). Molecular markers and concepts of plant evolutionary relationships: progress, promise, and future prospects. Crit Rev Plant Sci 28, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Chase MW (1999). Angiosperm phylogeny inferred from multiple genes as a tool for comparative biology. Nature 402, 402-404.
DOI |
| [43] |
Stamatakis A (2014). RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312-1313.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Sun M, Folk RA, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Chen ZD, Soltis DE, Guralnick RP (2020). Recent accelerated diversification in rosids occurred outside the tropics. Nat Commun 11, 3333.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Swofford DL (2002). PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (* and other methods). Version 4. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates. |
| [46] |
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021). MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38, 3022-3027.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997). The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25, 4876-4882.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | van der Niet T, Linder HP (2008). Dealing with incongruence in the quest for the species tree: a case study from the orchid genus Satyrium. Mol Phylogenet Evol 47, 154-174. |
| [49] | Wang W (2018). A primer to the use of herbarium specimens in plant phylogenetics. Bot Lett 165, 404-408. |
| [50] |
Wang W, Del Ortiz RC, Jacques FMB, Chung SW, Liu Y, Xiang XG, Chen ZD (2017). New insights into the phylogeny of Burasaieae (Menispermaceae) with the recognition of a new genus and emphasis on the southern Taiwanese and mainland Chinese disjunction. Mol Phylogenet Evol 109, 11-20.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Wang W, Del Ortiz RC, Jacques FMB, Xiang XG, Li HL, Lin L, Li RQ, Liu Y, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Chen ZD (2012). Menispermaceae and the diversification of tropical rainforests near the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. New Phytol 195, 470-478.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Wang W, Li HL, Chen ZD (2014a). Analysis of plastid and nuclear DNA data in plant phylogenetics—evaluation and improvement. Sci China Life Sci 57, 280-286.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Wang W, Li HL, Xiang XG, Chen ZD (2014b). Revisiting the phylogeny of Ranunculeae: implications for divergence time estimation and historical biogeography. J Syst Evol 52, 551-565.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Wang W, Wang HC, Chen ZD (2007). Phylogeny and morphological evolution of tribe Menispermeae (Menispermaceae) inferred from chloroplast and nuclear sequences. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 8, 141-154.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Whelan S, Liò P, Goldman N (2001). Molecular phylogenetics: state-of-the-art methods for looking into the past. Trends Genet 17, 262-272.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Xi ZX, Ruhfel BR, Schaefer H, Amorim AM, Sugumaran M, Wurdack KJ, Endress PK, Matthews ML, Stevens PF, Mathews S, Davis CC (2012). Phylogenomics and a posteriori data partitioning resolve the Cretaceous angiosperm radiation Malpighiales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 17519-17524.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Xiang QY, Manchester SR, Thomas DT, Zhang WH, Fan CZ (2005). Phylogeny, biogeography, and molecular dating of cornelian cherries (Cornus, Cornaceae): tracking Tertiary plant migration. Evolution 59, 1685-1700. |
| [58] |
Yang ZH, Rannala B (2012). Molecular phylogenetics: principles and practice. Nat Rev Genet 13, 303-314.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Wei Wang, Yang Liu. The current status, problems, and policy suggestions for reconstructing the plant tree of life [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(2): 176-188. |
| [2] | Wei Wang, Xiaoxia Zhang, Zhiduan Chen, Anming Lu. Comments on the APG’s classification of angiosperms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(4): 418-426. |
| [3] | Ge Yao;Shulian Xie. Progress in Molecular Systematics of Batrachospermales [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(02): 141-146. |
| [4] | LI Jing SHA Wei. Present Status of Molecular Systematics on the Bryophytes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2004, 21(02): 172-179. |
| [5] | Wang Zhongren. The genetic bases of allozyme analysis (Part 2) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1994, 02(4): 213-219. |
| [6] | Wang Zhongren. The genetic basies of allozyme analysis (Part 1) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1994, 02(3): 149-156. |
| [7] | Wang Zhongren. Allozyme analysis in studies of plant genetic diversity and systematics [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1994, 02(2): 91-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||