

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (5): 712-719.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22117 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22117
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shi Junxing1, Yan Yijia2, Dong Ru2, Tao Xuan3, Sun Xiaolong4, Huang Congcong5,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-07
Accepted:2022-11-15
Online:2023-09-01
Published:2023-09-21
Contact:
*E-mail: huangcong163@126.com
Shi Junxing, Yan Yijia, Dong Ru, Tao Xuan, Sun Xiaolong, Huang Congcong. The Arabidopsis HSP1 Mediates Chitin-induced Defense Response by Regulating CERK1 Protein Level[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 712-719.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ACTIN-F | TCCCTCAGCACATTCCAGCAGAT |
| ACTIN-R | AACGATTCCTGGACCTGCCTCATC |
| WRKY33-F | GGTCACAACAATCCGGAAGA |
| WRKY33-R | GGAGAGACAAGAGAAGGAGAGA |
| WRKY53-F | CGACGGCTGTTGCTGAGAC |
| WRKY53-R | TCCGTTTATCGATGCCGGAG |
Table 1 The primers used for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ACTIN-F | TCCCTCAGCACATTCCAGCAGAT |
| ACTIN-R | AACGATTCCTGGACCTGCCTCATC |
| WRKY33-F | GGTCACAACAATCCGGAAGA |
| WRKY33-R | GGAGAGACAAGAGAAGGAGAGA |
| WRKY53-F | CGACGGCTGTTGCTGAGAC |
| WRKY53-R | TCCGTTTATCGATGCCGGAG |
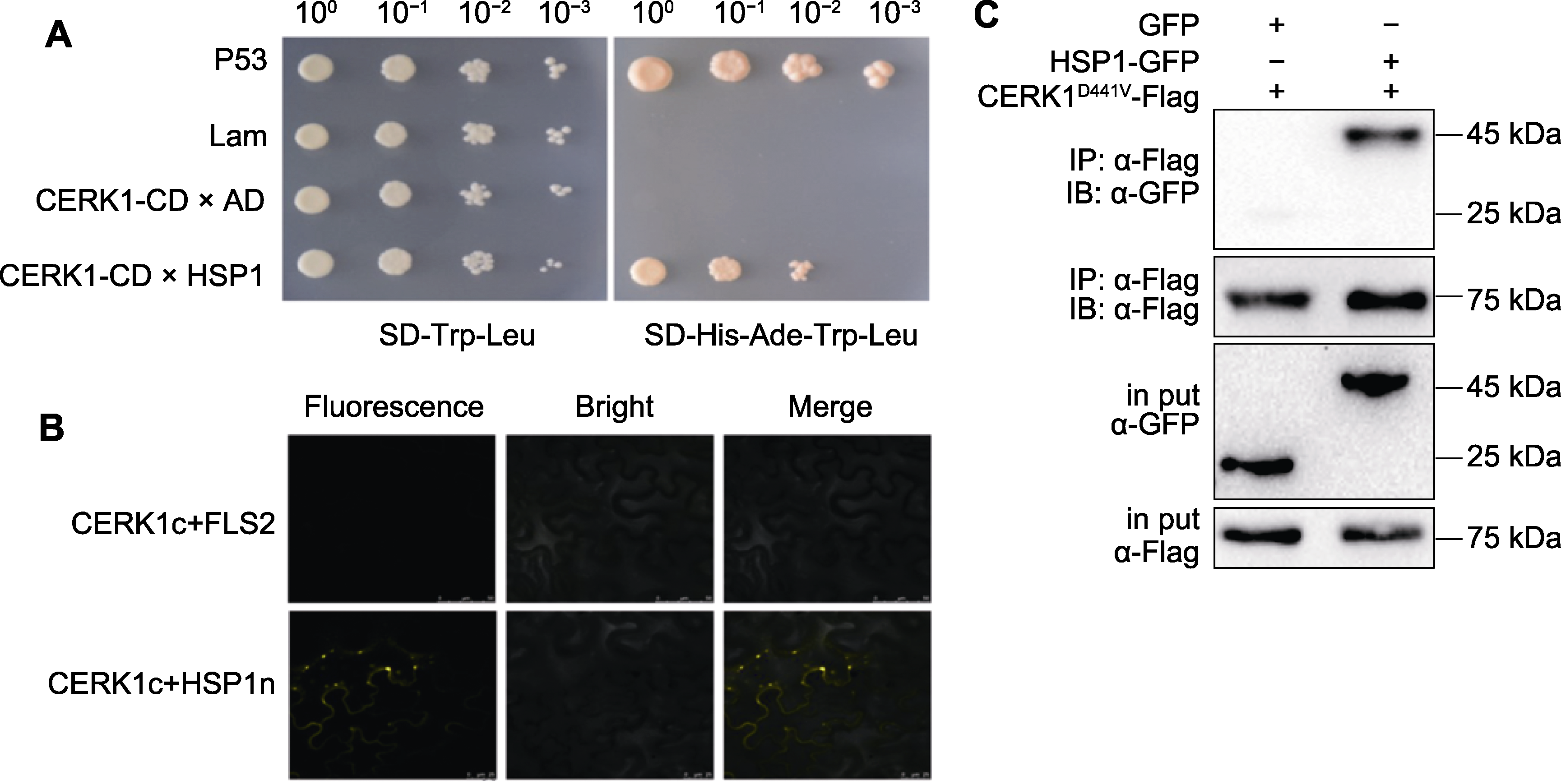
Figure 1 Interaction between CERK1-BD and HSP1-AD in yeast cells (A) The HSP1 protein was fused with AD at the N-terminal, and CERK1-CD was fused with BD at the C-terminal, then these two recombinants were transformed into Y187 and AH109 yeast strains, respectively. After hybridization, it was plated on SD-Trp-Leu/SD-Ade-Trp-Leu/SD-His-Ade-Trp-Leu plates, and cultivated at 28°C, P53 and Lam represent positive and negative controls, respectively. (B) C-terminal of CERK1 was fused with cYFP, HSP1 and CPK5 were fused with nYFP, and then co-injected into Nicotiana benthamiana mesophyll cells, CPK5 and HSP1 served as negative control. After 72 hours of injection, the fluorescence intensity of YFP fluorescent protein was detected under fluorescence microscope; (C) Interaction between HSP1 and CERK1 was detected in N. benthamiana by Western blot (WB). C-terminal of CERK1D441V was fused with Flag tag, and C-terminal of HSP1 was fused with GFP tag, then were co-injected into N. benthamiana mesophyll cell. The CERK1 protein was precipitated using a Flag antibody, and the HSP1-GFP was detected by CoIP. The experiment was repeated for three times with similar results.
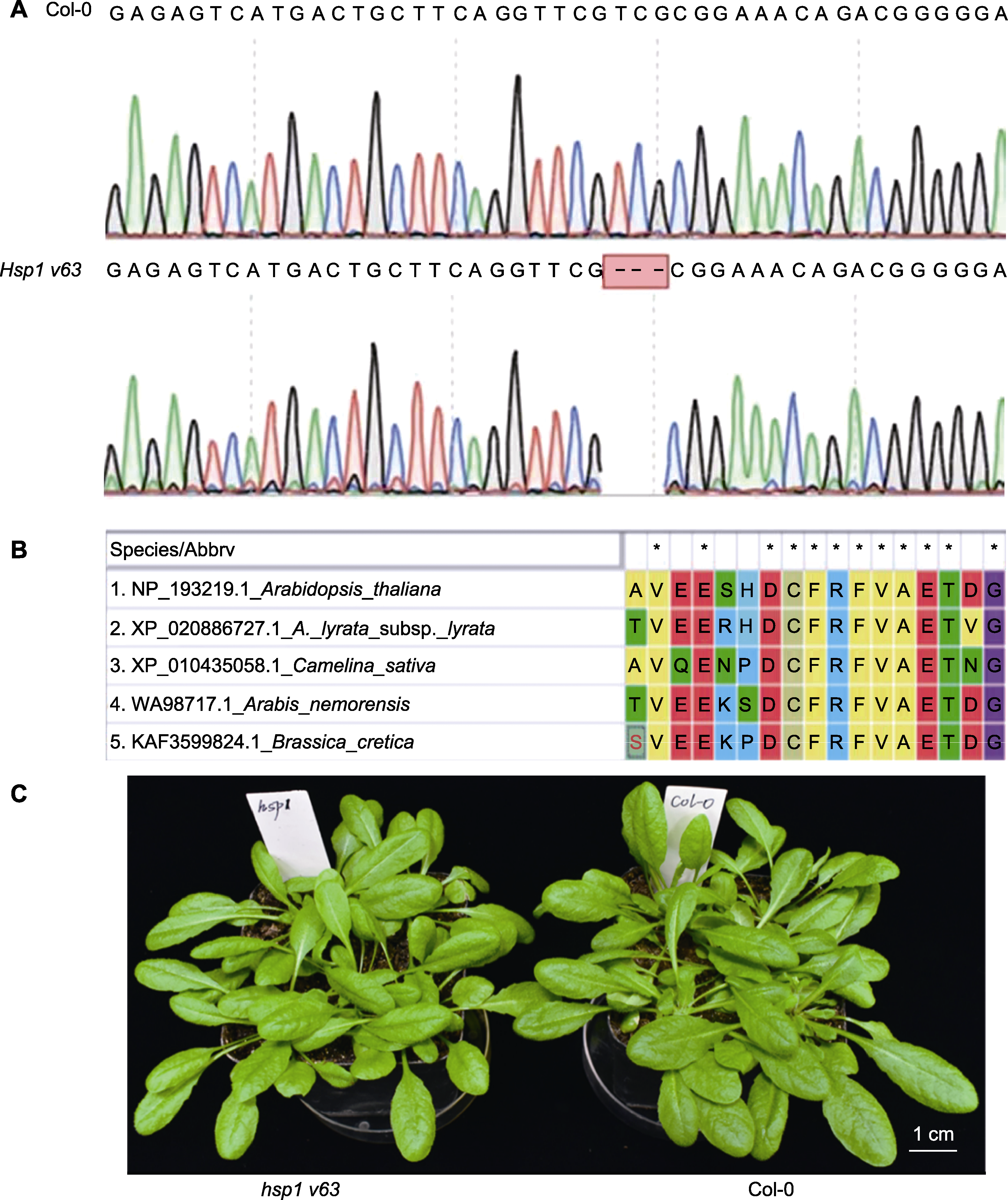
Figure 2 Identification of hsp1 v63 deletion mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana (A) The hsp1 genomic DNA was extracted, then the HSP1 gene was amplified by PCR, and the PCR product was used for sequencing analysis (by comparing the sequencing results, it was found that the 63 rd valine of HSP1 was knocked out, the blue sequence represents the target site of gRNA, and the red sequence represents the NGG sequence; (B) Analysis of the conservation of the amino acid sequence of HSP1 in Arabidopsis thaliana, A. lyrata, Camelina sativa, Arabis and Brassica using Clustal W alignment (* represent the conserved amino acid sites); (C) The hsp1 v63 deletion mutant (left) and Col-0 (right) grown for 4 weeks, and their growth conditions were similar.
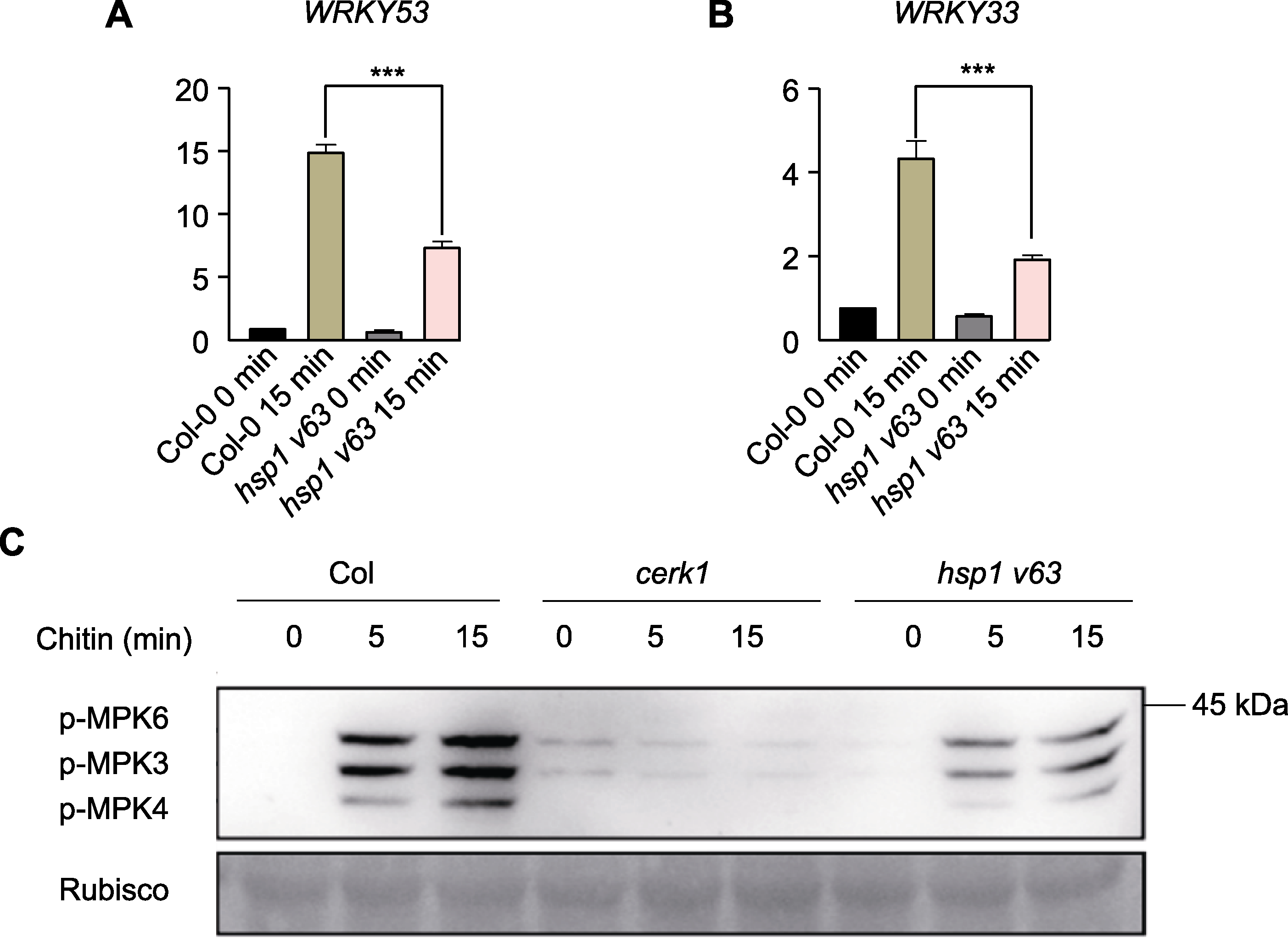
Figure 3 Determination of defense responses in the hsp1 v63 deletion mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana (A), (B) Chitin-induced gene expression analysis of WRKY53 and WRKY33 in Arabidopsis hsp1 v63 deletion mutant (the tran-scriptional level of WRKY53 and WRKY33 genes in hsp1 v63 deletion mutant and Col-0 seedlings was measured by qRT-PCR before and after chitin induction. All expression levels were normalized using the internal reference gene ACTIN2, data are pre-sented as means±SD, one-way ANOVA, Tukey post-test, *** P<0.001, n=3); (C) Chitin-induced MAPK activation experiments in Arabidopsis cerk1, hsp1 v63 deletion mutant, wild-type Col-0 (chitin-induced MAPK phosphorylation was examined in cerk1, hsp1 v63 deletion mutant and wild-type Col-0. The A. thaliana seedlings were treated with chitin for the time indicated in the figure. After the samples were collected, the phosphorylation of MAPK3/6 was detected by immunoblot. The antibody used in this experiment was Anti-P44/P42. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results).
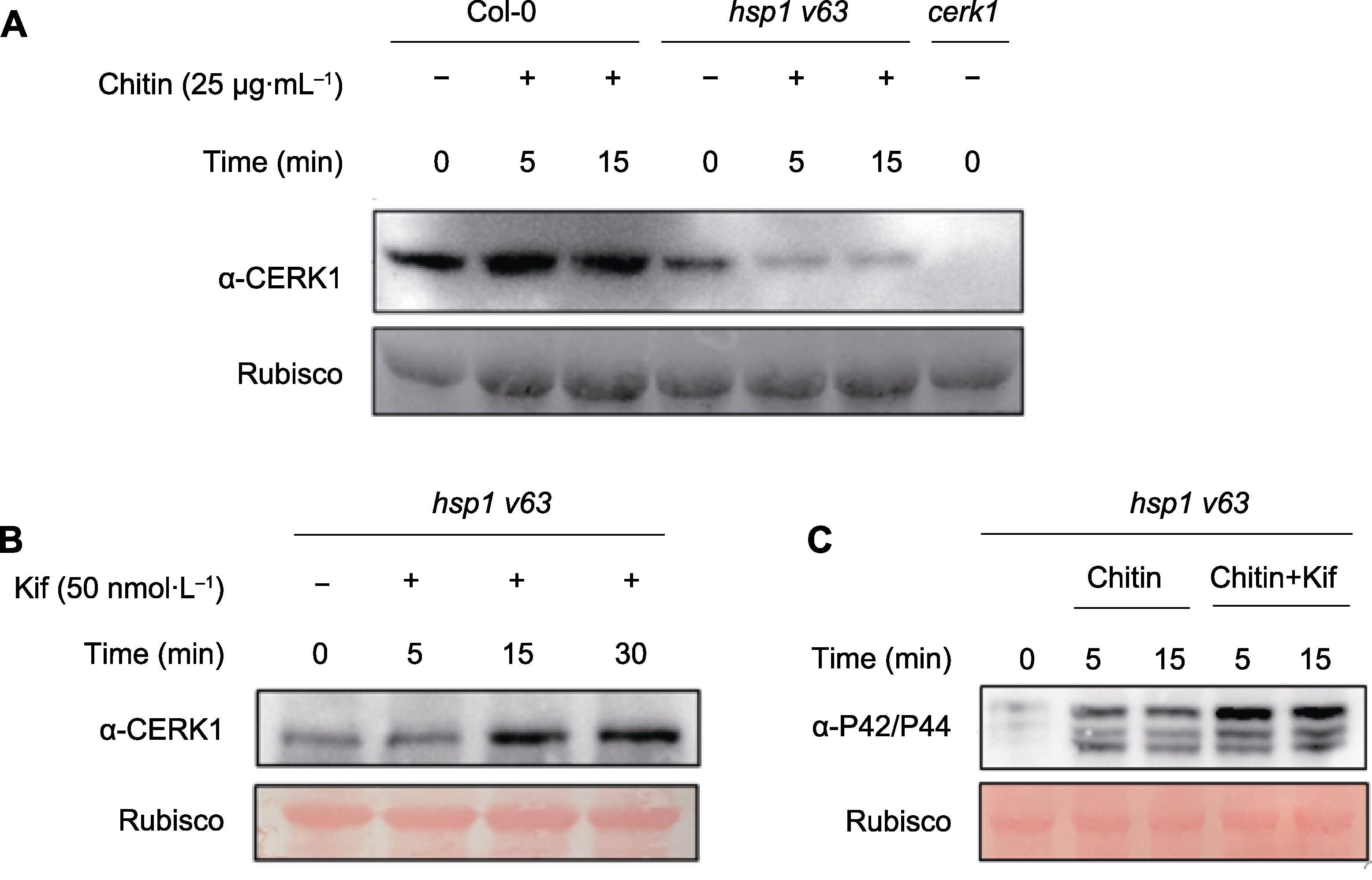
Figure 4 Detection of chitin-induced CERK1 protein levels in cerk1, hsp1 v63 deletion mutants and wild-type Col-0 of Arabidop-sis (A) Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings were soaked in MS plate for 7 days, and the seedlings were treated with 25 μg·mL-1 chitin for the indicated times as shown in the figure. After samples were collected, CERK1 protein level was detected by Western blot (WB) by CERK1 antibody; (B) CERK1 protein level were measured after treated with 50 nmol·L-1 Kif for 0, 5, 15, and 30 minutes under hsp1 v63 deletion mutant; (C) Comparison the phosphorylation of MAPK3/6 after treated by 25 μg·mL-1 Chitin or 25 μg·mL-1 Chitin and 50 nmol·L-1 Kif mixture for indicated time. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.
| [1] | 欧阳石文, 赵开军, 冯兰香 (2001). 植物几丁质酶的结构与功能、分类及进化. 植物学通报 18, 418-426. |
| [2] | 张静, 杨洪强, 魏钦平 (2003). 几丁质及其衍生物的生物活性与在农业中的应用. 植物学通报 20, 178-183. |
| [3] |
Antolín-Llovera M, Ried MK, Binder A, Parniske M (2012). Receptor kinase signaling path-ways in plant-microbe in-teractions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 50, 451-473.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Bi GZ, Zhou ZY, Wang WB, Li L, Rao SF, Wu Y, Zhang XJ, Menke FLH, Chen S, Zhou JM (2018). Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases directly link diverse pattern recogni-tion receptors to the activation of mitogen-activated pro-tein kinase cascades in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30, 1543-1561.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2015). Signaling mecha-nisms in pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Mol Plant 8, 521-539.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Chen LT, Hamada S, Fujiwara M, Zhu TH, Thao NP, Wong HL, Krishna P, Ueda T, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2010). The Hop/Sti1-Hsp90 chaperone complex facilitates the maturation and transport of a PAMP receptor in rice innate immunity. Cell Host Microbe 7, 185-196.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Gong BQ, Guo JH, Zhang NN, Yao XR, Wang HB, Li JF (2019). Cross-microbial protection via priming a conserved immune co-receptor through juxtamembrane phos-phorylation in plants. Cell Host Microbe 26, 810-822.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Hong Z, Jin H, Tzfira T, Li JM (2008). Multiple mechanism-mediated retention of adefective brassinosteroid receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 3418-3429.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Huang CC, Yan YJ, Zhao HL, Ye Y, Cao YR (2020). Ara-bidopsis CPK5 phosphorylates the chitinreceptor LYK5 to regulate plant innate immunity. Front Plant Sci 11, 702.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329.
DOI |
| [11] |
Li J, Zhao-Hui C, Batoux M, Nekrasov V, Roux M, Chin-chilla D, Zipfel C, Jones JDG (2009). Specific ER quality control components required for biogenesis of the plant innate immune receptor EFR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 15973-15978.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Li W, Deng YW, Ning YS, He ZH, Wang GL (2020). Ex-ploiting broad-spectrum disease resistance in crops: from molecular dissection to breeding. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71, 575-603.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Liu J, Liu B, Chen SF, Gong BQ, Chen LJ, Zhou Q, Xiong F, Wang ML, Feng DR, Li JF, Wang HB, Wang JF (2018). A tyrosine phosphorylation cycle regulates fungal activation of a plant receptor Ser/Thr kinase. Cell Host Microbe 23, 241-253.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Lu D, Lin W, Gao X, Wu S, Cheng C, Avila J, Heese A, Devarenne TP, He P, Shan L (2011). Direct ubiquitination of pattern recognition receptor FLS2 attenuates plant in-nate immunity. Science 332, 1439-1442.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Nagashima Y, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2018). Function of N-glycosylation in plants. Plant Sci 274, 70-79.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Savary S, Willocquet L, Pethybridge SJ, Esker P, McRoberts N, Nelson A (2019). The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat Ecol Evol 3, 430-439.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Strasser R (2018). Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 147-172.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Tang DZ, Wang GX, Zhou JM (2017). Receptor kinases in plant-pathogen interactions: more than pattern recognition. Plant Cell 29, 618-637.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Zhou JG, Liu DR, Wang P, Ma XY, Lin WW, Chen SX, Mishev K, Lu DP, Kumar R, Vanhoutte I, Meng XZ, He P, Russinova E, Shan LB (2018). Regulation of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 endocytosis and degradation by plant U-box PUB12/PUB-13-mediated ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E1906-E1915. |
| [20] |
Zou JJ, Wei FJ, Wang C, Wu JJ, Ratnasekera D, Liu WX, Wu WH (2010). Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK10 functions in abscisic acid- and Ca2+-mediated stomatal regulation in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol 154, 1232-1243.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Jing YANG Hong-Qiang WEI Qin-Ping. The Biological Activity of Chitin and Its Derivatives and Their Application in Agriculture [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 20(02): 178-183. |
| [2] | OUYANG Shi-WenZHAO Kai-JunFENG Lan-Xiang. The Structure and Function, Classification and Evolution of Plant Chitinases [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2001, 18(04): 418-426. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||