

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 699-714.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21100 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21100
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Meng Wang1, Ting Wang1,2, Zengqiang Xia1,3, Tingzhang Li1, Xiaohua Jin4, Yuehong Yan1, Jianbing Chen1,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-22
Accepted:2021-11-24
Online:2021-11-01
Published:2021-11-24
Contact:
Jianbing Chen
Meng Wang, Ting Wang, Zengqiang Xia, Tingzhang Li, Xiaohua Jin, Yuehong Yan, Jianbing Chen. Revealing the New Whole-genome Duplication Event of Four Paphiopedilum Species Based on Transcriptome Data[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 699-714.
| Paphiopedilum concolor | P. hirsutissimum | P. malipoense | P. armeniacum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession number | SRR1405683 | SRR1405685 | SRR5722160 | SRR9842184 |
| Tissues | Leaf | Leaf | Stem | Seed |
| Bases (Gb) | 3.6 | 3 | 14.1 | 8 |
| Number of transcripts | 156581 | 76006 | 239105 | 164515 |
| Average length of transcript (bp) | 907.1 | 1162.3 | 884.5 | 993.2 |
| N50 of transcript (bp) | 1486 | 1971 | 1627 | 1856 |
| Number of unigenes | 116919 | 62565 | 201606 | 139203 |
| Average length of unigene (bp) | 863.3 | 1071.1 | 815.6 | 906.4 |
| N50 of unigene (bp) | 1438 | 1829 | 1480 | 1704 |
| Source of raw data | Li et al., | Li et al., | Zhang et al., | Fang et al., |
Table 1 The statistics of raw data and de novo assembly
| Paphiopedilum concolor | P. hirsutissimum | P. malipoense | P. armeniacum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession number | SRR1405683 | SRR1405685 | SRR5722160 | SRR9842184 |
| Tissues | Leaf | Leaf | Stem | Seed |
| Bases (Gb) | 3.6 | 3 | 14.1 | 8 |
| Number of transcripts | 156581 | 76006 | 239105 | 164515 |
| Average length of transcript (bp) | 907.1 | 1162.3 | 884.5 | 993.2 |
| N50 of transcript (bp) | 1486 | 1971 | 1627 | 1856 |
| Number of unigenes | 116919 | 62565 | 201606 | 139203 |
| Average length of unigene (bp) | 863.3 | 1071.1 | 815.6 | 906.4 |
| N50 of unigene (bp) | 1438 | 1829 | 1480 | 1704 |
| Source of raw data | Li et al., | Li et al., | Zhang et al., | Fang et al., |
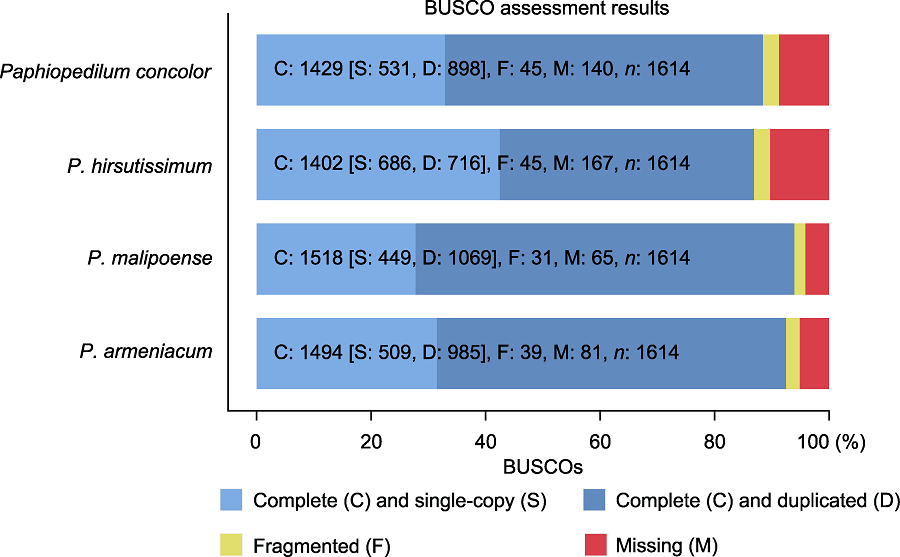
Figure 1 BUSCO assessment results C: Complete BUSCOs; S: Complete and single-copy BUSCOs; D: Complete and duplicated BUSCOs; F: Fragmented BUSCOs; M: Missing BUSCOs
| Paphiopedilum concolor | P. hirsutissimum | P. malipoense | P. armeniacum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of protein coding sequences | 56439 | 33207 | 79854 | 58575 |
| Average length of protein coding sequence (bp) | 936.1 | 994.9 | 829.1 | 914.7 |
| N50 of protein coding sequence (bp) | 1209 | 1308 | 1089 | 1215 |
| Number of CDS identified as transcription factor | 1950 | 1181 | 2586 | 2014 |
| Number of transcription factor families | 66 | 67 | 67 | 68 |
Table 2 The summary of protein coding sequence and transcription factor prediction
| Paphiopedilum concolor | P. hirsutissimum | P. malipoense | P. armeniacum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of protein coding sequences | 56439 | 33207 | 79854 | 58575 |
| Average length of protein coding sequence (bp) | 936.1 | 994.9 | 829.1 | 914.7 |
| N50 of protein coding sequence (bp) | 1209 | 1308 | 1089 | 1215 |
| Number of CDS identified as transcription factor | 1950 | 1181 | 2586 | 2014 |
| Number of transcription factor families | 66 | 67 | 67 | 68 |
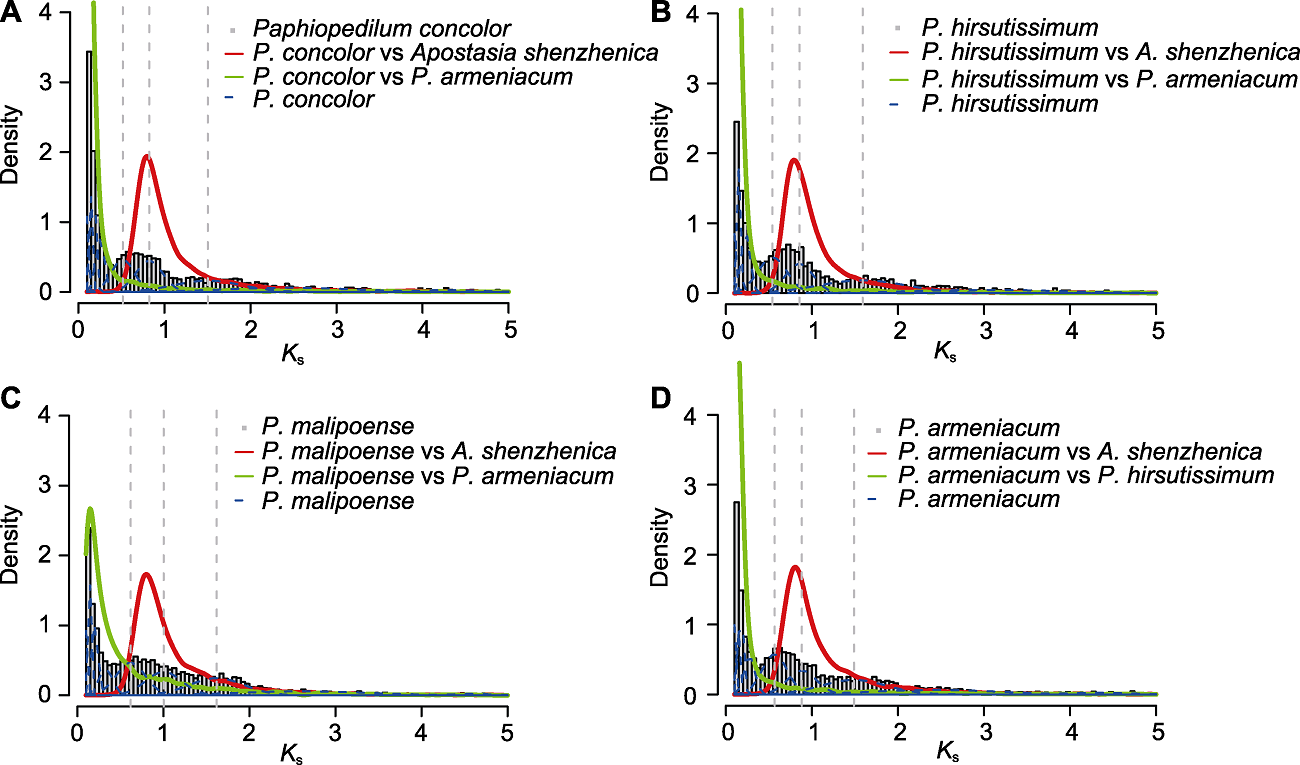
Figure 2 The density plot of Ks from four species of Paphiopedilum Histograms filled in grey: The density distributions of intraspecies paralogue Ks values; Red solid curves: The Ks density plots of interspecies orthologues between four species of Paphiopedilum and Apostasia shenzhenica; Green solid curves: The Ks density plots of interspecies orthologues between P. armeniacum and other three species of Paphiopedilum; Blue dashed curves: The fitting results based on Gaussian mixture modeling of intraspecies paralogue Ks values; Grey dashed lines: The Ks values of significant peaks identified by Gaussian mixture modeling.
| Species | No. of components | No. of duplicates | BIC | Variance | Mean (Ks) | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paphiopedilum concolor | 9 | 207 | -4673.731 | 0.0000 | 0.1077 | 0.0527 |
| 9 | 385 | -4673.731 | 0.0002 | 0.1314 | 0.1048 | |
| 9 | 416 | -4673.731 | 0.0007 | 0.1740 | 0.1194 | |
| 9 | 311 | -4673.731 | 0.0026 | 0.2517 | 0.0964 | |
| 9 | 522 | -4673.731 | 0.0175 | 0.5161 | 0.1544 | |
| 9 | 642 | -4673.731 | 0.0241 | 0.8236 | 0.1741 | |
| 9 | 567 | -4673.731 | 0.1557 | 1.5043 | 0.1594 | |
| 9 | 300 | -4673.731 | 0.5765 | 2.4529 | 0.1148 | |
| 9 | 90 | -4673.731 | 0.1277 | 4.3036 | 0.0240 | |
| P. hirsutissimum | 7 | 196 | -4604.688 | 0.0001 | 0.1146 | 0.0632 |
| 7 | 277 | -4604.688 | 0.0005 | 0.1504 | 0.0991 | |
| 7 | 290 | -4604.688 | 0.0026 | 0.2292 | 0.1109 | |
| 7 | 558 | -4604.688 | 0.0282 | 0.5407 | 0.2162 | |
| 7 | 508 | -4604.688 | 0.0260 | 0.8544 | 0.1693 | |
| 7 | 585 | -4604.688 | 0.2594 | 1.5894 | 0.2351 | |
| 7 | 236 | -4604.688 | 0.8550 | 3.0527 | 0.1062 | |
| Species | No. of components | No. of duplicates | BIC | Variance | Mean (Ks) | Proportion |
| P. malipoense | 9 | 377 | -14027.68 | 0.0000 | 0.1081 | 0.0399 |
| 9 | 751 | -14027.68 | 0.0003 | 0.1362 | 0.0890 | |
| 9 | 820 | -14027.68 | 0.0016 | 0.2006 | 0.1005 | |
| 9 | 579 | -14027.68 | 0.0067 | 0.3290 | 0.0768 | |
| 9 | 1611 | -14027.68 | 0.0287 | 0.6196 | 0.1983 | |
| 9 | 1464 | -14027.68 | 0.0447 | 1.0026 | 0.1778 | |
| 9 | 1634 | -14027.68 | 0.1002 | 1.6186 | 0.1952 | |
| 9 | 683 | -14027.68 | 0.5901 | 2.6205 | 0.1105 | |
| 9 | 105 | -14027.68 | 0.0568 | 4.5773 | 0.0121 | |
| P. armeniacum | 9 | 206 | -8261.607 | 0.0000 | 0.1063 | 0.0359 |
| 9 | 472 | -8261.607 | 0.0002 | 0.1296 | 0.0870 | |
| 9 | 478 | -8261.607 | 0.0008 | 0.1744 | 0.0950 | |
| 9 | 400 | -8261.607 | 0.0039 | 0.2729 | 0.0849 | |
| 9 | 1089 | -8261.607 | 0.0213 | 0.5664 | 0.2105 | |
| 9 | 778 | -8261.607 | 0.0287 | 0.8825 | 0.1457 | |
| 9 | 999 | -8261.607 | 0.1443 | 1.4888 | 0.1980 | |
| 9 | 455 | -8261.607 | 0.5375 | 2.4393 | 0.1195 | |
| 9 | 120 | -8261.607 | 0.1481 | 4.3256 | 0.0234 |
Table 3 The Ks value based on Gaussian mixture modeling
| Species | No. of components | No. of duplicates | BIC | Variance | Mean (Ks) | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paphiopedilum concolor | 9 | 207 | -4673.731 | 0.0000 | 0.1077 | 0.0527 |
| 9 | 385 | -4673.731 | 0.0002 | 0.1314 | 0.1048 | |
| 9 | 416 | -4673.731 | 0.0007 | 0.1740 | 0.1194 | |
| 9 | 311 | -4673.731 | 0.0026 | 0.2517 | 0.0964 | |
| 9 | 522 | -4673.731 | 0.0175 | 0.5161 | 0.1544 | |
| 9 | 642 | -4673.731 | 0.0241 | 0.8236 | 0.1741 | |
| 9 | 567 | -4673.731 | 0.1557 | 1.5043 | 0.1594 | |
| 9 | 300 | -4673.731 | 0.5765 | 2.4529 | 0.1148 | |
| 9 | 90 | -4673.731 | 0.1277 | 4.3036 | 0.0240 | |
| P. hirsutissimum | 7 | 196 | -4604.688 | 0.0001 | 0.1146 | 0.0632 |
| 7 | 277 | -4604.688 | 0.0005 | 0.1504 | 0.0991 | |
| 7 | 290 | -4604.688 | 0.0026 | 0.2292 | 0.1109 | |
| 7 | 558 | -4604.688 | 0.0282 | 0.5407 | 0.2162 | |
| 7 | 508 | -4604.688 | 0.0260 | 0.8544 | 0.1693 | |
| 7 | 585 | -4604.688 | 0.2594 | 1.5894 | 0.2351 | |
| 7 | 236 | -4604.688 | 0.8550 | 3.0527 | 0.1062 | |
| Species | No. of components | No. of duplicates | BIC | Variance | Mean (Ks) | Proportion |
| P. malipoense | 9 | 377 | -14027.68 | 0.0000 | 0.1081 | 0.0399 |
| 9 | 751 | -14027.68 | 0.0003 | 0.1362 | 0.0890 | |
| 9 | 820 | -14027.68 | 0.0016 | 0.2006 | 0.1005 | |
| 9 | 579 | -14027.68 | 0.0067 | 0.3290 | 0.0768 | |
| 9 | 1611 | -14027.68 | 0.0287 | 0.6196 | 0.1983 | |
| 9 | 1464 | -14027.68 | 0.0447 | 1.0026 | 0.1778 | |
| 9 | 1634 | -14027.68 | 0.1002 | 1.6186 | 0.1952 | |
| 9 | 683 | -14027.68 | 0.5901 | 2.6205 | 0.1105 | |
| 9 | 105 | -14027.68 | 0.0568 | 4.5773 | 0.0121 | |
| P. armeniacum | 9 | 206 | -8261.607 | 0.0000 | 0.1063 | 0.0359 |
| 9 | 472 | -8261.607 | 0.0002 | 0.1296 | 0.0870 | |
| 9 | 478 | -8261.607 | 0.0008 | 0.1744 | 0.0950 | |
| 9 | 400 | -8261.607 | 0.0039 | 0.2729 | 0.0849 | |
| 9 | 1089 | -8261.607 | 0.0213 | 0.5664 | 0.2105 | |
| 9 | 778 | -8261.607 | 0.0287 | 0.8825 | 0.1457 | |
| 9 | 999 | -8261.607 | 0.1443 | 1.4888 | 0.1980 | |
| 9 | 455 | -8261.607 | 0.5375 | 2.4393 | 0.1195 | |
| 9 | 120 | -8261.607 | 0.1481 | 4.3256 | 0.0234 |
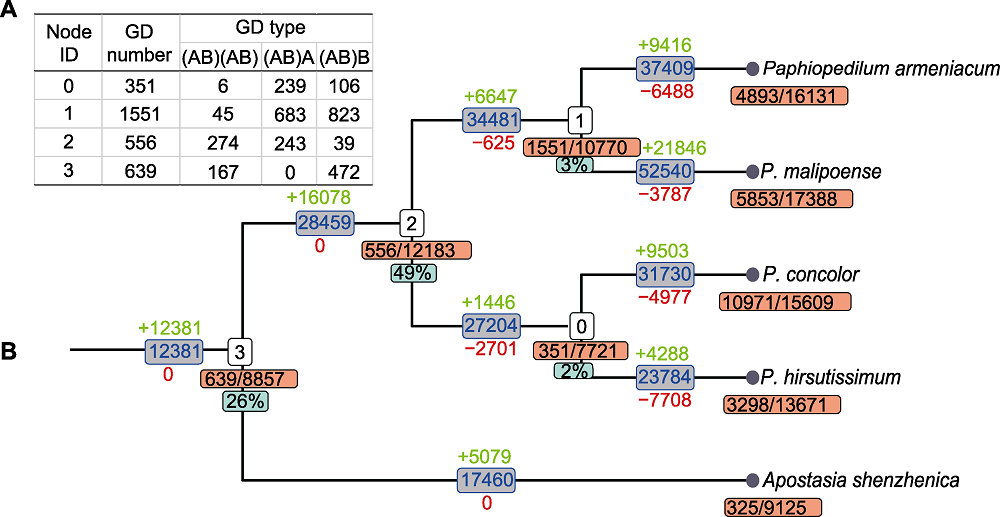
Figure 3 The detection of whole-genome duplication based on phylogenomics (A) The statistics of duplicated gene families, Node ID corresponds to the node number in (B); GD number is the number of duplicated gene families at each node; GD type is the number of each type of duplicated gene families; (B) The numbers in yellow box below nodes is the number of duplicated gene families/gene families, the corresponding green box is the percentage of (AB)(AB) types; numbers above (green) and below (red) branches indicate the expansion and contraction of gene families, respectively.
| Species | Name of WGD | Mean (Ks) | Age of WGD calculated by Ks mean value (Mya) | Age of WGD with 95% confidence interval (Mya) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paphiopedilum concolor | WGD3 | 0.5161 | 38.19 | 37.35-39.03 |
| WGD2 | 0.8236 | 60.95 | 60.06-61.83 | |
| WGD1 | 1.5043 | 111.32 | 108.91-113.72 | |
| P. hirsutissimum | WGD3 | 0.5407 | 40.01 | 38.98-41.04 |
| WGD2 | 0.8544 | 63.22 | 62.19-64.26 | |
| WGD1 | 1.5894 | 117.61 | 114.56-120.67 | |
| P. malipoense | WGD3 | 0.6196 | 45.85 | 45.24-46.46 |
| WGD2 | 1.0026 | 74.19 | 73.39-74.99 | |
| WGD1 | 1.6186 | 119.77 | 118.64-120.91 | |
| P. armeniacum | WGD3 | 0.5664 | 41.92 | 41.28-42.56 |
| WGD2 | 0.8825 | 65.31 | 64.43-66.19 | |
| WGD1 | 1.4888 | 110.17 | 108.42-111.91 |
Table 4 Dating the whole-genome duplication (WGD) event using Ks distribution peaks
| Species | Name of WGD | Mean (Ks) | Age of WGD calculated by Ks mean value (Mya) | Age of WGD with 95% confidence interval (Mya) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paphiopedilum concolor | WGD3 | 0.5161 | 38.19 | 37.35-39.03 |
| WGD2 | 0.8236 | 60.95 | 60.06-61.83 | |
| WGD1 | 1.5043 | 111.32 | 108.91-113.72 | |
| P. hirsutissimum | WGD3 | 0.5407 | 40.01 | 38.98-41.04 |
| WGD2 | 0.8544 | 63.22 | 62.19-64.26 | |
| WGD1 | 1.5894 | 117.61 | 114.56-120.67 | |
| P. malipoense | WGD3 | 0.6196 | 45.85 | 45.24-46.46 |
| WGD2 | 1.0026 | 74.19 | 73.39-74.99 | |
| WGD1 | 1.6186 | 119.77 | 118.64-120.91 | |
| P. armeniacum | WGD3 | 0.5664 | 41.92 | 41.28-42.56 |
| WGD2 | 0.8825 | 65.31 | 64.43-66.19 | |
| WGD1 | 1.4888 | 110.17 | 108.42-111.91 |
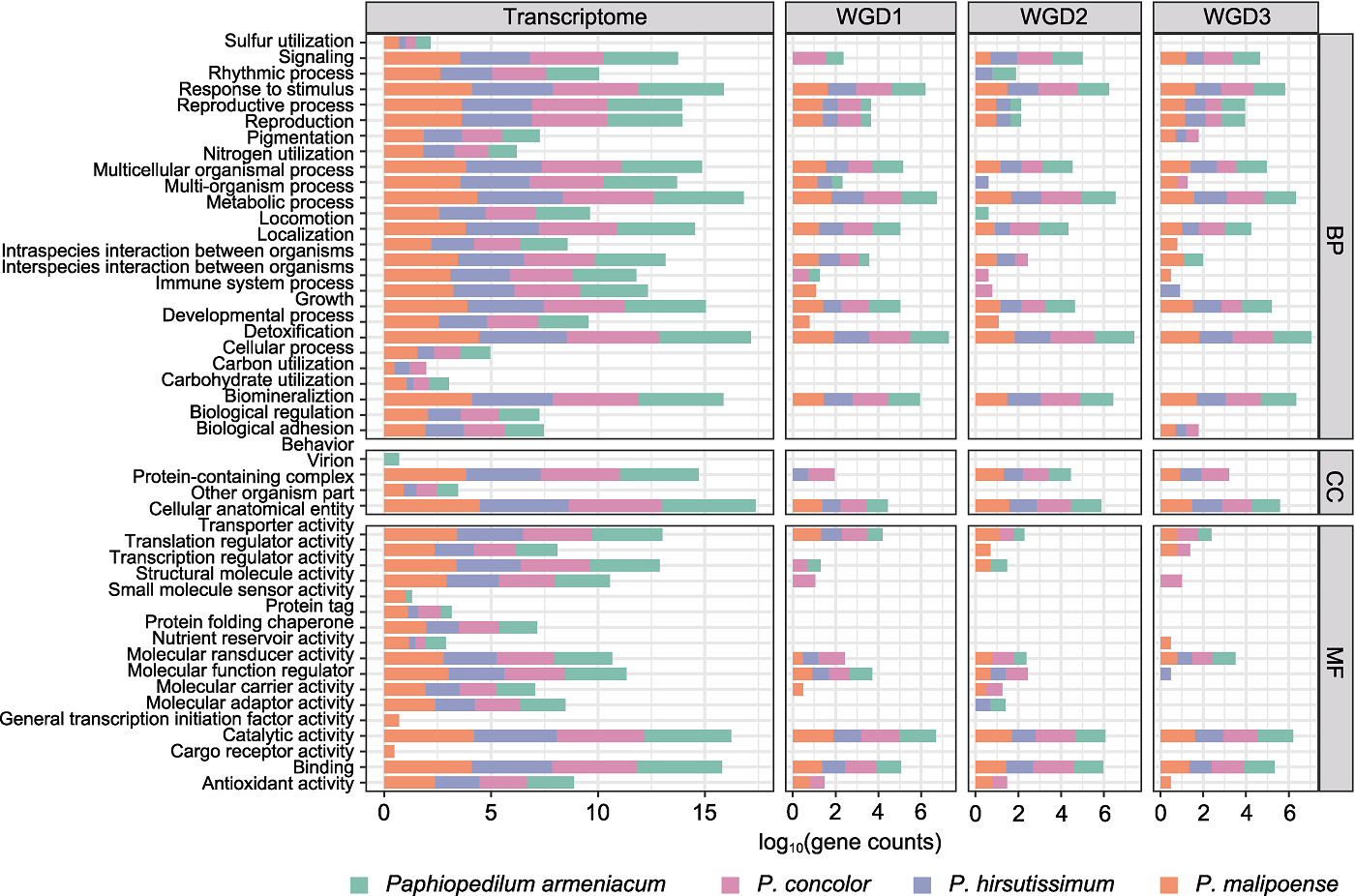
Figure 4 The level 2 GO categories of transcriptome functional annotation and duplicated gene functional enrichment Transcriptome: Results of transcriptome functional annotation; WGD1: Functional enrichment of duplicated gene from whole- genome duplication (WGD) event WGD1 (P<0.05); WGD2: Functional enrichment of duplicated gene from WGD2 (P<0.05); WGD3: Functional enrichment of duplicated gene from WGD3 (P<0.05); BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function
| [1] | 王芳, 王淇, 赵曦阳 (2019). 低温胁迫下植物的表型及生理响应机制研究进展. 分子植物育种 17, 5144-5153. |
| [2] |
汪浩, 张锐, 张娇, 沈慧, 戴锡玲, 严岳鸿 (2019). 转录组测序揭示翼盖蕨(Didymochlaena trancatula)的全基因组复制历史. 生物多样性 27, 1221-1227.
DOI |
| [3] | 王婷, 夏增强, 舒江平, 张娇, 王美娜, 陈建兵, 王慷林, 向建英, 严岳鸿 (2021). 全基因组复制事件的绝对定年揭示莲座蕨属植物的迟滞演化. 生物多样性 29, 722-734. |
| [4] | 王筠竹, 陈跃, 秦德辉, 陈丽萍, 孙崇波 (2019). 兰科植物染色体研究现状及前景. 分子植物育种 17, 3717-3725. |
| [5] | 王振怡, 王希胤 (2020). 染色体数目减少及B染色体产生的进化基因组学模型. 中国科学: 生命科学 50, 524-537. |
| [6] | 杨有新, 王峰, 蔡加星, 喻景权, 周艳虹 (2014). 光质和光敏色素在植物逆境响应中的作用研究进展. 园艺学报 41, 1861-1872. |
| [7] | 杨志娟 (2006). 兜兰属(Paphiopedilum)植物细胞学及其亲缘关系的研究. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 12-36. |
| [8] |
Adams KL, Wendel JF (2005). Polyploidy and genome evolution in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8, 135-141.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Badouin H, Gouzy J, Grassa CJ, Murat F, Staton SE, Cottret L, Lelandais-Brière C, Owens GL, Carrère S, Mayjonade B, Legrand L, Gill N, Kane NC, Bowers JE, Hubner S, Bellec A, Bérard A, Bergès H, Blanchet N, Boniface MC, Brunel D, Catrice O, Chaidir N, Claudel C, Donnadieu C, Faraut T, Fievet G, Helmstetter N, King M, Knapp SJ, Lai Z, Le Paslier MC, Lippi Y, Lorenzon L, Mandel JR, Marage G, Marchand G, Marquand E, Bret-Mestries E, Morien E, Nambeesan S, Nguyen T, Pegot-Espagnet P, Pouilly N, Raftis F, Sallet E, Schiex T, Thomas J, Vandecasteele C, Varès D, Vear F, Vautrin S, Crespi M, Mangin B, Burke JM, Salse J, Muños S, Vincourt P, Rieseberg LH, Langlade NB (2017). The sunflower genome provides insights into oil metabolism, flowering and Asterid evolution. Nature 546, 148-152.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004). Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16, 1667-1678.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114-2120.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Brunner I, Herzog C, Dawes MA, Arend M, Sperisen C (2015). How tree roots respond to drought. Front Plant Sci 6, 547.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Cai J, Liu X, Vanneste K, Proost S, Tsai WC, Liu KW, Chen LJ, He Y, Xu Q, Bian C, Zheng ZJ, Sun FM, Liu WQ, Hsiao YY, Pan ZJ, Hsu CC, Yang YP, Hsu YC, Chuang YC, Dievart A, Dufayard JF, Xu X, Wang JY, Wang J, Xiao XJ, Zhao XM, Du R, Zhang GQ, Wang MN, Su YY, Xie GC, Liu GH, Li LQ, Huang LQ, Luo YB, Chen HH, Van de Peer Y, Liu ZJ (2015). The genome sequence of the orchid Phalaenopsis equestris. Nat Genet 47, 65-72.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Castresana J (2000). Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17, 540-552.
PMID |
| [15] |
Chase MW, Cameron KM, Freudenstein JV, Pridgeon AM, Salazar G, van den Berg C, Schuiteman A (2015). An updated classification of Orchidaceae. Bot J Linn Soc 177, 151-174.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Chen SC, Liu ZJ, Zhu GH, Lang KY, Tsi ZH, Luo YB, Jin XH, Cribb PJ, Wood JJ, Gale SW, Ormerod P, Vermeulen JJ, Wood HP, Clayton D, Bell A (2009). Orchidaceae. In: Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY, eds. Flora of China, Vol. 25. Beijing: Science Press. pp. 381-382. |
| [17] |
Comai L (2005). The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6, 836-846.
PMID |
| [18] |
Cox AV, Abdelnour GJ, Bennett MD, Leitch IJ (1998). Genome size and karyotype evolution in the slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae: Orchidaceae). Am J Bot 85, 681-687.
PMID |
| [19] |
Cox AV, Pridgeon AM, Albert VA, Chase MW (1997). Phylogenetics of the slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae, Or-chidaceae): nuclear rDNA ITS sequences. Plant Syst Evol 208, 197-223.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Cui LY, Wall PK, Leebens-Mack JH, Lindsay BG, Soltis DE, Doyle JJ, Soltis PS, Carlson JE, Arumuganathan K, Barakat A, Albert VA, Ma H, dePamphilis CW (2006). Widespread genome duplications throughout the history of flowering plants. Genome Res 16, 738-749.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
da Conceição LP, de Oliveira ALPC, Barbosa LV (2006). Characterization of the species Epidendrum cinnabarium salzm. (Epidendroideae: Orchidaceae) occurring in dunas do abaeté-salvador, ba-brasil. Cytologia 71, 125-129.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2011). ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27, 1164-1165.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Das K, Roychoudhury A (2014). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2, 53. |
| [24] |
De Bodt S, Maere S, Van de Peer Y (2005). Genome duplication and the origin of angiosperms. Trends Ecol Evol 20, 591-597.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Edgar RC (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32, 1792-1797.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Emms DM, Kelly S (2019). OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol 20, 238.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Enright AJ, Van Dongen S, Ouzounis CA (2002). An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 1575-1584.
PMID |
| [28] |
Fang L, Xu X, Li J, Zheng F, Li MZ, Yan JW, Li Y, Zhang XH, Li L, Ma GH, Zhang AY, Lv FB, Wu KL, Zeng SJ (2020). Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the non-methylated lignin synthesis in Paphiopedilum armeniacum seed. BMC Genomics 21, 524.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Goldman N, Yang Z (1994). A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 11, 725-736.
PMID |
| [30] | Govaerts R, Bernet P, Kratochvil K, Gerlach G, Carr G, Alrich P, Pridgeon AM, Pfahl J, Campacci MA, Baptista DH, Tigges H, Shaw J, Cribb P, George A, Kreuz K, Wood J (2021). World checklist of Orchidaceae. https://wcsp.science.kew.org/. 2021-05-08. |
| [31] |
Gustafsson ALS, Verola CF, Antonelli A (2010). Reassessing the temporal evolution of orchids with new fossils and a Bayesian relaxed clock, with implications for the diversification of the rare South American genus Hoffmann seggella (Orchidaceae: Epidendroideae). BMC Evol Biol 10, 177.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, MacManes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, LeDuc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013). De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8, 1494-1512. |
| [33] |
Hasing T, Tang HB, Brym M, Khazi F, Huang TF, Chambers AH (2020). A phased Vanilla planifolia genome enables genetic improvement of flavour and production. Nat Food 1, 811-819.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Huang CH, Qi XP, Chen DY, Qi J, Ma H (2020). Recurrent genome duplication events likely contributed to both the ancient and recent rise of ferns. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 433-455.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Huerta-Cepas J, Forslund K, Coelho LP, Szklarczyk D, Jensen LJ, von Mering C, Bork P (2017). Fast genome- wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol Biol Evol 34, 2115-2122.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Huerta-Cepas J, Szklarczyk D, Heller D, Hernández-Plaza A, Forslund SK, Cook H, Mende DR, Letunic I, Rattei T, Jensen LJ, von Mering C, Bork P (2019). eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically anno- tated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res 47, D309-D314. |
| [37] |
Iorizzo M, Ellison S, Senalik D, Zeng P, Satapoomin P, Huang JY, Bowman M, Iovene M, Sanseverino W, Cavagnaro P, Yildiz M, Macko-Podgórni A, Moranska E, Grzebelus E, Grzebelus D, Ashrafi H, Zheng ZJ, Cheng SF, Spooner D, Van Deynze A, Simon P (2016). A high-quality carrot genome assembly provides new insights into carotenoid accumulation and asterid genome evolution. Nat Genet 48, 657-666.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Kim YK, Jo S, Cheon SH, Joo MJ, Hong JR, Kwak M, Kim KJ (2020). Plastome evolution and phylogeny of Orchidaceae, with 24 new sequences. Front Plant Sci 11, 22.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Klages JP, Salzmann U, Bickert T, Hillenbrand CD, Gohl K, Kuhn G, Bohaty SM, Titschack J, Müller J, Frederichs T, Bauersachs T, Ehrmann W, van de Flierdt T, Pereira PS, Larter RD, Lohmann G, Niezgodzki I, Uenzelmann-Neben G, Zundel M, Spiegel C, Mark C, Chew D, Francis JE, Nehrke G, Schwarz F, Smith JA, Freudenthal T, Esper O, Pälike H, Ronge TA, Dziadek R (2020). Temperate rainforests near the South Pole during peak Cretaceous warmth. Nature 580, 81-86.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Leinonen R, Sugawara H, Shumway M (2011). The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res 39, D19-D21. |
| [41] |
Leitch IJ, Kahandawala I, Suda J, Hanson L, Ingrouille MJ, Chase MW, Fay MF (2009). Genome size diversity in orchids: consequences and evolution. Ann Bot 104, 469-481.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Li D, Yin H, Zhao C, Zhu G, Lǚ F (2014). Transcriptome analysis of tessellated and green leaves in Paphiopedilum orchids using Illumina paired-end sequencing and discovery simple sequence repeat markers. J Plant Biochem Physiol 2, 1000136. |
| [43] |
Li MH, Zhang GQ, Lan SR, Liu ZJ,China Phylogeny Consortium (2016). A molecular phylogeny of Chinese orchids. J Syst Evol 54, 349-362.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Li WZ, Godzik A (2006). Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22, 1658-1659.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Mandáková T, Lysak MA (2018). Post-polyploid diploidization and diversification through dysploid changes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 42, 55-65.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
McInerney FA, Wing SL (2011). The paleocene-eocene thermal maximum: a perturbation of carbon cycle, climate, and biosphere with implications for the future. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 39, 489-516.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Ming R, VanBuren R, Wai CM, Tang HB, Schatz MC, Bowers JE, Lyons E, Wang ML, Chen J, Biggers E, Zhang JS, Huang LX, Zhang LM, Miao WJ, Zhang J, Ye ZY, Miao CY, Lin ZC, Wang H, Zhou HY, Yim WC, Priest HD, Zheng CF, Woodhouse M, Edger PP, Guyot R, Guo HB, Guo H, Zheng GY, Singh R, Sharma A, Min XJ, Zheng Y, Lee H, Gurtowski J, Sedlazeck FJ, Harkess A, McKain MR, Liao ZY, Fang JP, Liu J, Zhang XD, Zhang Q, Hu WC, Qin Y, Wang K, Chen LY, Shirley N, Lin YR, Liu LY, Hernandez AG, Wright CL, Bulone V, Tuskan GA, Heath K, Zee F, Moore PH, Sunkar R, Leebens-Mack JH, Mockler T, Bennetzen JL, Freeling M, Sankoff D, Paterson AH, Zhu XG, Yang XH, Smith JAC, Cushman JC, Paull RE, Yu QY (2015). The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nat Genet 47, 1435-1442.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Murat F, Armero A, Pont C, Klopp C, Salse J (2017). Reconstructing the genome of the most recent common ancestor of flowering plants. Nat Genet 49, 490-496.
DOI |
| [49] |
Oberlander KC, Dreyer LL, Goldblatt P, Suda J, Linder HP (2016). Species-rich and polyploid-poor: insights into the evolutionary role of whole-genome duplication from the Cape flora biodiversity hotspot. Am J Bot 103, 1336-1347.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
One Thousand Plant Transcriptomes Initiative (2019). One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 574, 679-685.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Chapman BA (2004). Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 9903-9908.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Ren R, Wang HF, Guo CC, Zhang N, Zeng LP, Chen YM, Ma H, Qi J (2018). Widespread whole genome duplications contribute to genome complexity and species diversity in angiosperms. Mol Plant 11, 414-428.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Salse J, Bolot S, Throude M, Jouffe V, Piegu B, Quraishi UM, Calcagno T, Cooke R, Delseny M, Feuillet C (2008). Identification and characterization of shared duplications between rice and wheat provide new insight into grass genome evolution. Plant Cell 20, 11-24.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Schlueter JA, Dixon P, Granger C, Grant D, Clark L, Doyle JJ, Shoemaker RC (2004). Mining EST databases to resolve evolutionary events in major crop species. Genome 47, 868-876.
PMID |
| [55] |
Scrucca L, Fop M, Murphy TB, Raftery AE (2016). Mclust 5: clustering, classification and density estimation using Gaussian finite mixture models. R J 8, 289-317.
PMID |
| [56] |
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015). BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31, 3210-3212.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Sollars ESA, Harper AL, Kelly LJ, Sambles CM, Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, Swarbreck D, Kaithakottil G, Cooper ED, Uauy C, Havlickova L, Worswick G, Studholme DJ, Zohren J, Salmon DL, Clavijo BJ, Li Y, He ZS, Fellgett A, McKinney LV, Nielsen LR, Douglas GC, Kjær ED, Downie JA, Boshier D, Lee S, Clark J, Grant M, Bancroft I, Caccamo M, Buggs RJA (2017). Genome sequence and genetic diversity of European ash trees. Nature 541, 212-216.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Stamatakis A (2014). RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312-1313.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Talavera G, Castresana J (2007). Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst Biol 56, 564-577.
PMID |
| [60] |
Tsai CC, Liao PC, Ko YZ, Chen CH, Chiang YC (2020). Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Paphiopedilum pfitzer (Orchidaceae) based on nuclear and plastid DNA. Front Plant Sci 11, 126.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Unruh SA, McKain MR, Lee YI, Yukawa T, McCormick MK, Shefferson RP, Smithson A, Leebens-Mack JH, Pires JC (2018). Phylotranscriptomic analysis and genome evolution of the Cypripedioideae (Orchidaceae). Am J Bot 105, 631-640.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Upchurch RG (2008). Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization, and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol Lett 30, 967-977.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Van de Peer Y, Ashman TL, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2021). Polyploidy: an evolutionary and ecological force in stressful times. Plant Cell 33, 11-26.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Van de Peer Y, Mizrachi E, Marchal K (2017). The evolutionary significance of polyploidy. Nat Rev Genet 18, 411-424. |
| [65] |
Vellekoop J, Esmeray-Senlet S, Miller KG, Browning JV, Sluijs A, van de Schootbrugge B, Damsté JSS, Brinkhuis H (2016). Evidence for Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary bolide ‘impact winter' conditions from New Jersey, USA. Geology 44, 619-622.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, Yadav G, Singh J, Mishra RK, Kumar V, Verma R, Upadhyay RG, Pandey M, Sharma S (2017). Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 8, 161.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Wang YS, Nie F, Shahid MQ, Baloch FS (2020). Molecular footprints of selection effects and whole genome duplication (WGD) events in three blueberry species: detected by transcriptome dataset. BMC Plant Biol 20, 250.
DOI URL |
| [68] | Wei CL, Yang H, Wang SB, Zhao J, Liu C, Gao LP, Xia EH, Lu Y, Tai YL, She GB, Sun J, Cao HS, Tong W, Gao Q, Li YY, Deng WW, Jiang XL, Wang WZ, Chen Q, Zhang SH, Li HJ, Wu JL, Wang P, Li PH, Shi CY, Zheng FY, Jian JB, Huang B, Shan D, Shi MM, Fang CB, Yue Y, Li FD, Li DX, Wei S, Han B, Jiang CJ, Yin Y, Xia T, Zhang ZZ, Bennetzen JL, Zhao SC, Wan XC (2018). Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E4151-E4158. |
| [69] |
Wendel JF (2000). Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42, 225-249.
PMID |
| [70] |
Wu SD, Han BC, Jiao YN (2020). Genetic contribution of paleopolyploidy to adaptive evolution in angiosperms. Mol Plant 13, 59-71.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Yang ZH (2007). PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24, 1586-1591.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Yu GC, Wang LG, Han YY, He QY (2012). ClusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS: J Integr Biol 16, 284-287.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Yuan Y, Jin XH, Liu J, Zhao X, Zhou JH, Wang X, Wang DY, Lai CS, Xu W, Huang JW, Zha LP, Liu DH, Ma X, Wang L, Zhou MY, Jiang Z, Meng HB, Peng HS, Liang YT, Li RQ, Jiang C, Zhao YY, Nan TG, Jin Y, Zhan ZL, Yang J, Jiang WK, Huang LQ (2018). The Gastrodia elata genome provides insights into plant adaptation to heterotrophy. Nat Commun 9, 1615.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Zachos J, Pagani H, Sloan L, Thomas E, Billups K (2001). Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 292, 686-693.
PMID |
| [75] |
Zhang CF, Huang CH, Liu M, Hu Y, Panero JL, Luebert F, Gao TG, Ma H (2021a). Phylotranscriptomic insights into Asteraceae diversity, polyploidy, and morphological innovation. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 1273-1293.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Zhang CF, Zhang TK, Luebert F, Xiang YZ, Huang CH, Hu Y, Rees M, Frohlich MW, Qi J, Weigend M, Ma H (2020). Asterid phylogenomics/phylotranscriptomics uncover morphological evolutionary histories and support phylogenetic placement for numerous whole-genome duplications. Mol Biol Evol 37, 3188-3210.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Zhang CL, Chen JH, Huang WX, Song XQ, Niu J (2021b). Transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal purine and phenylpropanoid metabolism response to drought stress in Dendrobium sinense, an endemic orchid species in Hainan island. Front Genet 12, 692702.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Zhang GQ, Liu KW, Li Z, Lohaus R, Hsiao YY, Niu SC, Wang JY, Lin YC, Xu Q, Chen LJ, Yoshida K, Fujiwara S, Wang ZW, Zhang YQ, Mitsuda N, Wang MN, Liu GH, Pecoraro L, Huang HX, Xiao XJ, Lin M, Wu XY, Wu WL, Chen YY, Chang SB, Sakamoto S, Ohme-Takagi M, Yagi M, Zeng SJ, Shen CY, Yeh CM, Luo YB, Tsai WC, Van de Peer Y, Liu ZJ (2017). The Apostasia genome and the evolution of orchids. Nature 549, 379-383.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Zhang GQ, Xu Q, Bian C, Tsai WC, Yeh CM, Liu KW, Yoshida K, Zhang LS, Chang SB, Chen F, Shi Y, Su YY, Zhang YQ, Chen LJ, Yin YY, Lin M, Huang HX, Deng H, Wang ZW, Zhu SL, Zhao X, Deng C, Niu SC, Huang J, Wang MN, Liu GH, Yang HJ, Xiao XJ, Hsiao YY, Wu WL, Chen YY, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M, Luo YB, Van de Peer Y, Liu ZJ (2016). The Dendrobium catenatum Lindl. genome sequence provides insights into polysaccharide synthase, floral development and adaptive evolution. Sci Rep 6, 19029.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Zhao YY, Zhang R, Jiang KW, Qi J, Hu Y, Guo J, Zhu RB, Zhang TK, Egan AN, Yi TS, Huang CH, Ma H (2021). Nuclear phylotranscriptomics and phylogenomics support numerous polyploidization events and hypotheses for the evolution of rhizobial nitrogen-fixing symbiosis in Fabaceae. Mol Plant 14, 748-773.
DOI URL |
| [81] | Zheng Y, Jiao C, Sun HH, Rosli HG, Pombo MA, Zhang PF, Banf M, Dai XB, Martin GB, Giovannoni JJ, Zhao PX, Rhee SY, Fei ZJ (2016). iTAK: a program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases. Mol Plant 9, 1667-1670. |
| [82] |
Zwaenepoel A, Van de Peer Y (2019). Wgd-simple command line tools for the analysis of ancient whole-genome duplications. Bioinformatics 35, 2153-2155.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Jixuan Yang, Xuefei Wang, Hongya Gu. Genetic Basis of Flowering Time Variations in Tibetan Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [2] | Zhaoyang Jing, Keguang Cheng, Heng Shu, Yongpeng Ma, Pingli Liu. Whole genome resequencing approach for conservation biology of endangered plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| [3] | Ting Wang, Zengqiang Xia, Jiangping Shu, Jiao Zhang, Meina Wang, Jianbing Chen, Kanglin Wang, Jianying Xiang, Yuehong Yan. Dating whole-genome duplication reveals the evolutionary retardation of Angiopteris [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 722-734. |
| [4] | Jun Zhang, Huanwen Peng, Fucai Xia, Wei Wang. A comparison of seed plants’ polyploids between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau alpine and the Pan-Arctic regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1470-1480. |
| [5] | Simiao Sun, Jixin Chen, Weiwei Feng, Chang Zhang, Kai Huang, Ming Guan, Jiankun Sun, Mingchao Liu, Yulong Feng. Plant strategies for nitrogen acquisition and their effects on exotic plant invasions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(1): 72-80. |
| [6] | TAN Ke, DONG Shu-Peng, LU Tao, ZHANG Ya-Jing, XU Shi-Tao, REN Ming-Xun. Diversity and evolution of samara in angiosperm [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2018, 42(8): 806-817. |
| [7] | Jun-Wei YE, Yang ZHANG, Xiao-Juan WANG. Phylogeographic breaks and the mechanisms of their formation in the Sino-Japanese floristic region [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2017, 41(9): 1003-1019. |
| [8] | Linfeng Li, Bao Liu. The roles of epigenetic variation in plant hybridization and polyploidization [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(6): 600-607. |
| [9] | Yuguo Wang. Natural hybridization and speciation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(6): 565-576. |
| [10] | Zhenna Qian, Qianwan Meng, Mingxun Ren. Pollination ecotypes and herkogamy variation of Hiptage benghalensis (Malpighiaceae) with mirror-image flowers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(12): 1364-1372. |
| [11] | Zhenna Qian, Mingxun Ren. Floral evolution and pollination shifts of the “Malpighiaceae route” taxa, a classical model for biogeographical study [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(1): 95-101. |
| [12] | HUANG Yan-Bo,WEI Yu-Kun,WANG Qi,XIAO Yue-E,YE Xi-Yang. Floral morphology and pollination mechanism of Salvia liguliloba, a narrow endemic species with degraded lever-like stamens [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(7): 753-761. |
| [13] | Tao Wang, Menglong Chen, Ling Liu, Chuanli Ning, Binhua Cai, Zhen Zhang, Yushan Qiao. Changes in Genome and Gene Expression During Plant Polyploidization [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(4): 504-515. |
| [14] | Qianghua Xu,Zhichao Wu,Liangbiao Chen. Biodiversity and adaptive evolution of Antarctic notothenioid fishes [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(1): 80-87. |
| [15] | Bao-Rong Lu, Hui Xia, Wei Wang, Xiao Yang. Impacts of natural hybridization and introgression on biological invasion of plant species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(6): 577-589. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||