

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (2): 138-141.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21040 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21040
• COMMENTARIES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xing Wen1,2, Lian Jin1,2, Hongwei Guo1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-24
Accepted:2021-02-26
Online:2021-03-01
Published:2021-03-17
Contact:
Hongwei Guo
Xing Wen, Lian Jin, Hongwei Guo. A Sweet Meet—New Mechanism on Nutrient and Hormone Regulation of Plant Growth[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 138-141.
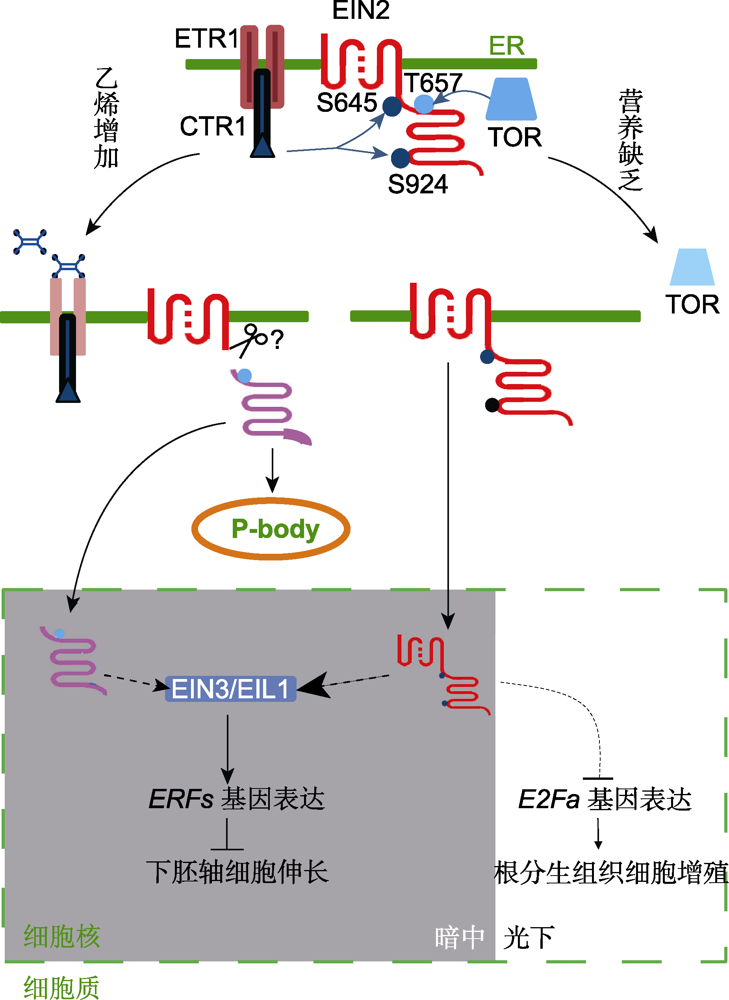
Figure 1 The mechanism of coordinated regulation of plant growth by nutrition and ethylene signaling Protein kinases CTR1 and TOR can interact and phosphorylate EIN2, respectively, in nutrition-rich medium or ethylene- free environment. When treated with ethylene, inactivation of the receptors leads to the suppression of CTR1 and the phosphorylation levels at two serine residues (S645 and S924) of EIN2 are decreased. EIN2 is therefore cleaved and the C terminus translocates into the nucleus and/or forms P-body in the cytoplasm. Consequently, the master transcription factors EIN3/EIL1 are stabilized and the downstream gene expression is activated (Li et al. 2015; Hao et al. 2017). When nutrition deficiency occurs, TOR is inhibited and the phosphorylation level of a threonine (T657) of EIN2 is decreased, followed by the nuclear shuttling of the full-length EIN2 protein. If it occurs in darkness, EIN3/EIL1 proteins would be promoted, thus to activate the expression of downstream ERF genes and to inhibit hypocotyl elongation. Alternatively, if in light, E2Fa gene expression would be down- regulated, thus to inhibit root meristem cell proliferation. Unbroken lines indicate established interactions, broken lines indicate indirect or hypothetical interactions, arrows indicate stimulatory interactions, bar-headed lines indicate inhibitory interactions.
| [1] | Chen RQ, Binder BM, Garrett WM, Tucker ML, Chang C, Cooper B (2011). Proteomic responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings treated with ethylene. Mol Biosyst 7,2637-2650. |
| [2] | Depaepe T, Hendrix S, van Rensburg HCJ Van den Ende W, Cuypers A, Van Der Straeten D (2021). At the crossroads of survival and death: the reactive oxygen species-ethylene-sugar triad and the unfolded protein response. Trends Plant Sci 26,338-351. |
| [3] | Fu LW, Liu YL, Qin GC, Wu P, Zi HL, Xu ZT, Zhao XD, Wang Y, Li YX, Yang SH, Peng C, Wong CCL, Yoo SD, Zuo ZC, Liu RY, Cho YH, Xiong Y (2021). The TOR- EIN2 axis mediates nuclear signaling to modulate plant growth. Nature 591,288-292. |
| [4] | Hagen C, Dent KC, Zeev-Ben-Mordehai T, Grange M, Bosse JB, Whittle C, Klupp BG, Siebert CA, Vasishtan D, Bäuerlein FJB, Cheleski J, Werner S, Guttmann P, Rehbein S, Henzler K, Demmerle J, Adler B, Koszinowski U, Schermelleh L, Schneider G, Enquist LW, Plitzko JM, Mettenleiter TC, Grünewald K (2015). Structural basis of vesicle formation at the inner nuclear membrane. Cell 163,1692-1701. |
| [5] | Hao DD, Sun XZ, Ma B, Zhang JS, Guo HW (2017). Ethylene. In: Li JY, Li CY, Smith SM, eds. Hormone Metabolism and Signaling in Plants. London: Academic Press. pp.203-241. |
| [6] | Ingargiola C, Duarte GT, Robaglia C, Leprince AS, Meyer C (2020). The plant target of rapamycin: a conductor of nutrition and metabolism in photosynthetic organisms. Genes (Basel) 11, 1285. |
| [7] | Ju CL, Yoon GM, Shemansky JM, Lin DY, Ying ZI, Chang J, Garrett WM, Kessenbrock M, Groth G, Tucker ML, Cooper B, Kieber JJ, Chang C, (2012). CTR1 phos- phorylates the central regulator EIN 2 to control ethylene hormone signaling from the ER membrane to the nucleus in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 19486-19491. |
| [8] | Klupp BG, Granzow H, Fuchs W, Keil GM, Finke S, Mettenleiter TC (2007). Vesicle formation from the nuclear membrane is induced by coexpression of two conserved herpesvirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104,7241-7246. |
| [9] | Li WY, Ma MD, Feng Y, Li HJ, Wang YC, Ma YT, Li MZ, An FY, Guo HW (2015). EIN2-directed translational regu- lation of ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Cell 163, 670- 683. |
| [10] | Pandey BK, Huang GQ, Bhosale R, Hartman S, Sturrock CJ, Jose L, Martin OC, Martin M, Voesenek LACJ, Ljung K, Lynch JP, Brown KM, Whalley WR, Mooney SJ, Zhang DB, Bennett MJ (2021). Plant roots sense soil compaction through restricted ethylene diffusion. Science 371,276-280. |
| [11] | Qiao H, Shen ZX, Huang SSC, Schmitz RJ, Urich MA, Briggs SP, Ecker JR (2012). Processing and subcellular trafficking of ER-tethered EIN2 control response to ethy- lene gas. Science 338,390-393. |
| [12] | Shen X, Li YL, Pan Y, Zhong SW (2016). Activation of HLS1 by mechanical stress via ethylene-stabilized EIN3 is crucial for seedling soil emergence. Front Plant Sci 7,1571. |
| [13] | Wang PC, Zhao Y, Li ZP, Hsu CC, Liu X, Fu LW, Hou YJ, Du YY, Xie SJ, Zhang CG, Gao JH, Cao MJ, Huang XS, Zhu YF, Tang K, Wang XG, Tao WA, Xiong Y, Zhu JK (2018). Reciprocal regulation of the TOR kinase and ABA receptor balances plant growth and stress response. Mol Cell 69,100-112. |
| [14] | Wen X, Zhang CL, Ji YS, Zhao Q, He WR, An FY, Jiang LW, Guo HW (2012). Activation of ethylene signaling is mediated by nuclear translocation of the cleaved EIN2 carboxyl terminus. Cell Res 22,1613-1616. |
| [15] | Wu Y, Shi L, Li LW, Fu LW, Liu YL, Xiong Y, Sheen J (2019). Integration of nutrient, energy, light, and hormone signaling via TOR in plants. J Exp Bot 70,2227-2238. |
| [16] | Xiong Y, McCormack M, Li L, Hall Q, Xiang CB, Sheen J (2013). Glucose-TOR signaling reprograms the transcriptome and activates meristems. Nature 496,181-186. |
| [17] | Yuan XB, Xu P, Yu YD, Xiong Y (2020). Glucose-TOR signaling regulates PIN2 stability to orchestrate auxin gradient and cell expansion in Arabidopsis root. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117,32223-32225. |
| [18] | Zhong SW, Shi H, Xue C, Wei N, Guo HW, Deng XW (2014). Ethylene-orchestrated circuitry coordinates a seedling’s response to soil cover and etiolated growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111,3913-3920. |
| [19] | Zhu FG, Deng J, Chen H, Liu P, Zheng LH, Ye QY, Li R, Brault M, Wen JQ, Frugier F, Dong JL, Wang T (2020). A cep peptide receptor-like kinase regulates auxin bio- synthesis and ethylene signaling to coordinate root growth and symbiotic nodulation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 32,2855-2877. |
| [1] | wei xin, JIANG Lan, Chen-Cheng Zheng, ZHU Jing Jing, Bo Chen, Wen zhou Li, Shu Yv Lai, Jinfu Liu, HE Zhong-Sheng. Distribution and influencing factors of woody plant sexual systems on the altitude gradient of Daiyun Mountain [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(预发表): 0-. |
| [2] | QIU Dan-Ni, 清 彭, ZHANG Hui-Ling, Wen Hui-hui, WU Fu-Zhong. Seasonal effects of typical canopy tree species on the dynamics of ant community in mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaf forests [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [3] | Jing Zhang Li JunPan Han XU Yi-De LI Hai ShengHe. Comparison of plant biomass in conifer and broadleaved mixed artificial forests in south subtropical area and analyses of the influential factors [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 0-0. |
| [4] | . A dataset of plant community characteristics of mixed evergreen and deciduous broadleaf forest and subalpine coniferous forest of Shennongjia Forest Ecosystem Research Station [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(典型生态系统数据集): 0-0. |
| [5] | SHEN Hui-Tao, YU Xiao-Ya, QIN Yan-Jie, WU Ai-Bin. Ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry and carbon storage along a chronosequence of Juglans regia plantations on the Eastern of Taihang Mountain, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 1-. |
| [6] | 黄 承玲, Han Li Rong, Ling Qing Hong, Xiong Yang Sheng, Ling Tian Xiao, Xia Guowei Xia Guowei, Ren Chen Zheng, Wei Zhou. Study on genetic conservation of Rhododendron liboense based on SNP molecular markers,a plant species with extremely small populations [J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [7] | Zhou xin-yu, huiliang liu, GAO Bei, LU Yuting, TAO Lingqing, WEN Xiaohu, ZHANG Lan, ZHANG Yuan-Ming. Reproductive Biology of the Endangered and Endemic Species Nymphaea candida C. Presl in Xinjiang [J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [8] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [9] | Huan Xu, Fengfei Xin, Hongliang Shi, Lin Yuan, Shunqi Bo, Xinyi Zhao, Shuaitao Deng, Tingting Pan, Jing Yu, Saisai Sun, Cheng Xue. Evaluation of effects of integrated ecological restoration technology on habitat and bird diversity improvement in the northern branch of Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [10] | HAO Jie, DIAO Hua-Jie, SU Yuan, WU Shuai-Kai, GAO Yang-Yang, LIANG Wen-Jun, NIU Hui-Min, YANG Qian-Wen, CHANG Jie, WANG Ge, XU Wen-Li, MA Teng-Fei, DONG Kuan-Hu, $\boxed{\hbox{WANG Chang-Hui}}$ . Precipitation regulates the response of salinized grassland net primary productivity to nitrogen addition and mowing in the agro-pastoral zone [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 710-719. |
| [11] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [12] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [13] | JIANG Xiao-Yu, YU Xin-Miao, LIAO Qin, ZHANG Jin-Wei, WU Xue-Feng, WANG Xu, PAN Jun-Tong, WANG Jun-Feng, MU Chun-Sheng, SHI Yu-Jie. Studies on the emission of nitrous oxide from terrestrial plants [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(4): 513-525. |
| [14] | Shunyu Wang, Yang Li, Xiaoqin Lü, Xin Li, Quanxiu Fan, Xiaoyue Wang. The color preference of bumblebee nectar robbing and its impact on the reproductive fitness of Lonicera calcarata [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24554-. |
| [15] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||