

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 644-657.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20029 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20029
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles
Yuanpeng Hao1,2,†, Jingyi Li1,†, Rui Yang1,2, Hui Li1, Hongtong Bai1, Lei Shi1,*( )
)
Received:2020-02-24
Accepted:2020-07-21
Online:2020-09-01
Published:2020-09-03
Contact:
Lei Shi
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Yuanpeng Hao, Jingyi Li, Rui Yang, Hui Li, Hongtong Bai, Lei Shi. Antimicrobial Activity of Aromatic Plant Essential Oils and Their Application in Animal Production[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 644-657.
| 物种 | 主要成分 | 作用菌种 | MIC | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 唇形科 (Lamiaceae) | 牛至(Origanum vulgare) | 香芹酚(64.86%)、对伞花烃(8.35%)和百里香酚(4.22%) | 耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 | 0.4 mg·mL-1 | |
| 百里香(Thymus vulga- ris) | 百里香酚(51.34%)、对伞花烃(18.35%)和石竹烯(4.26%) | 枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和耻垢分枝杆菌 | 0.075-1.1 mg· mL-1 | ||
| 迷迭香(Rosmarinus of- ficinalis) | 1,8-桉树脑(26.54%)、α-蒎烯(20.14%)和樟脑(12.88%) | 表皮葡萄球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草芽孢杆菌等 | 0.03%-1.0% (v/v) | ||
| 唇萼薄荷(Mentha pule- gium) | 长叶薄荷酮(70.66%)和新薄荷醇(11.21%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌等 | 1.25-10 μL· mL-1 | ||
| 土荆芥(Chenopodium ambrosioides) | α-萜品烯(40.73%)和对伞花烃(21.81%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | ≥1.024 mg·mL-1 | ||
| 薰衣草(Lavandula x in- termedia lavandin ‘G- rosso’) | 芳樟醇(35.8%)、1,8-桉树脑(19.8%)和α-蒎烯(8.7%) | 蜡状芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌 | 0.94-1.87 (v/v%) | ||
| 菊科 (Asteraceae) | 蓍(Achillea millefolium) | 大根香叶烯(1.1%-46.6%)、桧烯(4.0%-38.9%)和冰片(4.7%-24.9%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌、变形链球菌和肺炎克雷伯菌等 | 0.125-0.5 mg·mL-1 | |
| 金盏花(Calendula offi- cinalis) | α-杜松醇(20.6%)、香芹酮(17.9%)和荜澄茄烯(10.1%) | 表皮葡萄球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌等 | 10-200 mg· mL-1 | ||
| 伞形科 (Apiaceae) | 茴香(Foeniculum vul- gare) | 茴香脑(50.4%)、甲基胡椒酚(22.4%)和柠檬烯(11.4%) | 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌和大肠杆菌 | 0.0075-2.0 (v/v%) | |
| 禾本科 (Poaceae) | 亚香茅(Cymbopogon nardus) | 香叶醇(33.88%)、香茅醛(27.55%)和香茅醇(14.40%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌和粪肠球菌 | 0.125-8 mg· mL-1 | |
| 樟科 (Lauraceae) | 肉桂(Cinnamomum c- assia) | 肉桂醛(85.06%)和甲氧基肉桂醛(8.79%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、产气肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌和霍乱弧菌等 | 0.075-0.6 mg·mL-1 | |
| 山苍子(Litsea cubeba) | β-柠檬醛(39.25%)、α-柠檬醛(30.9%)和柠檬烯(8.28%) | 耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 | 0.5? mg·mL-1 | ||
| 猴樟(Cinnamomum bodinieri) | 芳樟醇(69.94%)和樟脑(10.90%) | 大肠杆菌 | 200 μL·L-1 | ||
| 桃金娘科(Myrtaceae) | 蓝桉(Eucalyptus globulus) | 对伞花烃(12.58%-37.82%)、α-蒎烯(10.41%-13.39%)和1,8-桉树脑(7.71%-13.23%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和蜡状芽孢杆菌等 | 1-4 mg·mL-1 |
Table 1 Major components of essential oils (EOs) extracted from common aromatic plants and their antimicrobial activities based on MIC values
| 物种 | 主要成分 | 作用菌种 | MIC | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 唇形科 (Lamiaceae) | 牛至(Origanum vulgare) | 香芹酚(64.86%)、对伞花烃(8.35%)和百里香酚(4.22%) | 耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 | 0.4 mg·mL-1 | |
| 百里香(Thymus vulga- ris) | 百里香酚(51.34%)、对伞花烃(18.35%)和石竹烯(4.26%) | 枯草芽孢杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和耻垢分枝杆菌 | 0.075-1.1 mg· mL-1 | ||
| 迷迭香(Rosmarinus of- ficinalis) | 1,8-桉树脑(26.54%)、α-蒎烯(20.14%)和樟脑(12.88%) | 表皮葡萄球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草芽孢杆菌等 | 0.03%-1.0% (v/v) | ||
| 唇萼薄荷(Mentha pule- gium) | 长叶薄荷酮(70.66%)和新薄荷醇(11.21%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌等 | 1.25-10 μL· mL-1 | ||
| 土荆芥(Chenopodium ambrosioides) | α-萜品烯(40.73%)和对伞花烃(21.81%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 | ≥1.024 mg·mL-1 | ||
| 薰衣草(Lavandula x in- termedia lavandin ‘G- rosso’) | 芳樟醇(35.8%)、1,8-桉树脑(19.8%)和α-蒎烯(8.7%) | 蜡状芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌 | 0.94-1.87 (v/v%) | ||
| 菊科 (Asteraceae) | 蓍(Achillea millefolium) | 大根香叶烯(1.1%-46.6%)、桧烯(4.0%-38.9%)和冰片(4.7%-24.9%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌、变形链球菌和肺炎克雷伯菌等 | 0.125-0.5 mg·mL-1 | |
| 金盏花(Calendula offi- cinalis) | α-杜松醇(20.6%)、香芹酮(17.9%)和荜澄茄烯(10.1%) | 表皮葡萄球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌等 | 10-200 mg· mL-1 | ||
| 伞形科 (Apiaceae) | 茴香(Foeniculum vul- gare) | 茴香脑(50.4%)、甲基胡椒酚(22.4%)和柠檬烯(11.4%) | 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌和大肠杆菌 | 0.0075-2.0 (v/v%) | |
| 禾本科 (Poaceae) | 亚香茅(Cymbopogon nardus) | 香叶醇(33.88%)、香茅醛(27.55%)和香茅醇(14.40%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌和粪肠球菌 | 0.125-8 mg· mL-1 | |
| 樟科 (Lauraceae) | 肉桂(Cinnamomum c- assia) | 肉桂醛(85.06%)和甲氧基肉桂醛(8.79%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、产气肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌和霍乱弧菌等 | 0.075-0.6 mg·mL-1 | |
| 山苍子(Litsea cubeba) | β-柠檬醛(39.25%)、α-柠檬醛(30.9%)和柠檬烯(8.28%) | 耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌 | 0.5? mg·mL-1 | ||
| 猴樟(Cinnamomum bodinieri) | 芳樟醇(69.94%)和樟脑(10.90%) | 大肠杆菌 | 200 μL·L-1 | ||
| 桃金娘科(Myrtaceae) | 蓝桉(Eucalyptus globulus) | 对伞花烃(12.58%-37.82%)、α-蒎烯(10.41%-13.39%)和1,8-桉树脑(7.71%-13.23%) | 金黄色葡萄球菌、耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌和蜡状芽孢杆菌等 | 1-4 mg·mL-1 |
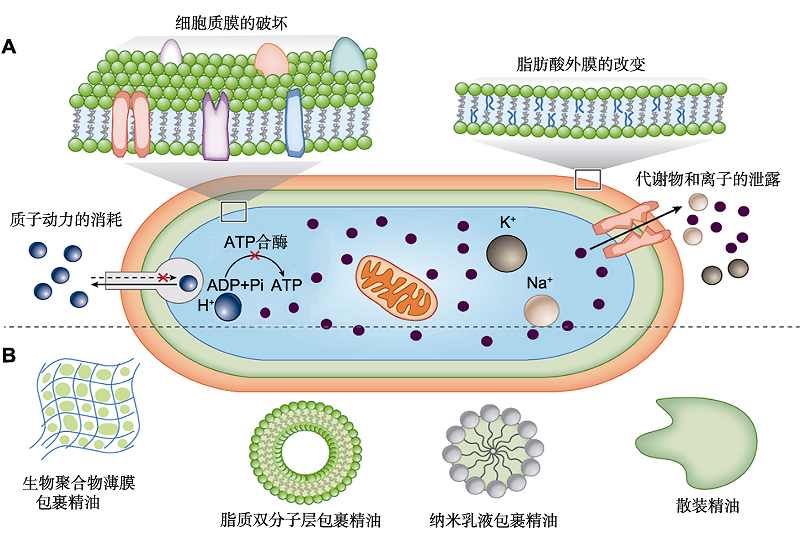
Figure 2 Mechanisms of action and delivery systems of essential oils (EOs) (modified by Rao et al., 2019) (A) Bulk essential oils (EOs) and different types of EO encapsulation; (B) Proposed mechanisms of action and target sites of EOs.
| 动物 | 植物材料 | 效果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 羊 | 牛至(Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum) | 抑制产甲烷菌, 改善瘤胃发酵 | |
| 迷迭香(Rosmarinus officinalis) | 影响生物氢化细菌, 促进瘤胃发酵 | ||
| 牛 | 百里香(Thymus vulgaris)和锡兰肉桂(Cinnamomum zeylanicum) | 产甲烷菌的相对丰度降低, 琥珀酸纤维杆菌和白色瘤胃球菌的 数量下降, 植物精油添加剂可作为瘤胃发酵调节剂 | |
| 百里香 | 对引起牛乳腺炎的金黄色葡萄球菌和乳房链球菌等有抑制作用 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制牛呼吸系统疾病相关的细菌病原体 | ||
| 猪 | 精油混合物 | 直肠大肠杆菌和总厌氧菌数量降低, 免疫球蛋白增多 | |
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸杆菌增多, 粪便中大肠杆菌数量减少 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸杆菌增多 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 粪便中乳酸菌增多, 大肠杆菌数量减少 | ||
| 鸡 | 牛至(O. vulgare) | 盲肠大肠杆菌减少, 乳酸菌无影响 | |
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸菌等肠道菌群发生变化 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制沙门氏菌繁殖, 减少交叉感染 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制产气荚膜梭状芽孢杆菌, 治疗坏死性肠炎 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 蛋白酶与精油具有协同作用, 回肠中乳杆菌密度增加而大肠 杆菌减少 | ||
| 鹌鹑 | 西亚百里香(T. spicata) | 改善肠道微生物组成, 有利于其健康生长 | |
| 迷迭香 | 大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌等肠道致病菌减少 | ||
| 鱼 | 盆牛至(O. onites) | 促进生长, 有效避免加氏乳球菌感染 | |
| 冬牛至(O. heracleoticum) | 促进生长, 对嗜水气单胞菌感染的抵抗力增强 | ||
| 甜橙(Citrus sinensis) | 抑制链球菌感染, 具有免疫调节作用 |
Table 2 Evaluation of the effects of essential oils extracted from common aromatic plants on animal production
| 动物 | 植物材料 | 效果 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 羊 | 牛至(Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum) | 抑制产甲烷菌, 改善瘤胃发酵 | |
| 迷迭香(Rosmarinus officinalis) | 影响生物氢化细菌, 促进瘤胃发酵 | ||
| 牛 | 百里香(Thymus vulgaris)和锡兰肉桂(Cinnamomum zeylanicum) | 产甲烷菌的相对丰度降低, 琥珀酸纤维杆菌和白色瘤胃球菌的 数量下降, 植物精油添加剂可作为瘤胃发酵调节剂 | |
| 百里香 | 对引起牛乳腺炎的金黄色葡萄球菌和乳房链球菌等有抑制作用 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制牛呼吸系统疾病相关的细菌病原体 | ||
| 猪 | 精油混合物 | 直肠大肠杆菌和总厌氧菌数量降低, 免疫球蛋白增多 | |
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸杆菌增多, 粪便中大肠杆菌数量减少 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸杆菌增多 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 粪便中乳酸菌增多, 大肠杆菌数量减少 | ||
| 鸡 | 牛至(O. vulgare) | 盲肠大肠杆菌减少, 乳酸菌无影响 | |
| 精油混合物 | 乳酸菌等肠道菌群发生变化 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制沙门氏菌繁殖, 减少交叉感染 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 抑制产气荚膜梭状芽孢杆菌, 治疗坏死性肠炎 | ||
| 精油混合物 | 蛋白酶与精油具有协同作用, 回肠中乳杆菌密度增加而大肠 杆菌减少 | ||
| 鹌鹑 | 西亚百里香(T. spicata) | 改善肠道微生物组成, 有利于其健康生长 | |
| 迷迭香 | 大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌等肠道致病菌减少 | ||
| 鱼 | 盆牛至(O. onites) | 促进生长, 有效避免加氏乳球菌感染 | |
| 冬牛至(O. heracleoticum) | 促进生长, 对嗜水气单胞菌感染的抵抗力增强 | ||
| 甜橙(Citrus sinensis) | 抑制链球菌感染, 具有免疫调节作用 |
| [1] | 陈梦玲, 蓝蔚青, 李函笑, 任智楚, 芦子萱, 谢晶 ( 2020). 牛至精油对腐生葡萄球菌抑制作用机制. 食品科学 41, 46-51. |
| [2] | 李慧, 白红彤, 王晓, 姜闯道, 张金政, 石雷 ( 2011). 椒样薄荷、薄荷和苏格兰留兰香精油与抗生素的协同抑菌功能. 植物学报 46, 37-43. |
| [3] | 潘岩, 白红彤, 李慧, 姜闯道, 石雷 ( 2012). 栽培地区、采收季节和株龄对迷迭香精油成分和抑菌活性的影响. 植物学报 47, 625-636. |
| [4] | 石雷, 潘岩, 李慧, 白红彤 ( 2015). 一种采收迷迭香的方法和制备具有抑菌活性提取物的方法. 中国专利, CN201210158838.4. 2015-07-01. |
| [5] | 于洋, 方亮星, 周宇峰, 孙坚, 廖晓萍, 刘雅红 ( 2019). 畜牧业发展中抗菌药应用的“利”与“刃”. 中国科学院院刊 34, 152-162. |
| [6] | 张永刚 ( 2012). 植物源抗菌剂香芹酚定点释放包被技术的开发. 博士论文. 长沙: 中国科学院亚热带农业生态研究所. pp. 1-194. |
| [7] | 周洋, 彭艳, 周小秋 ( 2018). 植物精油对动物生长和免疫力的影响及其作用机制. 动物营养学报 30, 37-43. |
| [8] |
Abdelli M, Moghrani H, Aboun A, Maachi R ( 2016). Algerian Mentha pulegium L. leaves essential oil: chemical composition, antimicrobial, insecticidal and antioxidant activities. Ind Crops Prod 94, 197-205.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Acar Ü, Kesbic OS, Yılmaz S, Gültepe N, Türker A ( 2015). Evaluation of the effects of essential oil extracted from sweet orange peel (Citrus sinensis) on growth rate of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and possible disease resistance against Streptococcus iniae. Aquaculture 437, 282-286.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Aksu T, Aksu MI, Önel SE, Yakan A, Kaya DA, Baylan M (2014). Effect of thyme oil (Thymbra spicata l. var. spicata) on meat quality in Japanese quails. Europ Poult Sci 78, 10.1399/eps.2013.6. |
| [11] |
Al Hafi M, El Beyrouthy M, Ouaini N, Stien D, Rutledge D, Chaillou S ( 2016). Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity ofOriganum libanoticum, Origanum ehrenber- gii, and Origanum syriacum growing wild in Lebanon. Chem Biodivers 13, 555-560.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Al Maqtari MAA, Alghalibi SM, Alhamzy EH ( 2011). Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oil ofThymus vulgaris from Yemen. Turk J Biochem 36, 342-349. |
| [13] |
Alali WQ, Hofacre CL, Mathis GF, Faltys G ( 2013). Effect of essential oil compound on shedding and colonization of Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg in broilers. Poult Sci 92, 836-841.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Aligiannis N, Kalpoutzakis E, Mitaku S, Chinou IB ( 2001). Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of two Origanum species. J Agric Food Chem 49, 4168-4170.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] | Amat S, Baines D, Alexander TW ( 2017). Antimicrobial activities of commercial essential oils against the bovine respiratory pathogen Mannheimia haemolytica and analysis of their chemical composition and cytotoxicity on bovine turbinate cells. J Anim Sci 95, 122-123. |
| [16] |
Ambrosio CMS, Ikeda NY, Miano AC, Saldaña E, Moreno AM, Stashenko E, Contreras-Castillo CJ, Da Gloria EM ( 2019). Unraveling the selective antibacterial activity and chemical composition of citrus essential oils. Sci Rep 9, 17719.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Asensio CM, Grosso NR, Juliani HR ( 2015). Quality characters, chemical composition and biological activities of oregano (Origanum spp.) essential oils from central and Southern Argentina. Ind Crops Prod 63, 203-213.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Bajpai VK, Sharma A, Baek KH ( 2013). Antibacterial mode of action of Cudrania tricuspidata fruit essential oil, affecting membrane permeability and surface characterristics of food-borne pathogens. Food Control 32, 582-590.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M ( 2008). Biological effects of essential oils. Food Chem Toxicol 46, 446-475.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Bassolé IHN, Juliani HR ( 2012). Essential oils in combination and their antimicrobial properties. Molecules 17, 3989-4006.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Bisht DS, Menon KRK, Singhal MK ( 2014). Comparative antimicrobial activity of essential oils of Cuminum cymi-num L. andFoeniculum vulgare Mill. seeds against Sal- monella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Essent Oil Bear Plants 17, 617-622.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Bouhaddouda N, Aouadi S, Labiod R ( 2016). Evaluation of chemical composition and biological activities of essential oil and methanolic extract of Origanum vulgare L. ssp. glandulosum (Desf.) Ietswaart from Algeria. Int J Pharmacogn Phytochem Res 8, 104-112. |
| [23] |
Burt S ( 2004). Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods. Int J Food Microbiol 94, 223-253.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Burt SA, van der Zee R, Koets AP, de Graaff AM, van Knapen F, Gaastra W, Haagsman HP, Veldhuizen EJA ( 2007). Carvacrol induces heat shock protein 60 and inhibits synthesis of flagellin in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl Environ Microbiol 73, 4484-4490.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Cao YF, Zhou AL, Zhou DG, Xiao XL, Yu YG, Li XF ( 2020). Cronobacter sakazakii CICC 21544 responds to the combination of carvacrol and citral by regulating proton motive force. LWT-Food Sci Technol 122, 109040.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Castillo-López RI, Gutiérrez-Grijalva EP, Leyva-López N, López-Martínez LX, Heredia JB ( 2017). Natural alternatives to growth-promoting antibiotics (GPA) in animal production. J Anim Plant Sci 27, 349-359. |
| [27] |
Chen CH, Yin HB, Upadhayay A, Brown S, Venkitanarayanan K ( 2019). Efficacy of plant-derived antimicrobials for controlling Salmonella Schwarzengrund on dry pet food. Int J Food Microbiol 296, 1-7.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
Cheng CS, Xia M, Zhang XM, Wang C, Jiang SW, Peng J ( 2018). Supplementing oregano essential oil in a reduced- protein diet improves growth performance and nutrient digestibility by modulating intestinal bacteria, intestinal morphology, and antioxidative capacity of growing-finishing pigs. Animals 8, 159.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Cui HY, Zhang CH, Li CZ, Lin L ( 2019). Antibacterial mechanism of oregano essential oil. Ind Crops Prod 139, 111498.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
de Araújo ACJ, Freitas PR, Barbosa CRD, Muniz DF, Rocha JE, da Silva ACA, Oliveira-Tintino ADD, Jaime RF, da Silva LE, Confortin C, do Amaral W, Deschamps C, Barbosa JM, de Lima NTR, Tintino SR, Coutinho HDM ( 2020). GC-MS-FID characterization and antibacterial activity of the Mikania cordifolia essential oil and limonene against MDR strains. Food Chem Toxicol 136, 111023.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
de Lange CFM, Pluske J, Gong J, Nyachoti CM ( 2010). Strategic use of feed ingredients and feed additives to stimulate gut health and development in young pigs. Livest Sci 134, 124-134.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
de Morais Oliveira-Tintino CD, Tintino SR, Limaverde PW, Figueredo FG, Campina FF, da Cunha FAB, da Costa RHS, Pereira PS, Lima LF, de Matos YMLS, Coutinho HDM, Siqueira-Júnior JP, Balbino VQ, da Silva TG ( 2018). Inhibition of the essential oil from Chenopodium ambrosioides L. and α-terpinene on the NorA efflux-pump of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Chem 262, 72-77.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Diler O, Gormez O, Diler I, Metin S ( 2017). Effect of oregano (Origanum onites L.) essential oil on growth, lysozyme and antioxidant activity and resistance against Lactococcus garvieae in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquacult Nutr 23, 844-851.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Garzoli S, Petralito S, Ovidi E, Turchetti G, Laghezza Masci V, Tiezzi A, Trilli J, Cesa S, Casadei MA, Giacomello P, Paolicelli P ( 2020). Lavandula x intermedia essential oil and hydrolate: evaluation of chemical composition and antibacterial activity before and after formulation in nanoemulsion. Ind Crops Prod 145, 112068.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Gerami F, Moghaddam PR, Ghorbani R, Hassani A ( 2016). Effects of irrigation intervals and organic manure on morphological traits, essential oil content and yield of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.). An Acad Bras Ciênc 88, 2375-2385.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Ghafari O, Sharifi A, Ahmadi A, Fasaei BN ( 2018). Antibacterial and anti-PmrA activity of plant essential oils against fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates. Lett Appl Microbiol 67, 564-569.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Giannenas I, Bonos E, Filliousis G, Stylianaki I, Kumar P, Lazari D, Christaki E, Florou-Paneri P ( 2019). Effect of a polyherbal or an arsenic-containing feed additive on growth performance of broiler chickens, intestinal microbiota, intestinal morphology, and lipid oxidation of breast and thigh meat J Appl Poult Res 28, 164-175.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Goñi P, López P, Sánchez C, Gómez-Lus R, Becerril R, Nerín C ( 2009). Antimicrobial activity in the vapour phase of a combination of cinnamon and clove essential oils. Food Chem 116, 982-989.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Guimarães AC, Meireles LM, Lemos MF, Guimaraes MCC, Endringer DC, Fronza M, Scherer R ( 2019). Antibacterial activity of terpenes and terpenoids present in essential oils. Molecules 24, 2471.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Guo JJ, Gao ZP, Xia JL, Ritenour MA, Li GY, Shan Y ( 2018). Comparative analysis of chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of citrus essential oils from the main cultivated varieties in China. LWT-Food Sci Technol 97, 825-839.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Gutierrez J, Barry-Ryan C, Bourke R ( 2008). The antimicrobial efficacy of plant essential oil combinations and interactions with food ingredients. Int J Food Microbiol 124, 91-97.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Han F, Ma GQ, Yang M, Yan L, Xiong W, Shu JC, Zhao ZD, Xu HL ( 2017). Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of essential oils from different parts of the oregano. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 18, 79-84.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] |
Helander IM, Alakomi HL, Latva-Kala K, Mattila-Sandholm T, Pol I, Smid EJ, Gorris LGM, von Wright A ( 1998). Characterization of the action of selected essential oil components on gram-negative bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 46, 3590-3595.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Hu W, Li CZ, Dai JM, Cui HY, Lin L ( 2019). Antibacterial activity and mechanism of Litsea cubeba essential oil against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Ind Crops Prod 130, 34-41.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Jamroz D, Wertelecki T, Houszka M, Kamel C ( 2006). Influence of diet type on the inclusion of plant origin active substances on morphological and histochemical characteristics of the stomach and jejunum walls in chicken. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 90, 255-268.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Jerzsele A, Szeker K, Csizinszky R, Gere E, Jakab C, Mallo JJ, Galfi P ( 2012). Efficacy of protected sodium butyrate, a protected blend of essential oils, their combination, andBacillus amyloliquefaciens spore suspension against artificially induced necrotic enteritis in broilers. Poult Sci 91, 837-843.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] |
Jia P, Xue YJ, Duan XJ, Shao SH ( 2011). Effect of cinnamaldehyde on biofilm formation and sarA expression by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lett Appl Microbiol 53, 409-416.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] |
Jiang Y, Wu N, Fu YJ, Wang W, Luo M, Zhao CJ, Zu YG, Liu XL ( 2011). Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of rosemary. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32, 63-68.
DOI URL PMID |
| [49] |
Kang JM, Liu L, Wu XX, Sun YY, Liu ZF ( 2018). Effect of thyme essential oil against Bacillus cereus planktonic growth and biofilm formation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 10209-10218.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] |
Kholif AE, Matloup OH, Morsy TA, Abdo MM, Abu Elella AA, Anele UY, Swanson KC ( 2017). Rosemary and lemongrass herbs as phytogenic feed additives to improve efficient feed utilization, manipulate rumen fermentation and elevate milk production of Damascus goats. Livest Sci 204, 39-46.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Khorrami B, Vakili AR, Mesgaran MD, Klevenhusen F ( 2015). Thyme and cinnamon essential oils: potential alternatives for monensin as a rumen modifier in beef production systems. Anim Feed Sci Technol 200, 8-16.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Kim HB, Borewicz K, White BA, Singer RS, Sreevatsan S, Tu ZJ, Isaacson RE ( 2012). Microbial shifts in the swine distal gut in response to the treatment with antimicrobial growth promoter, tylosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 15485-15490.
DOI URL PMID |
| [53] |
Kırkpınar F, Ünlü HB, Özdemir G ( 2011). Effects of oregano and garlic essential oils on performance, carcase, organ and blood characteristics and intestinal microflora of broilers. Livest Sci 137, 219-225.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Kosakowska O, Węglarz Z, Bączek K ( 2019). Yield and quality of ‘Greek oregano’ (Origanum vulgare L. subsp. hirtum) herb from organic production system in temperate climate. Ind Crops Prod 141, 111782.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Kot B, Sytykiewicz H, Sprawka I, Witeska M ( 2020). Effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on methicillin-resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus biofilm formation: metabolic activity assessment and analysis of the biofilm-associated genes expression. Int J Mol Sci 21, 102.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Kotronia M, Kavetsou E, Loupassaki S, Kikionis S, Vouyiouka S, Detsi A ( 2017). Encapsulation of oregano (Origanum onites L.) essential oil in β-cyclodextrin (β-CD): synthesis and characterization of the inclusion complexes. Bioengineering 4, 74.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Kurekci C, Padmanabha J, Bishop-Hurley SL, Hassan E, Al Jassim RAM, McSweeney CS ( 2013). Antimicrobial activity of essential oils and five terpenoid compounds against Campylobacter jejuni in pure and mixed culture experiments. Int J Food Microbiol 166, 450-457.
DOI URL PMID |
| [58] |
Lei ZM, Zhang K, Li C, Jiao T, Wu JP, Wei YB, Tian KC, Li C, Tang DF, Davis DI, Casper DP, Jiang H, Wang XL, Wang JF ( 2019). Ruminal metagenomic analyses of goat data reveals potential functional microbiota by supplementation with essential oil-cobalt complexes. BMC Microbiol 19, 30.
DOI URL PMID |
| [59] |
Li SY, Ru YJ, Liu M, Xu B, Péron A, Shi XG ( 2012). The effect of essential oils on performance, immunity and gut microbial population in weaner pigs. Livest Sci 145, 119-123.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Li Y, Fu XF, Ma X, Geng SJ, Jiang XM, Huang QC, Hu CH, Han XY ( 2018). Intestinal microbiome-metabolome responses to essential oils in piglets. Front Microbiol 9, 1988.
DOI URL PMID |
| [61] |
Lin B, Lu Y, Wang JH, Liang Q, Liu JX ( 2012). The effects of combined essential oils along with fumarate on rumen fermentation and methane production in vitro. J Anim Feed Sci 21, 198-210.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Liolios CC, Gortzi O, Lalas S, Tsaknis J, Chinou I ( 2009). Liposomal incorporation of carvacrol and thymol isolated from the essential oil of Origanum dictamnus L. and in vitro antimicrobial activity. Food Chem 112, 77-83.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Liu Y, Yang X, Xin HL, Chen S, Yang CB, Duan YL, Yang XJ ( 2017). Effects of a protected inclusion of organic acids and essential oils as antibiotic growth promoter alternative on growth performance, intestinal morphology and gut microflora in broilers. Anim Sci J 88, 1414-1424.
DOI URL PMID |
| [64] |
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou YL, Wang TT, Deng XM, Chu X, Zhou TZ ( 2019). Cinnamaldehyde inhibits type three secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by affecting the expression of key effector proteins. Vet Microbiol 239, 108463.
DOI URL PMID |
| [65] |
Low WL, Martin C, Hill DJ, Kenward MA ( 2013). Antimicrobial efficacy of liposome-encapsulated silver ions and tea tree oil against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. Lett Appl Microbiol 57, 33-39.
DOI URL PMID |
| [66] |
Mahgoub SAM, El-Hack MEA, Saadeldin IM, Hussein MA, Swelum AA, Alagawany M ( 2019). Impact of Ros-marinus officinalis cold-pressed oil on health, growth performance, intestinal bacterial populations, and immunocompetence of Japanese quail. Poult Sci 98, 2139-2149.
DOI URL PMID |
| [67] |
Manzanilla EG, Nofrarías M, Anguita M, Castillo M, Perez JF, Martín-Orúe SM, Kamel C, Gasa J ( 2006). Effects of butyrate, avilamycin, and a plant extract combination on the intestinal equilibrium of early-weaned pigs. J Anim Sci 84, 2743-2751.
DOI URL PMID |
| [68] |
Marinelli L, Di Stefano A, Cacciatore I ( 2018). Carvacrol and its derivatives as antibacterial agents. Phytochem Rev 17, 903-921.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Miladi H, Zmantar T, Kouidhi B, Chaabouni Y, Mahdouani K, Bakhrouf A, Chaieb K ( 2017). Use of carvacrol, thymol, and eugenol for biofilm eradication and resistance modifying susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strains to nalidixic acid. Microb Pathog 104, 56-63.
DOI URL PMID |
| [70] |
Mullen KAE, Lee AR, Lyman RL, Mason SE, Washburn SP, Anderson KL ( 2014). An in vitro assessment of the antibacterial activity of plant-derived oils. J Dairy Sci 97, 5587-5591.
DOI URL PMID |
| [71] |
Nafis A, Kasrati A, Jamali CA, Mezrioui N, Setzer W, Abbad A, Hassani L ( 2019). Antioxidant activity and evidence for synergism of Cannabis sativa (L.) essential oil with antimicrobial standards. Ind Crops Prod 137, 396-400.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Ooi LSM, Li YL, Kam SL, Wang H, Wong EYL, Ooi VEC ( 2006). Antimicrobial activities of cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the Chinese medicinal herb Cinna-momum cassia Blume. Am J Chin Med 34, 511-522.
DOI URL PMID |
| [73] |
Padalia RC, Verma RS, Chauhan A, Goswami P, Verma SK, Darokar MP ( 2015). Chemical composition of Melaleuca linarrifolia Sm. from India: a potential source of 1,8-cineole. Ind Crops Prod 63, 264-268.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Paraskevakis N ( 2018). Effects of dietary Greek oregano (Origanum vulgare ssp.hirtum) supplementation on rumen fermentation, enzyme profile and microbial communities in goats. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 102, 701-705.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Park JH, Kim IH ( 2018). Effects of a protease and essential oils on growth performance, blood cell profiles, nutrient retention, ileal microbiota, excreta gas emission, and breast meat quality in broiler chicks. Poult Sci 97, 2854-2860.
DOI URL PMID |
| [76] |
Połeć K, Broniatowski M, Wydro P, Hąc-Wydro K ( 2020). The impact of β-myrcene—the main component of the hop essential oil on the lipid films. J Mol Liq 308, 113028.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Pontes EKU, Melo HM, Nogueira JWA, Firmino NCS, de Carvalho MG, Catunda FEA, Cavalcante TTA ( 2019). Antibiofilm activity of the essential oil of citronella (Cymbopogon nardus) and its major component, geraniol, on the bacterial biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 633-639.
DOI URL PMID |
| [78] |
Radünz M, da Trindade MLM, Camargo TM, Radunz AL, Borges CD, Gandra EA, Helbig E ( 2019). Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of unencapsulated and encap-sulated clove (Syzygium aromaticum L.) essential oil. Food Chem 276, 180-186.
DOI URL PMID |
| [79] |
Rao JJ, Chen BC, McClements DJ ( 2019). Improving the efficacy of essential oils as antimicrobials in foods: mechanisms of action. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 10, 365-387.
DOI URL PMID |
| [80] |
Reyer H, Zentek J, Männer K, Youssef IMI, Aumiller T, Weghuber J, Wimmers K, Mueller AS ( 2017). Possible molecular mechanisms by which an essential oil blend from star anise, rosemary, thyme, and oregano and saponins increase the performance and ileal protein digestibility of growing broilers. J Agric Food Chem 65, 6821-6830.
DOI URL PMID |
| [81] | Roofchaee A, Irani M, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Akbari MR ( 2011). Effect of dietary oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil on growth performance, cecal microflora and serum antioxidant activity of broiler chickens. Afr J Biotechnol 10, 6177-6183. |
| [82] |
Saad NY, Muller CD, Lobstein A ( 2013). Major bioactivities and mechanism of action of essential oils and their components. Flavour Fragr J 28, 269-279.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Sahingil D ( 2019). GC/MS-olfactometric characterization of the volatile compounds, determination antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of essential oil from flowers of calendula (Calendula officinalis L.). J Essent Oil Bear Plant 22, 1571-1580.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Salehi B, Mishra AP, Shukla I, Sharifi-Rad M, del Mar Contreras M, Segura-Carretero A, Fathi H, Nasrabadi NN, Kobarfard F, Sharifi-Rad J ( 2018). Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: health and potential uses. Phytother Res 32, 1688-1706.
DOI URL PMID |
| [85] |
Salem N, Kefi S, Tabben O, Ayed A, Jallouli S, Feres N, Hammami M, Khammassi S, Hrigua I, Nefisi S, Sghaier A, Limam F, Elkahoui S ( 2018). Variation in chemical composition of Eucalyptus globulus essential oil under phenological stages and evidence synergism with antimicrobial standards. Ind Crops Prod 124, 115-125.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Santos FHR, De Paula MR, Lezier D, Silva JT, Santos G, Bittar CMM ( 2015). Essential oils for dairy calves: effects on performance, scours, rumen fermentation and intestinal fauna. Animal 9, 958-965.
DOI URL PMID |
| [87] |
Scandorieiro S, de Camargo LC, Lancheros CAC, Yamada-Ogatta SF, Nakamura CV, de Oliveira AG, Andrade CGTJ, Duran N, Nakazato G, Kobayashi RKT ( 2016). Synergistic and additive effect of oregano essential oil and biological silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacterial strains. Front Microbiol 7, 760.
DOI URL PMID |
| [88] |
Sharifi A, Mohammadzadeh A, Zahraei Salehi T, Mahmoodi P ( 2018). Antibacterial, antibiofilm and antiquorum sensing effects of Thymus daenensis and Satureja hortensis essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Appl Microbiol 124, 379-388.
DOI URL PMID |
| [89] |
Soltani M, Ghodratnama M, Ebrahimzadeh-Mosavi HA, Nikbakht-Brujeni G, Mohamadian S, Ghasemian M ( 2014). Shirazi thyme (Zataria multiflora Boiss) and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) essential oils repress expression of sagA, a streptolysin S-related gene in Streptococcus iniae. Aquaculture 430, 248-252.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Sotelo-Boyás M, Correa-Pacheco Z, Bautista-Baños S, Gómezy YGY ( 2017). Release study and inhibitory activity of thyme essential oil-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and nanocapsules against foodborne bacteria. Int J Biol Macromol 103, 409-414.
DOI URL PMID |
| [91] |
Swamy MK, Akhtar MS, Sinniah UR (2016). Antimicrobial properties of plant essential oils against human pathogens and their mode of action: an updated review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016, 3012462.
DOI URL PMID |
| [92] |
Verma RS, Joshi N, Padalia RC, Goswami P, Singh VR, Chauhan A, Verma SK, Iqbal H, Verma RK, Chanda D, Sundaresan V, Darokar MP ( 2017). Chemical com-position and allelopathic, antibacterial, antifungal andin vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of yarrow (Achillea millefolium L.) native to India. Ind Crops Prod 104, 144-155.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Wang CY, Chen YW, Hou CY ( 2019a). Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of seven predominant terpenoids. Int J Food Prop 22, 230-238.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Wang F, Wei FY, Song CX, Jiang B, Tian SY, Yi JW, Yu CL, Song ZB, Sun LG, Bao YL, Wu Y, Huang YX, Li YX ( 2017). Dodartia orientalis L. essential oil exerts antibacterial activity by mechanisms of disrupting cell structure and resisting biofilm. Ind Crops Prod 109, 358-366.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Wang YM, Dong WL, Odah KA, Kong LC, Ma HX ( 2019b). Transcriptome analysis reveals AI-2 relevant genes of multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in response to eugenol at Sub-MIC. Front Microbiol 10, 1159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [96] |
Wu KG, Lin YH, Chai XH, Duan XJ, Zhao XX, Chun C ( 2019). Mechanisms of vapor-phase antibacterial action of essential oil from Cinnamomum camphora var. linaloofera Fujita against Escherichia coli. Food Sci Nutr 7, 2546-2555.
DOI URL PMID |
| [97] |
Zeng ZK, Xu X, Zhang Q, Li P, Zhao PF, Li QY, Liu JD, Piao XS ( 2015). Effects of essential oil supplementation of a low-energy diet on performance, intestinal morphology and microflora, immune properties and antioxidant activities in weaned pigs. Anim Sci J 86, 279-285.
DOI URL PMID |
| [98] |
Zhai HX, Liu H, Wang SK, Wu JL, Kluenter AM ( 2018). Potential of essential oils for poultry and pigs. Anim Nutr 4, 179-186.
DOI URL PMID |
| [99] |
Zhang D, Gan RY, Zhang JR, Farha AK, Li HB, Zhu F, Wang XH, Corke H ( 2020). Antivirulence properties and related mechanisms of spice essential oils: a comprehensive review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 19, 1018-1055.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Zhang QQ, Ying GG, Pan CG, Liu YS, Zhao JL ( 2015 a). Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river Basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49, 6772-6782.
DOI URL PMID |
| [101] |
Zhang T, Zhou YF, Zou Y, Hu XM, Zheng LF, Wei HK, Giannenas I, Jin LZ, Peng J, Jiang SW ( 2015 b). Effects of dietary oregano essential oil supplementation on the stress response, antioxidative capacity, and HSPs mRNA expression of transported pigs. Livest Sci 180, 143-149.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Zhang ZF, Rolando AV, Kim IH ( 2016). Effects of benzoic acid, essential oils and Enterococcus faecium SF68 on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profiles, faecal microbiota and faecal noxious gas emission in weanling pigs. J Appl Anim Res 44, 173-179.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Zheng ZL, Tan JYW, Liu HY, Zhou XH, Xiang X, Wang KY ( 2009). Evaluation of oregano essential oil (Origanum heracleoticum L.) on growth, antioxidant effect and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 292, 214-218.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
Zhou F, Ji BP, Zhang H, Jiang H, Yang ZW, Li JJ, Li JH, Yan WJ ( 2007). The antibacterial effect of cinnamaldehyde, thymol, carvacrol and their combinations against the foodborne pathogen Salmonella typhimurium. J Food Saf 27, 124-133.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Zhu HM, Du M, Fox L, Zhu MJ ( 2016). Bactericidal effects of Cinnamon cassia oil against bovine mastitis bacterial pathogens. Food Control 66, 291-299.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||