

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 9-20.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19133 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19133
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xianjun Lai1,Yizheng Zhang2,Yinghong Gu2,Lang Yan1,*( )
)
Received:2019-07-05
Accepted:2019-09-24
Online:2020-01-01
Published:2019-12-20
Contact:
Lang Yan
Xianjun Lai,Yizheng Zhang,Yinghong Gu,Lang Yan. Transformation of Insect Derived Antifreeze Gene into Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) and Enhanced Its Freeze-tolerance[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(1): 9-20.
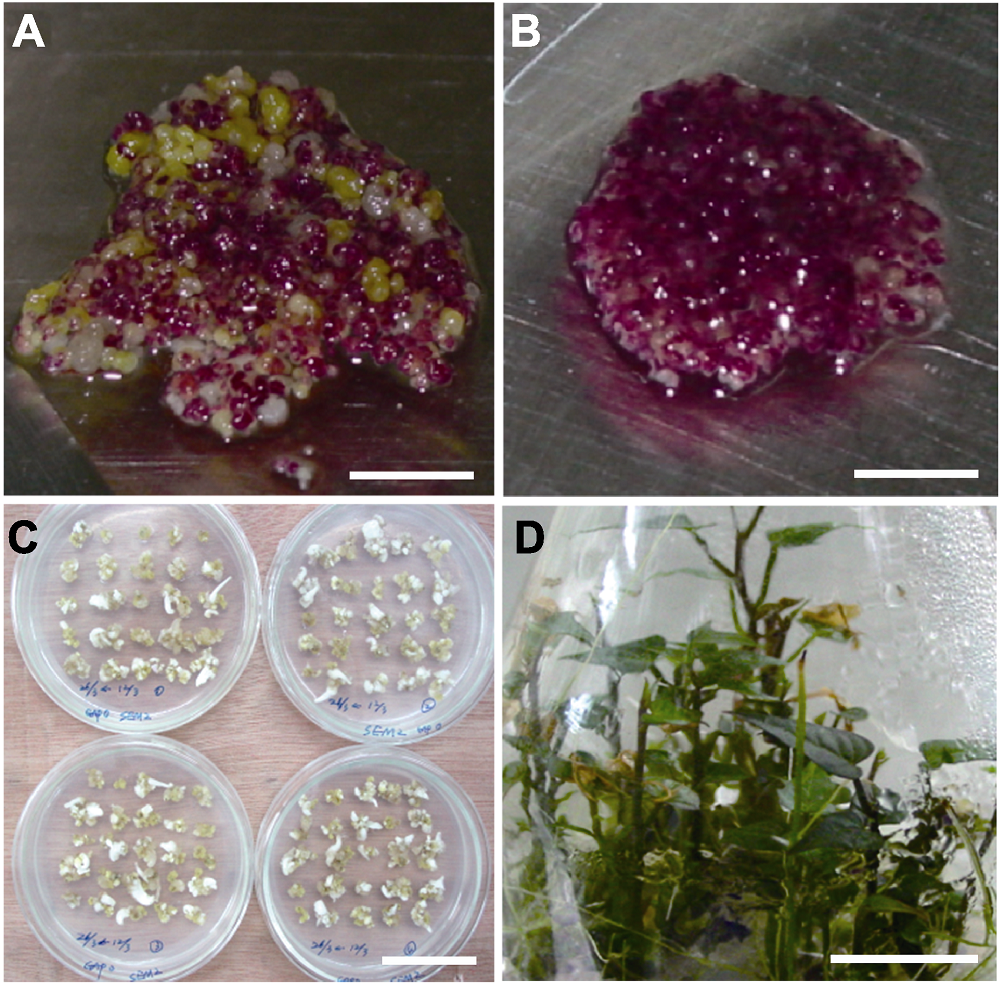

Figure 1 Transformation system of sweet potato (A), (B) Sweet potato embryogenic suspension cells at 18 and 22 weeks cultivated in MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D liquid medium, respectively; (C) Sweet potato embryogenic suspension cells at 8 weeks cultivated in MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D solid medium; (D) Sweet potato seedlings regenerated from somatic embryo. (A), (B), (D) Bars=1 cm; (C) Bar=4 cm
| Treatment | Components (mg·L-1) | Number of seedlings in average | * | ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MS | 44.8±5.22 | a | A |
| 2 | MS+ABA1.0 | 33.6±5.18 | b | AB |
| 3 | MS+GA31.0 | 30.2±4.73 | bc | B |
| 4 | MS+ABA1.0+GA31.0 | 23.2±6.29 | c | B |
| 5 | MS+ABA4.0+GA31.0 | 21.8±6.58 | c | B |
Table 1 Effect of different somatic embryo maturation medium on the regenerated seedlings
| Treatment | Components (mg·L-1) | Number of seedlings in average | * | ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MS | 44.8±5.22 | a | A |
| 2 | MS+ABA1.0 | 33.6±5.18 | b | AB |
| 3 | MS+GA31.0 | 30.2±4.73 | bc | B |
| 4 | MS+ABA1.0+GA31.0 | 23.2±6.29 | c | B |
| 5 | MS+ABA4.0+GA31.0 | 21.8±6.58 | c | B |
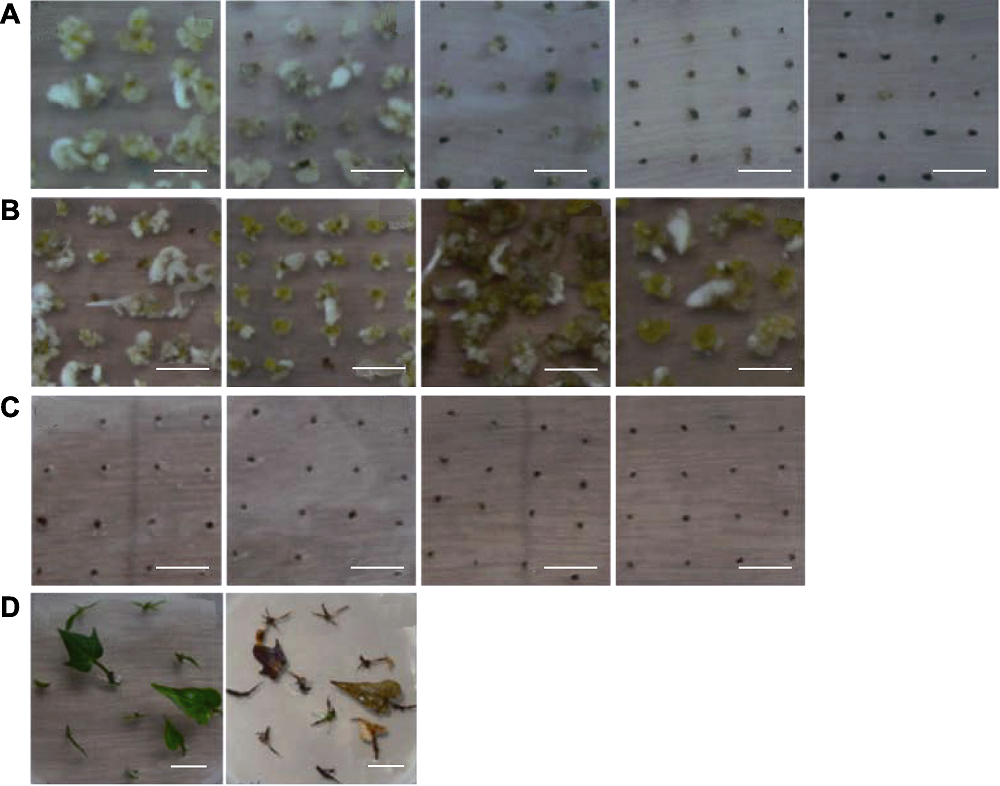
Figure 2 Effects of herbicide and antibiotic in different concentrations on embryogenic callus and regenerated seedlings of sweet potato (A) Sweet potato embryogenic suspension cells at 8 weeks cultivated in selective medium. The medium from left to right was MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D with 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 mg·L-1 GAP, respectively; (B) Embryogenic suspension cells at 6 weeks (the first and second from left to right) and 8 weeks (the third and fourth). The medium were MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D (the first and third) MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+100 mg·L-1 Carb (the second and fourth); (C) Embryogenic suspension cells at 8 weeks, the medium are MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+100 mg·L-1 Carb with 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4 mg·L-1 GAP, respectively; (D) Huachano stem tips cultivated 0 day and 3 weeks on medium of MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+0.8 mg·L-1 GAP+100 mg·L-1 Carb, respectively. (A), (B), (C) Bars=1 cm; (D) Bar=2 cm
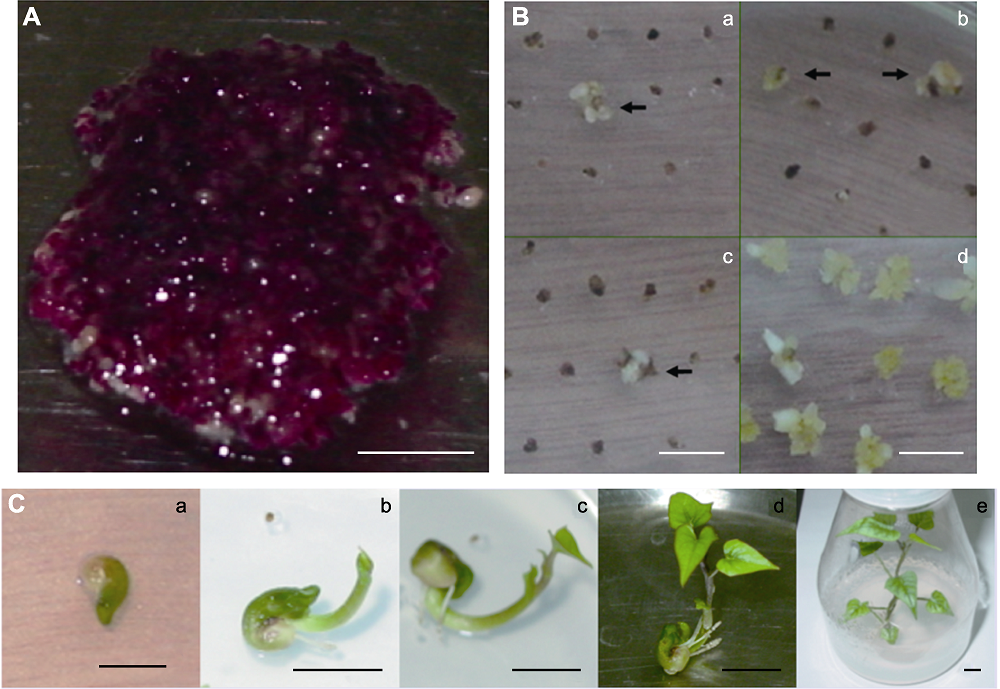

Figure 3 Sweet potato resistant somatic embryo and the regeneration of transgenic plants (A) Sweet potato embryogenic suspension cells cultivated in MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D liquid medium at 28°C for 32 weeks; (B) Embryogenic callus cultivated in selective and non-selective medium for 4 weeks, a-c: Embryogenic callus cultivated in selective medium (MS+0.2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+100 mg·L-1 Carb+0.8 mg·L-1 GAP), resistant callus was marked by arrows; d: Embryogenic callus cultivated in control medium without herbicide; (C) The processes of transgenic plant regeneration, a: Reproductive tissue; b: Bud; c: Leaf; d: Seedling; e: Reproductive plant. Bars=1 cm
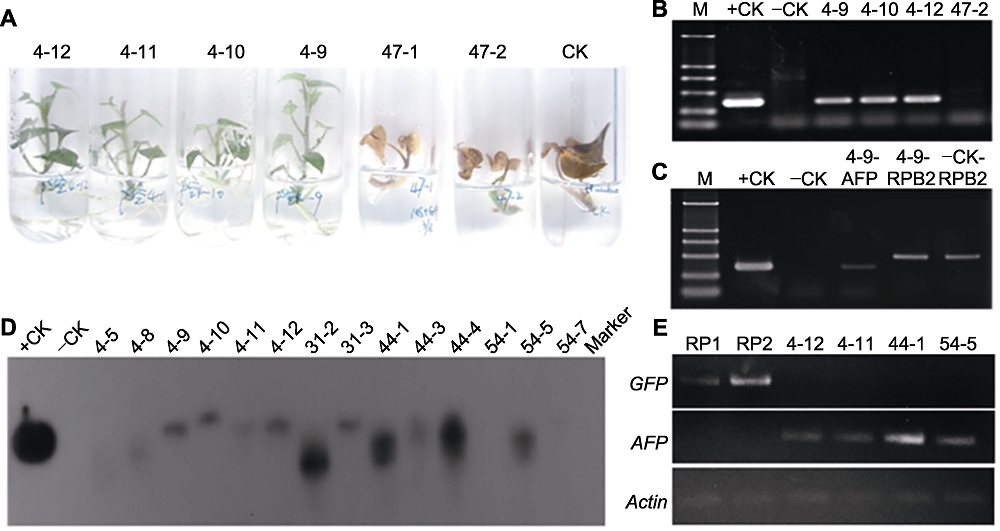
Figure 4 Detection of TmAFP in the transgenic sweet potato plants (A) Screening with 1.0 mg·L-1 GAP (Line 4-12, 4-11, 4-10, 4-9: Resistant seedlings; Line 47-1, 47-2: Non-resistant seedlings; CK: Non-transgenic control); (B) Amplified 353-bp fragment of AFP gene (M: D2000 molecular weight marker; +CK: pSUIBEV3-AFP vector as positive control; -CK: Non-transgenic seedlings as negative control; Line 4-9, 4-10, 4-12: GAP resistant seedlings; Line 47-2: Non-resistant seedlings); (C) PCR detection of transgenic seedlings (+CK: Amplifying AFP gene using pSUIBEV3-AFP as template; -CK: Amplifying AFP gene using non-transgenic seedling; 4-9-AFP: Amplifying AFP gene in transgenic seedling; 4-9-RPB2: Amplifying RPB2 gene in transgenic seedling; -CK-RPB2: Amplifying RPB2 gene in non-transgenic seedling); (D) Southern blotting analysis (+CK: pCAMBIA-AFP vector as positive control; -CK: Non-transgenic seedlings as negative control; The others represent different transgenic seedling lines); (E) RT-PCR detection of transgenic seedlings (RP1, RP2: Transgenic seedlings with empty pCAMBIA vector; Line 4-12, 4-11, 44-1, 54-5: Transgenic seedlings with pCAMBIA-AFP vector).
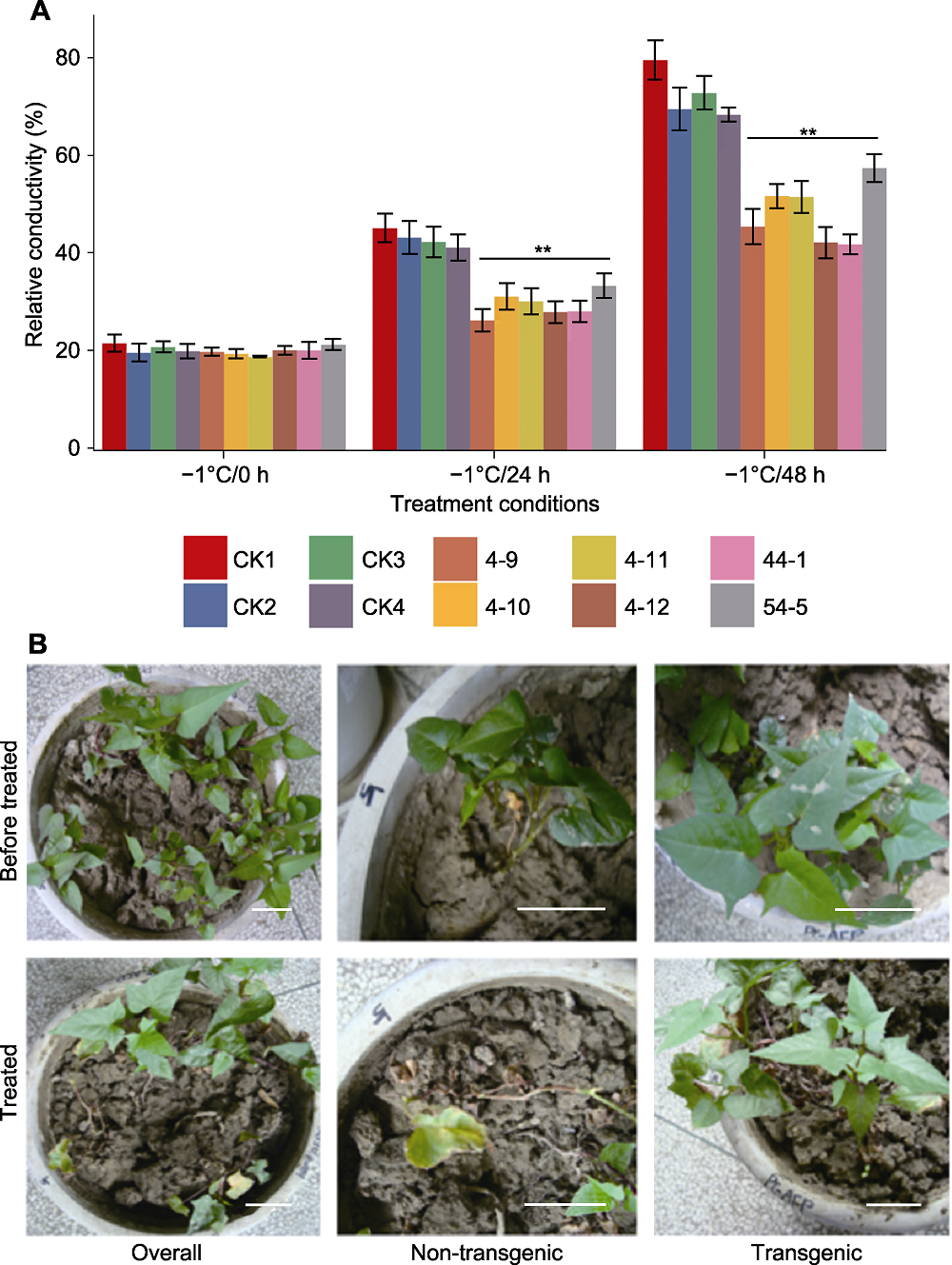
Figure 5 Detection of freezing-tolerance ability of TmAFP transgenic sweet potato plants (A) Conductivity assay under different freeze-treatments (CK1: Non-transgenic control; CK2-4: Transgenic plants with empty vector; 4-9, 4-10, 4-11, 4-12, 44-1, 54-5: TmAFP transgenic lines; ** indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01)); (B) Phenotypic changes of transgenic sweet potato plants and controls after 15 h treatment at -1°C (Overall: CK1, 4-9, 4-10, 4-11, 4-12 planted in the same pot; Non-transgenic: Zoomed in CK1; Transgenic: Zoomed in transgenic line 4-9). Bars=5 cm
| [1] | 蔺忠龙, 李维薇, 白现广, 吕广磊, 程在全 (2009). 植物抗冻基因最新研究进展. 北方园艺 ( 1), 119-123. |
| [2] | 刘忠渊, 王芸, 吕国栋, 王贤磊, 张富春, 马纪 (2006). Tenebriomolitor抗冻蛋白基因家族cDNA片段的克隆、序列分析及原核表达. 遗传 28, 1532-1540. |
| [3] | 马代夫, 李洪民, 李秀英, 谢逸平, 李强 (2005). 甘薯育种与甘薯产业发展. 见: 全国甘薯育种与产业化学术研讨会. 成都: 中国作物学会. pp. 3-10. |
| [4] | 阮龙, 高正良, 陈义红, 张玮, 张云华, 吴跃进, 邵希文 (2010). 干旱耐逆基因(HS1)转化甘薯获得转基因植株. 激光生物学报 19, 552-556. |
| [5] | 王欣, 过晓明, 李强, 唐忠厚, 郭尚洙, 马代夫 (2011). 转逆境诱导型启动子SWPA2驱动Cu/ZnSOD和APX基因甘薯(Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.)耐盐性. 分子植物育种 9, 754-759. |
| [6] | 王艳, 马纪, 黄薇, 邱立明, 叶锋, 张富春 (2009). 叶绿体型转昆虫抗冻蛋白基因烟草的耐寒性. 作物学报 35, 1253-1260. |
| [7] | 臧宁, 翟红, 王玉萍, 于波, 何绍贞, 刘庆昌 (2007). 表达bar基因的抗除草剂转基因甘薯的获得. 分子植物育种 5, 475-479. |
| [8] | 翟红, 何绍贞, 赵宁, 刘庆昌 (2017). 甘薯生物技术育种研究进展. 江苏师范大学学报(自然科学版) 35, 25-29. |
| [9] | 张振华, 陈介南, 卢孟柱, 章怀云, 刘伯斌 (2012). 胡萝卜与黄粉虫抗冻融合基因在拟南芥中的表达与抗冻性分析. 中国农学通报 28(31), 146-152. |
| [10] | 瓜谷郁三( 谢国生, 李合生译 ) (2004). 植物逆境生物化学及分子生物学: 着重热带薯类. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 202-204. |
| [11] | Cutler AJ, Saleem M, Kendall E, Gusta LV, Georges F, Fletcher GL (1989). Winter flounder antifreeze protein improves the cold hardiness of plant tissues. J Plant Physiol 135, 351-354. |
| [12] | Fan WJ, Zhang M, Zhang HX, Zhang P (2012). Improved tolerance to various abiotic stresses in transgenic sweet potato ( Ipomoea batatas) expressing spinach betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase. PLoS One 7, e37344. |
| [13] | Liu DG, He SZ, Song XJ, Zhai H, Liu N, Zhang DD, Ren ZT, Liu QC (2015). IbSIMT1, a novel salt-induced methyltransferase gene from Ipomoea batatas, is involved in salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120, 701-715. |
| [14] | Liu DG, He SZ, Zhai H, Wang LJ, Zhao Y, Wang B, Li RJ, Liu QC (2014a). Overexpression of IbP5CR enhances salt tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 117, 1-16. |
| [15] | Liu DG, Wang LJ, Zhai H, Song XJ, He SZ, Liu QC (2014b). A novel α/β-hydrolase gene IbMas enhances salt tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. PLoS One 9, e115128. |
| [16] | Liu QC (2011). Sweet potato omics and biotechnology in China. Plant Omics 4, 295-301. |
| [17] | Mwanga ROM, Andrade MI, Carey EE, Low JW, Yencho GC, Grüneberg WJ (2017). Sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.). In: Campos H, Caligari PDS, eds. Genetic Improvement of Tropical Crops. Cham: Springer. pp. 181-218. |
| [18] | Nada H, Furukawa Y (2011). Growth inhibition at the ice prismatic plane induced by a spruce budworm antifreeze protein: a molecular dynamics simulation study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13, 19936-19942. |
| [19] | Pearce RS (1999). Molecular analysis of acclimation to cold. Plant Growth Regul 29, 47-76. |
| [20] | Perl A, Perl-Treves R, Galili S, Aviv D, Shalgi E, Malkin S, Galun E (1993). Enhanced oxidative-stress defense in transgenic potato expressing tomato Cu, Zn superoxide dismutases. Theor Appl Genet 85, 568-576. |
| [21] | Ramya L, Ramakrishnan V (2016). Interaction of tenebrio molitor antifreeze protein with ice crystal: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Mol Inform 35, 268-277. |
| [22] | Wang B, Zhai H, He SZ, Zhang H, Ren ZT, Zhang DD, Liu QC (2016). A vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, IbNHX2, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. Sci Hortic 201, 153-166. |
| [23] | Wang C, Pakhomova S, Newcomer ME, Christner BC, Luo BH (2017). Structural basis of antifreeze activity of a bacterial multi-domain antifreeze protein. PLoS One 12, e0187169. |
| [24] | Wang LJ, He SZ, Zhai H, Liu DG, Wang YN, Liu QC (2013). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a salt tolerance-associated gene IbNFU1 from sweetpotato. J Integr Agric 12, 27-35. |
| [25] | Wang WX, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003). Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218, 1-14. |
| [26] | Yang Y, Guan S, Zhai H, He S, Liu Q (2009). Development and evaluation of a storage root-bearing sweetpotato somatic hybrid between Ipomoea batatas(L.) Lam. and I. triloba L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 99, 83-89. |
| [27] | Yue CW, Zhang YZ (2009). Cloning and expression of Tenebrio molitor antifreeze protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Rep 36, 529-536. |
| [28] | Zhai H, Wang FB, Si ZZ, Huo JX, Xing L, An YY, He SZ, Liu QC (2016). A myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene, IbMIPS1, enhances salt and drought tolerance and stem nematode resistance in transgenic sweet potato. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 592-602. |
| [29] | Zhang JH, Davies WJ (1987). Increased synthesis of ABA in partially dehydrated root tips and ABA transport from roots to leaves. J Exp Bot 38, 2015-2023. |
| [1] | Su Chen, Niu Yufan, Xu Hang, Wang Xiling, Yu Yingjun, He Yuqing, Wang Lei. Advances of Plant Circadian Clock Response to Light and Temperature Signals [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 315-341. |
| [2] | Xiaoyun Dong, Jiaping Wei, Junmei Cui, Zefeng Wu, Guoqiang Zheng, Hui Li, Ying Wang, Haiyan Tian, Zigang Liu. Research Progress in Plant Antifreeze Protein [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 966-981. |
| [3] | Bo Zhang, Changzhong Ren. Advances in Oat Genomic Research and Molecular Breeding [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 785-791. |
| [4] | Sanhe Li, Kai Liu, Wenjun Zha, Huashan Xu, Peide Li, Lei Zhou, Aiqing You. Effects of transgenic rice H23 with BPH9 and Bar genes resistant to brown planthopper and herbicide on non-target organisms [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(4): 488-494. |
| [5] | Jiaxin Li, Xia Li, Yinfeng Xie. Mechanism on Drought Tolerance Enhanced by Exogenous Trehalose in C4-PEPC Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 296-314. |
| [6] | LIU Li-Yan, FENG Jin-Xia, LIU Wen-Xin, WAN Xian-Chong. Effects of drought stress on photosynthesis, growth and root structure of transgenic PtPIP2;8 poplar 84K (Populus alba × P. glandulosa) [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2020, 44(6): 677-686. |
| [7] | Shuying Li, Jiabao Zhu, Xianyong Lu, Furu Cheng, Shufeng Zheng, Jinjie Cui, Junyu Luo, Yan Ma. The diversity of insect communities and its dynamic changes in transgenic RRM2 (RNA recognition motif 2) cotton fields [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1190-1203. |
| [8] | Junyu Luo, Shuai Zhang, Xiangzhen Zhu, Chunyi Wang, Limin Lü, Chunhua Li, Jinjie Cui. Insect community diversity in transgenic Bt cotton in saline and dry soils [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(3): 332-340. |
| [9] | Hua Liu, Xiaolei Chang, Wei Jiang, Lan Bai, Shufeng Zheng, Jinbin Wang, Wei Wang, Aihu Pan, Rongtan Wang, Xueming Tang. Effect of Cry1Ab/c protein residues from Bt cotton-producing areas in regions with marginal water in three provinces in eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(12): 1373-1380. |
| [10] | Xiaolong Liu, Xia Li, Baoyun Qian. Photosynthetic and Physiological Regulation of C4 Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxylase Transgenic Rice (Oryza sativa) by Exogenous Ca2+ Under Polyethylene Glycol Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 206-216. |
| [11] | Shixuan Chen, Zhennan Zhang, Bo Wang, Yan Zhu, Yuehua Gong, Dongmei Sun, Xin Deng. Cloning, Expression and Functional Analysis of a J-domain Protein- coding Gene, BhDNAJC2, from the Resurrection Plant Boea hygrometrica [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 180-190. |
| [12] | LUO Jun-Yu, LIU Chuan-Liang, ZHANG Shuai, WANG Chun-Yi, LÜ Li-Min, LI Chun-Hua, LI Fu-Guang, CUI Jin-Jie. Growth vigour and yield of transgenic RRM2 (RNA recognition motif 2) cotton and their effects on arthropod community in cotton field [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(7): 785-794. |
| [13] | Silan Dai, He Huang, Jianxin Fu, Yan Hong. Advances in Molecular Breeding of Ornamental Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(6): 589-607. |
| [14] | Weicai Yang. Plant Transgenic Technology: Past and Current Development [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 6-9. |
| [15] | Chaojie Ba, Jing Xue, Xuqing Chen, Fengping Yang, Liquan Zhang, Xianglong Li, Xiaodong Zhang. Rapid Screening of Cry1Ab/c Transgenic Maize Using an Anthocyanin Visualizing Track System [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 59-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||