

两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线
收稿日期: 2021-03-02
录用日期: 2021-03-05
网络出版日期: 2021-03-11
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(31830077)
Synergistic Cooperation Between Cell Surface and Intracellular Immune Receptors Potentiates to Activate Robust Plant Defense
Received date: 2021-03-02
Accepted date: 2021-03-05
Online published: 2021-03-11
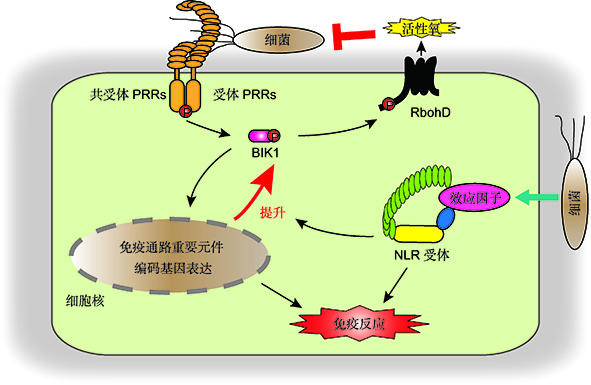
植物先天免疫系统在抵御病原菌入侵过程中发挥至关重要的作用, 主要包括两个层次, 即病原菌相关分子模式和效应因子分别触发的PTI和ETI免疫反应。PTI和ETI分别由植物细胞膜表面模式识别受体(PRRs)和胞内免疫受体(NLRs)激活, 具有特异的激活机制, 但是两者激活的下游免疫事件相互重叠。PTI和ETI是否为泾渭分明的两道防线, 以及ETI与PTI下游事件为何如此相似, 一直是植物免疫领域最受关注的问题之一。最近, 中国科学院分子植物科学卓越创新中心辛秀芳团队与合作者利用拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)与丁香假单胞杆菌(Pseudomonas syringae)互作系统对PTI和ETI在机制上的联系进行了研究。他们发现PRRs和共受体参与ETI, 而活性氧的产生是联系PRRs和NLRs所介导的免疫早期信号事件。他们还发现NLRs信号能够迅速增强PTI关键因子的转录和蛋白水平, PTI的增强在ETI免疫反应中不可或缺。该研究从机制上解析了植物免疫领域中长期悬而未决的PTI与ETI相似性之谜, 是该领域的一项突破性进展, 为未来作物分子设计育种提供了新的启示。
关键词: 植物免疫; 病原菌相关分子模式触发的免疫反应(PTI); 效应因子触发的免疫反应(ETI); 活性氧; NLRs; 模式识别受体(PRRs)
王伟 , 唐定中 . 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021 , 56(2) : 142 -146 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB21042
Innate immune system plays a crucial role to defend against pathogens attack and is classified into two layers, which include pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector-triggered immunity (ETI). The PTI and ETI are activated by cell-surface localized pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) and mostly intracellularly-localized nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat receptors (NLRs), respectively, with specific activation mechanisms, but largely overlapped downstream immune events and components. One of the top unanswered questions in the field of plant immunity is whether ETI and PTI are really distinct, considering the high similarity of the downstream of the recognition processes and components. Recently, a team led by Prof. Xiufang Xin, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used the Arabidopsis thaliana and Pseudomonas syringae pathosystem to study the functional link between PTI and ETI, and demonstrated that PRRs and the co-receptor of PRRs contribute to ETI, and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is the early signal event that connects PTI and ETI. They also showed that ETI enhances the transcript and protein levels of key components of PTI, and the increased PTI is crucial for full activation of ETI. This study provides mechanistic explanation to a long-lasting enigma in the field of plant immunity regarding the mechanistic connections of PTI and ETI, and the high similarity of these two layers of immunity. This work represents an important breakthrough in the field of plant immunity, and will have implications for the future molecular breeding in crops.

| [1] | Cesari S (2018). Multiple strategies for pathogen perception by plant immune receptors. New Phytol 219,17-24. |
| [2] | Couto D, Zipfel C (2016). Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signaling in plants. Nat Rev Immunol 16,537- 552. |
| [3] | Cui HT, Tsuda K, Parker JE (2015). Effector-triggered immunity: from pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66,487-511. |
| [4] | Daudi A, Cheng ZY, O'Brien JA, Mammarella N, Khan S, Ausubel FM, Bolwell GP (2012). The apoplastic oxidative burst peroxidase in Arabidopsis is a major component of pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 24,275-287. |
| [5] | Day B, Dahlbeck D, Huang J, Chisholm ST, Li DH, Staskawicz BJ (2005). Molecular basis for the RIN4 negative regulation of RPS2 disease resistance. Plant Cell 17,1292-1305. |
| [6] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444,323-329. |
| [7] | Kadota Y, Liebrand TWH, Goto Y, Sklenar J, Derbyshire P, Menke FLH, Torres MA, Molina A, Zipfel C, Coaker G, Shirasu K (2019). Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis reveals common regulatory mechanisms bet- ween effector- and PAMP-triggered immunity in plants. New Phytol 221,2160-2175. |
| [8] | Kim HS, Desveaux D, Singer AU, Patel P, Sondek J, Dangl JL (2005). The Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrRpt2 cleaves its C-terminally acylated target, RIN4, from Arabidopsis membranes to block RPM1 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102,6496-6501. |
| [9] | Lu DP, Wu SJ, Gao XQ, Zhang YL, Shan LB, He P (2010). A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107,496-501. |
| [10] | Monteiro F, Nishimura MT (2018). Structural, functional, and genomic diversity of plant NLR proteins: an evolved resource for rational engineering of plant immunity. Annu Rev Phytopathol 56,243-267. |
| [11] | Ngou BPM, Ahn HK, Ding PT, Jones JDG (2021). Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03315-7. |
| [12] | Qi JS, Wang JL, Gong ZZ, Zhou JM (2017). Apoplastic ROS signaling in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38,92-100. |
| [13] | Qi YP, Tsuda K, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F (2011). Physical association of pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effec-tor-triggered immunity (ETI) immune receptors in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Pathol 12, 702-708. |
| [14] | Shi H, Shen QJ, Qi YP, Yan HJ, Nie HZ, Chen YF, Zhao T, Katagiri F, Tang DZ (2013). BR-SIGNALING KINASE 1 physically associates with FLAGELLIN SENSING 2 and regulates plant innate immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 1143-1157. |
| [15] | Tang DZ, Wang GX, Zhou JM (2017). Receptor kinases in plant-pathogen interactions: more than pattern recogni- tion. Plant Cell 29,618-637. |
| [16] | Torres MA, Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2002). Arabidopsis gp91 phox homologues AtrbohD and AtrbohF are required for accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant defense response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99,517-522. |
| [17] | Wang W, Feng BM, Zhou JM, Tang DZ (2020). Plant immune signaling: advancing on two frontiers. J Integr Plant Biol 62,2-24. |
| [18] | Wei HL, Chakravarthy S, Mathieu J, Helmann TC, Stodghill P, Swingle B, Martin GB, Collmer A (2015). Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 Type III secretion effector polymutants reveal an interplay between HopAD1 and AvrPtoB. Cell Host Microbe 17, 752-762. |
| [19] | Yuan M, Jiang Z, Bi G, Nomura K, Liu M, Wang Y, Cai B, Zhou JM, He SY, Xin XF (2021). Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03316-6. |
| [20] | Zhang J, Li W, Xiang TT, Liu ZX, Laluk K, Ding XJ, Zou Y, Gao MH, Zhang XJ, Chen S, Mengiste T, Zhang YL, Zhou JM (2010). Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector. Cell Host Microbe 7,290-301. |
| [21] | Zhou JM, Zhang YL (2020). Plant immunity: danger percep- tion and signaling. Cell 181,978-989. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |