

快速、无损大豆种子连续取样技术及其DNA制备
收稿日期: 2020-05-26
录用日期: 2020-10-05
网络出版日期: 2020-10-11
基金资助
中国科学院重点部署项目(ZDRW-ZS-2019-2);中国科学院战略性科技先导专项(A类)(XDA24010105-4);国家自然科学基金(31771869);国家自然科学基金(31771818);国家自然科学基金(31971970)
A Rapid, Non-destructive and Continuous Sampling Technique and DNA Extraction for Soybean Seed
Received date: 2020-05-26
Accepted date: 2020-10-05
Online published: 2020-10-11
夏正俊 , 李玉卓 , 朱金龙 , 吴红艳 , 徐坤 , 翟红 . 快速、无损大豆种子连续取样技术及其DNA制备[J]. 植物学报, 2021 , 56(1) : 56 -61 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB20095
Establishment of a simple, quick, non-destructive, and continuous sampling procedure, can save planting cost and accelerate gene functional analysis and breeding procedures. In this study, we created a rapid, non-destructive, and continuous sampling technique using micro electric driller and air pump. We also optimized the high throughput DNA extraction method for the 384 deep-well plate and genotyping method. Furthermore, this technique could be applied in rice, maize and other crops for seed sampling and high throughput genotyping.
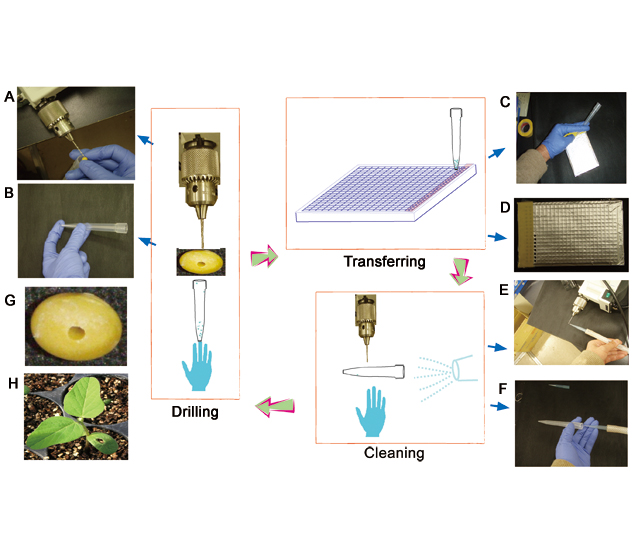
Key words: soybean (Glycine max); seed; drilling; continuing sampling; 384 deep-well plate; genotyping
| [1] | 程文, 夏正俊, 冯献忠, 杨素欣 (2016). 一种快速、无损大豆种子DNA提取方法的建立和应用. 植物学报 51, 68-73. |
| [2] | 薛勇彪, 种康, 韩斌, 桂建芳, 王台, 傅向东, 何祖华, 储成才, 田志喜, 程祝宽, 林少扬 (2015). 开启中国设计育种新篇章——“分子模块设计育种创新体系”战略性先导科技专项进展. 中国科学院院刊 30, 393-402. |
| [3] | Kamiya M, Kiguchi T (2003). Rapid DNA extraction method from soybean seeds. Breed Sci 53, 277-279. |
| [4] | King Z, Serrano J, Boerma HR, Li ZL (2014). Non-toxic and efficient DNA extractions for soybean leaf and seed chips for high-throughput and large-scale genotyping. Biotechnol Lett 36, 1875-1879. |
| [5] | McCarthy PL, Hansen JL, Zemetra RS, Berger PH (2002). Rapid identification of transformed wheat using a half- seed PCR assay. Biotechniques 32, 560-564. |
| [6] | von Post R, von Post L, Dayteg C, Nilsson M, Forster BP, Tuvesson S (2003). A high-throughput DNA extraction method for barley seed. Euphytica 130, 255-260. |
| [7] | Xia ZJ, Tsubokura Y, Hoshi M, Hanawa M, Yano C, Okamura K, Ahmed TA, Anai T, Watanabe S, Hayashi M, Kawai T, Hossain KG, Masaki H, Asai K, Yamanaka N, Kubo N, Kadowaki K, Nagamura Y, Yano M, Sasaki T, Harada K (2007). An integrated high-density linkage map of soybean with RFLP, SSR, STS, and AFLP markers using a single F2 population. DNA Res 14, 257-269. |
| [8] | Xia ZJ, Watanabe S, Yamada T, Tsubokura Y, Nakashima H, Zhai H, Anai T, Sato S, Yamazaki T, Lü SX, Wu HY, Tabata S, Harada K (2012). Positional cloning and characterization reveal the molecular basis for soybean maturity locus E1 that regulates photoperiodic flowering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, E2155-E2164. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |