

ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器
收稿日期: 2019-08-27
录用日期: 2019-09-17
网络出版日期: 2019-09-30
Discovery of ZmFBL41 Chang7-2 as A Key Weapon against Banded Leaf and Sheath Blight Resistance in Maize
Received date: 2019-08-27
Accepted date: 2019-09-17
Online published: 2019-09-30
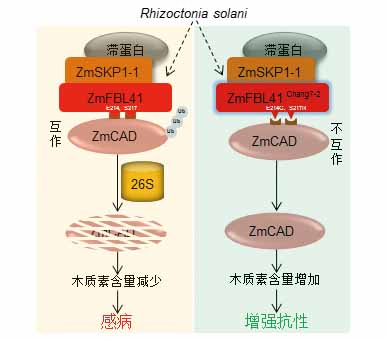
由真菌Rhizoctonia solani引起的纹枯病严重危害玉米(Zea mays)和水稻(Oryza sativa)等作物的安全生产。R. solani的宿主范围广且抗源少, 加之相关的抗性机制研究有限, 导致纹枯病的危害长期得不到有效控制。近期, 中国科学家通过对318份玉米自交系进行全基因组关联分析, 筛选到1个与纹枯病抗性相关的、编码F-box结构域蛋白的候选基因ZmFBL41 (GRMZM2G109140)。ZmFBL41蛋白是SCF (SKP1-Cullin-F-box) E3泛素连接酶复合体的一员, 能介导复合体对肉桂醇脱氢酶ZmCAD的降解, 从而降低木质素的积累, 使玉米易感纹枯病。玉米抗病自交系Chang7-2中, 蛋白ZmFBL41 Chang7-2因2个关键氨基酸的变异, 不能结合并降解底物ZmCAD, 使木质素含量增加, 从而提高玉米对纹枯病的抗性。该研究率先揭示了SCF复合体可通过降解肉桂醇脱氢酶来调控植物免疫反应的新型分子机制, 为提高玉米及其它作物对纹枯病的抗性提供了重要理论依据和基因资源。
李伟滔 , 贺闽 , 陈学伟 . ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019 , 54(5) : 547 -549 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB19166
The fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani causes banded leaf and sheath blight (BLSB) in maize (Zea mays) and sheath blight (ShB) in rice (Oryza sativa). R. solani has a wide range of host and severely threatens crop production. The lack of resistant resources against BLSB and the poor understanding of disease resistance mechanism hamper the development of effective approaches to control this fungal disease. Recently, Chinese scientists have made a breakthrough discovery that an F-box protein ZmFBL41 mediates the proteasomal degradation of cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase ZmCAD to regulate BLSB and ShB disease resistance. By genome-wide association analysis, GRMZM2G 109140 (ZmFBL41) was identified as a major QTL candidate gene associated with BLSB disease resistance. ZmFBL41 protein is a member of SKP1-Cullin-F-box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex which mediates the degradation of ZmCAD, thus reducing the accumulation of lignin and rendering maize more susceptible to R. solani. Interestingly, in the maize inbred line Chang7-2, the natural variation on two amino acids in ZmFBL41 Chang7-2 results in resistance against BLSB. Mechanistically, ZmFBL41 Chang7-2 fails to interact with and degrade its substrate ZmCAD, leading to the accumulation of lignin, which consequently enhances maize resistance. This study not only discovers a novel molecular mechanism underlying disease resistance of maize against R. solani, but also provides important theoretical basis and genetic resources for breeding maize and other crops with improved disease resistance.

Key words: plant immunity; SKP1-Cullin-F-box; lignin; banded leaf and sheath blight; maize; rice
| 1 | Baruah P, Lal S (1981). Hostrange of Rhizoctonia solani f. sp. sasakii, then incitant of banded sclerotial disease of maize. Indian Phytopath 34, 494-496. |
| 2 | Hooda KS, Khokhar MK, Parmar H, Gogoi R, Joshi D, Sharma SS, Yadav OP (2017). Banded leaf and sheath blight of maize: historical perspectives, current status and future directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 87, 1041-1052. |
| 3 | Li N, Lin B, Wang H, Li X, Yang F, Ding X, Yan J, Chu Z (2019). Natural variation in ZmFBL41 confers banded leaf and sheath blight resistance in maize. Nat Genet 51, 1540-1548. |
| 4 | Li Z, Pinson SRM, Marchetti MA, Stansel JW, Park WD (1995). Characterization of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in cultivated rice contributing to field resistance to sheath blight ( Rhizoctonia solani). Theor Appl Genet 91, 382-388. |
| 5 | Maeda S, Dubouzet JG, Kondou Y, Jikumaru Y, Seo S, Oda K, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Mori M (2019) The rice CYP78A gene BSR2 confers resistance to Rhizoctonia solani and affects seed size and growth in Arabidopsis and rice. Sci Rep 9, 587. |
| 6 | Ogoshi A (1987). Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and interspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Ann Rev Phytopathol 25, 125-143. |
| 7 | Peng X, Wang H, Jang JC, Xiao T, He H, Jiang D, Tang X (2016). OsWRKY80-OsWRKY4 module as a positive regulatory circuit in rice resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Rice 9, 63. |
| 8 | Richa K, Tiwari IM, Devanna BN, Botella JR, Sharma V, Sharma TR (2017). Novel chitinase gene LOC_Os 11g47510 from indica rice Tetep provides enhanced resistance against sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in rice. Front Plant Sci 8, 596. |
| 9 | Sharma RC, Srinivas P, Batsa BK (2002). Banded leaf and sheath blight of maize its epidemiology and management. In: Rajbhandari NP, Ransom JK, Adhikari K, Palmer AFE, eds. Proceedings of a Maize Symposium Held. Kathmandu: NARC and CIMMYT. pp. 108-112. |
| 10 | Sharma RR, Gour HN, Rathore RS (2004). Etiology of banded leaf and sheath blight symptoms on maize. J Mycol Plant Pathol 34, 56-59. |
| 11 | Singh BM, Sharma YR (1976). Evaluation of maize germplasm to banded sclerotial disease and assessment of yield loss. Indian Phytopath 29, 129-132. |
| 12 | Wang H, Meng J, Peng X, Tang X, Zhou P, Xiang J, Deng X (2015). Rice WRKY4 acts as a transcriptional activator mediating defense responses toward Rhizoctonia solani, the causing agent of rice sheath blight. Plant Mol Biol 89, 157-171. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |