

基于SSR分子标记的酸浆属植物亲缘关系研究
收稿日期: 2018-01-28
录用日期: 2018-05-09
网络出版日期: 2018-06-05
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.31470407)、浙江省科技计划(No.2014C32090)和杭州市科技局项目(No.20150932H04, No.20150932H03)
Genetic Relationship of Physalis Plants Revealed by Simple Sequence Repeat Markers
Received date: 2018-01-28
Accepted date: 2018-05-09
Online published: 2018-06-05
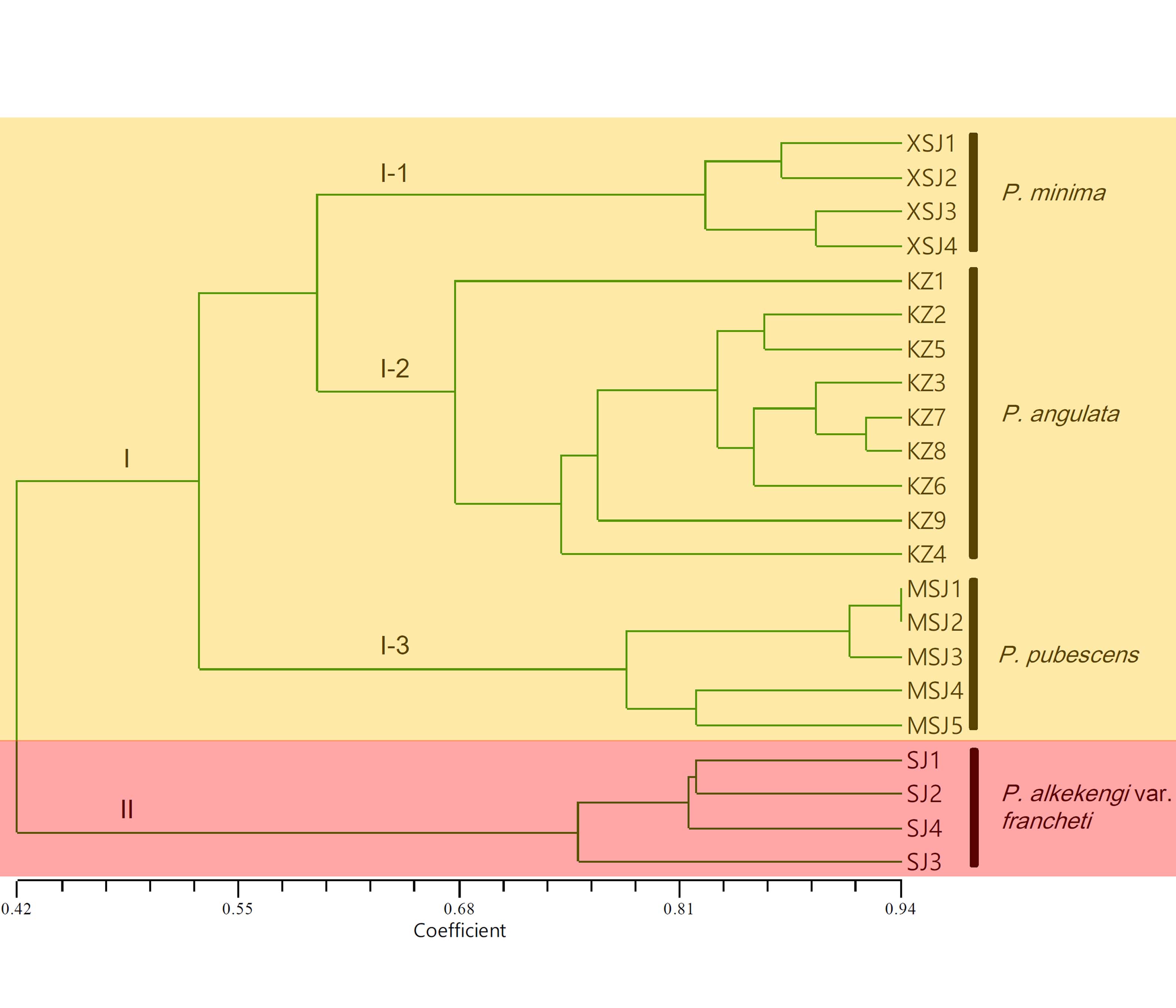
近年来, 由于营养价值高、果实可当水果食用且具有潜在的药用价值, 酸浆属(Physalis)植物在全球范围内受到了越来越多的关注。采用SSR分子标记技术对我国范围内主要分布的4种酸浆属植物的22份样品进行了亲缘关系研究, 结果表明, 20对SSR引物共扩增出118个位点, 其中107个(90.7%)为多态性位点; 平均种间遗传相似系数为0.501。UPGMA聚类和PCoA分析结果得出相似结论, 并且将供试酸浆属植物样品分为两大类。其中, 酸浆(P. alkekengi var. francheti)的所有样品与其它酸浆属植物的遗传距离最远, 单独聚为一类, 与前人的研究结果非常吻合。研究表明, SSR标记遗传信息丰富, 可以用于酸浆属植物的亲缘关系分析。研究结果为酸浆属种质资源保护提供了有效信息, 并且为酸浆属植物的分子辅助育种奠定了重要基础。
朱宇佳 , 焦凯丽 , 罗秀俊 , 冯尚国 , 王慧中 . 基于SSR分子标记的酸浆属植物亲缘关系研究[J]. 植物学报, 2018 , 53(3) : 305 -312 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB18027
In recent years, Physalis plants have attracted increasing attention worldwide due to their high nutritional value, edible fruit, and potential medicinal value. In this study, simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers were used to assess genetic relationships with 22 samples of four Physalis species mainly distributed in China. Twenty SSR primer pairs produced 118 loci, 90.7% (107) of which showed polymorphism. The average interspecies similarity coefficient was 0.501, which indicates a degree of genetic relationship among Physalis species. The results of UPGMA dendrography and PCoA plotting were similar, and all Physalis samples were grouped into two clusters. All P. alkekengi var. francheti samples, distant from any other Physalis species, constituted a separate cluster, which confirmed findings of previous studies. This study also indicated that SSR markers are rich in genetic information and could be used to assess the genetic diversity of Physalis species which provides rich useful information for protecting the Physalis germplasm resource and an important foundation for molecular assisted-breeding programs with Physalis.

Key words: Physalis; genetic relationship; SSR markers
| [1] | 国家药典委员会 (2015). 中华人民共和国药典(一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社. pp. 360-361. |
| [2] | 郭瑜, 吴东栋, 任志远, 王晓闻, 郭峰 (2017). 酸浆悬浮饮料的研制. 食品研究与开发 38(15), 89-92. |
| [3] | 贾远敏, 陈重, 许琼明, 李笑然, 杨世林 (2013). 毛酸浆浆果的化学成分研究. 中草药 9, 1086-1090. |
| [4] | 李晓岚, 陆嘉惠, 谢良碧, 张爱霞, 陈晓翠, 李学禹 (2015). 4种甘草属植物EST-SSR引物开发及其亲缘关系分析. 西北植物学报 35, 480-485. |
| [5] | 骆丽萍, 成凡钦, 季龙, 虞和永 (2015). 毛酸浆的化学成分研究. 中国中药杂志 22, 4424-4427. |
| [6] | 孙海涛, 高玉超 (2013). 毛酸浆番茄复合调味酱的研制. 中国调味品 38(12), 58-59, 67. |
| [7] | 王晓英, 刘长姣, 段连海, 霍岩 (2014). 毛酸浆开发利用的研究进展. 中国酿造 2, 5-8. |
| [8] | 王赢, 朱丹, 牛广财, 郑唯, 魏文毅, 刘鑫 (2017). 毛酸浆发酵果脯的研制. 中国酿造 36(8), 182-185. |
| [9] | 许亮, 王荣祥, 杨燕云, 王冰 (2009). 中国酸浆属植物药用资源研究. 中国野生植物资源 28, 21-23. |
| [10] | 杨金颖, 杨德草, 李津津 (2014). 酸浆的药理作用研究进展. 内蒙古中医药 33(25), 116-117. |
| [11] | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1978). 中国植物志(第67卷). 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 50. |
| [12] | Axelius B (1996). The phylogenetic relationships of the physaloid genera (Solanaceae) based on morphological data.Am J Bot 83, 118-124. |
| [13] | Ding H, Hu ZJ, Yu LY, Ma ZY, Ma XQ, Chen Z, Wang D, Zhao XF (2014). Induction of quinone reductase (QR) by withanolides isolated from Physalis angulata L. var. villosa Bonati (Solanaceae). Steroids 86, 32-38. |
| [14] | Feng SG, He RF, Lu JJ, Jiang MY, Shen XY, Jiang Y, Wang ZA, Wang HZ (2016a). Development of SSR markers and assessment of genetic diversity in medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivars. Front Genet 7, 113. |
| [15] | Feng SG, Jiang MY, Shi YJ, Jiao KL, Shen CJ, Lu JJ, Ying QC, Wang HZ (2016b). Application of the ribosomal DNA ITS2 region of Physalis ( Solanaceae): DNA barcoding and phylogenetic study. Front Plant Sci 7, 1047. |
| [16] | Feng SG, Jiao KL, Zhu YJ, Wang HF, Jiang MY, Wang HZ (2018). Molecular identification of species of Physalis ( Solanaceae) using a candidate DNA barcode: the chloroplast psbA-trnH intergenic region. Genome 61, 15-20. |
| [17] | Fu N, Wang PY, Liu XD, Shen HL (2014). Use of EST-SSR markers for evaluating genetic diversity and fingerprinting celery (Apium graveolens L.) cultivars. Molecules 19, 1939-1955. |
| [18] | Garzon-Martínez GA, Osorio-Guarín JA, Delgádillo-Duran P, Mayorga F, Enciso-Rodríguez FE, Landsman D, Mariño-Ramírez L, Barrero LS (2015). Genetic diversity and population structure in Physalis peruviana and related taxa based on InDels and SNPs derived from COSII and IRG markers. Plant Gene 4, 29-37. |
| [19] | Gower JC (1966). Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis.Biometrika 53, 325-338. |
| [20] | Ji L, Yuan YL, Ma ZJ, Chen Z, Gan LS, Ma XQ, Huang DS (2013). Induction of quinone reductase (QR) by withanolides isolated from Physalis pubescens L. ( Solanaceae). Steroids 78, 860-865. |
| [21] | Li X, Zhao JP, Yang M, Liu YL, Li ZC, Li RY, Li XR, Li N, Xu QM, Khan IA, Yang SL (2014). Physalins and withanolides from the fruits ofPhysalis alkekengi L. var. fran- chetii ( Mast.) Makino and the inhibitory activities against human tumor cells. Phytochem Lett 10, 95-100. |
| [22] | Maggie WPS, Manos PS (2005). Untangling Physalis ( Solanaceae) from the physaloids: a two-gene phylogeny of the Physalinae. Syst Bot 30, 216-230. |
| [23] | Nei M, Li WH (1979). Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76, 5269-5273. |
| [24] | Olmstead RG, Bohs L, Migid HA, Santiago-Valentin E, Garcia VF, Collier SM (2008). A molecular phylogeny of the Solanaceae.Taxon 57, 1159-1181. |
| [25] | Rohlf FJ (2000). NTSYS-PC: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.00. Setauket, New York:Exeter Software. |
| [26] | Simbaqueba J, Sánchez P, Sanchez E, Zarantes VMN, Chacon MI, Barrero LS, Mariño-Ramírez L (2011). Development and characterization of microsatellite markers for the cape gooseberry Physalis peruviana. PLoS One 6, e26719. |
| [27] | Sun CP, Nie XF, Kang N, Zhao F, Chen LX, Qiu F (2017). A new phenol glycoside from Physalis angulata. Nat Prod Res 31, 1059-1065. |
| [28] | Teshome A, Bryngelsson T, Dagne K, Geleta M (2015). Assessment of genetic diversity in Ethiopian field pea ( Pisum sativum L.) accessions with newly developed EST- SSR markers. BMC Genet 16, 102. |
| [29] | Wang F, Yang T, Burlyaeva M, Li L, Jiang JY, Fang L, Redden R, Zong XX (2015). Genetic diversity of grasspea and its relative species revealed by SSR markers.PLoS One 10, e0118542. |
| [30] | Wei JL, Hu XR, Yang JJ, Yang WC (2012). Identification of single-copy orthologous genes between Physalis and Solanum lycopersicum and analysis of genetic diversity in Physalis using molecular markers. PLoS One 7, e50164. |
| [31] | Xu XM, Guan YZ, Shan SM, Luo JG, Kong LY (2016). Withaphysalin-type withanolides from Physalis minima. Phytochem Lett 15, 1-6. |
| [32] | Yang YK, Xie SD, Xu WX, Nian Y, Liu XL, Peng XR, Ding ZT, Qiu MH (2016). Six new physalins from Physalis alkekengi var. franchetii and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. Fitoterapia 112, 144-152. |
| [33] | Zamora-Tavares P, Vargas-Ponce O, Sanchez-Martínez J, Cabrera-Toledo D (2015). Diversity and genetic structure of the husk tomato ( Physalis philadelphica Lam.) in Wes- tern Mexico. Genet Res Crop Evol 62, 141-153. |
| [34] | Zhang WN, Tong WY (2016). Chemical constituents and biological activities of plants from the genus Physalis. Chem Biodivers 13, 48-65. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |