

长杂谷系列谷子杂交种产量优势及其生理机制
收稿日期: 2024-12-02
录用日期: 2025-03-18
网络出版日期: 2025-03-26
基金资助
山西农业大学科技创新提升工程(CXGC2023098)
Heterosis in Yield and Its Physiological Mechanism of Changzagu Series Millet Hybrids
Received date: 2024-12-02
Accepted date: 2025-03-18
Online published: 2025-03-26
阐明谷子(Setaria italica var. germanica)杂种优势的生理机制是提高谷子杂交种产量的重要基础。2023-2024年, 以3个高产谷子杂交种长杂谷466、长杂谷2922和长杂谷333及其亲本为供试材料, 测定杂交种及其亲本的产量性状及生理指标, 对杂交种的产量优势及其影响因子进行系统分析, 初步解析了杂种优势的生理机制。结果表明, 在整个生育期内, 3个杂交种的叶绿素含量均高于双亲, 其中长杂谷466在拔节期的叶绿素含量最高, 达13.86 mg∙g-1 FW。在苗期和拔节期, 3个杂交种的根系活力均显著高于双亲, 其中长杂谷466在苗期的根系活力最高, 为1.76 mg∙g-1∙h-1, 分别为其父母本的7.8倍和5.5倍; 长杂谷2922在苗期的根系活力较父母本分别高0.38和0.66 mg∙g-1∙h-1; 而长杂谷333在拔节期优势更为显著, 较父母本分别高0.31和0.62 mg∙g-1∙h-1。在产量形成性状方面, 与双亲相比, 杂交种的灌浆速率和颖花数均显著提高, 长杂谷466在花后19天灌浆速率达最大值, 为1.58 g∙d-1 per panicle; 长杂谷466和长杂谷333颖花数极显著高于其亲本, 长杂谷2922颖花数显著增加。此外, 杂交种根系的氮素积累量和氮素转运效率也表现出一定的优势, 其中长杂谷2922根系氮素积累优势最大且氮素转运效率(近56%)最高, 显著高于其父本M22。综上表明, 长杂谷系列杂交种通过提高光合能力、养分吸收利用效率、籽粒灌浆速率和颖花数实现产量增加。
郭宇荣 , 刘红 , 王振华 , 田岗 , 刘鑫 , 郭杰 , 李春勇 , 李会霞 . 长杂谷系列谷子杂交种产量优势及其生理机制[J]. 植物学报, 2025 , 60(6) : 931 -943 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB24187
INTRODUCTION: In agricultural production, the utilization of heterosis has brought significant benefits to society and economic development by markedly increasing crop yield, stress resistance, and quality. Foxtail millet (Setaria italica var. germanica), as an important coarse grain crop in the arid and semi-arid regions of northern China, holds a significant position in dry land ecological agriculture. However, the slow increase in the yield of foxtail millet has limited the further realization of its production potential. Utilizing heterosis has thus become one of the effective ways to increase the yield of foxtail millet. Nevertheless, research on the physiological and molecular mechanisms of its heterosis is still relatively weak, and the mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, to understand the physiological mechanisms of heterosis in foxtail millet is of great importance for improving the yield of hybrid varieties.
RATIONALE: The Changzagu series of foxtail millet hybrids (Changzagu466, Changzagu2922, and Changzagu333) exhibit significant heterosis in yield. In order to elucidate its mechanism, we systematically analyzed the yield advantages of these hybrids and their influencing factors by measuring yield-related traits and key physiological indicators of the hybrids and their parental lines.
RESULTS: Throughout the entire growth period, the chlorophyll content of the three hybrid varieties was higher than that of their parents. Among them, Changzagu466 exhibited the highest chlorophyll content at the jointing stage, reaching 13.86 mg∙g-1 FW. During the seedling and jointing stages, the root activity of the three hybrids was significantly higher than that of their parents. Specifically, Changzagu466 showed the highest root activity at the seedling stage, measuring 1.76 mg∙g-1∙h-1, which was 7.8 times and 5.5 times higher than its female and male parents, respectively. The root activity values of Changzagu2922 at the seedling stage were 0.38 and 0.66 mg∙g-1∙h-1 higher than its female and male parents, respectively. Meanwhile, Changzagu333 displayed pronounced advantages at the jointing stage, with root activity values 0.31 and 0.62 mg∙g-1∙h-1 higher than its female and male parents, respectively. In terms of yield-related traits, compared to their parents, the hybrids showed significant improvements in both grain filling rate and spikelet number. Changzagu466 reached its maximum grain filling rate of 1.58 g∙d-1 per panicle at 19 days after flowering. Both Changzagu466 and Changzagu333 had significantly higher spikelet numbers than their parents, while Changzagu2922 also showed a significant increase in spikelet numbers. In addition, the hybrid varieties also demonstrate certain advantages in root nitrogen accumulation and nitrogen translocation efficiency. Among them, Changzagu2922 exhibits the strongest root nitrogen accumulation advantage and the highest nitrogen translocation efficiency (nearly 56%), both are significantly higher than that of its male parent line M22.
CONCLUSION: The Changzagu series of foxtail millet hybrids effectively enhances photosynthetic capacity, nutrient absorption and utilization efficiency by significantly increasing chlorophyll content, root activity during the early growth stages, and root nitrogen accumulation. Meanwhile, the significant increase in grain filling rate and spikelet number of the hybrids further enhances both grain weight and grain number per panicle, ultimately achieving high yield.
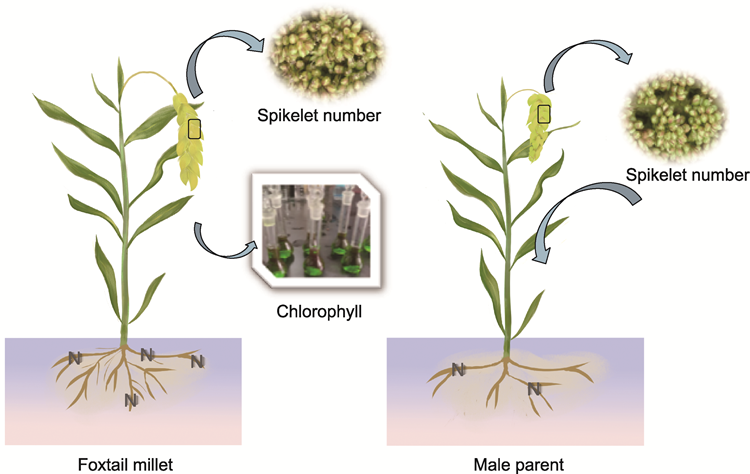
Foxtail millet and parental trait comparison chart

Key words: hybrid millet; physiological index; grain filling rate; agronomic traits; yield
| [1] | Chen YF (2015). Correlation between root activity and yield of different rice hybrid combinations. Jiangsu Agric Sci 43(12), 93-94. (in Chinese) |
| 陈云风 (2015). 不同水稻杂交组合根系活力及其产量相关性. 江苏农业科学 43(12), 93-94. | |
| [2] | Chuan XK, Yang CJ, Li GS, Yin PX, Wang JY, Kang HC, Zhang Y, Duan HP (2024). Heterosis and correlation analysis of main economic traits in high-altitude two-line japonica hybrid rice. Hybrid Rice 39(5), 40-46. (in Chinese) |
| 钏兴宽, 杨钏杰, 李国生, 尹鹏熙, 王锦艳, 康洪灿, 张义, 段浩平 (2024). 高原两系杂交粳稻主要经济性状杂种优势和相关性分析. 杂交水稻 39(5), 40-46. | |
| [3] | Du RQ, Li ZJ, Xiang YZ, Sun T, Liu XC, Shi HZ, Li WY, Huang XY, Tang ZJ, Lu JS, Chen JY, Zhang FC (2024). Drip fertigation increases maize grain yield by affecting phenology, grain filling process, biomass accumulation and translocation: a 4-year field trial. Plants 13, 1903. |
| [4] | Gao JF (2006). Experimental Guidance for Plant Physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press. pp. 74-77. (in Chinese) |
| 高俊凤 (2006). 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 74-77. | |
| [5] | Gou YJ, Zhu XY, Liu YG, Wang HY, Shen RX (2023). Genetic mechanism of heterosis utilization of key traits in indica-japonica rice. In: Proceedings of the 20th Chinese Crop Society Annual Meeting. Changsha: Chinese Crop Society. pp. 21. (in Chinese) |
| 苟亚军, 朱新宇, 刘耀光, 王海洋, 沈荣鑫 (2023). 籼粳稻杂种优势利用关键性状的遗传机理. 见: 第二十届中国作物学会学术年会论文摘要集. 长沙: 中国作物学会. pp. 21. | |
| [6] | Hou M (2023). Pan-genome Assembly of Maize Founder Inbred Lines and Analysis of Heterosis Mechanism. PhD dissertation. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. pp. 31-56. (in Chinese) |
| 侯美 (2023). 玉米骨干亲本自交系泛基因组组装及杂种优势机理解析. 博士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. pp. 31-56. | |
| [7] | Huang L, Gao Y, Li XQ, Qiu XQ, Shen XJ, Liu ZD, Uzokwe PA, Duan AW (2013). Effects of water stress on dry matter accumulation and translocation in winter wheat cultivars planted at different ages. Chin J Eco-Agric 21, 943-950. (in Chinese) |
| 黄玲, 高阳, 李新强, 邱新强, 申孝军, 刘战东, Uzokwe PA, 段爱旺 (2013). 水分胁迫下不同年代冬小麦品种干物质积累与转运特性. 中国生态农业学报 21, 943-950. | |
| [8] | Li DY, Huang ZY, Song SH, Xin YY, Mao DH, Lv QM, Zhou M, Tian DM, Tang MF, Wu Q, Liu X, Chen TT, Song XW, Fu XQ, Zhao BR, Liang CZ, Li AH, Liu GZ, Li SG, Hu SN, Cao XF, Yu J, Yuan LP, Chen CY, Zhu LH (2016). Integrated analysis of phenome, genome, and transcriptome of hybrid rice uncovered multiple heterosis-related loci for yield increase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E6026-E6035. |
| [9] | Li SY, Cui YJ, Dou BF, Liu ZL (2023). Research progress and discussion on related issues of heterosis utilization of foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] in China. Chin Agric Bull 39(9), 24-32. (in Chinese) |
| 李素英, 崔燕娇, 窦宝峰, 刘正理 (2023). 中国谷子杂优利用研究进展及相关问题的探讨. 中国农学通报 39(9), 24-32. | |
| [10] | Li SY, Liu D, Li Q, Dai XD, Han YL, Chen C, Li JX, Liu ZL (2018). Phenotype identification in heterosis of yield and yield traits of foxtail millet hybrids. J Henan Agric Sci 47(8), 28-34. (in Chinese) |
| 李素英, 刘丹, 李强, 代小冬, 韩燕丽, 陈超, 李君霞, 刘正理 (2018). 谷子杂交种产量及产量性状杂种优势的表现型鉴定. 河南农业科学 47(8), 28-34. | |
| [11] | Liu T, Xia WJ, Peng XA, Lu MA, Cao L, Zhang L, He XF, Zhu YL (2024). Effects of nitrogen fertilizer operation on grain filling, dry matter transport after anthesis and sugar content in wheat plants. J Sichuan Agric Univ 42, 771-779. (in Chinese) |
| 刘童, 夏文君, 彭小爱, 卢茂昂, 曹磊, 张玲, 何贤芳, 朱玉磊 (2024). 氮肥运筹对小麦籽粒灌浆、花后干物质转运及植株糖含量影响. 四川农业大学学报 42, 771-779. | |
| [12] | Lu HB, Li HQ, Gong XC, Qiao YM, Zhao ZH, Zhao NN (2016). Study on the heterobeltiosis characteristics of Zhangza millet during filling stage. Hubei Agric Sci 55, 293-295, 309. (in Chinese) |
| 卢海博, 李鸿强, 龚学臣, 乔永明, 赵治海, 赵娜娜 (2016). 张杂谷灌浆期杂种优势的研究. 湖北农业科学 55, 293-295, 309. | |
| [13] | Peng CL (2020). Effects of Different Agronomic Measures on Physiology, Fruit Yield and Quality of Tomato Cultivated in Medium. Master’s thesis. Alar: Tarim University. pp. 1-53. (in Chinese) |
| 彭翠兰 (2020). 不同农艺措施对基质栽培番茄生理、果实产量和品质的影响. 硕士论文. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学. pp. 1-53. | |
| [14] | Pi K, Huang Y, Duan LL, Mo ZJ, Luo W, Ke YZ, Wang PS, Zeng SB, Liu RX (2022). Performance of heterosis in tobacco roots and differential expression analysis of related genes. J Southern Agric 53, 3028-3036. (in Chinese) |
| 皮凯, 黄莺, 段丽丽, 莫泽君, 罗雯, 柯渔洲, 王平松, 曾帅波, 刘仁祥 (2022). 烟草根系杂种优势表现及相关基因差异表达分析. 南方农业学报 53, 3028-3036. | |
| [15] | Ren Q, Ma JJ, Sun XH, Guo XH, Duan Y, Li RF (2021). Effects of irrigation and fertilization methods on chlorophyll content and yield of waxy corn. Yellow River 43(11), 150-153. (in Chinese) |
| 任青, 马娟娟, 孙西欢, 郭向红, 段勇, 李若帆 (2021). 灌溉与施肥方式对糯玉米叶绿素与产量的影响. 人民黄河 43(11), 150-153. | |
| [16] | Shalby N, Mohamed IAA, Xiong J, Hu KN, Yang YBT, Nishawy E, Yi B, Wen J, Ma CZ, Shen JX, Fu TD, Tu JX (2021). Overdominance at the gene expression level plays a critical role in the hybrid root growth of Brassica napus. Int J Mol Sci 22, 9246. |
| [17] | Shi GS, Shi GY, Yang CY, Ma HF, Chen Y (2016). Grey correlative degree analysis and comprehensive evaluation of main agronomic characters of millet hybrids. J Agric 6(5), 1-5. (in Chinese) |
| 史根生, 史关燕, 杨成元, 麻慧芳, 陈瑛 (2016). 谷子杂交种主要农艺性状的灰色关联度分析及综合评价. 农学学报 6(5), 1-5. | |
| [18] | Shi GY, Wang XQ, Han YH, Yang CY, Ma HF, Zhao XW, Qiao ZJ (2021). Heterosis and genetic characteristics analysis for yield and quality related characters in Setaria italica. J Trop Subtrop Bot 29, 349-359. (in Chinese) |
| 史关燕, 王啸旗, 韩渊怀, 杨成元, 麻慧芳, 赵雄伟, 乔治军 (2021). 谷子产量和品质相关性状的杂种优势及遗传特性分析. 热带亚热带植物学报 29, 349-359. | |
| [19] | Song H, Wang T, Yan HS, Xing L, Xie HF, Li L, Wang SJ, Song ZQ, He Q, Liu JR, Feng BL (2022). Study on the relationship between the photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation, grain filling parameter and yield of different genotypes foxtail millet cultivars/lines. J China Agric Univ 27(7), 58-72. (in Chinese) |
| 宋慧, 王涛, 闫宏山, 邢璐, 解慧芳, 李龙, 王淑君, 宋中强, 何庆, 刘金荣, 冯佰利 (2022). 不同类型谷子品种(系)光合性能、干物质积累转运和籽粒灌浆特性对产量的影响. 中国农业大学学报 27(7), 58-72. | |
| [20] | Tang XW, Shi Y, Yu ZW, Zhang YL, Zhao JY (2020). Effect of soil moisture content at anthesis on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of wheat varieties with different spike types. J Triticeae Crops 40, 609-614. (in Chinese) |
| 唐兴旺, 石玉, 于振文, 张永丽, 赵俊晔 (2020). 开花期土壤水分含量对不同穗型小麦品种光合特性及产量的影响. 麦类作物学报 40, 609-614. | |
| [21] | Wang L, Zhang XP, Yan ZS, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Zhao HP, Tang HC, Ma SL, Lin ZR, Zhang ZQ, Cai XB (2024). Comparison of photosynthetic characteristics, grain filling characteristics and source-sink relationship among different types of barley. Acta Agric Boreali-Sin 39(3), 114-123. (in Chinese) |
| 王蕾, 张想平, 严宗山, 徐也, 张燕, 赵海鹏, 唐辉春, 马树琳, 蔺泽荣, 张自强, 蔡小斌 (2024). 不同类型大麦光合特性、灌浆特征差异及源库关系比较. 华北农学报 39(3), 114-123. | |
| [22] | Wei W, Zhao F, Zhang XL, Li SD, Song GL, Zhu XH, Zhao ZH (2019). Grey correlation degree analysis of main agronomic traits and yield of Zhangzagu millet. Bull Agric Sci Technol (9), 182-188. (in Chinese) |
| 魏玮, 赵芳, 张晓磊, 李双东, 宋国亮, 朱学海, 赵治海 (2019). 张杂谷谷子主要农艺性状与产量的灰色关联度分析. 农业科技通讯 (9), 182-188. | |
| [23] | Wu HX, Song XH, Waqas-Amjid W, Chen C, Zhang DY, Guo WZ (2024). Mining elite loci and candidate genes for root morphology-related traits at the seedling stage by genome-wide association studies in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). J Integr Agric 23, 3406-3418. |
| [24] | Wu LD, Liu YT, Qiu YH, Lin ST, Shang W, Li YQ, Zhang R, Zhong LQ (2024). Prediction of heterosis of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) pun-gency degree based on genetic distance and combining ability. J Southern Agric 55, 2580-2590. (in Chinese) |
| 吴立东, 刘亚婷, 邱胤晖, 林淑婷, 尚伟, 李永清, 张锐, 钟柳青 (2024). 基于遗传距离和配合力预测辣椒辣度杂种优势. 南方农业学报 55, 2580-2590. | |
| [25] | Xiao CL, Zhang HQ, Ma H (2015). Principle and Utilization of Plant Heterosis. Beijing: Higher Education Press. pp. 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| 肖层林, 张海清, 麻浩 (2015). 植物杂种优势原理与利用. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 1-2. | |
| [26] | Xu TJ, Zhang Y, Zhao JR, Wang RH, Lü TF, Liu HW, Liu YE, Cai WT, Zhang RY, Song W, Xing JF, Wang YD (2021). Evaluation of grain filling and dehydration rate of maize inbred lines in different heterosis groups. J Plant Genet Resour 22, 1595-1605. (in Chinese) |
| 徐田军, 张勇, 赵久然, 王荣焕, 吕天放, 刘宏伟, 刘月娥, 蔡万涛, 张如养, 宋伟, 邢锦丰, 王元东 (2021). 不同杂种优势群玉米自交系籽粒灌浆和脱水速率评价. 植物遗传资源学报 22, 1595-1605. | |
| [27] | Yang YJ, Guo PY, Cao YF, Wang HF, Wang YG, Yuan XY, Xing GF, Shao DH, Qi X, Xie LL, Nie ME, Guo J, Ning N (2012). Effects of fertilizer and planting density on yield and yield components in foxtail millet hybrid Zhangzagu5. Acta Agron Sin 38, 2278-2285. (in Chinese) |
| 杨艳君, 郭平毅, 曹玉凤, 王宏富, 王玉国, 原向阳, 邢国芳, 邵东红, 祁祥, 解丽丽, 聂萌恩, 郭俊, 宁娜 (2012). 施肥水平和种植密度对张杂谷5号产量及其构成要素的影响. 作物学报 38, 2278-2285. | |
| [28] | Zhang X, Feng YZ (2017). Analysis of main agronomic characters and yield of different millet varieties in Shenmu County. Acta Agric Boreali-Occident Sin 26, 32-37. (in Chinese) |
| 张霞, 冯永忠 (2017). 神木县不同谷子品种主要农艺性状及产量分析. 西北农业学报 26, 32-37. | |
| [29] | Zhang XC, Liu XL, Wang L, Zhao QC, Yu Y, Du RR, Xu YD, Zhen WC, Wang YD (2024). Wheat yield and grain-filling characteristics due to cultivar replacement in the Haihe Plain in China. Front Plant Sci 15, 1374453. |
| [30] | Zhou H, Dai LJ, Li YP, Huang XL, Ma YP (2020). Grey correlation analysis and evaluation of main agronomic characters of 11 new millet cultivars. Gansu Agric Sci Technol (12), 25-30. (in Chinese) |
| 周花, 戴丽君, 李永平, 黄小兰, 马亚平 (2020). 11个谷子新品种的主要农艺性状灰色关联度分析与综合评价. 甘肃农业科技 (12), 25-30. | |
| [31] | Zhu CC, Fu SJ, Qin N, Wang CY, Dai ST, Song YH, Wei X, Li JX (2023). Effects of phosphorus fertilizer application depth on root distribution, nitrogen uptake and utilization and yield of foxtail millet. J Henan Agric Sci 52(12), 22-30. (in Chinese) |
| 朱灿灿, 付森杰, 秦娜, 王春义, 代书桃, 宋迎辉, 魏昕, 李君霞 (2023). 磷肥施用深度对谷子根系分布、氮素吸收利用和产量的影响. 河南农业科学 52(12), 22-30. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |