

植物学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 257-264.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15086 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15086
白云俊1,2,7, 魏雪苹1,3,7, 秦锋4, 李亚蒙5, 李金锋1, Parminder S. Ranhotra6, 王宇飞1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2015-05-18
接受日期:2015-08-04
出版日期:2016-03-01
发布日期:2016-03-31
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Yunjun Bai1,2,7, Xueping Wei1,3,7, Feng Qin4, Yameng Li5, Jinfeng Li1, Parminder S. Ranhotra6, Yufei Wang1,*( )
)
Received:2015-05-18
Accepted:2015-08-04
Online:2016-03-01
Published:2016-03-31
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要: 上新世−更新世过渡期是新生代全球气候变化的重要拐点之一, 此期气候经历了由“暖室”向“冰室”的转变。研究该气候转型期的特征可为科学界和国家层面应对现在和未来的全球气候变暖提供理论基础和实践指导。通过深入研究中国华北山西榆社盆地张村组上新世−更新世过渡期地层中保存的植物大化石、孢粉以及硅藻组合, 为重建该时段陆地生态系统中植被演替和气候变化提供坚实的生物学证据。在综合回顾张村组化石植物研究历史的基础上, 侧重介绍最近5年在古植被、古气候、古环境以及古大气CO2浓度重建等方面的最新进展。这些新成果定性及定量地刻画了第三纪−第四纪之交中国北方黄土高原东南缘气候变干、变凉的转型过程及其陆地生态系统中大气CO2浓度先升后降的变化趋势。
白云俊, 魏雪苹, 秦锋, 李亚蒙, 李金锋, Parminder S. Ranhotra, 王宇飞. 华北上新世−更新世过渡期植被、气候与大气CO2研究进展. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 257-264.
Yunjun Bai, Xueping Wei, Feng Qin, Yameng Li, Jinfeng Li, Parminder S. Ranhotra, Yufei Wang. Research Highlights of the Vegetation, Climate and Atmospheric CO2 in Yushe Basin, Shanxi, North China During the Plio-Pleistocene Transition. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 257-264.
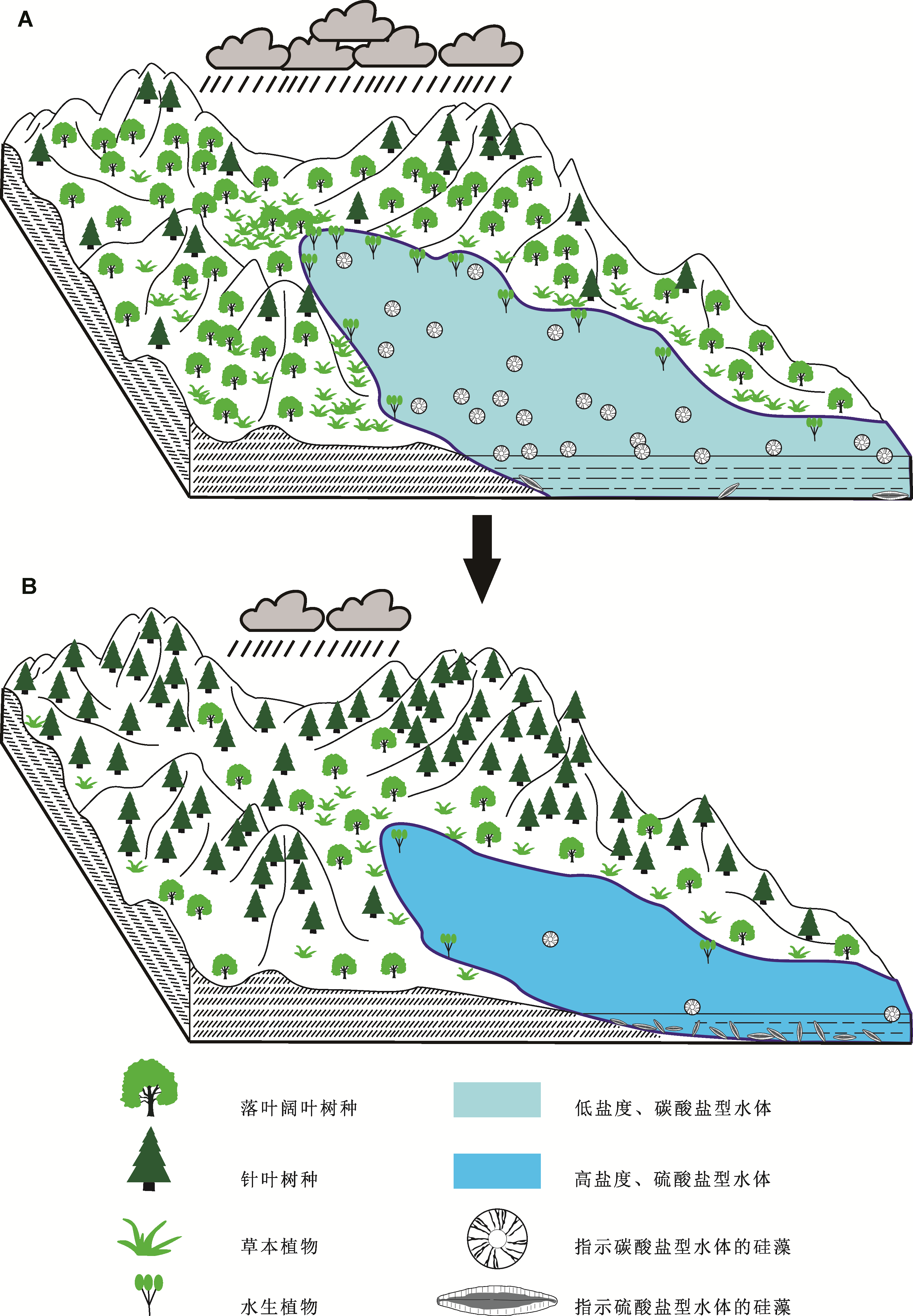
图1 中国华北张村地区上新世−更新世过渡期古环境由温暖湿润(A)向寒冷干燥(B)演化示意图
Figure 1 The sketch map of paleoenvironmental evolution from warm and wet (A) to cold and dry (B) during the Plio-Pleistocene transition in Zhangcun region, Shanxi, North China
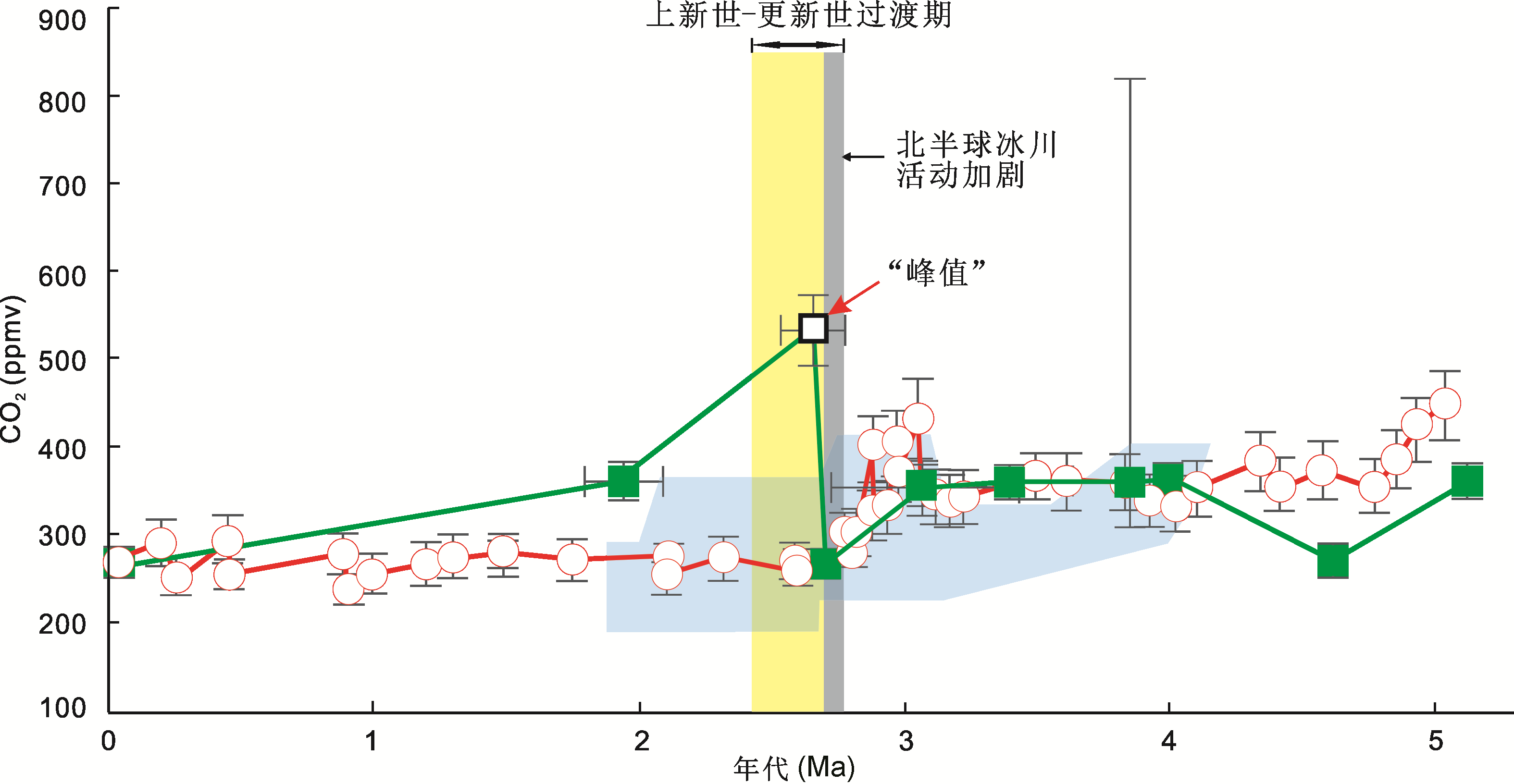
图2 5 Ma以来古CO2浓度变化(改自Bai et al., 2015) 绿线连接的是利用气孔参数重建的古大气CO2浓度; 红线连接的是基于海相酮及硼同位素重建的古水合CO2浓度; 水平浅蓝色阴影指示基于海相硼同位素重建的古水合CO2浓度。
Figure 2 Reconstructed paleo-CO2 since 5 Ma (modified from Bai et al., 2015) The green line indicates the paleo-[CO2]atm estimated by stomatal parameters; the red line indicates the paleo-[CO2]aq estimated by marine alkenone and boron isotope; the horizontal light blue shade indicates the paleo-[CO2]aq estimated by marine boron isotope.
| [1] | 曹家欣, 崔海亭 (1989). 山西榆社盆地上新世植物群及其环境意义. 地质科学 24, 369-375. |
| [2] | 方小敏, 吴福莉, 韩文霞, 王亚东, 张玺正, 张伟林 (2008). 上新世-第四纪亚洲内陆干旱化过程——柴达木中部鸭湖剖面孢粉和盐类化学指标证据. 第四纪研究 28, 874-882. |
| [3] | 秦锋, 杨健, 李金锋, 刘海明, 王宇飞 (2010). 中国山西张村上新世气候与海拔的初步研究. 地学前缘 17, 345-360. |
| [4] | 吴靖宇 (2009). 云南腾冲上新世团田植物群及其古环境分析. 博士论文. 兰州: 兰州大学. pp. 1-121. |
| [5] | An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001). Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411, 62-66. |
| [6] | Bai YJ, Chen LQ, Ranhotra PS, Wang Q, Wang YF, Li CS (2015). Reconstructing atmospheric CO2 during the Plio-Pleistocene transition by fossil Typha. Glob Change Biol 21, 874-881. |
| [7] | Bartoli G, Hönisch B, Zeebe RE (2011). Atmospheric CO2 decline during the Pliocene intensification of Northern Hemisphere glaciations. Paleoceanography 26, PA4213. |
| [8] | Beerling DJ, Birks HH, Woodward FI (1995). Rapid late-glacial atmospheric CO2 changes reconstructed from the stomatal density record of fossil leaves. J Quaternary Sci 10, 379-384. |
| [9] | Beerling DJ, Royer DL (2011). Convergent Cenozoic CO2 history. Nat Geoscience 4, 418-420. |
| [10] | Bintanja R, van de Wal RSW (2008). North American ice-sheet dynamics and the onset of 100,000-year glacial cycles. Nature 454, 869-872. |
| [11] | Bonnefille R (2010). Cenozoic vegetation, climate changes and hominid evolution in tropical Africa. Glob Planet Change 72, 390-411. |
| [12] | Coxall HK, Wilson PA, Pälike H, Lear CH, Backman J (2005). Rapid stepwise onset of Antarctic glaciation and deeper calcite compensation in the Pacific Ocean. Nature 433, 53-57. |
| [13] | Davis OK, Moutoux TE (1998). Tertiary and Quaternary vegetation history of the Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. J Paleolimnol 19, 417-427. |
| [14] |
DeMenocal PB (1995). Plio-Pleistocene African climate. Science 270, 53-59.
PMID |
| [15] | Ding ZL, Derbyshire E, Yang SL, Sun JM, Liu TS (2005). Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution. Earth Planet Sc Lett 237, 45-55. |
| [16] | Etourneau J, Khélifi N (2010). Workshop on Pliocene climate. Scientific Drilling 9, 52-53. |
| [17] | Etourneau J, Schneider R, Blanz T, Martinezb P (2010). Intensification of the Walker and Hadley atmospheric circulations during the Pliocene-Pleistocene climate transition. Earth Planet Sc Lett 297, 103-110. |
| [18] | Guo ZT, Peng SZ, Hao QZ, Biscaye PE, An ZS, Liu TS (2004). Late Miocene-Pliocene development of Asian aridification as recorded in the Red-Earth Formation in northern China. Global Planet Change 41, 135-145. |
| [19] | Haug GH, Ganopolski A, Sigman DM, Rosell-Mele A, Swann GEA, Tiedemann R, Jaccard SL, Bollmann J, Maslin MA, Leng MJ (2005). North Pacific seasonality and the glaciation of North America 2.7 million years ago. Nature 433, 821-825. |
| [20] | Iwauchi A (1994). Late Cenozoic vegetational and climatic changes in Kyushu, Japan. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl Palaeoecol 108, 229-280. |
| [21] |
Kürschner WM, Kvacek Z, Dilcher DL (2008). The impact of Miocene atmospheric carbon dioxide fluctuations on climate and the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 449-453.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Kürschner WM, van der Burgh J, Visscher H, Dilcher DL (1996). Oak leaves as biosensors of late Neogene and early Pleistocene paleoatmospheric CO2concentrations. Mar Micropaleontol 27, 299-312. |
| [23] | Li XQ, Li CS, Lu HY, Dodson JR, Wang YF (2004). Paleo- vegetation and paleoclimate in middle-late Pliocene, Shanxi, central China. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl Palaeoecol 210, 57-66. |
| [24] | Li YM, Ferguson DK, Zhao Q, Wang YF, Wang RX, Li CS (2015). Diatom-inferred salinity changes from the Yushe paleolake indicate an aridification during the Pliocene- Pleistocene transition in north China. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl Palaeoecol 417, 544-553. |
| [25] | Liu GW, Leopold EB, Liu Y, Wang WM, Yu ZY, Tong GB (2002). Palynological record of Pliocene climate events in North China. Rev Palaeobot Palyno 119, 335-340. |
| [26] | Liu XQ, Li CS, Wang YF (2005). Bolboschoenus (Ascherson) Palla (Cyperaceae) from Pliocene of China. J Integr Plant Biol 47, 524-529. |
| [27] | Locker S, Martini E (1989). Phytoliths at DSDP Site 591 in the southwest Pacific and the aridification of Australia. Geol Rundsch 78, 1165-1172. |
| [28] | Lu H, Wang X, Li L (2010). Aeolian sediment evidence that global cooling has driven late Cenozoic stepwise aridification in central Asia. In: Clift PD, Tada R, Zheng H, eds. Monsoon Evolution and Tectonics-Climate Linkage in Asia. Vol. 342. London: Geological Society, Special Publications. pp. 29-44. |
| [29] | Lunt DJ, Foster GL, Haywood AM, Stone EJ (2008). Late Pliocene Greenland glaciation controlled by a decline in atmospheric CO2 levels. Nature 454, 1102-1105. |
| [30] | Maslin MA, Haug GH, Sarnthein M, Tiedemann R (1996). The progressive intensification of northern hemisphere glaciation as seen from the North Pacific. Geol Rundsch 85, 452-465. |
| [31] | Maslin MA, Li XS, Loutre MF, Berger A (1998). The contribution of orbital forcing to the progressive intensification of Northern Hemisphere glaciation. Quaternary Sci Rev 17, 411-426. |
| [32] | Momohara A (1994). Floral and paleoenvironmental history from the late Pliocene to middle Pleistocene in and around central Japan. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl Palaeoecol 108, 281-293. |
| [33] | Mudelsee M, Raymo ME (2005). Slow dynamics of the Northern Hemisphere glaciation. Paleoceanography 20, PA4002. |
| [34] | Pearson PN, Foster GL, Wade BS (2009). Atmospheric carbon dioxide through the Eocene-Oligocene climate transition. Nature 461, 1110-1113. |
| [35] | Qiang XK, Li ZX, Powell CA, Zheng HB (2001). Magnetostratigraphic record of the Late Miocene onset of the East Asian monsoon, and Pliocene uplift of northern Tibet. Earth Planet Sc Lett 187, 83-93. |
| [36] | Qin F, Ferguson DK, Zetter R, Wang YF, Syabryaj S, Li JF, Yang J, Li CS (2011). Late Pliocene vegetation and climate of Zhangcun region, Shanxi, North China. Glob Change Biol 17, 1850-1870. |
| [37] | Ravelo AC, Andreasen DH, Lyle M, Olivarez Lyle A, Wara MW (2004). Regional climate shifts caused by gradual global cooling in the Pliocene epoch. Nature 429, 263-267. |
| [38] |
Reed KE (1997). Early hominid evolution and ecological change through the African Plio-Pleistocene. J Hum Evol 32, 289-322.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Rohling EJ, Foster GL, Grant KM, Marino G, Roberts AP, Tamisiea ME, Williams F (2014). Sea-level and deep- sea-temperature variability over the past 5.3 million years. Nature 508, 477-482. |
| [40] |
Royer DL (2001). Stomatal density and stomatal index as indicators of paleoatmospheric CO2 concentration. Rev Palaeobot Palyno 114, 1-28.
PMID |
| [41] | Ruddiman WF, Kutzbach JE (1989). Forcing of late Cenozoic Northern Hemisphere climate by plateau uplift in southern Asia and the American west. J Geophys Res (1984-2012) 94, 18409-18427. |
| [42] | Rundgren M, Beerling DJ (1999). A Holocene CO2 record from the stomatal index of subfossil Salix herbacea L. leaves from northern Sweden. Holocene 9, 509-513. |
| [43] | Seki O, Foster GL, Schmidt DN, Mackensen A, Kawamura K, Pancost RD (2010). Alkenone and boron-based Pliocene pCO2 records. Earth Planet Sc Lett 292, 201-211. |
| [44] | Shi N, Cao JX, Königsson LK (1993). Late Cenozoic vegetational history and the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary in the Yushe basin, S. E. Shanxi, China. Grana 32, 260-271. |
| [45] | Stults DZ, Wagner-Cremer F, Axsmith BJ (2011). Atmospheric paleo-CO2 estimates based on Taxodium distichum (Cupressaceae) fossils from the Miocene and Pliocene of Eastern North America. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl Palaeoecol 309, 327-332. |
| [46] | Tripati AK, Roberts CD, Eagle RA (2009). Coupling of CO2 and ice sheet stability over major climate transitions of the last 20 million years. Science 326, 1394-1397. |
| [47] |
van der Burgh J, Visscher H, Dilcher DL, Kürschner WM (1993). Paleoatmospheric signatures in Neogene fossil leaves. Science 260, 1788-1790.
PMID |
| [48] | Wagner F, Kouwenberg LLR, van Hoof TB, Visscher H (2004). Reproducibility of Holocene atmospheric CO2 records based on stomatal frequency. Quaternary Sci Rev 23, 1947-1954. |
| [49] | Woodward FI (1987). Stomatal numbers are sensitive to increases in CO2from pre-industrial levels. Nature 327, 617-618. |
| [50] | Wu FL, Fang XM, Herrmann M, Mosbrugger V, Miao YF (2011). Extended drought in the interior of Central Asia since the Pliocene reconstructed from sporopollen records. Glob Planet Change 76, 16-21. |
| [51] | Xie SP, Sun BN, Wu JY, Lin ZC, Yan DF, Liang X (2012). Palaeoclimatic estimates for the late Pliocene based on leaf physiognomy from western Yunnan, China. Turk J Earth Sci 21, 251-261. |
| [52] |
Zachos JC (2001) Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 292, 686-693.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Zachos JC, Dickens GR, Zeebe RE (2008). An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics. Nature 451, 279-283. |
| [54] | Zachos JC, Quinn TM, Salamy KA (1996). High-resolution (104 years) deep-sea foraminiferal stable isotope records of the Eocene-Oligocene climate transition. Paleoceano- graphy 11, 251-266. |
| [55] | Zhang YG, Pagani M, Liu ZH, Bohaty SM, DeConto R (2013). A 40-million-year history of atmospheric CO2. Philos T Roy Soc A 371, 20130096. |
| [56] | Zhao LC, Collinson ME, Li CS (2004). Fruits and seeds of Ruppia (Potamogetonaceae) from the Pliocene of Yushe Basin, Shanxi, northern China and their ecological implications. Bot J Linn Soc 145, 317-329. |
| [1] | 张琳, 袁伟影, 宋创业, 吴冬秀. 1998~2010年中国典型生态系统环境要素、物种丰富度和生物量动态数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(典型生态系统数据集): 1-. |
| [2] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [3] | 王堃莹, 邱贵福, 刘子赫, 孟君, 刘宇轩, 贾国栋. 气候变化对不同退化程度小叶杨林分生长和内在水分利用效率的调节[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 343-355. |
| [4] | 史倩, 同小娟, 许玲玲, 孟平, 于裴洋, 李俊, 杨铭鑫. 油松早晚材径向生长对气候因子的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(8): 988-1000. |
| [5] | 张鹏, 焦亮, 薛儒鸿, 魏梦圆, 杜达石, 吴璇, 王旭鸽, 李倩. 干旱强度影响祁连山西段不同海拔青海云杉的生长恢复[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(8): 977-987. |
| [6] | 陈以恒, 玉素甫江•如素力, 阿卜杜热合曼•吾斯曼. 2001-2020年天山新疆段草地植被覆盖度时空变化及驱动因素分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(5): 561-576. |
| [7] | 梁逸娴, 王传宽, 臧妙涵, 上官虹玉, 刘逸潇, 全先奎. 落叶松径向生长和生物量分配对气候变暖的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 459-468. |
| [8] | 臧妙涵, 王传宽, 梁逸娴, 刘逸潇, 上官虹玉, 全先奎. 基于纬度移栽的落叶松叶、枝、根生态化学计量特征对气候变暖的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 469-482. |
| [9] | 吴茹茹, 刘美珍, 谷仙, 常馨月, 郭立月, 蒋高明, 祁如意. 气候变化对巨柏适宜生境分布的潜在影响和预测[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 445-458. |
| [10] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [11] | 张计深, 史新杰, 刘宇诺, 吴阳, 彭守璋. 气候变化下中国潜在自然植被生态系统碳储量动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 428-444. |
| [12] | 张启, 程雪寒, 王树芝. 北京西山老龄树记载的森林干扰历史[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(3): 341-348. |
| [13] | 杨宇萌, 来全, 刘心怡. 气候变化和人类活动对内蒙古植被总初级生产力的定量影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(3): 306-316. |
| [14] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [15] | 郭强, 韩子琛, 夏允, 杨柳明, 范跃新, 杨玉盛. 土壤微生物固碳机理及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(11): 1406-1421. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||