

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 559-578.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22031 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22031
收稿日期:2022-02-22
接受日期:2022-05-10
出版日期:2022-09-01
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
朱瑞良
作者简介:*E-mail: rlzhu@bio.ecnu.edu.cn基金资助:Received:2022-02-22
Accepted:2022-05-10
Online:2022-09-01
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
Zhu Ruiliang
About author:*E-mail: rlzhu@bio.ecnu.edu.cn摘要: 全球气候变暖是人类面临最严峻的环境挑战。有效控制碳排放, 充分发挥生态系统的固碳能力是实现碳中和目标的重要手段。作为碳封存能力最强的一种湿地类型, 泥炭地是加快实现碳中和目标的关键陆地生态系统。作为泥炭地“有效的生态系统工程师”, 泥炭藓(Sphagnum)在泥炭地的碳汇功能、过滤淡水及保护土地免受洪水侵袭等方面具有极其重要的作用。100多年来, 泥炭藓广泛应用于医药保健、污染监测和废水处理等领域, 尤其是作为一类最值得信赖的土壤介质和保湿材料一直被广泛用于园艺产业。在全球气候变暖和“双碳”目标的大背景下, 泥炭藓已经成为生命科学和生态学研究的热点。该文主要从泥炭藓的形态、物种多样性和起源、生境与分布、繁殖和保护、培养与种植、环境指示和监测、用途和应用, 以及碳封存、储水和酸化能力等方面进行综述, 旨在为泥炭藓研究、泥炭地的保护和恢复以及泥炭藓开发利用和产业发展提供借鉴与参考。
朱瑞良. 泥炭藓: 一类具有重要生态、经济和科学价值的碳封存植物. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 559-578.
Zhu Ruiliang. Peat Mosses (Sphagnum): Ecologically, Economically, and Scientifically Important Group of Carbon Sequestration Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 559-578.

图1 泥炭藓的二型性 (A) 野生居群(bar=4 mm); (B) 细胞的二型性: 透明细胞和绿色细胞(bar=10 μm); (C), (D) 叶的二型性(bars=200 μm): (C) 茎叶; (D) 枝叶; (E) 枝的二型性: 左边箭头示展枝, 右边箭头示垂枝(bar=3 mm)。凭证标本为朱瑞良20181128-100 (HSNU)。
Figure 1 Dimorphism of Sphagnum palustre (A) Native population (bar=4 mm); (B) Dimorphism of cells: hyalocyst and chlorocyst (bar=10 μm); (C), (D) Dimorphism of leaves (bars=200 μm): (C) stem leaf; (D) branch leaf; (E) Dimorphism of branches, spreading branch (left arrow) and pendent branch (right arrow) (bar=3 mm). All from voucher specimen RL Zhu 20181128-100 (HSNU).
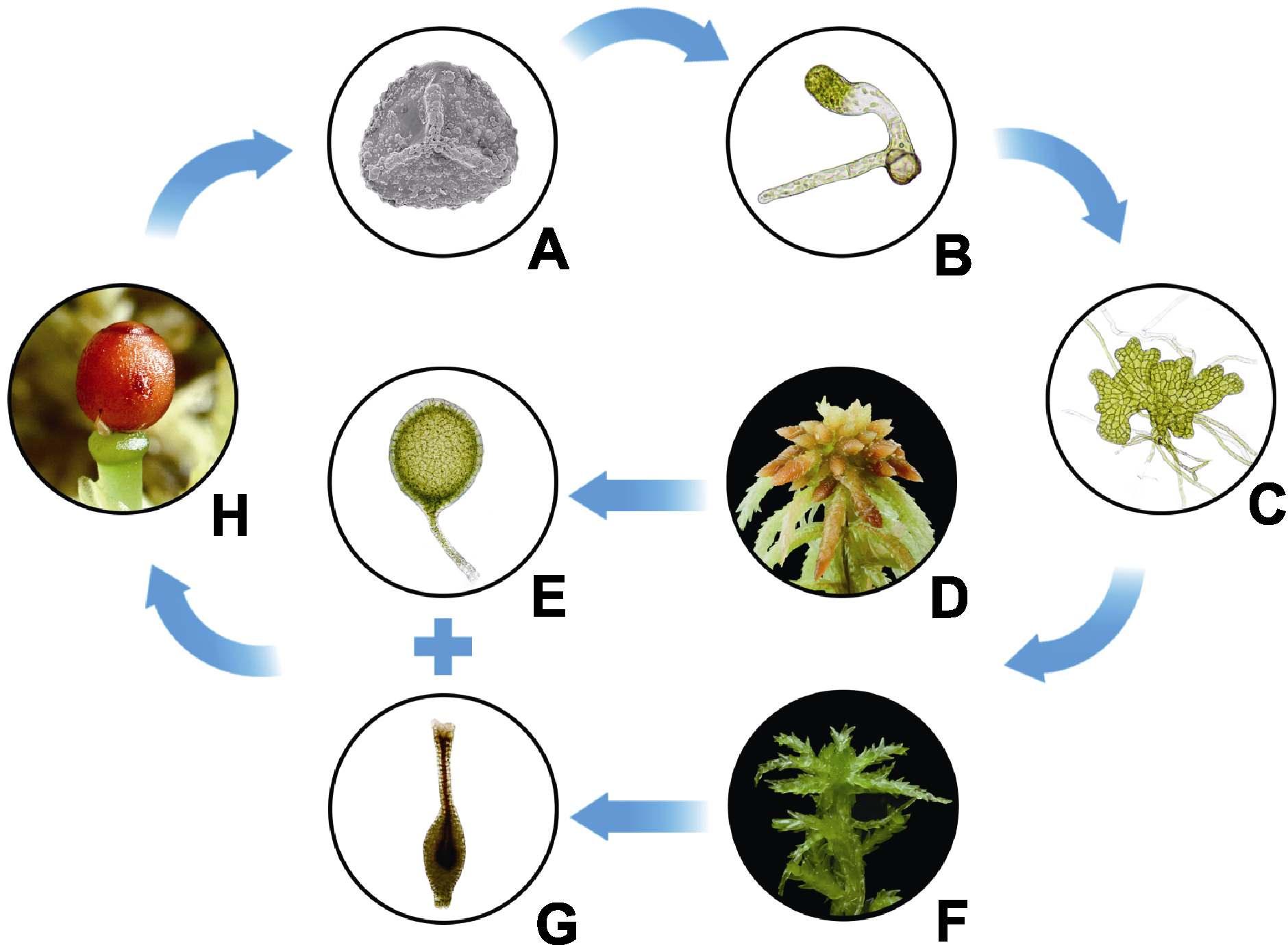
图2 泥炭藓的生活史 (A) 孢子(扫描电镜, 近轴面); (B) 丝状原丝体; (C) 叶状原丝体; (D) 配子体(雄株); (E) 精子器; (F) 配子体(雌株); (G) 颈卵器; (H) 孢子体(含孢蒴基部残留的颈卵器)
Figure 2 Life cycle of Sphagnum palustre (A) Spore (proximal view from scanning electron microscope); (B) Filamentous protonema; (C) Thalloid protonema; (D) Male gametophyte; (E) Antheridium; (F) Female gametophyte; (G) Archegonium; (H) Sporophyte (with an archegonium unfertilized at the bottom of capsule)

图3 我国南方代表性泥炭藓生境 (A) 高山湖泊周围湿地(云南高黎贡山, 海拔3 552 m; 各种泥炭藓); (B) 森林河岸(四川达古冰川, 海拔3 597 m; 粗叶泥炭藓); (C) 高山针叶林林下(云南高黎贡山, 海拔2 951 m; 刺叶泥炭藓); (D) 林缘岩石(浙江凤阳山, 海拔1 270 m; 泥炭藓和暖地泥炭藓)
Figure 3 Representative habitats of Sphagnum in Southern China (A) Wetlands around alpine lakes (Gaoligong Mountain, Yunnan, 3 552 m; various peat moss); (B) Riverbank of forests (Dagu glacier, Sichuan, 3 597 m; S. squarrosurn); (C) Understory of alpine coniferous forest (Gaoligong Mountain, Yunnan, 2 951 m; S. pungifolium); (D) Forest edge rock (Fengyangshan, Zhejiang, 1 270 m; S. palustre and S. junghuhnianum)

图4 我国东北泥炭地的泥炭藓群落 (A) a: 锈色泥炭藓; b: 桧叶金发藓; c: 赤茎藓; d: 小叶泥炭藓; e: 阔边泥炭藓(凭证标本为马晓英等20210815-21 (HSNU)); (B) a: 毛壁泥炭藓; b: 阔边泥炭藓; c: 神奇泥炭藓; d: 皱蒴藓(凭证标本为马晓英等20210813-13 (HSNU))。Bars=5 mm
Figure 4 Sphagnum communities in peatland of northeast China (A) a: S. fuscum; b: Polytrichum juniperinum; c: Pleurozium schreberi; d: S. angustifolium; e: S. warnstorfii (Voucher specimen XY Ma et al. 20210815-21 (HSNU)); (B) a: S. imbricatum; b: S. warnstorfii; c: S. divinum; d: Aulacomnium palustre (Voucher specimen XY Ma et al. 20210813-13 (HSNU)). Bars=5 mm
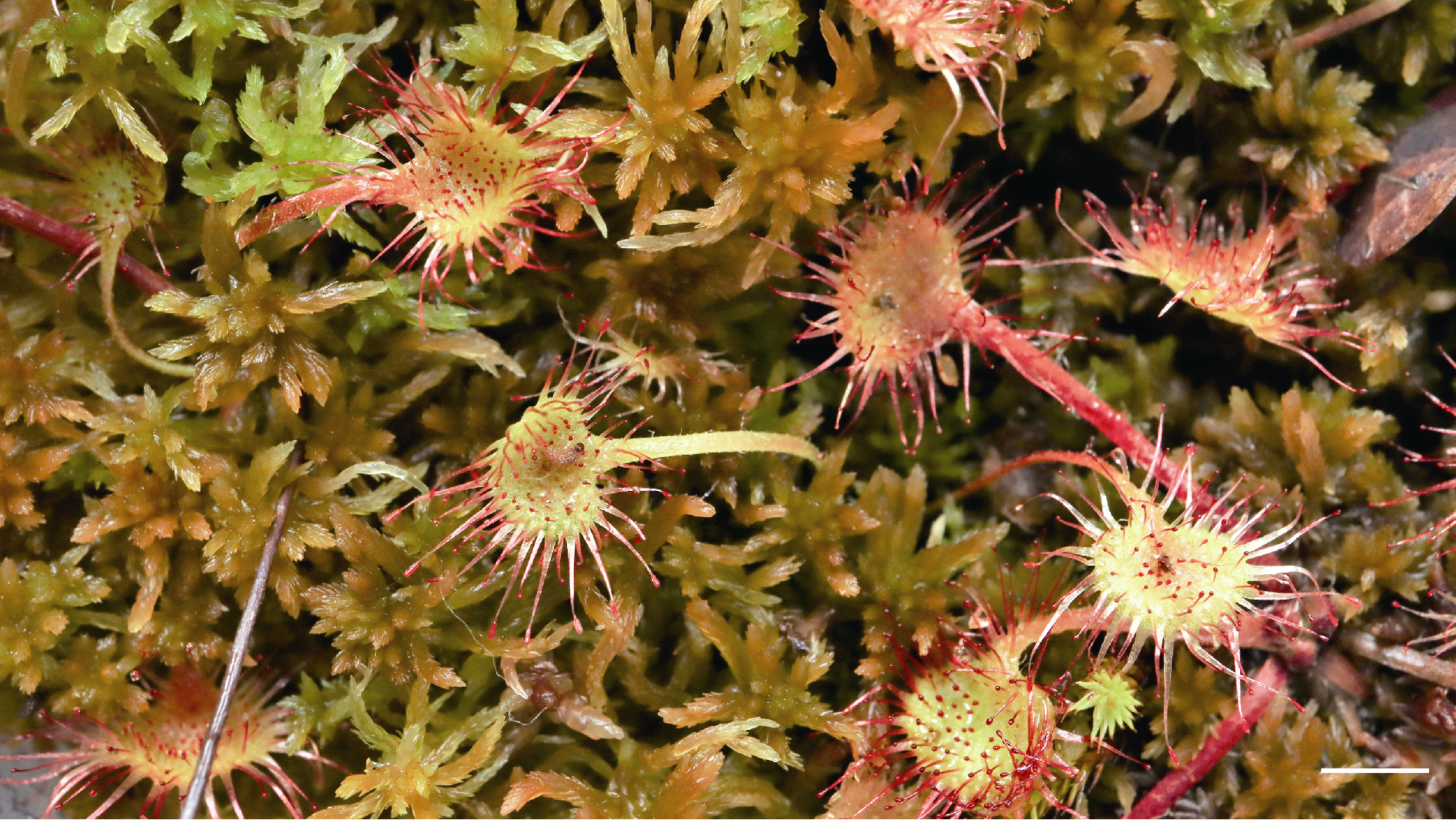

图5 我国东北泥炭地的锈色泥炭藓与食虫植物圆叶茅膏菜 Bar=3 mm
Figure 5 Sphagnum fuscum and the carnivorous plant Drosera rotundifolia on the peatland of northeast China Bar=3 mm
| 中文名(植物学名) | 分布 | 生境 |
|---|---|---|
| 印尼泥炭藓(新拟名) (Sphagnum antarense) | 新几内亚和苏拉威西 | 海拔3000 m以上的云雾林 |
| 斯里兰卡泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. ceylonicum) | 斯里兰卡 | 云雾林 |
| 吕宋泥炭藓(S. luzonense) | 中国、泰国、菲律宾和越南 | 高海拔或中海拔的酸性贫营养到中营养沼泽 |
| 尼泊尔泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. nepalense) | 尼泊尔 | 不详 |
| 新几内亚泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. novoguineense) | 布干维尔、印度尼西亚和新几内亚 | 高海拔云雾林林缘或洼地 |
| 卵叶泥炭藓(S. ovatum) | 中国、印度、尼泊尔和泰国 | 高海拔酸性贫营养到中营养沼泽 |
表1 亚洲濒危泥炭藓及其生境
Table 1 Endangered peat mosses and their habitats in Asia
| 中文名(植物学名) | 分布 | 生境 |
|---|---|---|
| 印尼泥炭藓(新拟名) (Sphagnum antarense) | 新几内亚和苏拉威西 | 海拔3000 m以上的云雾林 |
| 斯里兰卡泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. ceylonicum) | 斯里兰卡 | 云雾林 |
| 吕宋泥炭藓(S. luzonense) | 中国、泰国、菲律宾和越南 | 高海拔或中海拔的酸性贫营养到中营养沼泽 |
| 尼泊尔泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. nepalense) | 尼泊尔 | 不详 |
| 新几内亚泥炭藓(新拟名) (S. novoguineense) | 布干维尔、印度尼西亚和新几内亚 | 高海拔云雾林林缘或洼地 |
| 卵叶泥炭藓(S. ovatum) | 中国、印度、尼泊尔和泰国 | 高海拔酸性贫营养到中营养沼泽 |
| [1] | 卜兆君, 王升忠, 谢宗航 (2005). 泥炭沼泽学若干基本概念的再认识. 东北师大学报(自然科学版) 37, 105-110. |
| [2] | 陈邦杰, 黎兴江 (1956). 中国泥炭藓属植物的初步观察. 植物分类学报 5, 165-203. |
| [3] | 陈治民, 潘银山 (2017). 海花草种植技术研究与探讨. 农业开发与装备 (4), 140. |
| [4] | 韩锦华, 张朝晖, 王智慧 (2022). 水位控制对农田泥炭藓产量影响的研究. 生态学报 42, 1-10. |
| [5] | 贺琼 (2017). 神奇的泥炭藓. 大自然 (3), 12-15. |
| [6] | 晋建勇, 孟宪民 (2006). 国外泥炭藓种植业的研究进展. 腐植酸 (5), 6-8, 17. |
| [7] | 黎兴江 (1984). 西藏泥炭藓属一新种. 云南植物研究 6, 77-78. |
| [8] | 黎兴江 (1993). 中国泥炭藓属的新种及新记录种. 云南植物研究 15, 257-259. |
| [9] | 黎兴江 (1994). 泥炭藓科. 见: 高谦主编. 中国苔藓志, 第1卷. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 2-54. |
| [10] | 鲁兆莉, 覃海宁, 金效华, 张志翔, 杨庆文, 洪德元, 李德铢, 李开凡, 袁良琛, 周志华 (2021). 《国家重点保护野生植物名录》调整的必要性、原则和程序. 生物多样性 29, 1577-1582. |
| [11] | 麻俊虎, 彭涛, 李大华 (2017). 中国泥炭藓属植物研究进展. 贵州师范大学学报( 自然科学版) 35(1), 114-120. |
| [12] | 王利松, 贾渝, 张宪春, 覃海宁 (2018). 中国生物物种名录, 第1卷. 植物总名录. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 134-136. |
| [13] | 杨盼盼, 刘宇, 卜兆君, 马进泽, 王升忠, 陈旭, 杨云荷 (2019). 水位提升和泥炭藓繁殖体移植对泥炭地植被恢复的影响. 植物研究 39, 699-706. |
| [14] | Anderson LE, Crosby MR (1965). The protonema of Sphagnum meridense (Hampe) C. Muell. Bryologist 68, 47-54. |
| [15] | Baker RGE, Boatman DJ (1992). The effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon dioxide on cell development in branch leaves of Sphagnum. J Bryol 17, 35-46. |
| [16] | Bang S, Lee SW, Kim JY, Yu DI, Kang YK, Kim KW (2006). Adsorption of cadmium, copper, and lead on Sphagnum peat moss. Econ Environ Geol 39, 103-109. |
| [17] | Beike AK, Spagnuolo V, Lüth V, Steinhart F, Ramos- Gómez J, Krebs M, Adamo P, Rey-Asensio AI, Fernández JA, Giordano S, Decker EL, Reski R (2015). Clonal in vitro propagation of peat mosses (Sphagnum L.) as novel green resources for basic and applied research. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120, 1037-1049. |
| [18] | Bengtsson F, Rydin H, Baltzer JL, Bragazza L, Bu ZJ, Caporn SJM, Dorrepaal E, Flatberg KI, Galanina O, Gałka M, Ganeva A, Goia I, Goncharova N, Hájek M, Haraguchi A, Harris LI, Humphreys E, Jiroušek M, Kajukalo K, Karofeld R, Kooronatova NG, Kosykh NP, Laine AM, Lamentowicz M, Lapshina E, Limpens J, Linkosalmi M, Ma JZ, Mauritz M, Mitchell EAD, Munir TM, Natali SM, Natcheva R, Payne RJ, Philippov DA, Rice SK, Robinson S, Robroek BJM, Rochefort L, Singer D, Stenøien HK, Tuittila ES, Vellak K, Waddington JM, Granath G (2021). Environmental drivers of Sphagnum growth in peatlands across the Holarctic region. J Ecol 109, 417-431. |
| [19] | Berg A, Danielsson Å, Svensson BH (2013). Transfer of fixed-N from N2-fixing cyanobacteria associated with the moss Sphagnum riparium results in enhanced growth of the moss. Plant Soil 362, 271-278. |
| [20] | Bescherelle É (1892). Musci yunnanensis. Ann Sci Nat Bo Sér 7 15, 47-94. |
| [21] | Blievernicht A, Irrgang S, Zander M, Ulrichs C (2011). Produktion von Torfmoosen (Sphagnum sp.) als torfersatz im erwerbsgartenbau. Gesunde Pflanz 62, 125-131. |
| [22] | Blievernicht A, Irrgang S, Zander M, Ulrichs C (2013). Sphagnum biomass—the next generation of growing media. Peat Int 1, 32-35. |
| [23] | Bu ZJ, Sundberg S, Feng L, Li HK, Zhao HY, Li HC (2017). The Methuselah of plant diaspores: Sphagnum spores can survive in nature for centuries. New Phytol 214, 1398-1402. |
| [24] | Campbell C, Granath G, Rydin H (2021). Climatic drivers of Sphagnum species distributions. Front Biogeog 13, e51-146. |
| [25] | Cao T, Vitt DH (1986). Spore surface structure of Sphagnum. Nova Hedwigia 43, 191-220. |
| [26] | Capozzi F, Adamo P, Di Palma A, Aboal JR, Bargagli R, Fernandez AJ, Mahia PL, Reski R, Tretiach M, Spagnuolo V, Giordano S (2017). Sphagnum palustre clone vs native Pseudoscleropodium purum: a first trial in the field to validate the future of the moss bag technique. Environ Pollut 225, 323-328. |
| [27] | Cardona-Correa C, Piotrowski MJ, Knack JJ, Kodner RE, Geary DH, Graham LE (2016). Peat moss-like vegetative remains from ordovician carbonates. Int J Plant Sci 177, 523-538. |
| [28] | Clymo RS (1987). The ecology of peatlands. Sci Prog Oxf 71, 593-614. |
| [29] | Clymo RS, Duckett JG (1986). Regeneration of Sphagnum. New Phytol 102, 589-614. |
| [30] | Clymo RS, Hayward PM (1982). The ecology of Sphagnum. In: Smith AJE, ed. Bryophyte Ecology. London: Chapman and Hall. pp. 229-289. |
| [31] | Costa DP (2021). A synopsis of the family Sphagnaceae in Brazil. Syst Bot Monog 111, 1-142. |
| [32] | Crum HA (2000). The Structural Diversity of Bryophytes. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Herbarium. pp. 1-379. |
| [33] | Crump J (ed.) (2017). Smoke on water—countering global threats from peatland loss and degradation. A UNEP Rapid Response Assessment. Arendal, Nairobi, and Arendal: United Nations Environment Programme and GRID. pp. 1-70. |
| [34] | Daniels RE, Eddy A (1985). Handbook of European Sphagna. London: HMSO. pp. 1-262. |
| [35] | Devos N, Szövényi P, Weston DJ, Rothfels CJ, Johnson MG, Shaw AJ (2016). Analyses of transcriptome sequences reveal multiple ancient large-scale duplication events in the ancestor of Sphagnopsida (Bryophyta). New Phytol 211, 300-318. |
| [36] | Díaz MF, Silva W (2012). Improving harvesting techniques to ensure Sphagnum regeneration in Chilean peatlands. Chil J Agric Res 72, 296-300. |
| [37] | Duckett JG, Pressel S, P'ng KMY, Renzaglia KS (2009). Exploding a myth: the capsule dehiscence mechanism and the function of pseudostomata in Sphagnum. New Phytol 183, 1053-1063. |
| [38] | Duffy AM, Aguero B, Stenøien HK, Flatberg KI, Ignatov MS, Hassel K, Shaw AJ (2020). Phylogenetic structure in the Sphagnum recurvum complex (Bryophyta) in relation to taxonomy and geography. Am J Bot 107, 1283-1295. |
| [39] | Fernandez-Pozo N, Haas FB, Gould SB, Rensing SA (2022). An overview of bioinformatics, genomics, and transcriptomics resources for bryophytes. J Exp Bot 73, 4291-4305. |
| [40] | Freeman C, Ostle N, Kang H (2001). An enzymic 'latch' on a global carbon store. Nature 409, 149. |
| [41] | Fritsch R (1991). Index to bryophyte chromosome counts. Bryophyt Bibliot 40, 1-352. |
| [42] | Gagnon ZE, Glime JM (1992). The pH-lowering ability of Sphagnum magellanicum Brid. J Bryol 17, 47-57. |
| [43] | Gaudig G, Fengler F, Krebs M, Prager A, Schulz J, Wichmann S, Joosten H (2014). Sphagnum farming in Germany—a review of progress. Mires Peat 13, 1-11. |
| [44] | Gaudig G, Joosten H (2002). Peat moss (Sphagnum) as a renewable resource—an alternative to Sphagnum peat in horticulture. In: SchmilewskiG, Rochefort L, eds. Peat in Horticulture:Quality and Environmental Challenges. Jyväskylä: International Peat Society. pp. 117-125. |
| [45] | Gaudig G, Krebs M, Prager A, Wichmann S, Barney M, Caporn SJM, Emmel M, Fritz C, Graf M, Grobe A, Pacheco SG, Hogue-Hugron S, Holzträger S, Irrgang S, Kämäräinen A, Karofeld E, Koch G, Koebbing JF, Kumar S, Matchutadze I, Oberpaur C, Oestmann J, Raabe P, Rammes D, Rochefort L, Schmilewksi G, Sendžikaitė J, Smolders A, St-Hilaire B, van de Riet B, Wright B, Wright N, Zoch L, Joosten H (2017). Sphagnum farming from species selection to the production of growing media: a review. Mires Peat 20, 13. |
| [46] | Glime JM (2020). Bryophyte ecology. -15. |
| [47] | Gonzalez AG, Pokrovsky OS, Beike AK, Reski R, Di Palma A, Adamo P, Giordano S, Fernandez JA (2016). Metal and proton adsorption capacities of natural and cloned Sphagnum mosses. J Colloid Interf Sci 461, 326-334. |
| [48] | Gorham E (1991). Northern peatlands: role in the carbon cycle and probable responses to climatic warming. Ecol Appl 1, 182-195. |
| [49] | Gunnarsson U (2005). Global patterns of Sphagnum productivity. J Bryol 27, 269-279. |
| [50] | Gunnarsson U, Granberg G, Nilsson M (2004). Growth, production and interspecific competition in Sphagnum: effects of temperature, nitrogen and sulphur treatments on a boreal mire. New Phytol 163, 349-359. |
| [51] | Günther A, Jurasinski G, Albrecht K, Gaudig G, Krebs M, Glatzel S (2017). Greenhouse gas balance of an establishing Sphagnum culture on a former bog grassland in Germany. Mires Peat 20, 1-16. |
| [52] | Hájek T (2014). Physiological ecology of peatland bryophytes. In: Hanson DT, Rice SK, eds. Photosynthesis in Bryophytes and Early Land Plants. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 233-252. |
| [53] | Hallingbäck T (2009). Report from the Asian bryophyte conservation workshop held in Singapore, Feb 28-2 March 2008. Bryol Times 128, 20-25. |
| [54] | Hallingbäck T, Hodgetts N (2000). Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan for Bryophytes. Gland, Cambridge: IUCN/SSC Bryophyte Specialist Group. pp. 1-103. |
| [55] | Haraguchi A (1996). Effect of pH on photosynthesis of five Sphagnum species in mires in Ochiishi, northern Japan. Wetlands 16, 10-14. |
| [56] | Haraguchi A, Hasegawa T, Iyobe T, Nishijima H (2003). The pH dependence of photosynthesis and elongation of Sphagnum squarrosum and S. girgensohnii in the Picea glehnii mire forest in Cape Ochiishi, north-eastern Japan. Aquat Ecol 37, 101-104. |
| [57] | Hassel K, Kyrkjeeide MO, Yousefi N, Prestø T, Stenøien HK, Shaw JA, Flatberg KI (2018). Sphagnum divinum (sp. nov.). and S. medium Limpr. and their relationship to S. magellanicum Brid. J Bryol 40, 197-222. |
| [58] | He Q, Zhu RL (2010). Spore output in 24 Asian bryophytes. Acta Bryolichenol Asiat 3, 125-129. |
| [59] | He XL, He KS, Hyvönen J (2016). Will bryophytes survive in a warming world? Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 19, 49-60. |
| [60] | Heck MA, Lüth VM, van Gessel N, Krebs M, Kohl M, Prager A, Joosten H, Decker EL, Reski R (2021). Axenic in vitro cultivation of 19 peat moss (Sphagnum L.) species as a resource for basic biology, biotechnology, and paludiculture. New Phytol 229, 861-876. |
| [61] | Hedenäs L, Bisang I (2011). The overlooked dwarf males in mosses—unique among green land plants. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 13, 121-135. |
| [62] | Hofmeister W (1854). Zur Morphologie der Moose. Ber Ver Königl Sächs Akad Wiss 6, 92-106. |
| [63] | Högström S (1997). Habitats and increase of Sphagnum in the Baltic Sea island Gotland, Sweden. Lindbergia 22, 69-74. |
| [64] | Hoshi Y (2017). Sphagnum growth in floating cultures: effect of planting design. Mires Peat 20, 8. |
| [65] | Hoshi Y, Kido M, Nagano K, Ichikawa T, Deguchi H (2012). A comparative study of water environment effect and Sphagnum growing with companion plant rice by two different culture systems of Sphagnum palustre L. Hikobia 16, 79-83. |
| [66] | Hotson JW (1918). Sphagnum as a surgical dressing. Science 48, 203-208. |
| [67] | IPCC (2013). Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM, eds. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1-121. |
| [68] | Iwatsuki Z, Furuki T, Kanda H, Hasegawa J, Higuchi M (2008). New red list of bryophytes of Japan, 2007. Bryol Res 9, 259-267. |
| [69] | Jassey VEJ, Signarbieux C (2019). Effects of climate warming on Sphagnum photosynthesis in peatlands depend on peat moisture and species-specific anatomical traits. Global Change Biol 25, 3859-3870. |
| [70] | Johnson LC, Damman AWH (1991). Species-controlled Sphagnum decay on a South Swedish raised bog. Oikos 61, 234-242. |
| [71] | Joosten H (2015). Peatlands, Climate Change Mitigation and Biodiversity Conservation: An Issue Brief on the Importance of Peatlands for Carbon and Biodiversity Conservation and the Role of Drained Peatlands as Greenhouse Gas Emission Hotspots. Copenhagen: Nordic Co-operation. pp. 1-16. |
| [72] | Kostka JE, Weston DJ, Glass JB, Lilleskov EA, Shaw AJ, Turetsky MR (2016). The Sphagnum microbiome: new insights from an ancient plant lineage. New Phytol 211, 57-64. |
| [73] | Kox MAR, Smolders AJP, Speth DR, Lamers LPM, Op den Camp HJM, Jetten MSM, van Kessel MAHJ (2021). A novel laboratory-scale mesocosm setup to study methane emission mitigation by Sphagnum mosses and associated methanotrophs. Front Microbiol 12, 652486. |
| [74] | Krebs M, Gaudig G, Matchutadze I, Joosten H (2018). Sphagnum regrowth after cutting. Mires Peat 20, 12. |
| [75] | Küttim M, Küttim L, Ilomets M, Laine AM (2020). Controls of Sphagnum growth and the role of winter. Ecol Res 35, 219-234. |
| [76] | Kyrkjeeide MO, Hassel K, Aguero B, Temsch EM, Afonina OM, Shaw AJ, Stenøien HK, Flatberg KI (2019). Sphagnum × lydiae, the first allotriploid peat moss in the northern hemisphere. Bryologist 122, 38-61. |
| [77] | Kyrkjeeide MO, Hassel K, Flatberg KI, Shaw AJ, Yousefi N, Stenøien HK (2016). Spatial genetic structure of the abundant and widespread peat moss Sphagnum magellanicum Brid. PLoS One 11, e0148447. |
| [78] | Laine J, Flatberg KI, Harju P, Timonen T, Minkkinen K, Laine AM, Tuittila ES, Vasander H (2018). Sphagnum Mosses: The Stars of European Mires. Helsinki: University of Helsinki. pp. 1-326. |
| [79] | Laine J, Harju P, Timonen T, Laine AM, Tuittila ES, Minkkinen K, Vasander H (2009). The Intricate Beauty of Sphagnum Mosses: a Finnish Guide for Identification. Helsinki: University of Helsinki Department of Forest Ecology. pp. 1-190. |
| [80] | León CA, Neila-Pivet M, Benítez-Mora A, Lara L (2019). Effect of phosphorus and nitrogen on Sphagnum regeneration and growth: an experience from Patagonia. Wetl Ecol Manag 27, 257-266. |
| [81] | Li FW, Nishiyama T, Waller M, Frangedakis E, Keller J, Li Z, Fernandez-Pozo N, Barker MS, Bennett T, Blázquez MA, Cheng SF, Cuming AC, de Vries J, de Vries S, Delaux PM, Diop IS, Harrison CJ, Hauser D, Hernández-García J, Kirbis A, Meeks JC, Monte I, Mutte SK, Neubauer A, Quandt D, Robison T, Shimamura M, Rensing SA, Villarreal JC, Weijers D, Wicke S, Wong GKS, Sakakibara K, Szövényi P (2020). Anthoceros genomes illuminate the origin of land plants and the unique biology of hornworts. Nat Plants 6, 259-272. |
| [82] | Li TT, Lei Y, Dai C, Yang LF, Li ZQ, Wang ZX (2018). Effects of both substrate and nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on Sphagnum palustre growth in subtropical high- mountain regions and implications for peatland recovery. Wetl Ecol Manag 26, 651-663. |
| [83] | Li TT, Liu T, Lei Y, Li ZQ, Dai C, Wang ZX (2019a). Effects of the substrate and planting method on Sphagnum palustre growth in subtropical high-mountain regions and the underlying mechanisms. Wetlands 39, 879-893. |
| [84] | Li TT, Wang ZX, Bu GJ, Lin LQ, Lei Y, Liu CY, Yang LF, Zheng CL (2019b). Effects of microtopography and water table on Sphagnum palustre L. in subtropical high mountains and implications for peatland restoration. J Bryol 41, 121-134. |
| [85] | Li XJ, He S (1999). Sphagnaceae. In: Gao C, Crosby MR, eds. Moss Flora of China, Vol. 1. Beijing: Science Press; St. Louis: Missouri Botanical Garden. pp. 3-49. |
| [86] | Limpens J, Berendse F (2003). How litter quality affects mass loss and N loss from decomposing Sphagnum. Oikos 103, 537-547. |
| [87] | Limpens J, Berendse F, Klees H (2004). How phosphorus availability affects the impact of nitrogen deposition on Sphagnum and vascular plants in bogs. Ecosystems 7, 793-804. |
| [88] | Limpens J, Granath G, Aerts R, Heijmans MMPD, Sheppard LJ, Bragazza L, Williams BL, Rydin H, Bubier J, Moore T, Rochefort L, Mitchell EAD, Buttler A, van den Berg LJL, Gunnarsson U, Francez AJ, Gerdol R, Thormann M, Grosvernier P, Wiedermann MM, Nilsson MB, Hoosbeek MR, Bayley S, Nordbakken JF, Paulissen MPCP, Hotes S, Breeuwer A, Ilomets M, Tomassen HBM, Leith I, Xu B (2012). Glasshouse vs field experiments: do they yield ecologically similar results for assessing N impacts on peat mosses? New Phytol 195, 408-418. |
| [89] | Liu Y, Johnson MG, Cox CJ, Medina R, Devos N, Vanderpoorten A, Hedenäs L, Bell NE, Shevock JR, Aguero B, Quandt D, Wickett NJ, Shaw AJ, Goffinet B (2019). Resolution of the ordinal phylogeny of mosses using targeted exons from organellar and nuclear genomes. Nat Commun 10, 1485. |
| [90] | Loisel J, Gallego-Sala AV, Yu Z (2012). Global-scale pattern of peatland Sphagnum growth driven by photosynthetically active radiation and growing season length. Biogeosciences 9, 2737-2746. |
| [91] | Maksimova V, Klavina L, Bikovens O, Zicmanis A, Purmalis O (2013). Structural characterization and chemical classification of some bryophytes found in Latvia. Chem Biodivers 10, 1284-1294. |
| [92] | McNeil P, Waddington JM (2003). Moisture controls on Sphagnum growth and CO2 exchange on a cutover bog. J Appl Ecol 40, 354-367. |
| [93] | Meleshko O, Martin MD, Korneliussen TS, Schröck C, Lamkowski P, Schmutz J, Healey A, Piatkowski BT, Shaw AJ, Weston DJ, Flatberg KI, Szövényi P, Hassel K, Stenøien HK (2021). Extensive genome-wide phylogenetic discordance is due to incomplete lineage sorting and not ongoing introgression in a rapidly radiated bryophyte genus. Mol Biol Evol 38, 2750-2766. |
| [94] | Meleshko O, Stenøien HK, Speed JDM, Flatberg KI, Kyrkjeeide MO, Hassel K (2018). Is interspecific gene flow and speciation in peat mosses (Sphagnum) constrained by phylogenetic relationship and life-history traits? Lindbergia 41, 1-14. |
| [95] | Merced A (2015). Novel insights on the structure and composition of pseudostomata of Sphagnum. Am J Bot 102, 329-335. |
| [96] | Michaelis D (2019). The Sphagnum Species of the World. Stuttgart: Schweizerbart Science Publishers. pp. 1-435. |
| [97] | Müller K (1909). Untersuchungeniiber die wasseraufnamedurch moose und verschiedeneandere pflanzen und pflanzenteile. Jahrb Wiss Bot 46, 587-598. |
| [98] | Nawaschin S (1897). Ueber die spoorenausschleudering beiden torfmoosen. Flora 83, 151-159. |
| [99] | Newman TR, Wright N, Wright B, Sjögersten S (2018). Interacting effects of elevated atmospheric CO2and hydrology on the growth and carbon sequestration of Sphagnum moss. Wetl Ecol Manag 26, 763-774. |
| [100] | Nichols GE (1920). Sphagnum moss: war substitute for cotton in absorbent surgical dressings. Publ Smiths Inst 2558 (US Nat Mus Rep),221-234. |
| [101] | Nishida Y (1970). Studies on the differentiation of the protonema in two species of Sphagnaceae. Bot Mag (Tokyo) 83, 249-253. |
| [102] | Norby RJ, Childs J, Hanson PJ, Warren JM (2019). Rapid loss of an ecosystem engineer: Sphagnum decline in an experimentally warmed bog. Ecol Evol 9, 12571-12585. |
| [103] | Oke TA, Hager HA (2017). Assessing environmental attributes and effects of climate change on Sphagnum peatland distributions in North America using single- and multi-species models. PLoS One 12, e0175978. |
| [104] | Oke TA, Hager HA (2020). Plant community dynamics and carbon sequestration in Sphagnum-dominated peatlands in the era of global change. Global Ecol Biogeogr 29, 1610-1620. |
| [105] | One Thousand Plant Transcriptomes Initiative (2019). One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 574, 679-685. |
| [106] | Painter TJ (1983). Carbohydrate origin of aquatic humus from peat. Carbohydr Res 124, C22-C26. |
| [107] | Painter TJ (1991). Lindow man, tollund man and other peat-bog bodies: the preservative and antimicrobial action of Sphagnan, a reactive glycuronoglycan with tanning and sequestering properties. Carbohyd Polym 15, 123-142. |
| [108] | Pilkington M, Walker J, Fry C, Eades P, Meade R, Pollett N, Rogers T, Helliwell T, Chandler D, Fawcett E, Keatley T (2021). Diversification of Molinia-dominated blanket bogs using Sphagnum propagules. Ecol Solut Evid 2, e12113. |
| [109] | Porter JB (1917). Sphagnum surgical dressings. Int J Surgery 30, 129-135. |
| [110] | Puttick MN, Morris JL, Williams TA, Cox CJ, Edwards D, Kenrick P, Pressel S, Wellman CH, Schneider H, Pisani D, Donoghue PCJ (2018). The interrelationships of land plants and the nature of the ancestral embryophyte. Curr Biol 28, 733-745. |
| [111] | Raghoebarsing AA, Smolders AJP, Schmid MC, Rijpstra WIC, Wolters-Arts M, Derksen J, Jetten MSM, Schouten S, Damsté JSS, Lamers LPM, Roelofs JGM, Op den Camp HJM, Strous M (2005). Methanotrophic symbionts provide carbon for photosynthesis in peat bogs. Nature 436, 1153-1156. |
| [112] | Rasmussen S, Rudolph H (1992). Do phenolics in the cell wall of Sphagnum serve in a function similar to that of lignin? In: Sassen MMA, ed. 6th Cell Wall Meeting. Nijmegen: University Press. pp. 142. |
| [113] | Rochefort L (2000). Sphagnum—a keystone genus in habitat restoration. Bryologist 103, 503-508. |
| [114] | Rochefort L, Campeau S, Bugnon JL (2002). Does prolonged flooding prevent or enhance regeneration and growth of Sphagnum? Aquat Bot 74, 327-341. |
| [115] | Rudolph H, Kabsch U, Schmidt-Stohn G (1977). Änderungen des Chloroplastenpigment-spiegels bei Sphagnum magellanicum im verlauf der synthese von sphagnorubin und anderer membranochromer pigmente. Zeits Pflanzenphysiol 82, 107-116. |
| [116] | Rudolph H, Samland J (1985). Occurrence and metabolism of Sphagnum acid in the cell walls of bryophytes. Phytochemistry 24, 745-749. |
| [117] | Rydin H, Jeglum JK (2013). The Biology of Peatlands, 2nd edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 1-382. |
| [118] | Schofield WB (1985). Introduction to Bryology. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co. pp. 1-431. |
| [119] | Shaw AJ, Carter BE, Aguero B, da Costa DP, Crowl AA (2019). Range change evolution of peat mosses (Sphagnum) within and between climate zones. Global Change Biol 25, 108-120. |
| [120] | Shaw AJ, Cox CJ, Buck WR, Devos N, Buchanan AM, Cave L, Seppelt R, Shaw B, Larraín J, Andrus R, Greilhuber J, Temsch EM (2010a). Newly resolved relationships in an early land plant lineage: bryophyta class Sphagnopsida (peat mosses). Am J Bot 97, 1511-1531. |
| [121] | Shaw AJ, Devos N, Cox CJ, Boles SB, Shaw B, Buchanan AM, Cave L, Seppelt RD (2010b). Peat moss (Sphagnum) diversification associated with Miocene Northern Hemisphere climatic cooling? Mol Phylogenet Evol 55, 1139-1145. |
| [122] | Shaw AJ, Devos N, Liu Y, Cox CJ, Goffinet B, Flatberg KI, Shaw B (2016a). Organellar phylogenomics of an emerging model system: Sphagnum (peat moss). Ann Bot 118, 185-196. |
| [123] | Shaw AJ, Schmutz J, Devos N, Shu S, Carrell AA, Weston DJ (2016b). The Sphagnum genome project: a new model for ecological and evolutionary genomics. Adv Bot Res 78, 167-187. |
| [124] | Silvan N, Jokinen K (2016). Early snowmelt enhances the carbon sequestration of hummock-forming Sphagnum mosses on boreal wetlands. Open J Ecol 6, 103-112. |
| [125] | Stevenson R (2012). From soap to suppositories—'new' uses of Sphagnum. Field Bryol 108, 28-29. |
| [126] | Stokes JR, Alspach PA, Stanley J (1999). Effect of water table on growth of three New Zealand Sphagnum species: implications for S. cristatum management. J Bryol 21, 25-29. |
| [127] | Sundberg S (2002). Sporophyte production and spore dispersal phenology in Sphagnum: the importance of summer moisture and patch characteristics. Can J Bot 80, 543-556. |
| [128] | Sundberg S (2013). Spore rain in relation to regional sources and beyond. Ecography 36, 364-373. |
| [129] | Sundberg S, Rydin H (2002). Habitat requirements for establishment of Sphagnum from spores. J Ecol 90, 268-278. |
| [130] | Svensson BM (1995). Competition between Sphagnum fuscum and Drosera rotundifolia: a case of ecosystem engineering. Oikos 74, 205-212. |
| [131] | Tan BC, Nosratinia S, Ignatov MS, Ignatova EA, Mishler BD (2018). New species of Sphagnum from the Philippines with remarkable morphological characters. Philipp J Syst Biol 12, 24-36. |
| [132] | Taskila S, Särkelä R, Tanskanen J (2016). Valuable applications for peat moss. Biomass Conv Bioref 6, 115-126. |
| [133] | Temmink RJM, Fritz C, van Dijk G, Hensgens G, Lamers LPM, Krebs M, Gaudig G, Joosten H (2017). Sphagnum farming in a eutrophic world: the importance of optimal nutrient stoichiometry. Ecol Eng 98, 196-205. |
| [134] | Temsch EM, Greilhuber J, Krisai R (1998). Genome size in Sphagnum (peat moss). Bot Acta 111, 325-330. |
| [135] | Theander O (1954). Studies on Sphagnum peat. III. A quantitative study on the carbohydrate constituents of Sphagnum mosses and Sphagnum peat. Acta Chem Scand 8, 989-1000. |
| [136] | Tuittila ES, Vasander H, Laine J (2004). Sensitivity of C sequestration in reintroduced Sphagnum to water-level variation in a cutaway peatland. Restor Ecol 12, 483-493. |
| [137] | van Breemen N (1995). How Sphagnum bogs down other plants. Trends Ecol Evol 10, 270-275. |
| [138] | van Winden JF, Kip N, Reichart GJ, Jetten MSM, Op den Camp HJM, Damsté JSS (2010). Lipids of symbiotic methane-oxidizing bacteria in peat moss studied using stable carbon isotopic labelling. Org Geochem 41,1040-1044. |
| [139] | Vitt DH, Wieder RK (2008). The structure and function of bryophyte-dominated peatlands. In: Goffinet B, Shaw AJ, eds. Bryophyte Biology, 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 357-391. |
| [140] | Wagner DJ, Titus JE (1984). Comparative desiccation tolerance of two Sphagnum mosses. Oecologia 62, 182-187. |
| [141] | Weston DJ, Turetsky MR, Johnson MG, Granath G, Lindo Z, Belyea LR, Rice SK, Hanson DT, Engelhardt KAM, Schmutz J, Dorrepaal E, Euskirchen ES, Stenøien HK, Szövényi P, Jackson M, Piatkowski BT, Muchero W, Norby RJ, Kostka JE, Glass JB, Rydin H, Limpens J, Tuittila ES, Ullrich KK, Carrell A, Benscoter BW, Chen JG, Oke TA, Nilsson MB, Ranjan P, Jacobson D, Lilleskov EA, Clymo RS, Shaw AJ (2018). The Sphagnome project: enabling ecological and evolutionary insights through a genus-level sequencing project. New Phytol 217, 16-25. |
| [142] | Whinam J, Copson G (2006). Sphagnum moss: an indicator of climate change in the sub-Antarctic. Polar Rec 42, 43-49. |
| [143] | Whinam J, Hope GS, Clarkson BR, Buxton RP, Alspach PA, Adam P (2003). Sphagnum in peatlands of Australasia: their distribution, utilisation and management. Wetl Ecol Manag 11, 37-49. |
| [144] | Whitaker DL, Edwards J (2008). Sphagnum moss disperses spores with vortex rings. Science 329, 406. |
| [145] | Wichmann S, Krebs M, Kumar S, Gaudig G (2020). Paludiculture on former bog grassland: profitability of Sphagnum farming in North West German. Mires Peat 26, 1-18. |
| [146] | Xu JR, Morris PJ, Liu JG, Holden J (2018). PEATMAP: refining estimates of global peatland distribution based on a meta-analysis. Catena 160, 134-140. |
| [147] | Zhang J, Fu XX, Li RQ, Zhao X, Liu Y, Li MH, Zwaenepoel A, Ma H, Goffinet B, Guan YL, Xue JY, Liao YY, Wang QF, Wang QH, Wang JY, Zhang GQ, Wang ZW, Jia Y, Wang MZ, Dong SS, Yang JF, Jiao YN, Guo YL, Kong HZ, Lu AM, Yang HM, Zhang SZ, Van de Peer Y, Liu ZJ, Chen ZD (2020). The hornwort genome and early land plant evolution. Nat Plants 6, 107-118. |
| [148] | Zhao WQ, Li ZL, Hu YY, Wang M, Zheng SR, Li QP, Wang YF, Xu L, Li XF, Zhu RL, Reski R, Sun Y (2019). Development of a method for protonema proliferation of peat moss (Sphagnum squarrosum) through regeneration analysis. New Phytol 221, 1160-1171. |
| [1] | 杜旭龙, 黄锦学, 杨智杰, 熊德成. 增温对植物叶片和细根氧化损伤与防御特征及其相互关联影响的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 135-146. |
| [2] | 黄玫, 石岳, 孙文娟, 赵霞, 常锦峰, 方精云. 云南省生态系统碳汇及其对碳中和的贡献[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(10): 1243-1255. |
| [3] | 吴晨, 陈心怡, 刘源豪, 黄锦学, 熊德成. 增温对森林细根生长、死亡及周转特征影响的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(8): 1043-1054. |
| [4] | 陈心怡, 吴晨, 黄锦学, 熊德成. 增温对林木细根物候影响的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(11): 1471-1482. |
| [5] | 党宏忠, 张学利, 韩辉, 石长春, 葛玉祥, 马全林, 陈帅, 刘春颖. 樟子松固沙林林水关系研究进展及对营林实践的指导[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(9): 971-983. |
| [6] | 牛铜钢, 刘为. 双碳战略背景下城市生态系统的碳汇功能与生物多样性可以兼得[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22168-. |
| [7] | 罗明没, 陈悦, 杨刚, 胡斌, 李玮, 陈槐. 若尔盖退化泥炭地土壤原核微生物群落结构对水位恢复的短期响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(5): 552-561. |
| [8] | 方精云. 碳中和的生态学透视[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(11): 1173-1176. |
| [9] | 冯璐, 卜兆君, 吴玉环, 刘莎莎, 刘超. 泥炭地特征性环境因子促进泥炭藓持久孢子库的形成[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(6): 512-520. |
| [10] | 刘媛媛, 马进泽, 卜兆君, 王升忠, 张雪冰, 张婷玉, 刘莎莎, 付彪, 康媛. 地理来源与生物化学属性对泥炭地植物残体分解的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(7): 713-722. |
| [11] | 李瑞, 胡朝臣, 许士麒, 吴迪, 董玉平, 孙新超, 毛瑢, 王宪伟, 刘学炎. 大兴安岭泥炭地植物叶片碳氮磷含量及其化学计量学特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(12): 1154-1167. |
| [12] | 黎磊, 陈家宽. 气候变化对野生植物的影响及保护对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 549-563. |
| [13] | 牛书丽, 韩兴国, 马克平, 万师强. 全球变暖与陆地生态系统研究中的野外增温装置[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(2): 262-271. |
| [14] | 倪健. 全球变化与野生物种:观测和预测[J]. 生物多样性, 1999, 07(2): 132-139. |
| [15] | 杨永辉, 托尼·哈里森, 费尔·安纳逊. 山地草原生物量的垂直变化及其与气候变暖和施肥的关系[J]. 植物生态学报, 1997, 21(3): 234-241. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
