

植物学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 89-101.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16231 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16231
所属专题: 水稻生物学专辑 (2017年52卷1期)
收稿日期:2016-11-29
接受日期:2016-12-12
出版日期:2017-01-01
发布日期:2017-01-23
通讯作者:
陈光
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:Guang Chen1,2*, Zhenyu Gao1, Guohua Xu2
Received:2016-11-29
Accepted:2016-12-12
Online:2017-01-01
Published:2017-01-23
Contact:
Chen Guang
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要: 钾是植物体内含量最大的阳离子, 在植物生长发育过程的诸多生理生化反应中起关键作用。缺钾会抑制植株根系的生长, 使根冠比降低; 同时阻碍光合产物的合成和向韧皮部转运, 导致生物量下降。因此, 提高植物钾营养的吸收转运和利用效率对于作物品种改良和增产具有重要的理论和生产实践意义。该文综述了植物响应低钾的生理机制和提高植物钾利用效率的四大策略, 并对改善钾营养吸收利用以提高作物产量和品质进行了讨论及展望。
陈光, 高振宇, 徐国华. 植物响应缺钾胁迫的机制及提高钾利用效率的策略. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 89-101.
Guang Chen, Zhenyu Gao, Guohua Xu. Adaption of Plants to Potassium Deficiency and Strategies to Improve Potassium Use Efficiency. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(1): 89-101.
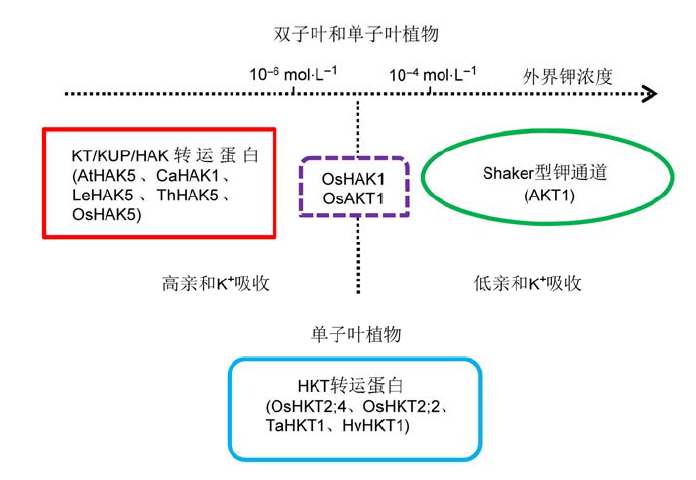
图1 植物中参与土壤高、低亲和钾吸收的转运体系(改自Chérel et al., 2014)
Figure 1 Transport systems involved in high- and low-affinity K+ uptake from soil in plant (modified from Chérel et al., 2014)
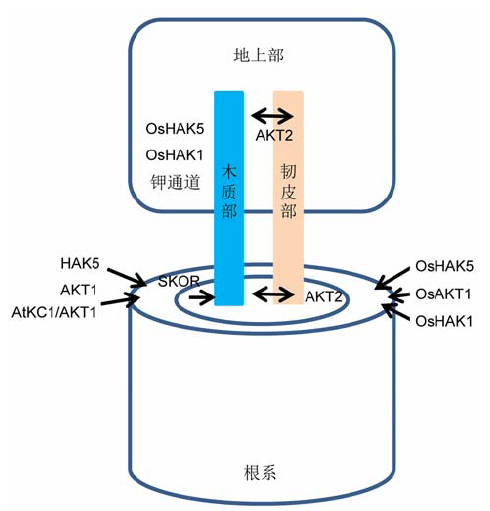
图2 拟南芥与水稻中参与钾吸收和维管组织钾分配的转运体系(改自Chérel et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2015b)
Figure 2 Transport systems involved in K+ uptake and its distribution in the plant vasculature of Arabidopsis and rice (modified from Chérel et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2015b)
| [1] | 陈艳丽, 吴伟明, 程式华, 曹立勇 (2012). 水稻耐低钾胁迫研究进展. 中国稻米 18, 9-13. |
| [2] | 王毅, 武维华 (2009). 植物钾营养高效分子遗传机制. 植物学报 44, 27-36. |
| [3] | 邢军, 常汇琳, 王敬国, 刘化龙, 孙健, 郑洪亮, 赵宏伟, 邹德堂 (2015). 盐、碱胁迫条件下粳稻Na+、K+浓度的QTL分析. 中国农业科学 48, 604-612. |
| [4] | 杨树明, 曾亚文, 王荔, 杜娟, 普晓英, 杨涛 (2015). 不同生长环境下水稻氮、磷、钾利用相关性状的QTL定位分析. 植物营养与肥料学报 21, 823-835. |
| [5] | Ache P, Becker D, Deeken R, Dreyer I, Weber H, Fromm J, Hedrich R (2001). VFK1, a Vicia faba K+ channel involved in phloem unloading.Plant J 27, 571-580. |
| [6] | Adams E, Shin R (2014). Transport, signaling, and homeo- stasis of potassium and sodium in plants.J Integr Plant Biol 56, 231-249. |
| [7] | Ahn SJ, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2004). Expression of KT/KUP genes in Arabidopsis and the role of root hairs in K+ uptake.Plant Physiol 134, 1135-1145. |
| [8] | Alemán F, Nieves-Cordones M, Martínez V, Rubio F (2009). Differential regulation of the HAK5 genes encod- ing the high-affinity K+ transporters of Thellungiella halophila and Arabidopsis thaliana.Environ Exp Bot 65, 263-269. |
| [9] | Amtmann A, Blatt MR (2009). Regulation of macronutrient transport.New Phytol 181, 35-52. |
| [10] | Amtmann A, Hammond JP, Armengaud P, White PJ (2005). Nutrient sensing and signaling in plants: potas- sium and phosphorus.Adv Bot Res 43, 209-257. |
| [11] | Aranda-Sicilia MN, Cagnac O, Chanroj S, Sze H, Rodrí- guez-Rosales MP, Venema K (2012). Arabidopsis KEA2, a homolog of bacterial KefC, encodes a K+/H+ antiporter with a chloroplast transit peptide.BBA-Biomembranes 1818, 2362-2371. |
| [12] | Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004). The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling.Plant Physiol 136, 2556-2576. |
| [13] | Ashley MK, Grant M, Grabov A (2006). Plant responses to potassium deficiencies: a role for potassium transport proteins.J Exp Bot 57, 425-436. |
| [14] | Bañuelos MA, Garciadeblas B, Cubero B, Rodrı?guez- Navarro A (2002). Inventory and functional characterization of the HAK potassium transporters of rice.Plant Physiol 130, 784-795. |
| [15] | Berthomieu P, Conéjéro G, Nublat A, Brackenbury WJ, Lambert C, Savio C, Uozumi N, Oiki S, Yamada K, Cellier F, Gosti F, Simonneau T, Essah PA, Tester M, Véry AA, Sentenac H, Casse F (2003). Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na+ recirculation by the phloem is crucial for salt tolerance.EMBO J 22, 2004-2014. |
| [16] | Breuninger H, Rikirsch E, Hermann M, Ueda M, Laux T (2008). Differential expression of WOX genes mediates apical-basal axis formation in the Arabidopsis embryo.Dev Cell 14, 867-876. |
| [17] | Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2008). Cellular mechanisms of potassium transport in plants.Physiol Plantarum 133, 637-650. |
| [18] | Cai J, Chen L, Qu H, Lian J, Liu W, Hu Y, Xu G (2012). Alteration of nutrient allocation and transporter genes expression in rice under N, P, K, and Mg deficiencies.Acta Physiol Plant 34, 939-946. |
| [19] | Cakmak I, Hengeler C, Marschner H (1994a). Partitioning of shoot and root dry matter and carbohydrates in bean plants suffering from phosphorus, potassium and magnesium deficiency.J Exp Bot 45, 1245-1250. |
| [20] | Cakmak I, Hengeler C, Marschner H (1994b). Changes in phloem export of sucrose in leaves in response to phosphorus, potassium and magnesium deficiency in bean plants.J Exp Bot 45, 1251-1257. |
| [21] | Chao DY, Dilkes B, Luo H, Douglas A, Yakubova E, Lahner B, Salt DE (2013). Polyploids exhibit higher potassium uptake and salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis.Science 341, 658-659. |
| [22] | Chen G, Feng H, Hu Q, Qu H, Chen A, Yu L, Xu G (2015a). Improving rice tolerance to potassium deficiency by enhancing OsHAK16p:WOX11-controlled root development.Plant Biotechnol J 13, 833-848. |
| [23] | Chen G, Hu Q, Luo L, Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Yu L, Xu G (2015b). Rice potassium transporter OsHAK1 is essential for maintaining potassium-mediated growth and functions in salt tolerance over low and high potassium concentration ranges.Plant Cell Environ 38, 2747-2765. |
| [24] | Cheng S, Huang Y, Zhu N, Zhao Y (2014). The rice WUSCHEL-related homeobox genes are involved in reproductive organ development, hormone signaling and abiotic stress response.Gene 549, 266-274. |
| [25] | Chérel I, Lefoulon C, Boeglin M, Sentenac H (2014). Molecular mechanisms involved in plant adaptation to low K+ availability.J Exp Bot 65, 833-848. |
| [26] | Chérel I, Michard E, Platet N, Mouline K, Alcon C, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB (2002). Physical and functional interaction of the Arabidopsis K+ channel AKT2 and phosphatase AtPP2CA.Plant Cell 14, 1133-1146. |
| [27] | Cho SH, Yoo SC, Zhang H, Pandeya D, Koh HJ, Hwang JY, Kim GT, Paek NC (2013). The rice narrow leaf2 and narrow leaf3 loci encode WUSCHEL-related homeobox 3A (OsWOX3A) and function in leaf, spikelet, tiller and lateral root development.New Phytol 198, 1071-1084. |
| [28] | Corratgé-Faillie C, Jabnoune M, Zimmermann S, Véry AA, Fizames C, Sentenac H (2010). Potassium and so- dium transport in non-animal cells: the Trk/Ktr/HKT trans- porter family.Cell Mol Life Sci 67, 2511-2532. |
| [29] | Damas JM, Oliveira ASF, Baptista AM, Soares CM (2011). Structural consequences of ATP hydrolysis on the ABC transporter NBD dimer: molecular dynamics studies of HlyB.Protein Sci 20, 1220-1230. |
| [30] | Daram P, Urbach S, Gaymard F, Sentenac H, Chérel I (1997). Tetramerization of the AKT1 plant potassium channel involves its C-terminal cytoplasmic domain.EMBO J 16, 3455-3463. |
| [31] | Davenport RJ, Muñoz-mayor Alicia, Jha D, Essah PA, Rus ANA, Tester M (2007). The Na+ transporter AtHKT1;1 controls retrieval of Na+ from the xylem in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Environ 30, 497-507. |
| [32] | Dean G, Casson S, Lindsey K (2004). KNAT6 gene of Arabidopsis is expressed in roots and is required for correct lateral root formation.Plant Mol Biol 54, 71-84. |
| [33] | Deeken R, Geiger D, Fromm J, Koroleva O, Ache P, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Sauer N, May ST, Hedrich R (2002). Loss of the AKT2/3 potassium channel affects sugar loading into the phloem of Arabidopsis.Planta 216, 334-344. |
| [34] | Deeken R, Ivashikina N, Czirjak T, Philippar K, Becker D, Ache P, Hedrich R (2003). Tumour development in Arabidopsis thaliana involves the Shaker-like K+ channels AKT1 and AKT2/3.Plant J 34, 778-787. |
| [35] | Desbrosses G, Josefsson C, Rigas S, Hatzopoulos P, Dolan L (2003). AKT1 and TRH1 are required during root hair elongation in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot 54, 781-788. |
| [36] | Drew MC, Saker LR, Barber SA, Jenkins W (1984). Changes in the kinetics of phosphate and potassium absorption in nutrient-deficient barley roots measured by a solution-depletion technique.Planta 160, 490-499. |
| [37] | Duby G, Hosy E, Fizames C, Alcon C, Costa A, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB (2008). AtKC1, a conditionally targeted Shaker-type subunit, regulates the activity of plant K+ channels.Plant J 53, 115-123. |
| [38] | Epstein E, Rains DW, Elzam OE (1963). Resolution of dual mechanisms of potassium absorption by barley roots.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 49, 684-692. |
| [39] | Fu HH, Luan S (1998). AtKUP1: a dual-affinity K+ transporter from Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 10, 63-73. |
| [40] | Fulgenzi FR, Peralta ML, Mangano S, Danna CH, Vallejo AJ, Puigdomenech P, Santa-María GE (2008). The ionic environment controls the contribution of the barley Hv- HAK1 transporter to potassium acquisition.Plant Physiol 147, 252-262. |
| [41] | Garciadeblas B, Senn ME, Banuelos MA, Rodríguez- Navarro A (2003). Sodium transport and HKT transporters: the rice model.Plant J 34, 788-801. |
| [42] | Gattward JN, Almeida AAF, Souza JO, Gomes FP, Kronzucker HJ (2012). Sodium-potassium synergism in Theobroma cacao: stimulation of photosynthesis, water- use efficiency and mineral nutrition.Physiol Plantarum 146, 350-362. |
| [43] | Geiger D, Becker D, Vosloh D, Gambale F, Palme K, Rehers M, Anschuetz U, Dreyer I, Kudla J, Hedrich R (2009). Heteromeric AtKC1·AKT1 channels in Arabidopsis roots facilitate growth under K+-limiting conditions.J Biol Chem 284, 21288-21295. |
| [44] | Gerardeaux E, Jordan-Meille L, Constantin J, Pellerin S, Dingkuhn M (2010). Changes in plant morphology and dry matter partitioning caused by potassium deficiency in Gossypium hirsutum (L.).Environ Exp Bot 67, 451-459. |
| [45] | Gierth M, Mäser P, Schroeder JI (2005). The potassium transporter AtHAK5 functions in K+ deprivation-induced high-affinity K+ uptake and AKT1 K+ channel contribution to K+ uptake kinetics in Arabidopsis roots.Plant Physiol 137, 1105-1114. |
| [46] | Grabov A (2007). Plant KT/KUP/HAK potassium transpor- ters: single family-multiple functions.Ann Bot 99, 1035-1041. |
| [47] | Gupta M, Qiu X, Wang L, Xie W, Zhang C, Xiong L, Lian X, Zhang Q (2008). KT/HAK/KUP potassium transporters gene family and their whole-life cycle expression profile in rice (Oryza sativa).Mol Genet Genomics 280, 437-452. |
| [48] | Hao J, Tu L, Hu H, Tan J, Deng F, Tang W, Nie Y, Zhang X (2012). GbTCP, a cotton TCP transcription factor, confers fibre elongation and root hair development by a complex regulating system.J Exp Bot 63, 6267-6281. |
| [49] | Hastings DF, Gutknecht J (1978). Potassium and turgor pressure in plants.J Theor Biol 73, 363-366. |
| [50] | Hermans C, Hammond JP, White PJ, Verbruggen N (2006). How do plants respond to nutrient shortage by biomass allocation?Trends Plant Sci 11, 610-617. |
| [51] | Hirsch RE, Lewis BD, Spalding EP, Sussman MR (1998). A role for the AKT1 potassium channel in plant nutrition.Science 280, 918-921. |
| [52] | Høgh-Jensen H, Pedersen MB (2003). Morphological plasticity by crop plants and their potassium use efficiency.J Plant Nutr 26, 969-984. |
| [53] | Hong JP, Takeshi Y, Kondou Y, Schachtman DP, Matsui M, Shin R (2013). Identification and characterization of transcription factors regulating Arabidopsis HAK5.Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1478-1490. |
| [54] | Horie T, Brodsky DE, Costa A, Kaneko T, Schiavo FL, Katsuhara M, Schroeder JI (2011a). K+ transport by the OsHKT2;4 transporter from rice with a typical Na+ transport properties and competition in permeation of K+ over Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions.Plant Physiol 156, 1493-1507. |
| [55] | Horie T, Costa A, Kim TH, Han MJ, Horie R, Leung HY, Miyao A, Hirochika H, An G, Schroeder JI (2007). Rice OsHKT2; 1 transporter mediates large Na+ influx component into K+-starved roots for growth.EMBO J 26, 3003-3014. |
| [56] | Horie T, Sugawara M, Okada T, Taira K, Kaothien- Nakayama P, Katsuhara M, Shinmyo A, Nakayama H (2011b). Rice sodium-insensitive potassium transporter, OsHAK5, confers increased salt tolerance in tobacco BY2 cells.J Biosci Bioeng 111, 346-356. |
| [57] | Horie T, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Yamada K, Oiki S, Shinmyo A (2001). Two types of HKT transporters with different properties of Na+ and K+ transport in Oryza sativa.Plant J 27, 129-138. |
| [58] | Huertas R, Rubio L, Cagnac O, García-sánchez MJ, Alché JDD, Venema K, Fernández JA, Rodríguez- Rosales MP (2013). The K+/H+ antiporter LeNHX2 increases salt tolerance by improving K+ homeostasis in transgenic tomato.Plant Cell Environ 36, 2135-2149. |
| [59] | Ivashikina N, Becker D, Ache P, Meyerhoff O, Felle HH, Hedrich R (2001). K+ channel profile and electrical pro- perties of Arabidopsis root hairs.FEBS Lett 508, 463-469. |
| [60] | Ivashikina N, Deeken R, Fischer S, Ache P, Hedrich R (2005). AKT2/3 subunits render guard cell K+ channels Ca2+ sensitive.J Gen Physiol 125, 483-492. |
| [61] | Jeanguenin L, Alcon C, Duby G, Boeglin M, Chérel I, Gaillard I, Zimmermann S, Sentenac H, Véry AA (2011). AtKC1 is a general modulator of Arabidopsis inward Shaker channel activity. Plant J 67, 570-582. |
| [62] | Jung JY, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2009). Ethylene mediates response and tolerance to potassium deprivation in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 607-621. |
| [63] | Kanai S, Ohkura K, Adu-Gyamfi JJ, Mohapatra PK, Nguyen NT, Saneoka H, Fujita K (2007). Depression of sink activity precedes the inhibition of biomass production in tomato plants subjected to potassium deficiency stress.J Exp Bot 58, 2917-2928. |
| [64] | Kellermeier F, Chardon F, Amtmann A (2013). Natural variation of Arabidopsis root architecture reveals complementing adaptive strategies to potassium starvation.Plant Physiol 161, 1421-1432. |
| [65] | Kim MJ, Ciani S, Schachtman DP (2010). A peroxidase contributes to ROS production during Arabidopsis root response to potassium deficiency.Mol Plant 3, 420-427. |
| [66] | Kim MJ, Ruzicka D, Shin R, Schachtman DP (2012). The Arabidopsis AP2/ERF transcription factor RAP2.11 modu- lates plant response to low-potassium conditions.Mol Plant 5, 1042-1057. |
| [67] | Kirik V, Simon M, Huelskamp M, Schiefelbein J (2004). The enhancer of TRY and CPC1 gene acts redundantly with TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE in trichome and root hair cell patterning in Arabidopsis.Dev Biol 268, 506-513. |
| [68] | Kochian LV, Lucas WJ (1983). Potassium transport in corn roots II. The significance of the root periphery.Plant Physiol 73, 208-215. |
| [69] | Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner R, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001). Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice.Plant Physiol 125, 406-422. |
| [70] | Lan WZ, Lee SC, Che YF, Jiang YQ, Luan S (2011). Mechanistic analysis of AKT1 regulation by the CBL- CIPK-PP2CA interactions.Mol Plant 4, 527-536. |
| [71] | Lan WZ, Wang W, Wang SM, Li LG, Buchanan BB, Lin HX, Gao JP, Luan S (2010). A rice high-affinity potassium transporter (HKT) conceals a calcium-permeable cation channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 7089-7094. |
| [72] | Lang A (1983). Turgor-regulated translocation.Plant Cell Environ 6, 683-689. |
| [73] | Leigh RA, Wyn Jones RG (1984). A hypothesis relating critical potassium concentrations for growth to the distribution and functions of this ion in the plant cell.New Phytol 97, 1-13. |
| [74] | Liesche J, Schulz A, Krügel U, Grimm B, Kühn C (2008). Dimerization and endocytosis of the sucrose transporter StSUT1 in mature sieve elements.Plant Signal Behav 3, 1136-1137. |
| [75] | Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004). QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance.Theor Appl Genet 108, 253-260. |
| [76] | Liu K, Li L, Luan S (2006). Intracellular K+ sensing of SKOR, a Shaker-type K+ channel from Arabidopsis.Plant J 46, 260-268. |
| [77] | Lu Y, Chanroj S, Zulkifli L, Johnson MA, Uozumi N, Cheung A, Sze H (2011). Pollen tubes lacking a pair of K+ transporters fail to target ovules in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 23, 81-93. |
| [78] | Ma TL, Wu WH, Wang Y (2012). Transcriptome analysis of rice root responses to potassium deficiency.BMC Plant Biol 12, 161. |
| [79] | Maathuis FJ, Ichida AM, Sanders D, Schroeder JI (1997). Roles of higher plant K+ channels.Plant Physiol 114, 1141. |
| [80] | Maathuis FJ, Sanders D (1992). Plant membrane transport.Curr Opin Cell Biol 4, 661-669. |
| [81] | Maathuis FJ, Sanders D (1993). Energization of potassium uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana.Planta 191, 302-307. |
| [82] | Martin T, Frommer WB, Salanoubat M, Willmitzer L (1993). Expression of an Arabidopsis sucrose synthase gene indicates a role in metabolization of sucrose both during phloem loading and in sink organs. Plant J 4, 367-377. |
| [83] | Mäser P, Hosoo Y, Goshima S, Horie T, Eckelman B, Yamada K, Yoshida K, Bakker EP, Shinmyo A, Oiki S, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2002). Glycine residues in potassium channel-like selectivity filters determine potassium selectivity in four-loop-per-subunit HKT transporters from plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 6428-6433. |
| [84] | Mäser P, Thomine S, Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke IN, Amtmann A, Maathuis FJM, Sanders D, Harper JF, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans MW, Salt DE, Kim SA, Guerinot ML (2001). Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 126, 1646-1667. |
| [85] | Montiel G, Gantet P, Jay-Allemand C, Breton C (2004). Transcription factor networks. Pathways to the knowledge of root development.Plant Physiol 136, 3478-3485. |
| [86] | Nieves-Cordones M, Alemán F, Martínez V, Rubio F (2010). The Arabidopsis thaliana HAK5 K+ transporter is required for plant growth and K+ acquisition from low K+ solutions under saline conditions.Mol Plant 3, 326-333. |
| [87] | Nieves-Cordones M, Martínez-Cordero M, Martínez V, Rubio F (2007). An NH4+-sensitive component dominates high-affinity K+ uptake in tomato plants.Plant Sci 172, 273-280. |
| [88] | Nieves-Cordones M, Miller AJ, Alemán F, Martínez V, Rubio F (2008). A putative role for the plasma membrane potential in the control of the expression of the gene encoding the tomato high-affinity potassium transporter HAK5.Plant Mol Biol 68, 521-532. |
| [89] | Pandit A, Rai V, Bal S, Sinha S, Kumar V, Chauhan M, Gautam RK, Singh R, Sharma PC, Singh AK, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Mohapatra T, Singh NK (2010). Combining QTL mapping and transcriptome profiling of bulked RILs for identification of functional polymorphism for salt tolerance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Mol Genet Genomics 284, 121-136. |
| [90] | Peel AJ, Rogers S (1982). Stimulation of sugar loading into sieve elements of willow by potassium and sodium salts.Planta 154, 94-96. |
| [91] | Pettigrew WT (2008). Potassium influences on yield and quality production for maize, wheat, soybean and cotton.Physiol Plantarum 133, 670-681. |
| [92] | Philippar K, Ivashikina N, Ache P, Christian M, Lüthen H, Palme K, Hedrich R (2004). Auxin activates KAT1 and KAT2, two K+-channel genes expressed in seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J 37, 815-827. |
| [93] | Pilot G, Gaymard F, Mouline K, Chérel I, Sentenac H (2003). Regulated expression of Arabidopsis Shaker K+ channel genes involved in K+ uptake and distribution in the plant.Plant Mol Biol 51, 773-787. |
| [94] | Qi Z, Hampton CR, Shin R, Barkla BJ, White PJ, Schachtman DP (2008). The high affinity K+ transporter AtHAK5 plays a physiological role in planta at very low K+ concentrations and provides a caesium uptake pathway in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot 59, 595-607. |
| [95] | Qi Z, Spalding EP (2004). Protection of plasma membrane K+ transport by the salt overly sensitive1 Na+-H+ antiporter during salinity stress.Plant Physiol 136, 2548-2555. |
| [96] | Ren XL, Qi GN, Feng HQ, Zhao S, Zhao SS, Wang Y, Wu WH (2013). Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+ homeostasis in Ara- bidopsis.Plant J 74, 258-266. |
| [97] | Rengel Z, Damon PM (2008). Crops and genotypes differ in efficiency of potassium uptake and use.Physiol Plantarum 133, 624-636. |
| [98] | Rigas S, Debrosses G, Haralampidis K, Vicente-Agullo F, Feldmann KA, Grabov A, Dolan L, Hatzopoulos P (2001). TRH1 encodes a potassium transporter required for tip growth in Arabidopsis root hairs.Plant Cell 13, 139-151. |
| [99] | Rodríguez-Rosales MP, Jiang X, Gálvez FJ, Aranda MN, Cubero B, Venema K (2008). Overexpression of the tomato K+/H+ antiporter LeNHX2 confers salt tolerance by improving potassium compartmentalization.New Phytol 179, 366-377. |
| [100] | Ros R, Lemaillet G, Fonrouge AG, Daram P, Enjuto M, Salmon JM, Thibaud JB, Sentenac H (1999). Molecular determinants of the Arabidopsis AKT1 K+ channel ionic selectivity investigated by expression in yeast of randomly mutated channels.Physiol Plantarum 105, 459-468. |
| [101] | Rubio F, Santa-María GE, Rodríguez-Navarro A (2000). Cloning of Arabidopsis and barley cDNAs encoding HAK potassium transporters in root and shoot cells.Physiol Plantarum 109, 34-43. |
| [102] | Santa-María GE, Rubio F, Dubcovsky J, Rodríguez- Navarro A (1997). The HAK1 gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter.Plant Cell 9, 2281-2289. |
| [103] | Sassi A, Mieulet D, Khan I, Moreau B, Gaillard I, Sentenac H, Véry AA (2012). The rice monovalent cation transporter OsHKT2;4: revisited ionic selectivity.Plant Physiol 160, 498-510. |
| [104] | Schachtman DP, Shin R (2007). Nutrient sensing and signaling: NPKS.Annu Rev Plant Biol 58, 47-69. |
| [105] | Schellmann S, Schnittger A, Kirik V, Wada T, Okada K, Beermann A, Thumfahrt J, Jürgens G, Hülskamp M (2002). TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE mediate lateral inhibition during trichome and root hair patterning in Arabidopsis.EMBO J 21, 5036-5046. |
| [106] | Sharma T, Dreyer I, Riedelsberger J (2013). The role of K+ channels in uptake and redistribution of potassium in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci 4, 224. |
| [107] | Sheng XF, He LY (2006). Solubilization of potassium- bearing minerals by a wild-type strain of Bacillus eda- phicus and its mutants and increased potassium uptake by wheat.Can J Microbiol 52, 66-72. |
| [108] | Shimizu A, Guerta CQ, Gregorio GB, Kawasaki S, Ikehashi H (2005). QTLs for nutritional contents of rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) in solution cultures and its implication to tolerance to iron-toxicity.Plant Soil 275, 57-66. |
| [109] | Shin R (2014). Strategies for improving potassium use efficiency in plants.Mol Cells 37, 575-584. |
| [110] | Shin R, Burch AY, Huppert KA, Tiwari SB, Murphy AS, Guilfoyle TJ, Schachtman DP (2007). The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB77 modulates auxin signal trans- duction.Plant Cell 19, 2440-2453. |
| [111] | Shin R, Schachtman DP (2004). Hydrogen peroxide mediates plant root cell response to nutrient deprivation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 8827-8832. |
| [112] | Song Z, Yang S, Zhu H, Jin M, Su Y (2014). Heterologous expression of an alligatorweed high-affinity potassium transporter gene enhances salinity tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana.Am J Bot 101, 840-850. |
| [113] | Spalding EP, Hirsch RE, Lewis DR, Qi Z, Sussman MR, Lewis BD (1999). Potassium uptake supporting plant growth in the absence of AKT1 channel activity inhibition by ammonium and stimulation by sodium.J Gen Physiol 113, 909-918. |
| [114] | Sun J, Bankston JR, Payandeh J, Hinds TR, Zagotta WN, Zheng N (2014). Crystal structure of the plant dual-affinity nitrate transporter NRT1.1.Nature 507, 73-77. |
| [115] | Szczerba MW, Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2009). K+ transport in plants: physiology and molecular biology.J Plant Physiol 166, 447-466. |
| [116] | Tominaga-Wada R, Iwata M, Nukumizu Y, Sano R, Wada T (2012). A full-length R-like basic-helix-loop-helix trans- cription factor is required for anthocyanin upregulation whereas the N-terminal region regulates epidermal hair formation. Plant Sci 183, 115-122. |
| [117] | Véry AA, Sentenac H (2003). Molecular mechanisms and regulation of K+ transport in higher plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol 54, 575-603. |
| [118] | Vicente-Agullo F, Rigas S, Desbrosses G, Dolan L, Hatzopoulos P, Grabov A (2004). Potassium carrier TRH1 is required for auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots.Plant J 40, 523-535. |
| [119] | Voelker C, Schmidt D, Mueller-Roeber B, Czempinski K (2006). Members of the Arabidopsis AtTPK/KCO family form homomeric vacuolar channels in planta.Plant J 48, 296-306. |
| [120] | Wada T, Kurata T, Tominaga R, Koshino-Kimura Y, Tachibana T, Goto K, Marks MD, Shimura Y, Okada K (2002). Role of a positive regulator of root hair development, CAPRICE, in Arabidopsis root epidermal cell differentiation.Development 129, 5409-5419. |
| [121] | Walker DJ, Leigh RA, Miller AJ (1996). Potassium homeostasis in vacuolate plant cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 10510-10514. |
| [122] | Wang JG, Zhang FS, Zhang XL, Cao YP (2000). Release of potassium from K-bearing minerals: effect of plant roots under P deficiency.Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 56, 45-52. |
| [123] | Wang TB, Gassmann W, Rubio F, Schroeder JI, Glass AD (1998). Rapid up-regulation of HKT1, a high-affinity potassium transporter gene, in roots of barley and wheat following withdrawal of potassium.Plant Physiol 118, 651-659. |
| [124] | Wang W, Li G, Zhao J, Chu H, Lin W, Zhang D, Wang Z, Liang W (2014). DWARF TILLER1, a WUSCHEL-related homeobox transcription factor, is required for tiller growth in rice.PLoS Genet 10, e1004154. |
| [125] | Wang Y, Wu WH (2013). Potassium transport and signaling in higher plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 451-476. |
| [126] | Wang Y, Wu WH (2015). Genetic approaches for improvement of the crop potassium acquisition and utilization efficiency.Curr Opin Plant Biol 25, 46-52. |
| [127] | Wang YH, Garvin DF, Kochian LV (2002). Rapid induction of regulatory and transporter genes in response to phosphorus, potassium, and iron deficiencies in tomato roots. Evidence for cross talk and root/rhizosphere-mediated signals. Plant Physiol 130, 1361-1370. |
| [128] | White PJ, George TS, Dupuy LX, Karley AJ, Valentine TA, Wiesel L, Wishart J (2013a). Root traits for infertile soils.Front Plant Sci 4, 193. |
| [129] | White PJ, George TS, Gregory PJ, Bengough AG, Hallett PD, McKenzie BM (2013b). Matching roots to their environment.Ann Bot 112, 207-222. |
| [130] | White PJ, Hammond JP, King GJ, Bowen HC, Hayden RM, Meacham MC, Spracklen WP, Broadley MR (2010). Genetic analysis of potassium use efficiency in Brassica oleracea.Ann Bot 105, 1199-1210. |
| [131] | Wu P, Ni JJ, Luo AC (1998). QTLs underlying rice tolerance to low-potassium stress in rice seedlings.Crop Sci 38, 1458-1462. |
| [132] | Wu X, Dabi T, Weigel D (2005). Requirement of homeobox gene STIMPY/WOX9 for Arabidopsis meristem growth and maintenance.Curr Biol 15, 436-440. |
| [133] | Xie Q, Frugis G, Colgan D, Chua NH (2000). Arabidopsis NAC1 transduces auxin signal downstream of TIR1 to promote lateral root development.Gene Dev 14, 3024-3036. |
| [134] | Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ, Wang Y, Liu LL, He L, Wu WH (2006). A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis.Cell 125, 1347-1360. |
| [135] | Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Wu F, Hu Q, Chen G, Cai J, Wu T, Moran N, Yu L, Xu G (2014). The role of a potassium transporter OsHAK5 in potassium acquisition and transport from roots to shoots in rice at low potassium supply levels.Plant Physiol 166, 945-959. |
| [136] | Yang Z, Gao Q, Sun C, Li W, Gu S, Xu C (2009). Molecular evolution and functional divergence of HAK potassium transporter gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Genet Genomics 36, 161-172. |
| [137] | Yao WZ, Hadjeb N, Berkowitz GA (1997). Molecular cloning and characterization of the first plant K (Na)/proton antiporter.Plant Physiol 114S, 200. |
| [138] | Yong Z, Kotur Z, Glass AD (2010). Characterization of an intact two-component high-affinity nitrate transporter from Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 63, 739-748. |
| [139] | Yoo SC, Cho SH, Paek NC (2013). Rice WUSCHEL-related homeobox 3A (OsWOX3A) modulates auxin-transport gene expression in lateral root and root hair development.Plant Signal Behav 8, e25929. |
| [140] | Zhang H, Forde BG (1998). An Arabidopsis MADS box gene that controls nutrient-induced changes in root architecture.Science 279, 407-409. |
| [141] | Zhao F, Guo XQ, Wang P, He LY, Huang Z, Sheng XF (2013). Dyella jiangningensis sp. nov., a γ-proteobacter- ium isolated from the surface of potassium-bearing rock. Int J Syst Evol Micr 63, 3154-3157. |
| [142] | Zhao Y, Hu Y, Dai M, Huang L, Zhou DX (2009). The WUSCHEL-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice.Plant Cell 21, 736-748. |
| [143] | Zörb C, Senbayram M, Peiter E (2014). Potassium in agriculture—status and perspectives.J Plant Physiol 171, 656-669. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
