

植物学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 77-88.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16192 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16192
所属专题: 水稻生物学专辑 (2017年52卷1期)
收稿日期:2016-10-07
接受日期:2016-12-13
出版日期:2017-01-01
发布日期:2017-01-23
通讯作者:
向珣朝
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:Jiafu Wu†, Bowen Yang†, Xunchao Xiang*, Liang Xu, Limei Yan
Received:2016-10-07
Accepted:2016-12-13
Online:2017-01-01
Published:2017-01-23
Contact:
Xiang Xunchao
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要: 以21份水稻(Oryza sativa)种质为材料, 用1.5%NaCl处理种子8天后测定发芽率。在苗期用不同浓度NaCl水培处理10天, 测定叶片死亡率等指标和高亲和性K+转运基因(HKT)家族变异。在成株期选3份种质, 用不同浓度NaCl盆栽处理, 在开花期和籽粒蜡熟期测定植株可溶性糖和生物量等指标, 以明确各种质不同生育期的耐盐差异和关键指标。结果表明, 在NaCl胁迫下, 种子发芽率受到显著影响。苗期盐胁迫后, 各种质的平均叶片死亡率变幅最大。在被鉴定的8个耐盐种质中, HKT家族的7个基因除OsHKT2;4外均存在。在≤1 g·kg-1盐胁迫下植株可溶性糖含量表现出刺激增长效应。CG15R单株生物量与盐浓度呈正相关, 且随盐浓度的增加而缓慢增长。在≤1 g·kg-1时, 中花9号的生物量随盐浓度的增加而增加。水稻耐盐性具有明显的阶段发育特异性, 且不同发育阶段的耐盐性之间无相关性。叶片死亡率与蜡熟期生物量可分别作为苗期和成株期耐盐鉴定的关键指标。CG15R可作为高耐盐种质进行深入分析和利用。
吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许亮, 颜李梅. 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 77-88.
Jiafu Wu, Bowen Yang, Xunchao Xiang, Liang Xu, Limei Yan. Identification of Salt Tolerance in Different Rice Germplasm at Different Growth Stages. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(1): 77-88.
| No. | Germplasm | Subspecies | No. | Germplasm | Subspecies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C190 | Indica | 12 | CG131R | Indica |
| 2 | CG133R | Indica | 13 | CG158R | Indica |
| 3 | HD63 | Indica | 14 | CG111R | Indica |
| 4 | CG15R | Indica | 15 | CG114R | Indica |
| 5 | Javanica 22 | Japonica | 16 | CG173R | Indica |
| 6 | Shuhui527 | Indica | 17 | CG132R | Indica |
| 7 | 3301R | Indica | 18 | CG151R | Indica |
| 8 | Lehui188 | Indica | 19 | CG159R | Indica |
| 9 | Zhonghua9 | Japonica | 20 | CG240R | Indica |
| 10 | Jing925 | Japonica | 21 | BR207-2 | Indica |
| 11 | BR207-1 | Indica |
表1 供试材料及类型
Table 1 Materials and their type for this study
| No. | Germplasm | Subspecies | No. | Germplasm | Subspecies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C190 | Indica | 12 | CG131R | Indica |
| 2 | CG133R | Indica | 13 | CG158R | Indica |
| 3 | HD63 | Indica | 14 | CG111R | Indica |
| 4 | CG15R | Indica | 15 | CG114R | Indica |
| 5 | Javanica 22 | Japonica | 16 | CG173R | Indica |
| 6 | Shuhui527 | Indica | 17 | CG132R | Indica |
| 7 | 3301R | Indica | 18 | CG151R | Indica |
| 8 | Lehui188 | Indica | 19 | CG159R | Indica |
| 9 | Zhonghua9 | Japonica | 20 | CG240R | Indica |
| 10 | Jing925 | Japonica | 21 | BR207-2 | Indica |
| 11 | BR207-1 | Indica |
| Gene | Sequence of primers (5'-3') | Tm | Length for genome amplified (bp) | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsHKT1;1 | F: GAGCACTGTGGAGGAATTTTACCG R: TAGTGAGTAGCCTACATTGCCGAAA | 61.1 | 389 | Chr.04 |
| OsHKT1;3 | F: GCTTACTTTGCCCTGATCTCCT R: TGAATACCTCACCACCAATC | 58.0 | 214 | Chr.02 |
| OsHKT1;4 | F: GCGACTCTGGCAAACTGATA R: GGTTCCTGTCTATGTGAAAATGAATA | 57.5 | 211 | Chr.04 |
| OsHKT2;1 | F: GTTAATTTTGTTGTTCTAGC R: ATGAGGCTGGAAAGTGTCAG | 53.3 | 200 | Chr.06 |
| OsHKT2;3 | F: CTGCCATGAGAAGGCGTACAA R: ATCGCATACTGATCGCTTCTGAT | 59.2 | 152 | Chr.01 |
| OsHKT2;4 | F: CTTGCCATGAGAAGCCATACAG R: CTTGATTCTTGCATAACATCATCA | 57.6 | 146 | Chr.06 |
| OsHKT1;5 | F: ACGACCCCATCAACTACAGCGTCC R: TGCTCCACTTCCCTGAGAAGCCAAC | 65.3 | 833 | Chr.01 |
表2 HKT家族基因引物信息
Table 2 Primers information of HKT family genes
| Gene | Sequence of primers (5'-3') | Tm | Length for genome amplified (bp) | Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsHKT1;1 | F: GAGCACTGTGGAGGAATTTTACCG R: TAGTGAGTAGCCTACATTGCCGAAA | 61.1 | 389 | Chr.04 |
| OsHKT1;3 | F: GCTTACTTTGCCCTGATCTCCT R: TGAATACCTCACCACCAATC | 58.0 | 214 | Chr.02 |
| OsHKT1;4 | F: GCGACTCTGGCAAACTGATA R: GGTTCCTGTCTATGTGAAAATGAATA | 57.5 | 211 | Chr.04 |
| OsHKT2;1 | F: GTTAATTTTGTTGTTCTAGC R: ATGAGGCTGGAAAGTGTCAG | 53.3 | 200 | Chr.06 |
| OsHKT2;3 | F: CTGCCATGAGAAGGCGTACAA R: ATCGCATACTGATCGCTTCTGAT | 59.2 | 152 | Chr.01 |
| OsHKT2;4 | F: CTTGCCATGAGAAGCCATACAG R: CTTGATTCTTGCATAACATCATCA | 57.6 | 146 | Chr.06 |
| OsHKT1;5 | F: ACGACCCCATCAACTACAGCGTCC R: TGCTCCACTTCCCTGAGAAGCCAAC | 65.3 | 833 | Chr.01 |
| No. | Average germination rate (%) | Relative salt damage rate (%) | Salt tolerance | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NaCl (1.5%) | ||||
| 1 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 36.67±0.01 cC | 63.08 | Weak | 7 |
| 2 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 7.78±1.92 ghFG | 92.17 | Very weak | 9 |
| 3 | 83.33±0.01 gG | 13.33±0.01 efgEFG | 84.00 | Very weak | 9 |
| 4 | 60.20±0.34 lL | 8.84±3.08 ghFG | 85.97 | Very weak | 9 |
| 5 | 73.33±0.01 jJ | 11.67±1.67 fghEFG | 84.08 | Very weak | 9 |
| 6 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 28.00±15.62 dCD | 71.68 | Weak | 7 |
| 7 | 83.33±0.01 gG | 14.00±6 efgEFG | 83.20 | Very weak | 9 |
| 8 | 86.67±0.01 fF | 13.34±8.80 efgEFG | 84.60 | Very weak | 9 |
| 9 | 93.34±0.01 dD | 15.00±5 efgEF | 83.93 | Very weak | 9 |
| 10 | 90.00±0.02 eE | 81.67±1.67 aA | 9.26 | Very strong | 1 |
| 11 | 73.33±0.01 jJ | 16.89±3.00 efDEF | 71.96 | Weak | 7 |
| 12 | 93.34±0.02 dD | 3.33±0.01 hG | 96.43 | Very weak | 9 |
| 13 | 93.34±0.02 dD | 26.67±3.34 dCD | 71.43 | Weak | 7 |
| 14 | 80.00±0.02 hH | 10.00±2 fghFG | 87.50 | Very weak | 9 |
| 15 | 86.68±0.02 fF | 21.67±1.67 deDE | 75.00 | Weak | 7 |
| 16 | 66.68±0.02 kK | 50.00±0.02 bB | 25.02 | Strong | 3 |
| 17 | 98.02±0.02 bB | 13.33±7.02 efgEFG | 86.39 | Very weak | 9 |
| 18 | 96.67±0.01 cC | 7.33±3.05 ghFG | 92.41 | Very weak | 9 |
| 19 | 76.67±0.01 iI | 8.89±5.09 fghFG | 88.41 | Very weak | 9 |
| 20 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 8.89±5.09 fghFG | 91.09 | Very weak | 9 |
| 21 | 93.34±0.01 dD | 16.89±3.06 efDEF | 81.90 | Very weak | 9 |
表3 不同水稻种质的发芽率及相对盐害率
Table 3 Germination rate of different varieties and their relative salt damage rate
| No. | Average germination rate (%) | Relative salt damage rate (%) | Salt tolerance | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NaCl (1.5%) | ||||
| 1 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 36.67±0.01 cC | 63.08 | Weak | 7 |
| 2 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 7.78±1.92 ghFG | 92.17 | Very weak | 9 |
| 3 | 83.33±0.01 gG | 13.33±0.01 efgEFG | 84.00 | Very weak | 9 |
| 4 | 60.20±0.34 lL | 8.84±3.08 ghFG | 85.97 | Very weak | 9 |
| 5 | 73.33±0.01 jJ | 11.67±1.67 fghEFG | 84.08 | Very weak | 9 |
| 6 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 28.00±15.62 dCD | 71.68 | Weak | 7 |
| 7 | 83.33±0.01 gG | 14.00±6 efgEFG | 83.20 | Very weak | 9 |
| 8 | 86.67±0.01 fF | 13.34±8.80 efgEFG | 84.60 | Very weak | 9 |
| 9 | 93.34±0.01 dD | 15.00±5 efgEF | 83.93 | Very weak | 9 |
| 10 | 90.00±0.02 eE | 81.67±1.67 aA | 9.26 | Very strong | 1 |
| 11 | 73.33±0.01 jJ | 16.89±3.00 efDEF | 71.96 | Weak | 7 |
| 12 | 93.34±0.02 dD | 3.33±0.01 hG | 96.43 | Very weak | 9 |
| 13 | 93.34±0.02 dD | 26.67±3.34 dCD | 71.43 | Weak | 7 |
| 14 | 80.00±0.02 hH | 10.00±2 fghFG | 87.50 | Very weak | 9 |
| 15 | 86.68±0.02 fF | 21.67±1.67 deDE | 75.00 | Weak | 7 |
| 16 | 66.68±0.02 kK | 50.00±0.02 bB | 25.02 | Strong | 3 |
| 17 | 98.02±0.02 bB | 13.33±7.02 efgEFG | 86.39 | Very weak | 9 |
| 18 | 96.67±0.01 cC | 7.33±3.05 ghFG | 92.41 | Very weak | 9 |
| 19 | 76.67±0.01 iI | 8.89±5.09 fghFG | 88.41 | Very weak | 9 |
| 20 | 99.33±1.15 aA | 8.89±5.09 fghFG | 91.09 | Very weak | 9 |
| 21 | 93.34±0.01 dD | 16.89±3.06 efDEF | 81.90 | Very weak | 9 |
| No. | NaCl concentration | Average | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.1% | |||||||||||||
| Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | ||||||
| 1 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.47 | 0.82 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.88 | 0.54 | |||||
| 3 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 0.66 | |||||
| 4 | 0.85 | 1.69 | 0.85 | 1.24 | 1.01 | 1.44 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 1.22 | |||||
| 5 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.53 | 0.83 | 0.42 | 0.83 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 0.59 | |||||
| 6 | 0.95 | 1.30 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1.25 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.94 | 1.08 | |||||
| 7 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.62 | 0.91 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 0.79 | |||||
| 8 | 1.02 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.82 | |||||
| 9 | 1.07 | 1.61 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.03 | 1.51 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 1.13 | |||||
| 10 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 1.03 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.97 | |||||
| 11 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 1.05 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |||||
| 12 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 0.83 | 1.04 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 1.01 | |||||
| 14 | 0.96 | 1.09 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.86 | |||||
| 16 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.96 | |||||
| 17 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 0.76 | |||||
| 19 | 0.89 | 1.35 | 0.92 | 1.06 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 0.90 | |||||
| 20 | 0.87 | 1.19 | 0.86 | 1.84 | 1.02 | 1.56 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 0.95 | 1.28 | 0.94 | 1.41 | |||||
| 21 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.98 | |||||
表4 不同浓度盐处理下部分水稻种质的相对苗高与相对根长
Table 4 Relative seedling height and relative root length of part rice germplasms under different salt concentration treatments
| No. | NaCl concentration | Average | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.1% | |||||||||||||
| Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | Relative seedling height | Relative root length | ||||||
| 1 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.47 | 0.82 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.88 | 0.54 | |||||
| 3 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 0.66 | |||||
| 4 | 0.85 | 1.69 | 0.85 | 1.24 | 1.01 | 1.44 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 1.22 | |||||
| 5 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.53 | 0.83 | 0.42 | 0.83 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 0.59 | |||||
| 6 | 0.95 | 1.30 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1.25 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.94 | 1.08 | |||||
| 7 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.62 | 0.91 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 0.79 | |||||
| 8 | 1.02 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.01 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.82 | |||||
| 9 | 1.07 | 1.61 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.03 | 1.51 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 1.13 | |||||
| 10 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 1.03 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.97 | |||||
| 11 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 1.05 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |||||
| 12 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 0.83 | 1.04 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 1.01 | |||||
| 14 | 0.96 | 1.09 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.86 | |||||
| 16 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.96 | |||||
| 17 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 0.76 | |||||
| 19 | 0.89 | 1.35 | 0.92 | 1.06 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.48 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 0.90 | |||||
| 20 | 0.87 | 1.19 | 0.86 | 1.84 | 1.02 | 1.56 | 0.99 | 1.20 | 0.95 | 1.28 | 0.94 | 1.41 | |||||
| 21 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.98 | |||||
| No. | NaCl concentration | Average | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortal- ity (%) | |||||||
| 1 | 71.60 | 13.37 | 69.37 | 39.50 | 71.93 | 24.06 | 68.13 | 53.68 | 63.25 | 56.66 | 66.72 | 89.04 | 67.88 eE | 52.59 qQ | ||||||
| 3 | 72.54 | 37.44 | 68.31 | 57.27 | 67.33 | 65.58 | 64.50 | 89.79 | 65.15 | 90.05 | 61.47 | 94.35 | 65.35 hH | 79.41 gG | ||||||
| 4 | 65.21 | 43.64 | 60.9 | 86.26 | 62.25 | 97.12 | 63.94 | 93.69 | 54.00 | 100.00 | 58.90 | 100.00 | 60.02 kK | 95.41 aA | ||||||
| 5 | 58.99 | 32.17 | 58.32 | 49.48 | 44.24 | 61.40 | 45.09 | 81.67 | 49.40 | 99.20 | 41.81 | 100.00 | 47.77 pP | 78.35 hH | ||||||
| 6 | 65.96 | 28.14 | 55.80 | 64.53 | 54.95 | 59.88 | 55.27 | 78.24 | 53.96 | 91.49 | 64.07 | 93.80 | 56.81 lL | 77.59 iI | ||||||
| 7 | 51.76 | 34.30 | 59.98 | 56.32 | 50.71 | 84.40 | 48.66 | 86.47 | 51.56 | 100.00 | 63.01 | 100.00 | 54.78 oO | 85.44 dD | ||||||
| 8 | 61.72 | 15.12 | 51.85 | 42.46 | 53.95 | 87.83 | 42.69 | 84.49 | 41.18 | 100.00 | 42.93 | 100.00 | 46.52 qQ | 82.96 fF | ||||||
| 9 | 74.42 | 29.95 | 75.18 | 26.63 | 70.04 | 71.48 | 69.25 | 84.12 | 73.10 | 97.96 | 67.05 | 100.00 | 70.92 cC | 76.04 kK | ||||||
| 10 | 75.25 | 33.66 | 72.65 | 53.65 | 73.23 | 84.40 | 73.17 | 81.00 | 73.96 | 97.07 | 72.16 | 100.00 | 73.03 bB | 83.22 eE | ||||||
| 11 | 67.27 | 19.64 | 65.62 | 42.87 | 68.42 | 44.97 | 68.54 | 47.71 | 65.62 | 91.48 | 68.66 | 100.00 | 67.37 fF | 61.41 oO | ||||||
| 12 | 69.14 | 13.52 | 70.96 | 44.81 | 68.32 | 30.92 | 65.46 | 70.89 | 65.19 | 93.70 | 63.54 | 99.49 | 66.70 gG | 67.96 mM | ||||||
| 14 | 71.15 | 20.27 | 68.51 | 55.58 | 70.12 | 60.57 | 70.75 | 81.07 | 70.76 | 88.92 | 70.22 | 99.60 | 70.07 dD | 77.15 jJ | ||||||
| 16 | 61.67 | 14.11 | 64.32 | 50.08 | 63.70 | 87.71 | 65.50 | 95.07 | 63.77 | 100.00 | 61.30 | 100.00 | 63.72 iI | 86.57 cC | ||||||
| 17 | 52.96 | 4.87 | 55.11 | 75.41 | 58.78 | 90.19 | 56.18 | 100.00 | 53.77 | 100.00 | 56.23 | 100.00 | 56.02 mM | 93.12 bB | ||||||
| 19 | 76.00 | 40.14 | 75.79 | 54.37 | 75.74 | 73.99 | 75.14 | 74.93 | 71.70 | 81.24 | 70.60 | 84.52 | 73.79 aA | 73.81 lL | ||||||
| 20 | 60.01 | 33.42 | 55.99 | 79.19 | 50.96 | 53.49 | 59.31 | 83.03 | 59.75 | 50.41 | 52.32 | 71.36 | 55.67 nN | 67.50 nN | ||||||
| 21 | 58.84 | 18.89 | 64.62 | 14.35 | 67.90 | 47.86 | 64.07 | 42.02 | 61.10 | 92.95 | 58.82 | 100.00 | 63.30 jJ | 59.44 pP | ||||||
表5 不同浓度盐处理下部分水稻种质的叶片死亡率和含水量
Table 5 Leaf mortality and water content of part rice germplasms under different salt concentration treatments
| No. | NaCl concentration | Average | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortality (%) | Water content (%) | Leaf mortal- ity (%) | |||||||
| 1 | 71.60 | 13.37 | 69.37 | 39.50 | 71.93 | 24.06 | 68.13 | 53.68 | 63.25 | 56.66 | 66.72 | 89.04 | 67.88 eE | 52.59 qQ | ||||||
| 3 | 72.54 | 37.44 | 68.31 | 57.27 | 67.33 | 65.58 | 64.50 | 89.79 | 65.15 | 90.05 | 61.47 | 94.35 | 65.35 hH | 79.41 gG | ||||||
| 4 | 65.21 | 43.64 | 60.9 | 86.26 | 62.25 | 97.12 | 63.94 | 93.69 | 54.00 | 100.00 | 58.90 | 100.00 | 60.02 kK | 95.41 aA | ||||||
| 5 | 58.99 | 32.17 | 58.32 | 49.48 | 44.24 | 61.40 | 45.09 | 81.67 | 49.40 | 99.20 | 41.81 | 100.00 | 47.77 pP | 78.35 hH | ||||||
| 6 | 65.96 | 28.14 | 55.80 | 64.53 | 54.95 | 59.88 | 55.27 | 78.24 | 53.96 | 91.49 | 64.07 | 93.80 | 56.81 lL | 77.59 iI | ||||||
| 7 | 51.76 | 34.30 | 59.98 | 56.32 | 50.71 | 84.40 | 48.66 | 86.47 | 51.56 | 100.00 | 63.01 | 100.00 | 54.78 oO | 85.44 dD | ||||||
| 8 | 61.72 | 15.12 | 51.85 | 42.46 | 53.95 | 87.83 | 42.69 | 84.49 | 41.18 | 100.00 | 42.93 | 100.00 | 46.52 qQ | 82.96 fF | ||||||
| 9 | 74.42 | 29.95 | 75.18 | 26.63 | 70.04 | 71.48 | 69.25 | 84.12 | 73.10 | 97.96 | 67.05 | 100.00 | 70.92 cC | 76.04 kK | ||||||
| 10 | 75.25 | 33.66 | 72.65 | 53.65 | 73.23 | 84.40 | 73.17 | 81.00 | 73.96 | 97.07 | 72.16 | 100.00 | 73.03 bB | 83.22 eE | ||||||
| 11 | 67.27 | 19.64 | 65.62 | 42.87 | 68.42 | 44.97 | 68.54 | 47.71 | 65.62 | 91.48 | 68.66 | 100.00 | 67.37 fF | 61.41 oO | ||||||
| 12 | 69.14 | 13.52 | 70.96 | 44.81 | 68.32 | 30.92 | 65.46 | 70.89 | 65.19 | 93.70 | 63.54 | 99.49 | 66.70 gG | 67.96 mM | ||||||
| 14 | 71.15 | 20.27 | 68.51 | 55.58 | 70.12 | 60.57 | 70.75 | 81.07 | 70.76 | 88.92 | 70.22 | 99.60 | 70.07 dD | 77.15 jJ | ||||||
| 16 | 61.67 | 14.11 | 64.32 | 50.08 | 63.70 | 87.71 | 65.50 | 95.07 | 63.77 | 100.00 | 61.30 | 100.00 | 63.72 iI | 86.57 cC | ||||||
| 17 | 52.96 | 4.87 | 55.11 | 75.41 | 58.78 | 90.19 | 56.18 | 100.00 | 53.77 | 100.00 | 56.23 | 100.00 | 56.02 mM | 93.12 bB | ||||||
| 19 | 76.00 | 40.14 | 75.79 | 54.37 | 75.74 | 73.99 | 75.14 | 74.93 | 71.70 | 81.24 | 70.60 | 84.52 | 73.79 aA | 73.81 lL | ||||||
| 20 | 60.01 | 33.42 | 55.99 | 79.19 | 50.96 | 53.49 | 59.31 | 83.03 | 59.75 | 50.41 | 52.32 | 71.36 | 55.67 nN | 67.50 nN | ||||||
| 21 | 58.84 | 18.89 | 64.62 | 14.35 | 67.90 | 47.86 | 64.07 | 42.02 | 61.10 | 92.95 | 58.82 | 100.00 | 63.30 jJ | 59.44 pP | ||||||
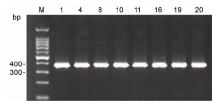
图2 不同水稻种质OsHKT1;1基因的PCR检测结果^M: 分子量标准; 1: C190; 4: CG15R; 8: Lehui188; 10: Jing- 925; 11: BR207-1; 16: CG173R; 19: CG159R; 20: CG240R
Figure 2 Electrophoretic results of PCR detection on Os- HKT1;1 for different rice germplasms^M: DNA marker; 1: C190; 4: CG15R; 8: Lehui188; 10: Jing- 925; 11: BR207-1; 16: CG173R; 19: CG159R; 20: CG240R
| Primers | 1-C190 | 4-CG15R | 8-Lehui188 | 10-Jing925 | 11-BR207-1 | 16-CG173R | 19-CG159R | 20-CG240R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsHKT1;1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| OsHKT2;1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT2;3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT2;4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表6 不同水稻种质的PCR条带统计
Table 6 Statistics of PCR results for different rice germplasms
| Primers | 1-C190 | 4-CG15R | 8-Lehui188 | 10-Jing925 | 11-BR207-1 | 16-CG173R | 19-CG159R | 20-CG240R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsHKT1;1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT1;5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| OsHKT2;1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT2;3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| OsHKT2;4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
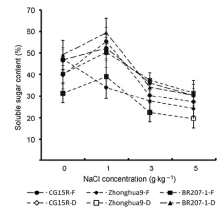
图3 盐胁迫下水稻开花期和蜡熟期可溶性糖含量的比较^F: 开花期; D: 蜡熟期
Figure 3 Comparison of soluble sugar content in flowering and dough period of rice under salt stress^F: Flowering stage; D: Dough stage
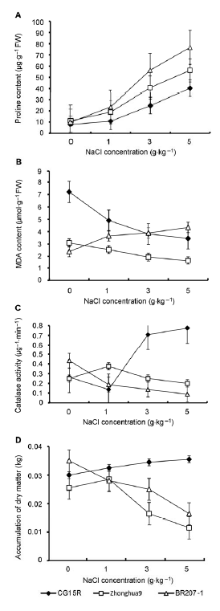
图4 盐胁迫对水稻成株期不同生理指标的影响^(A) 脯氨酸含量; (B) 丙二醛含量; (C) 过氧化氢酶活性; (D) 蜡熟期干物质量
Figure 4 Effects of salt stress on different physiological indices of rice in adult period^(A) Proline content; (B) Malondialdehyde (MDA) content; (C) Catalase activity; (D) Accumulation of dry matter in dough stage
| [1] | 陈志德, 仲维功, 杨杰, 黄转运 (2004). 水稻新种质资源的耐盐性鉴定评价. 植物遗传资源学报 5, 351-355. |
| [2] | 方先文, 汤陵华, 王艳平 (2004). 耐盐水稻种质资源的筛选. 植物遗传资源学报 5, 295-298. |
| [3] | 顾兴友, 郑少玲, 严小龙, 杨崇, 卢永根 (1998). 盐浓度对水稻苗期耐盐指标变异度的影响. 华南农业大学学报 19, 30-34. |
| [4] | 管志勇, 陈发棣, 滕年军, 陈素梅, 刘浦生 (2010). 5种菊花近缘种属植物的耐盐性比较. 中国农业科学 43, 787-794. |
| [5] | 郭望模, 傅亚萍, 孙宗修, 郑镇一 (2003). 盐胁迫下不同水稻种质形态指标与耐盐性的相关分析. 植物遗传资源学报 4, 245-251. |
| [6] | 胡时开, 陶红剑, 钱前, 郭龙彪 (2010). 水稻耐盐性的遗传和分子育种的研究进展. 分子植物育种 8, 629-640. |
| [7] | 李小兵, 黎华寿, 张泽民, 陈桂葵 (2014). 水稻盐分胁迫研究进展. 广东农业科学 41, 6-11. |
| [8] | 陆嘉惠, 吕新, 梁永超, 林海荣 (2013). 新疆胀果甘草幼苗耐盐性及对NaCl胁迫的离子响应. 植物生态学报 37, 839-850. |
| [9] | 潘晓飚, 段敏, 谢留杰, 陈剑, 黄善军, 徐建龙 (2014). 盐胁迫下杂交水稻种子发芽特性及耐盐性评价. 中国农学通报 30, 75-79. |
| [10] | 潘晓飚, 黄善军, 陈凯, 孟丽君, 徐建龙 (2012). 大田全生育期盐水灌溉胁迫筛选水稻耐盐恢复系. 中国水稻科学 26, 49-54. |
| [11] | 祁栋灵, 韩龙植, 张三元 (2005). 水稻耐盐/碱性鉴定评价方法. 植物遗传资源学报 6, 226-230. |
| [12] | 孙健, 赵宏伟, 王敬国, 刘化龙, 谢冬微, 刘忠良, 郭丽颖, 邹德堂 (2012). 水稻孕穗期剑叶形态和蒸腾特性与耐盐性的关系. 华北农学报 (6), 84-91. |
| [13] | 王学奎 (2006). 植物生理生化试验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 134-206. |
| [14] | 吴延寿 (2008). 水稻钠离子转运蛋白OsHKT2;4的功能分析. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 61-85. |
| [15] | 向珣朝, 李季航, 何立斌, 李平 (2007). ZmC4Ppc基因水稻的标记辅助选择及其后代的产量性状分析. 中国水稻科学 21, 25-30. |
| [16] | 肖文斐, 马华升, 陈文岳, 裘劼人, 童建新, 郑桂珍, 忻雅, 王淑珍, 方献平, 阮松林 (2013). 籼稻耐盐性与稻米品质性状的关联分析. 核农学报 27, 1938-1947. |
| [17] | 藏金萍, 孙勇, 王韵, 杨静, 李芳, 周永力, 朱苓华, Reys Jessica, Fotokian Mohammadhosein, 徐建龙, 黎志康 (2008). 利用回交导入系剖析水稻苗期和分蘖期耐盐性的遗传重叠. 中国科学(C辑) 38, 841-850. |
| [18] | Andrew D (2012). The short- and medium- term impacts of rises in staple food prices.Food Secur 4, 633-645. |
| [19] | Berthomieu P, Conéjéro G, Nublat A, Brackenbury WJ, Lambert C, Savio C, Uozumi N, Oiki S, Yamada K, Cellier F, Gosti F, Simonneau T, Essah PA, Tester M, Véry AA, Sentenac H, Casse F (2003). Functional analysis of AtHKT1 in Arabidopsis shows that Na+ recirculation by the phloem is cddrucial for salt tolerance.EMBO J 22, 2004-2014. |
| [20] | Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W, James RA, Lagudah ES, Dennis ES, Tester M, Munns R (2007). HKT1;5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143, 1918-1928. |
| [21] | Foolad MR, Lin GY (1997). Absence of a relationship bet- ween salt tolerance during germination and vegetative growth in tomato.Plant Breed 116, 363-367. |
| [22] | Horie T, Hauser F, Schroeder JI (2009). HKT transporter- mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants.Trends Plant Sci 14, 660-668. |
| [23] | Jabnoune M, Espeout S, Mieulet D, Fizames C, Verdeil JL, Conéjéro G, Rodríguez-Navarro A, Sentenac H, Guid- erdoni E, Abdelly C, Véry AA (2009). Diversity in expression patterns and functional properties in the rice HKT transporter family.Plant Physiol 150, 1955-1971. |
| [24] | Johnson DW, Smith SE, Dobrenz AK (1992). Genetic and phenotypic relationships in response to NaCl at different developmental stages in alfalfa.Theor Appl Genet 83, 833-838. |
| [25] | Karsten U, Franklin LA, Luning K, Wiencke C (1998). Natural ultraviolet radiation and photosynthetically active radiation induce formation of mycosporine- line amino aci- ds in the marine macroalga Chondrus crispus (Phodophyta).Planta 205, 257-262. |
| [26] | Li XJ, Yang MF, Zhu Y, Liang Y, Shen SH (2011). Proteomic analysis of salt stress responses in rice shoot.J Plant Biol 54, 384-395. |
| [27] | Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004). QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance.Theor Appl Genet 108, 253-260. |
| [28] | Mäser P, Hosoo Y, Goshima S, Horie T, Eckelman B, Yamada K, Yoshida K, Bakker EP, Shinmyo A, Oiki S, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2002). Glycine residues in potassium channel-like selectivity filters determine potassium selectivity in four-loop-per-subunit HKT transporters from plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 6428-6433. |
| [29] | Munns R, James RA, Xu B, Athman A, Conn SJ, Jordans C, Byrt CS, Hare RA, Tyerman SD, Tester M, Plett D, Gilliham M (2012). Wheat grain yield on saline soils is improved by an ancestral Na+ transporter gene.Nature Biotechnol 30, 360-364. |
| [30] | Plett D, Safwat G, Gilliham M, Skrumsager Møller I, Roy S, Shirley N, Jacobs A, Johnson A, Tester M (2010). Improved salinity tolerance of rice through cell type-specific expression of AtHKT1;1.PLoS One 5, e12571. |
| [31] | Ren Z, Gao J, Li L, Cai X, Huang W, Chao D, Zhu M, Wang Z, Luan S, Lin H (2005). A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter.Nat Genet 37, 1141-1146. |
| [32] | Shereen A, Mumtaz S, Raza S, Khan MA, Solangi S (2014). Salinity effects on seedling growth and yield components of different inbred rice lines.Pakistan J Bot 37, 131-139. |
| [33] | Sunarpi, Horie T, Motoda J, Kubo M, Yang H, Yoda K, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Hattori K, Konomi M, Osumi M, Yamagami M, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2005). Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells.Plant J 44, 928-938. |
| [34] | Vinocur B, Ahman A (2005). Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to a biotic stress: achievements and limitations.Curr Opin Biotechnol 16, 123-132. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
