

Research Advances on Lectin Receptor-like Kinases in Plants
Received date: 2019-07-10
Accepted date: 2019-09-24
Online published: 2019-10-09
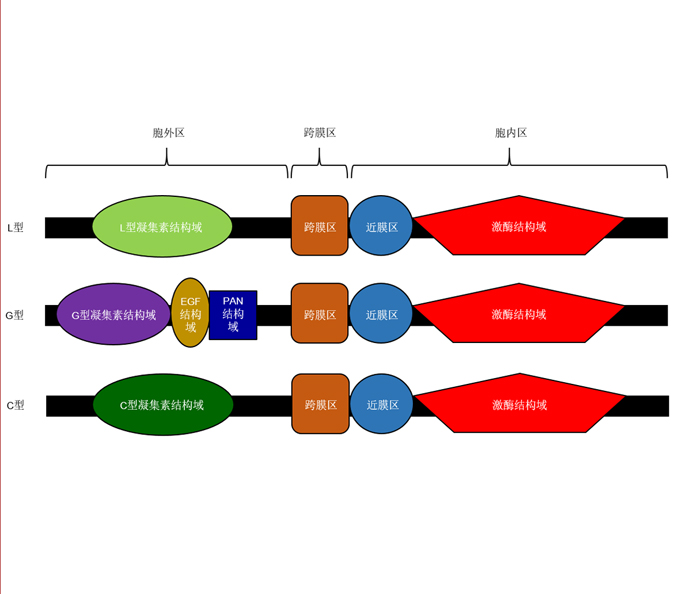
Plant growth and development are affected by various environmental factors. In response to various environmental changes, plants have evolved a series of signal recognition and transduction proteins, such as the plasma membrane-localized receptor-like kinases (RLKs), to cope with the environmental conditions. The lectin receptor-like kinases (LecRLKs) are a subfamily of RLKs that contain three structural domains: the extracellular lectin domain, transmembrane domain, and the intracellular kinase domain. Based on the structural difference of the extracellular lectin domain, LecRLKs are classified into three subclasses: L-, G-, and C-type. Recent studies have shown that LecRLKs play a vital role in plant development and biotic/abiotic stress responses. In this review, we discribe the research history, structural features and classification, and biological functions of LecRLKs, and emphasize on the functions of LecRLKs in plants in response to biotic/abiotic stresses and in regulating development. This review provides a view for future functional study on LecRLKs and crop improvement by elaborating different types and functions of LecRLKs.
Menglong Wang,Xiaoqun Peng,Zhufeng Chen,Xiaoyan Tang . Research Advances on Lectin Receptor-like Kinases in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020 , 55(1) : 96 -105 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB19130
| [1] | 毕真真 (2013). 水稻OsL-LecRK7基因的功能研究. 硕士论文. 新乡: 河南师范大学. pp. 1-82. |
| [2] | Barre A, Hervé C, Lescure B, Rougé R (2002). Lectin receptor kinases in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 21, 379-399. |
| [3] | Becraft PW, Stinard PS, McCarty DR (1996). CRINKLY4: a TNFR-like receptor kinase involved in maize epidermal differentiation. Science 273, 1406-1409. |
| [4] | Bellande K, Bono JJ, Savelli B, Jamet E, Canut H (2017). Plant lectins and lectin receptor-like kinases: how do they sense the outside? Int J Mol Sci 18, 1164. |
| [5] | Bonaventure G (2011). The Nicotiana attenuata lectin receptor kinase 1 is involved in the perception of insect feeding. Plant Signal Behav 6, 2060-2063. |
| [6] | Bouwmeester K, Govers F (2009). Arabidopsis L-type lectin receptor kinases: phylogeny, classification, and expression profiles. J Exp Bot 60, 4383-4396. |
| [7] | Brewin NJ, Kardailsky IV (1997). Legume lectins and nodulation by Rhizobium. Trends Plant Sci 2, 92-98. |
| [8] | Brill LM, Evans CJ, Hirsch AM (2001). Expression of MsLEC1- and MsLEC2-antisense genes in alfalfa plant lines causes severe embryogenic, developmental and reproductive abnormalities. Plant J 25, 453-461. |
| [9] | Cambi A, Koopman M, Figdor CG (2005). How C-type lectins detect pathogens. Cell Microbiol 7, 481-488. |
| [10] | Chen XW, Shang JJ, Chen DX, Lei CL, Zou Y, Zhai WX, Liu GZ, Xu JC, Ling ZH, Cao G, Ma BT, Wang YP, Zhao XF, Li SG, Zhu LH (2006). A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J 46, 794-804. |
| [11] | Choi J, Tanaka K, Cao YR, Qi Y, Qiu J, Liang Y, Lee SY, Stacey G (2014). Identi?cation of a plant receptor for extracellular ATP. Science 343, 290-294. |
| [12] | Deng KQ, Wang QM, Zeng JX, Guo XH, Zhao XY, Tang DY, Liu XM (2009). A lectin receptor kinase positively regulates ABA response during seed germination and is involved in salt and osmotic stress response. J Plant Biol 52, 493-500. |
| [13] | Desclos-Theveniau M, Arnaud D, Huang TY, Lin GJC, Chen WY, Lin YC, Zimmerli L (2012). The Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinase LecRK-V.5 represses stomatal immunity induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. PLoS Pathog 8, e1002513. |
| [14] | Edelman GM, Wang JL (1978). Binding and functional properties of concanavalin A and its derivatives. III. Interactions with indoleacetic acid and other hydrophobic ligands. J Biol Chem 253, 3016-3022. |
| [15] | Epstein J, Eichbaum Q, Sheriff S, Ezekowitz RAB (1996). The collectins in innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 8, 29-35. |
| [16] | Fan JB, Bai PF, Ning YS, Wang JY, Shi XT, Xiong YH, Zhang K, He F, Zhang CY, Wang RY, Meng XZ, Zhou JG, Wang M, Shirsekar G, Park CH, Bellizzi M, Liu WD, Jeon JS, Xia Y, Shan LB, Wang GL (2018). The monocot-specific receptor-like kinase SDS2 controls cell death and immunity in rice. Cell Host Microbe 23, 498-510. |
| [17] | Gilardoni PA, Hettenhausen C, Baldwin IT, Bonaventure G (2011). Nicotiana attenuata LECTIN RECEPTOR KINASE 1 suppresses the insect-mediated inhibition of induced defense responses during Manduca sexta herbivory. Plant Cell 23, 3512-3532. |
| [18] | Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang RL, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong JP, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang SP, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen LL, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002). A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296, 92-100. |
| [19] | Gouhier-Darimont C, Schmiesing A, Bonnet C, Lassueur S, Reymond P (2013). Signaling of Arabidopsis thaliana response to Pieris brassicae eggs shares similarities with PAMP-triggered immunity. J Exp Bot 64, 665-674. |
| [20] | Hawgood S, Akiyama J, Brown C, Allen L, Li G, Poulain FR (2001). GM-CSF mediates alveolar macrophage proliferation and type II cell hypertrophy in SP-D gene-targeted mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280, L1148-L1156. |
| [21] | He XJ, Zhang ZG, Yan DQ, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2004). A salt-responsive receptor-like kinase gene regulated by the ethylene signaling pathway encodes a plasma membrane serine/threonine kinase. Theor Appl Genet 109, 377-383. |
| [22] | Hervé C, dabos P, Galaud JP, Rougé P, Lescure B (1996). Characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene that defines a new class of putative plant receptor kinases with an extracellular lectin-like domain. J Mol Biol 258, 778-788. |
| [23] | Hervé C, Serres J, Dabos P, Canut H, Barre A, Rougé P, Lescure B (1999). Characterization of the Arabidopsis lecRK-a genes: members of a superfamily encoding putative receptors with an extracellular domain homologous to legume lectins. Plant Mol Biol 39, 671-682. |
| [24] | Hu X, Reddy ASN (1997). Cloning and expression of a PR5-like protein from Arabidopsis: inhibition of fungal growth by bacterially expressed protein. Plant Mol Biol 34, 949-959. |
| [25] | Hunter T (1991). Protein Kinase Classication. Methods Enzymol 200, 3-37. |
| [26] | Joshi A, Dang HD, Vaid N, Tuteja N (2010). Pea lectin receptor-like kinase promotes high salinity stress tolerance in bacteria and expresses in response to stress in planta. Glycoconj J 27, 133-150. |
| [27] | Kanzaki H, Saitoh H, Takahashi Y, Berberich T, Ito A, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2008). NbLRK1, a lectin-like receptor kinase protein of Nicotiana benthamiana, interacts with Phytophthora infestans INF1 elicitin and mediates INF1-induced cell death. Planta 228, 977-987. |
| [28] | Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001). The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11, 725-732. |
| [29] | Kusaba M, Dwyer K, Hendershot J, Vrebalov J, Nasrallah JB, Nasrallah ME (2001). Self-incompatibility in the genus Arabidopsis: characterization of the S locus in the outcrossing A. lyrata and its autogamous relative A. thaliana. Plant Cell 13, 627-643. |
| [30] | Labbé J, Muchero W, Czarnecki O, Wang J, Wang XP, Bryan AC, Zheng KJ, Yang YL, Xie M, Zhang J, Wang DF, Meidl P, Wang HM, Morrell-Falvey JL, Cope KR, Maia LGS, Ané JM, Mewalal R, Jawdy SS, Gunter LE, Schackwitz W, Martin J, Le Tacon F, Li T, Zhang ZH, Ranjan P, Lindquist E, Yang XH, Jacobson DA, Tschaplinski TJ, Barry K, Schmutz J, Chen JG, Tuskan GA (2019). Mediation of plant-mycorrhizal interaction by a lectin receptor-like kinase. Nat Plants 5, 676-680. |
| [31] | Li CH, Wang G, Zhao JL, Zhang LQ, Ai LF, Han YF, Sun DY, Zhang SW, Sun Y (2014). The receptor-like kinase SIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice. Plant Cell 26, 2538-2553. |
| [32] | Li HY, Gray JE (1997). Pollination-enhanced expression of a receptor-like protein kinase related gene in tobacco styles. Plant Mol Biol 33, 653-665. |
| [33] | Loris R (2002). Principles of structures of animal and plant lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1572, 198-208. |
| [34] | Luo XM, Xu N, Huang JK, Gao F, Zou HS, Boudsocq M, Coaker G, Liu J (2017). A lectin receptor-like kinase mediates pattern-triggered salicylic acid signaling. Plant Physiol 174, 2501-2514. |
| [35] | Ma N, Liu CX, Li H, Wang JY, Zhang BL, Lin J, Chang YH (2018). Genome-wide identification of lectin receptor kinases in pear: functional characterization of the L-type LecRLK gene PbLRK138. Gene 661, 11-21. |
| [36] | Morillo SA, Tax FE (2006). Functional analysis of receptor-like kinases in monocots and dicots. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9, 460-469. |
| [37] | Naithani S, Chookajorn T, Ripoll DR, Nasrallah JB (2007). Structural modules for receptor dimerization in the S-locus receptor kinase extracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 12211-12216. |
| [38] | Navarro-Gochicoa MT, Camut S, Timmers ACJ, Niebel A, Hervé C, Boutet E, Bono JJ, Imberty A, Cullimore JV (2003). Characterization of four lectin-like receptor kinases expressed in roots of Medicago truncatula. Structure, location, regulation of expression, and potential role in the symbiosis with Sinorhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol 133, 1893-1910. |
| [39] | Newman T, de Bruijn FJ, Green P, Keegstra K, Kende H, McIntosh L, Ohlrogge J, Raikhel N, Somerville S, Thomashow M, Retzel E, Somerville C (1994). Genes galore: a summary of methods for accessing results from large-scale partial sequencing of anonymous Arabidopsis cDNA clones. Plant Physiol 106, 1241-1255. |
| [40] | Nishiguchi M, Yoshida K, Sumizono T, Tazaki K (2002). A receptor-like protein kinase with a lectin-like domain from Lombardy poplar: gene expression in response to wounding and characterization of phosphorylation activity. Mol Genet Genomics 267, 506-514. |
| [41] | Peumans WJ, van Damme EJM (1995). The role of lectins in plant defence. Histochem J 27, 253-271. |
| [42] | Ranf S, Gisch N, Sch?ffer M, Illig T, Westphal L, Knirel YA, Smánchez-Carballo PM, Z?hringer U, Hückelhoven R, Lee J, Scheel D (2015). A lectin S-domain receptor kinase mediates lipopolysaccharide sensing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Immunol 16, 426-433. |
| [43] | Riou C, Hervé C, Pacquit V, Dabos P, Lescure B (2002). Expression of an Arabidopsis lectin kinase receptor gene, lecRK-a1, is induced during senescence, wounding and in response to oligogalacturonic acids. Plant Physiol Biochem 40, 431-438. |
| [44] | Rüdiger H, Gabius HJ (2001). Plant lectins: occurrence, biochemistry, functions and applications. Glycoconj J 18, 589-613. |
| [45] | Sanabria NM, van Heerden H, Dubery IA (2012). Molecular characterisation and regulation of a Nicotiana tabacum S- domain receptor-like kinase gene induced during an early rapid response to lipopolysaccharides. Gene 501, 39-48. |
| [46] | Sherman-Broyles S, Boggs N, Farkas A, Liu P, Vrebalov J, Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (2007). S locus genes and the evolution of self-fertility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 19, 94-106. |
| [47] | Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001). Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 10763-10768. |
| [48] | Singh P, Kuo YC, Mishra S, Tsai CH, Chien CC, Chen CW, Desclos-Theveniau M, Chu PW, Schulze B, Chinchilla D, Boller T, Zimmerli L (2012). The lectin receptor kinase-VI.2 is required for priming and positively regulates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 24, 1256-1270. |
| [49] | Sun XL, Yu QY, Tang LL, Ji W, Bai X, Cai H, Liu XF, Ding XD, Zhu YM (2013). GsSRK, a G-type lectin S-receptor- like serine/threonine protein kinase, is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 170, 505-515. |
| [50] | Tanksley SD, Loaiza-Figueroa F (1985). Gametophytic self-incompatibility is controlled by a single major locus on chromosome 1 in Lycopersicon peruvianum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82, 5093-5096. |
| [51] | Tordai H, Bányai L, Patthy L (1999). The PAN module: the N-terminal domains of plasminogen and hepatocyte growth factor are homologous with the apple domains of the prekallikrein family and with a novel domain found in numerous nematode proteins. FEBS Lett 461, 63-67. |
| [52] | Vaid N, Macovei A, Tuteja N (2013). Knights in action: lectin receptor-like kinases in plant development and stress responses. Mol Plant 6, 1405-1418. |
| [53] | Vaid N, Pandey P, Srivastava VK, Tuteja N (2015). Pea lectin receptor-like kinase functions in salinity adaptation without yield penalty, by alleviating osmotic and ionic stresses and upregulating stress-responsive genes. Plant Mol Biol 88, 193-206. |
| [54] | Vaid N, Pandey PK, Tuteja N (2012). Genome-wide analysis of lectin receptor-like kinase family from Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol 80, 365-388. |
| [55] | Walker JC (1994). Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 26, 1599-1609. |
| [56] | Walker JC, Zhang R (1990). Relationship of a putative receptor protein kinase from maize to the S-locus glycoproteins of Brassica. Nature 345, 743-746. |
| [57] | Wan JR, Patel A, Mathieu M, Kim SY, Xu D, Stacey G (2008). A lectin receptor-like kinase is required for pollen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67, 469-482. |
| [58] | Wang GL, Ruan DL, Song WY, Sideris S, Chen LL, Pi LY, Zhang SP, Zhang Z, Fauquet C, Gaut BS, Whalen MC, Ronald PC (1998). Xa21D encodes a receptor-like molecule with a leucine-rich repeat domain that determines race-specific recognition and is subject to adaptive evolution. Plant Cell 10, 765-779. |
| [59] | Wang Y, Cordewener JHG, America AHP, Shan WX, Bouwmeester K, Govers F (2015). Arabidopsis lectin receptor kinases LecRK-IX.1 and LecRK-IX.2 are functional analogs in regulating Phytophthora resistance and plant cell death. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28, 1032-1048. |
| [60] | Xin ZY, Wang A, Yang GH, Gao P, Zheng ZL (2009). The Arabidopsis A4 subfamily of lectin receptor kinases negatively regulates abscisic acid response in seed germination. Plant Physiol 149, 434-444. |
| [61] | Yu J, Hu SN, Wang J, Wong GKS, Li SG, Liu B, Deng YJ, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang XQ, Cao ML, Liu J, Sun JD, Tang JB, Chen YJ, Huang XB, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong LJ, Geng JN, Han YJ, Li L, Li W, Hu GQ, Huang XG, Li WJ, Li J, Liu ZW, Li L, Liu JP, Qi QH, Liu JS, Li L, Li T, Wang XG, Lu H, Wu TT, Zhu M, Ni PX, Han H, Dong W, Ren XY, Feng XL, Cui P, Li XR, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai WX, Xu Z, Zhang JS, He SJ, Zhang JG, Xu JC, Zhang KL, Zheng XW, Dong JH, Zeng WY, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren XD, Chen XW, He J, Liu DF, Tian W, Tian CG, Xia HA, Bao QY, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao WM, Li P, Chen W, Wang XD, Zhang Y, Hu JF, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang GY, Xiong YQ, Li ZJ, Mao L, Zhou CS, Zhu Z, Chen RS, Hao BL, Zheng WM, Chen SY, Guo W, Li GJ, Liu SQ, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu LH, Yuan LP, Yang HM (2002). A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296, 79-92. |
| [62] | Zhang C, Guo XH, Xie HL, Li JY, Liu XQ, Zhu BD, Liu SC, Li HL, Li ML, He MQ, Chen P (2019). Quantitative phosphoproteomics of lectin receptor-like kinase VI.4 dependent abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol Plant 165, 728-745. |
| [63] | Zuo KJ, Zhao JY, Wang J, Sun XF, Tan KX (2004). Molecular cloning and characterization of GhLecRK, a novel kinase gene with lectin-like domain from Gossypium hirsutum. DNA Seq 15, 58-65. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |