Isolation and Functional Characterization of Heat-stressresponsive Gene TaWTF1 from Wheat
- QIN Dan-Dan ,
- XIE Rong-Zhao ,
- LIU Gang ,
- NIE Zhong-Fu ,
- YAO Ying-Ken ,
- XUN Ji-Shen ,
- PENG Hui-Ru
- 1Institute of Food Crops, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Science, Wuhan 430064, China;
2China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China;
3Northwest Agriculture and Forest University, Yangling 712100, China
Received date: 2012-05-22
Revised date: 2012-07-26
Online published: 2012-11-01
Abstract
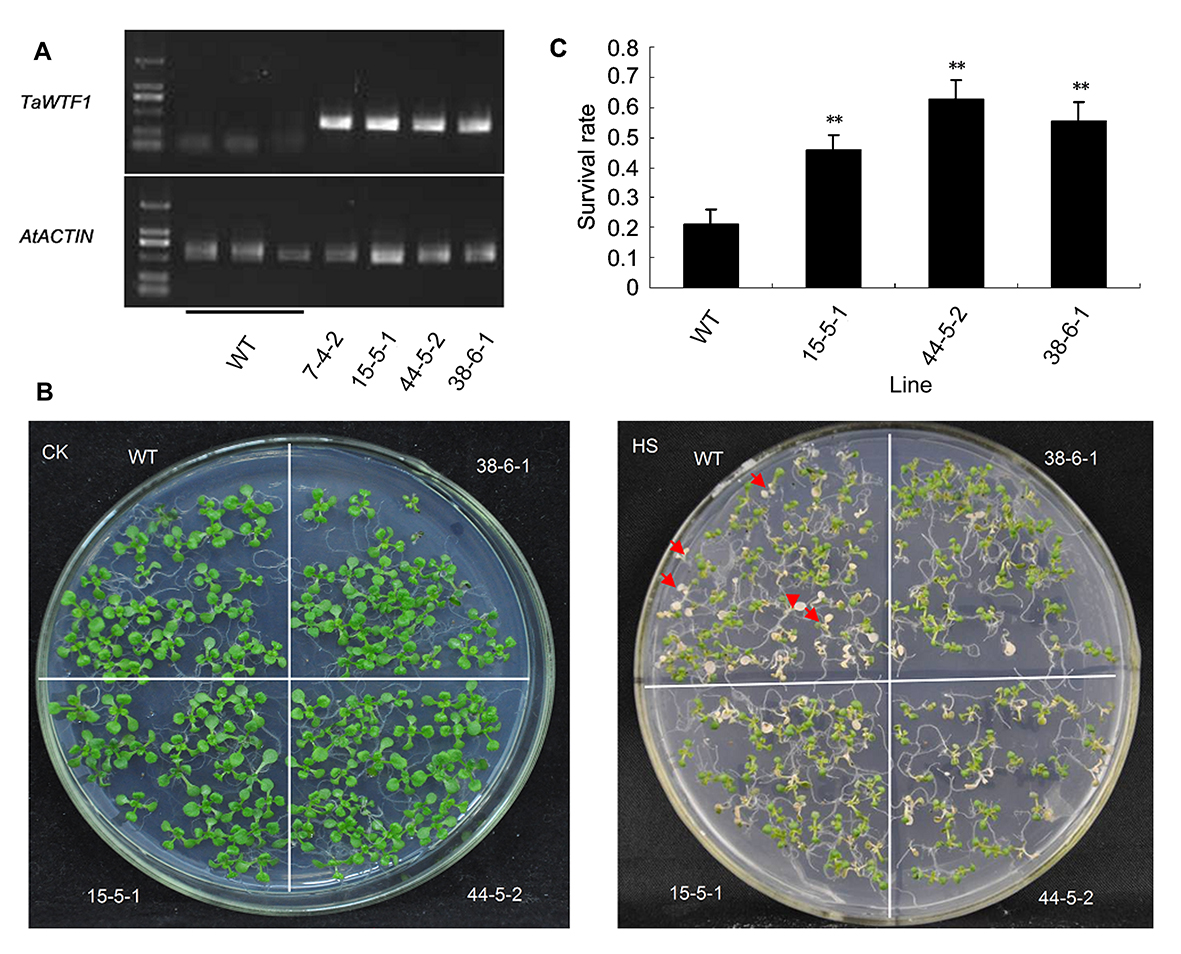
Key words: heat stress; unknown function; wheat; WTF1
Cite this article
QIN Dan-Dan , XIE Rong-Zhao , LIU Gang , NIE Zhong-Fu , YAO Ying-Ken , XUN Ji-Shen , PENG Hui-Ru . Isolation and Functional Characterization of Heat-stressresponsive Gene TaWTF1 from Wheat[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013 , 48(1) : 34 -41 . DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2013.00034
References
[2] Konishi M, Sugiyama M (2006). A Novel Plant-Specific Family Gene, ROOT PRIMORDIUM DEFECTIVE 1, Is Required for the Maintenance of Active Cell Proliferation. Plant Physiol 140, 591-602
[3] Qin DD, Wu HY, Peng HR, Ni ZF, Yao YY, Li ZX, Zhou CL, Sun QX (2008). Heat stress-responsive transcriptome analysis in heat susceptible and tolerant wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by using Wheat Genome Array. BMC Genomics 9, 432
[4] Song L, Sultan C, Jeffery H, John C, Ron M (2008). Enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants expressing proteins of unknown function. Plant Physiol 148, 280-292
[5] Tiffany SK, Kenneth PW, Giulia F, Klaas JW, Alice B (2009). A plant-specific RNA-binding domain revealed through analysis of chloroplast group II intron splicing. PNAS 106, 4537-4542
[6] 秦丹丹 (2008). 小麦苗期热胁迫转录谱分析及相关基因的克隆和功能鉴定. 博士论文. 北京:中国农业大学. pp. 19-51
[7] 张庆波 (2009). 植物杂交种和亲本基因差异表达与mRNA稳定性和可变剪接的关系研究. 博士论文. 北京:中国农业大学. pp. 39