

Functional Diversity of Ulmus lamellosa Community in the Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi
Received date: 2015-02-12
Accepted date: 2015-09-21
Online published: 2016-03-31
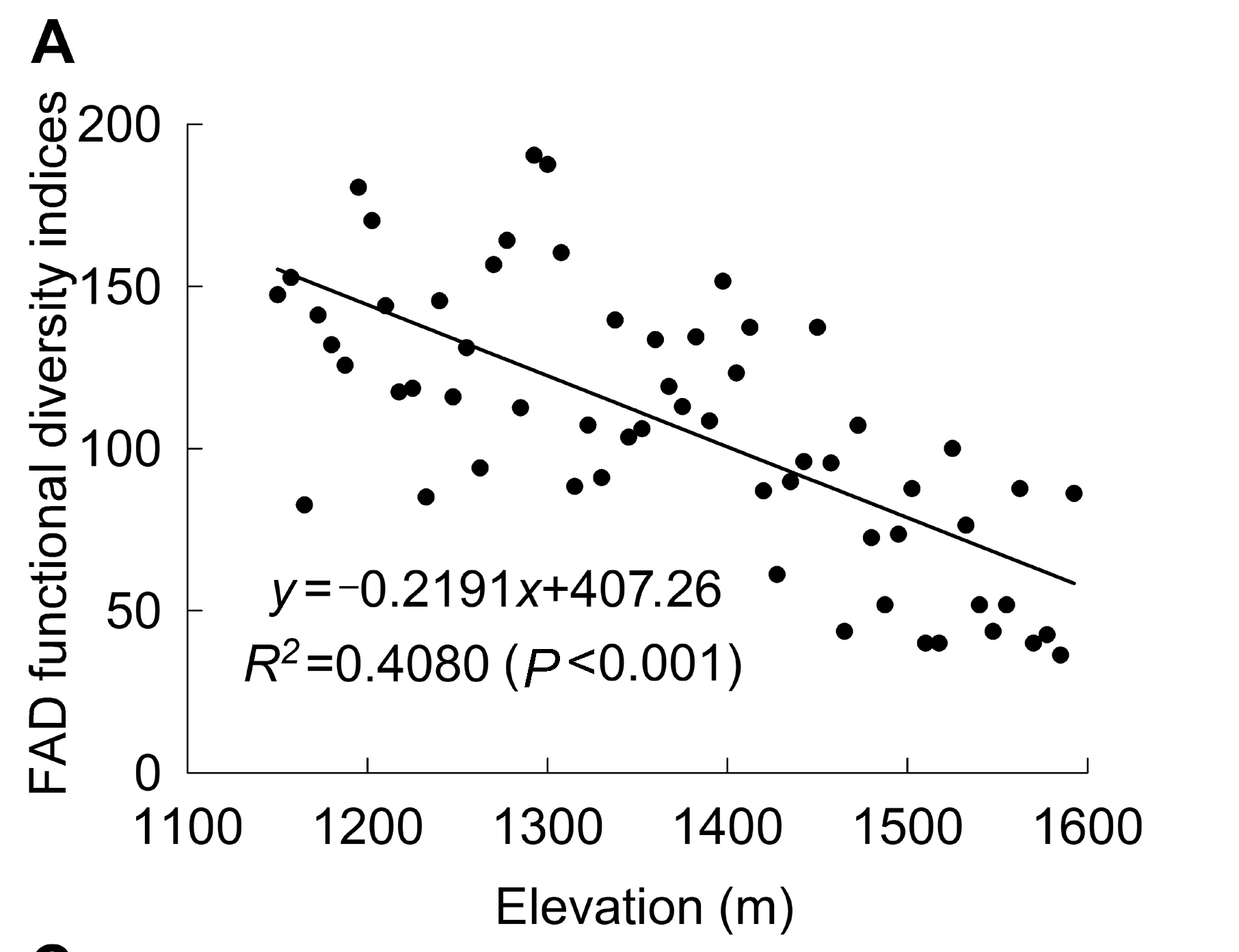
As a component of biodiversity, plant functional diversity is considered a key factor in understanding the link between ecosystem functioning and biodiversity. In this study, we researched the functional diversity of the Ulmus lamellosa community in the Taiyue Mountain area of Shanxi. We investigated 11 traits, including habitat type, spread of seeds, pollination, type of nitrogen fixation, life history, life form, leaf type, plant height, coverage, flowering period and flowering time. The functional diversity of 7 U. lamellosa associations and the elevation pattern were analyzed by using FAD, Rao’s, SL and CL indices. Results showed that, the FAD, SL, CL indices decreased from association I to VII, and the Rao’s indices increased, and both implied the functional diversity decreased in this order. Regression models indicated that elevation was the primary determinant of the functional diversity, and functional diversity decreased with increasing elevation.
Qindi Zhang , Xiaomei Duan , Yufang Bai , Yiling Wang , Jintun Zhang . Functional Diversity of Ulmus lamellosa Community in the Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016 , 51(2) : 218 -225 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB15033
| [1] | 白永飞, 李凌浩, 黄建辉, 陈佐忠 (2001). 内蒙古高原针茅草原植物多样性与植物功能群组成对群落初级生产力稳定性的影响. 植物学报 43, 280-287. |
| [2] | 毕润成, 陈李芳, 李培玉 (2003a). 山西南部脱皮榆群落生态特征及其物种多样性的研究. 武汉植物学研究 21, 109-116. |
| [3] | 毕润成, 尹文兵, 王艳妮 (2003b). 山西南部脱皮榆种群生态位的研究. 西北植物学报 23, 1266-1271. |
| [4] | 毕润成, 张杰, 苏俊霞 (2002). 山西稀有濒危植物脱皮榆的生态学特征. 植物资源与环境学报 11, 45-50. |
| [5] | 杜盛, 古松, 谷瑞英 (1994). 脱皮榆离体培养中丛生芽形成与生长的研究. 内蒙古林学院学报 16, 24-28. |
| [6] | 杜盛, 闫美杰 (1996). 脱皮榆离体培养再生植株的研究. 内蒙古林学院学报(自然科学版) 4, 15-17. |
| [7] | 段晓梅, 白玉芳, 张钦弟, 张金屯 (2016). 山西太岳山脱皮榆群落的生态梯度分析及环境解释. 植物学报 51, 40-48. |
| [8] | 范丽宏 (2011). 植物功能多样性的度量方法和应用. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京师范大学. pp. 17-18. |
| [9] | 黄建辉, 白永飞, 韩兴国 (2001). 物种多样性与生态系统功能: 影响机制及有关假说. 生物多样性 9, 1-7. |
| [10] | 黄忠良, 孔国辉, 何道泉 (2000). 鼎湖山植物群落多样性的研究. 生态学报 20, 193-198. |
| [11] | 茹文明, 张桂萍, 毕润成, 张峰, 张金屯 (2007). 濒危植物脱皮榆种群结构与分布格局研究. 应用与环境生物学报 13, 14-17. |
| [12] | 上官铁梁, 马子清, 谢树莲 (1998). 山西省珍稀濒危保护植物. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社. pp. 77-90. |
| [13] | 孙国钧, 张荣, 周立 (2003). 植物功能多样性与功能群研究进展. 生态学报 23, 1430-1435. |
| [14] | 唐志尧, 方精云 (2004). 植物物种多样性的垂直分布格局. 生物多样性 12, 20-28. |
| [15] | 汪殿蓓, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏 (2001). 植物群落物种多样性研究综述. 生态学杂志 20, 55-60. |
| [16] | 王晓霞, 张钦弟, 毕润成, 白玉芳 (2013). 山西稀有濒危植物脱皮榆种内和种间竞争. 生态学杂志 32, 1756-1761. |
| [17] | 闫桂琴, 任鹰, 张变红, 李钻青 (2004). 三种木本植物基因组DNA的提取及纯度检测. 山西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 18, 72-77. |
| [18] | 张金屯, 范丽宏 (2011). 物种功能多样性及其研究方法. 山地学报 29, 513-519. |
| [19] | Cornelissen J, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Diaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich D, Reich P, Ter Steege H, Morgan H, Van Der Heijden M (2003). A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot 51, 335-380. |
| [20] | Díaz S, Cabido M (2001). Vive la difference: plant functional diversity matters to ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol Evol 16, 646-655. |
| [21] | Gower JC (1971). A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 27, 857-871. |
| [22] | Lep? J, Bello F, Lavorel S, Berman S (2006). Quantifying and interpreting functional diversity of natural communities: practical consideration smatter. Preslia 78, 481-501. |
| [23] | Mason N, Mouillot D, Lee W, Wilson J (2005). Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: the primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 111, 112-118. |
| [24] | Mouillot D, Mason WHN, Dumay O, Wilson J (2005). Functional regularity: a neglected aspect of functional diversity. Oecologia 142, 353-359. |
| [25] | Petchey O, Gaston K (2002a). Extinction and the loss of functional diversity. P Roy Soc Lond B Biol 269, 1721-1727. |
| [26] | Petchey O, Gaston K (2002b). Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecol Lett 5, 402-411. |
| [27] | Podani J (1999). Extending Gower’s general coefficient of similarity to ordinal characters. Taxon 48, 331-340. |
| [28] | Podani J, Schmera D (2006). On dendrogram based measu- res of functional diversity. Oikos 115, 179-185. |
| [29] | Ricotta C (2005). A note on functional diversity measures. Basic Appl Ecol 6, 479-486. |
| [30] | Tilman D (2001). Functional Diversity. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 109-120. |
| [31] | Walker B, Kinzig A, Langridge J (1999). Plant attribute diversity, resilience, and ecosystem function: the nature and significance of dominant and minor species. Ecosystems 2, 95-113. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |