

Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Rice Disease Resistance
Received date: 2025-01-20
Accepted date: 2025-02-22
Online published: 2025-02-26
Rice (Oryza sativa) is one of the most vital food crops globally, and its yield plays a crucial role in ensuring food security. However, various diseases affecting rice pose significant threats to this security. Among these, rice blast, bacterial blight, and sheath blight are the three predominant diseases impacting global rice production. Consequently, there is an urgent need to breed and cultivate rice varieties with broad-spectrum disease resistance. In recent years, substantial advancements have been made in understanding the regulatory mechanisms underlying disease resistance in rice. This paper reviews these mechanisms from multiple perspectives, including the plant’s intrinsic immune responses and the functional dynamics of resistance genes. Furthermore, it highlights pressing issues that require immediate attention to facilitate broad-spectrum disease-resistant breeding efforts for rice.
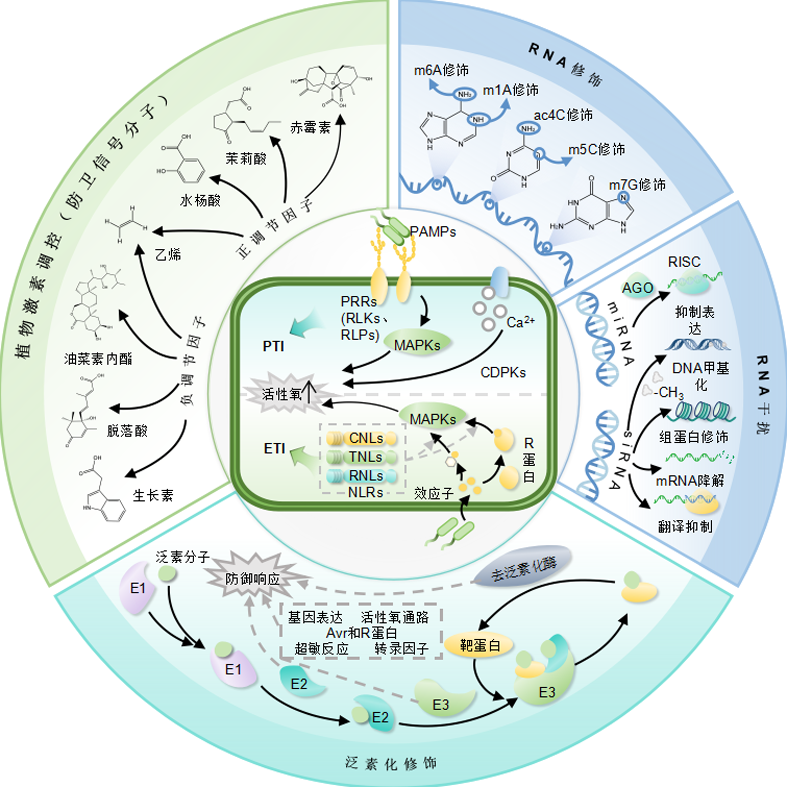
Jiang Yanan , Xu Yuqing , Wei Yiting , Chen Jun , Zhang Rongwan , Zhao Beibei , Lin Yuxiang , Rao Yuchun . Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Rice Disease Resistance[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025 , 60(5) : 734 -748 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB25011
| [1] | Andaya CB, Ronald PC (2003). A catalytically impaired mutant of the rice Xa21 receptor kinase confers partial resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pvoryzae. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 62, 203-208. |
| [2] | Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M (2008). Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance. Genetics 180, 2267-2276. |
| [3] | Boutrot F, Zipfel C (2017). Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad- spectrum disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55, 257-286. |
| [4] | Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia YL, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000). A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12, 2033-2046. |
| [5] | Cao WL, Zhang HM, Zhou Y, Zhao JH, Lu SB, Wang XQ, Chen XJ, Yuan LM, Guan HY, Wang GD, Shen WX, De Vleesschauwer D, Li ZQ, Shi XP, Gu JF, Guo M, Feng ZM, Chen ZX, Zhang YF, Pan XB, Liu WD, Liang GH, Yan CJ, Hu KM, Liu QQ, Zuo SM (2022). Suppressing chlorophyll degradation by silencing OsNYC3 improves rice resistance to Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of sheath blight. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 335-349. |
| [6] | Cao YL, Duan L, Li HJ, Sun XL, Zhao Y, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP (2007). Functional analysis of Xa3/Xa26 family members in rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae. Theor Appl Genet 115, 887-895. |
| [7] | Césari S, Kanzaki H, Fujiwara T, Bernoux M, Chalvon V, Kawano Y, Shimamoto K, Dodds P, Terauchi R, Kroj T (2014). The NB-LRR proteins RGA4 and RGA5 interact functionally and physically to confer disease resistance. EMBO J 33, 1941-1959. |
| [8] | Chen J, Peng P, Tian JS, He YG, Zhang LP, Liu ZX, Yin DD, Zhang ZH (2015). Pike, a rice blast resistance allele consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR genes, was identified as a novel allele at the Pik locus. Mol Breed 35, 117. |
| [9] | Chen XF, Liu PC, Mei L, He XL, Chen L, Liu H, Shen SR, Ji ZD, Zheng XX, Zhang YC, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Ma BJ (2021). Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun 2, 100143. |
| [10] | Cheng XY, Zhou GH, Chen W, Tan L, Long QS, Cui FS, Tan L, Zou GX, Tan Y (2024). Current status of molecular rice breeding for durable and broad-spectrum resistance to major diseases and insect pests. Theor Appl Genet 137, 219. |
| [11] | Chu J, Xu H, Dong H, Xuan YH (2021). Loose plant architecture 1-interacting kinesin-like protein KLP promotes rice resistance to sheath blight disease. Rice (NY) 14, 60. |
| [12] | Chu ZH, Yuan M, Yao JL, Ge XJ, Yuan B, Xu CG, Li XH, Fu BY, Li ZK, Bennetzen JL, Zhang QF, Wang SP (2006). Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice. Genes Dev 20, 1250-1255. |
| [13] | Das A, Soubam D, Singh PK, Thakur S, Singh NK, Sharma TR (2012). A novel blast resistance gene, Pi54rh cloned from wild species of rice, Oryza rhizomatis confers broad spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Funct Integr Genom 12, 215-228. |
| [14] | De Vleesschauwer D, Van Buyten E, Satoh K, Balidion J, Mauleon R, Choi IR, Vera-Cruz C, Kikuchi S, H?fte M (2012). Brassinosteroids antagonize gibberellin- and salicylate-mediated root immunity in rice. Plant Physiol 158, 1833-1846. |
| [15] | Deng YW, Zhai KR, Xie Z, Yang DY, Zhu XD, Liu JZ, Wang X, Qin P, Yang YZ, Zhang GM, Li Q, Zhang JF, Wu SQ, Milazzo J, Mao BZ, Wang ET, Xie HA, Tharreau D, He ZH (2017). Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance. Science 355, 962-965. |
| [16] | Devanna NB, Vijayan J, Sharma TR (2014). The blast resistance gene Pi54 of cloned from Oryza officinalis interacts with Avr-Pi54 through its novel non-LRR domains. PLoS One 9, 104840. |
| [17] | Dong JF, Zhou L, Feng AQ, Zhang SH, Fu H, Chen L, Zhao JL, Yang TF, Yang W, Ma YM, Wang J, Zhu XY, Liu Q, Liu B (2021). The OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 positively regulate panicle blast resistance in rice. Rice (NY) 14, 51. |
| [18] | Fan J, Quan WL, Li GB, Hu XH, Wang Q, Wang H, Li XP, Luo XT, Feng Q, Hu ZJ, Feng H, Pu M, Zhao JQ, Huang YY, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang WM (2020). circRNAs are involved in the rice-Magnaporthe oryzae interaction. Plant Physiol 182, 272-286. |
| [19] | Feng T, Zhang ZY, Gao P, Feng ZM, Zuo SM, Ouyang SQ (2023). Suppression of rice Osa-miR444.2 improves the resistance to sheath blight in rice mediating through the phytohormone pathway. Int J Mol Sci 24, 3653. |
| [20] | Figueroa-Macías JP, García YC, Nú?ez M, Díaz K, Olea AF, Espinoza L (2021). Plant growth-defense trade-offs: molecular processes leading to physiological changes. Int J Mol Sci 22, 693. |
| [21] | Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Yano M (2009). Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 325, 998-1001. |
| [22] | Fukuoka S, Yamamoto SI, Mizobuchi R, Yamanouchi U, Ono K, Kitazawa N, Yasuda N, Fujita Y, Nguyen TTT, Koizumi S, Sugimoto K, Matsumoto T, Yano M (2014). Multiple functional polymorphisms in a single disease resistance gene in rice enhance durable resistance to blast. Sci Rep 4, 4550. |
| [23] | Gao Y, Xiang XJ, Zhang YX, Cao YR, Wang BF, Zhang Y, Wang C, Jiang M, Duan WJ, Chen DB, Zhan XD, Cheng SH, Liu QE, Cao LY (2022). Disruption of OsPHD1, encoding a UDP-glucose epimerase, causes JA accumulation and enhanced bacterial blight resistance in rice. Int J Mol Sci 23, 751. |
| [24] | Gao ZQ, Liu QE, Zhang YX, Chen DB, Zhan XD, Deng CW, Cheng SH, Cao LY (2020). OsCUL3a-associated molecular switches have functions in cell metabolism, cell death, and disease resistance. J Agric Food Chem 68, 5471-5482. |
| [25] | Gu KY, Yang B, Tian DS, Wu LF, Wang DJ, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu ZQ, Wang GL, White FF, Yin ZC (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122-1125. |
| [26] | Guo F, Huang YZ, Qi PP, Lian GW, Hu XM, Han N, Wang JH, Zhu MY, Qian Q, Bian HW (2021). Functional analysis of auxin receptor OsTIR1/OsAFB family members in rice grain yield, tillering, plant height, root system, germination, and auxinic herbicide resistance. New Phytol 229, 2676-2692. |
| [27] | Hayashi K, Fujita Y, Ashizawa T, Suzuki F, Nagamura Y, Hayano-Saito Y (2016). Serotonin attenuates biotic stress and leads to lesion browning caused by a hypersensitive response to Magnaporthe oryzae penetration in rice. Plant J 85, 46-56. |
| [28] | Hayashi N, Inoue H, Kato T, Funao T, Shirota M, Shimizu T, Kanamori H, Yamane H, Hayano-Saito Y, Matsumoto T, Yano M, Takatsuji H (2010). Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS- LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication. Plant J 64, 498-510. |
| [29] | He M, Yin JJ, Feng ZM, Zhu XB, Zhao JH, Zuo SM, Chen XW (2020). Methods for evaluation of rice resistance to blast and sheath blight diseases. Chin Bull Bot 55, 577-587. (in Chinese) |
| 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟 (2020). 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法. 植物学报 55, 577-587. | |
| [30] | Hu KM, Cao JB, Zhang J, Xia F, Ke YG, Zhang HT, Xie WY, Liu HB, Cui Y, Cao YL, Sun XL, Xiao JH, Li XH, Zhang QL, Wang SP (2017). Improvement of multiple agronomic traits by a disease resistance gene via cell wall reinforcement. Nat Plants 3, 17009. |
| [31] | Hu XH, Shen S, Wu JL, Liu J, Wang H, He JX, Yao ZL, Bai YF, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Li GB, Zhao JH, You XM, Xu J, Ji YP, Li DQ, Pu M, Zhao ZX, Zhou SX, Zhang JW, Huang YY, Li Y, Ning YS, Lu YL, Huang F, Wang WM, Fan J (2023). A natural allele of proteasome maturation factor improves rice resistance to multiple pathogens. Nat Plants 9, 228-237. |
| [32] | Hua LX, Wu JZ, Chen CX, Wu WH, He XY, Lin F, Wang L, Ashikawa I, Matsumoto T, Wang L, Pan QH (2012). The isolation of Pi1, an allele at the Pik locus which confers broad spectrum resistance to rice blast. Theor Appl Genet 125, 1047-1055. |
| [33] | Hutin M, Sabot F, Ghesquière A, Koebnik R, Szurek B (2015). A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice. Plant J 84, 694-703. |
| [34] | Im JH, Choi C, Park SR, Hwang DJ (2022). The OsWRKY6 transcriptional cascade functions in basal defense and Xa1-mediated defense of rice against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Planta 255, 47. |
| [35] | Inukai T, Nagashima S, Kato M (2019). Pid3-I1 is a race- specific partial-resistance allele at the Pid3 blast resistance locus in rice. Theor Appl Genet 132, 395-404. |
| [36] | Iyer AS, McCouch SR (2004). The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17, 1348-1354. |
| [37] | Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087. |
| [38] | Jiao L, Fu SF, Zhang YL, Lu J (2016). U-box E3 ubiquitin ligases regulate stress tolerance and growth of plants. Chin Bull Bot 51, 724-735. (in Chinese) |
| 缴莉, 付淑芳, 张雅丽, 卢江 (2016). U-box泛素连接酶调控植物抗逆和生长发育. 植物学报 51, 724-735. | |
| [39] | Jones JDG, Staskawicz BJ, Dangl JL (2024). The plant immune system: from discovery to deployment. Cell 187, 2095-2116. |
| [40] | Kim P, Xue CY, Song HD, Gao Y, Feng L, Li YH, Xuan YH (2021). Tissue-specific activation of DOF11 promotes rice resistance to sheath blight disease and increases grain weight via activation of SWEET14. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 409-411. |
| [41] | Lee SK, Song MY, Seo YS, Kim HK, Ko S, Cao PJ, Suh JP, Yi G, Roh JH, Lee S, An G, Hahn TR, Wang GL, Ronald P, Jeon JS (2009). Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two coiled-coil-nucleotide-binding-leucine-rich repeat genes. Genetics 181, 1627-1638. |
| [42] | Li DY, Zhou J, Zheng C, Zheng ES, Liang WF, Tan XJ, Xu RM, Yan CQ, Yang Y, Yi KK, Liu XL, Chen JP, Wang XM (2022). OsTGAL1 suppresses the resistance of rice to bacterial blight disease by regulating the expression of salicylic acid glucosyltransferase OsSGT1. Plant Cell Environ 45, 1584-1602. |
| [43] | Li N, Wei ST, Chen J, Yang FF, Kong LG, Chen CX, Ding XH, Chu ZH (2018). OsASR2 regulates the expression of a defence-related gene, Os2H16, by targeting the GT-1 cis-element. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 771-783. |
| [44] | Li WT, Chern M, Yin JJ, Wang J, Chen XW (2019). Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 114-120. |
| [45] | Li XC, Liao YY, Leung DWM, Wang HY, Chen BL, Peng XX, Liu EE (2015). Divergent biochemical and enzymatic properties of oxalate oxidase isoforms encoded by four similar genes in rice. Phytochemistry 118, 216-223. |
| [46] | Lin F, Chen S, Que ZQ, Wang L, Liu XQ, Pan QH (2007). The blast resistance gene Pi37 encodes a nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a resistance gene cluster on rice chromosome 1. Genetics 177, 1871-1880. |
| [47] | Liu JP, Nie B, Yu BL, Xu FY, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Xu WF (2023). Rice ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme OsUbc13 negatively regulates immunity against pathogens by enhancing the activity of OsSnRK1a. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 1590-1610. |
| [48] | Liu QS, Yuan M, Zhou Y, Li XH, Xiao JH, Wang SP (2011). A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Environ 34, 1958-1969. |
| [49] | Liu X, Song LL, Zhang H, Lin YJ, Shen XL, Guo JY, Su ML, Shi GS, Wang ZH, Lu GD (2021a). Rice ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme OsUBC26 is essential for immunity to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant Pathol 22, 1613-1623. |
| [50] | Liu XQ, Zhang D, Zhang XM, Wang CT, Liu XQ, Tan YP, Wu YH (2012). Study on the interaction between methyl jasmonate and the coiled-coil domain of rice blast resistance protein Pi36 by spectroscopic methods. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 88, 72-76. |
| [51] | Liu XY, Zhang ZG (2022). A double-edged sword: reactive oxygen species (ROS) during the rice blast fungus and host interaction. FEBS J 289, 5505-5515. |
| [52] | Liu Y, Liu B, Zhu XY, Yang JY, Bordeos A, Wang GL, Leach JE, Leung H (2013). Fine-mapping and molecular marker development for Pi56(t), a NBS-LRR gene conferring broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Theor Appl Genet 126, 985-998. |
| [53] | Liu ZQ, Zhu YJ, Shi HB, Qiu JH, Ding XH, Kou YJ (2021b). Recent progress in rice broad-spectrum disease resistance. Int J Mol Sci 22, 11658. |
| [54] | Lu X, He Y, Guo JQ, Wang Y, Yan Q, Xiong Q, Shi H, Hou QQ, Yin JJ, An YB, Chen YD, Yang CS, Mao Y, Zhu XB, Tang YY, Liu JL, Bi Y, Song L, Wang L, Yang YH, He M, Li WT, Chen XW, Wang J (2024). Dynamics of epitranscriptomes uncover translational reprogramming directed by ac4C in rice during pathogen infection. Nat Plants 10, 1548-1561. |
| [55] | Lu Y, Tsuda K (2021). Intimate association of PRR- and NLR-mediated signaling in plant immunity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 34, 3-14. |
| [56] | Ma J, Lei CL, Xu XT, Hao K, Wang JL, Cheng ZJ, Ma XD, Ma J, Zhou KN, Zhang X, Guo XP, Wu FQ, Lin QB, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wang HY, Wan JM (2015). Pi64, encoding a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to leaf and neck blast in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28, 558-568. |
| [57] | Ma JN, Morel JB, Riemann M, Nick P (2022). Jasmonic acid contributes to rice resistance against Magnaporthe oryzae. BMC Plant Biol 22, 601. |
| [58] | Ma L, Fang Y, Xiao SQ, Zhou C, Jin ZL, Ye WL, Rao YC (2018). QTL exploration of bacterial leaf streak and their gene expression in rice. Chin Bull Bot 53, 468-476. (in Chinese) |
| 马路, 方媛, 肖飒清, 周纯, 金哲伦, 叶雯澜, 饶玉春 (2018). 水稻条斑病抗性QTL的挖掘及相关基因的表达. 植物学报 53, 468-476. | |
| [59] | Mohan Babu R, Sajeena A, Vijaya Samundeeswari A, Sreedhar A, Vidhyasekaran P, Seetharaman K, Reddy MS (2003). Induction of systemic resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by salicylic acid in Oryza sativa (L.). J Plant Dis Prot 110, 419-431. |
| [60] | Moon H, Jeong AR, Kwon OK, Park CJ (2022). Oryza- specific orphan protein triggers enhanced resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Front Plant Sci 13, 859375. |
| [61] | Nabi Z, Manzoor S, Nabi SU, Wani TA, Gulzar H, Farooq M, Arya VM, Baloch FS, Vl?dulescu C, Popescu SM, Mansoor S (2024). Pattern-triggered immunity and effector-triggered immunity: crosstalk and cooperation of PRR and NLR-mediated plant defense pathways during host-pathogen interactions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 30, 587-604. |
| [62] | Nahar K, Kyndt T, Hause B, H?fte M, Gheysen G (2013). Brassinosteroids suppress rice defense against root-knot nematodes through antagonism with the jasmonate pathway. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26, 106-115. |
| [63] | Ngou BPM, Jones JDG, Ding PT (2022). Plant immune networks. Trends Plant Sci 27, 255-273. |
| [64] | Okuyama Y, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Tamiru M, Saitoh H, Fujibe T, Matsumura H, Shenton M, Galam DC, Undan J, Ito A, Sone T, Terauchi R (2011). A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR protein genes. Plant J 66, 467-479. |
| [65] | Panthapulakkal Narayanan S, Lung SC, Liao P, Lo C, Chye ML (2020). The overexpression of OsACBP5 protects transgenic rice against necrotrophic, hemibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens. Sci Rep 10, 14918. |
| [66] | Park SC, Kim IR, Kim JY, Lee Y, Yoo SH, Jung JH, Cheong GW, Lee SY, Jang MK, Lee JR (2019). Functional characterization of a rice thioredoxin protein OsTrxm and its cysteine mutant variant with antifungal activity. Antioxidants (Basel) 8, 598. |
| [67] | Peng XQ, Wang ML (2022). Research advances on resistance genes to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Physiol J 58, 472-482. (in Chinese) |
| 彭小群, 王梦龙 (2022). 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因研究进展. 植物生理学报 58, 472-482. | |
| [68] | Peng YJ, Yang JF, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 761-791. |
| [69] | Phukan UJ, Jeena GS, Shukla RK (2016). WRKY transcription factors: molecular regulation and stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci 7, 760. |
| [70] | Rao YC, Luo YL, Ye YH, Xu JM (2025). Research progress on hormones and regulation of rice leaf senescence. J. Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 48, 1-11. (in Chinese) |
| 饶玉春, 罗怡琳, 叶语涵, 徐江民 (2025). 激素与水稻叶片衰老调控的研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 48, 1-11. | |
| [71] | Rao YC, Wu RC, Liu FY, Dai RH (2024). On research progress of RNAi application in prevention and control of rice pests and diseases. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 47, 361-369. (in Chinese) |
| 饶玉春, 吴日成, 刘富远, 戴若惠 (2024). RNAi在水稻病虫害防控中的应用研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 47, 361-369. | |
| [72] | Ren ZY, Tang BZ, Xing JJ, Liu CY, Cai X, Hendy A, Kamran M, Liu H, Zheng L, Huang JB, Chen XL (2022). MTA1-mediated RNA m6A modification regulates autophagy and is required for infection of the rice blast fungus. New Phytol 235, 247-262. |
| [73] | Sahu PK, Sao R, Choudhary DK, Thada A, Kumar V, Mondal S, Das BK, Jankuloski L, Sharma D (2022). Advancement in the breeding, biotechnological and genomic tools towards development of durable genetic resistance against the rice blast disease. Plants 11, 2386. |
| [74] | Shao J, Zhang ZJ, Shi Y, Jiang WQ, Siddique F, Chen LY, Liu GY, Zhu JK, Luo XF, Liu YQ, An JX, Yang CJ, Cui ZN (2024). Application and mechanism of cryptolepine and neocryptolepine derivatives as T3SS inhibitors for control of bacterial leaf blight on rice. J Agric Food Chem 72, 6988-6997. |
| [75] | Sharma TR, Rai AK, Gupta SK, Singh NK (2010). Broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi-kh cloned from rice line tetep designated as Pi54. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 19, 87-89. |
| [76] | Shen XL, Liu HB, Yuan B, Li XH, Xu CG, Wang SP (2011). OsEDR1 negatively regulates rice bacterial resistance via activation of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ 34, 179-191. |
| [77] | Shi H, Yin JJ, Zhao ZJ, Yu H, Yi H, Xu L, Tong HM, He M, Zhu XB, Lu X, Xiong Q, Li WT, Tang YY, Hou QQ, Song L, Wang L, Chen XQ, Sun CH, Li T, Fan J, Li Y, Qin P, Wang WM, Li SG, Chen XW, Li JY, Wang J (2024). Fine-tuning of IPA1 transactivation activity by E3 ligase IPI7-mediated non-proteolytic K29-ubiquitination during Magnaporthe oryzae infection. Nat Commun 15, 7608. |
| [78] | Shinde H, Dudhate A, Kadam US, Hong JC (2023). RNA methylation in plants: an overview. Front Plant Sci 14, 1132959. |
| [79] | Su J, Wang WJ, Han JL, Chen S, Wang CY, Zeng LX, Feng AQ, Yang JY, Zhou B, Zhu XY (2015). Functional divergence of duplicated genes results in a novel blast resistance gene Pi50 at the Pi2/9 locus. Theor Appl Genet 128, 2213-2225. |
| [80] | Suzuki G, Fukuda M, Lucob-Agustin N, Inukai Y, Gomi K (2022). The mutation of rice MEDIATOR25, OsMED25, induces rice bacterial blight resistance through altering jasmonate- and auxin-signaling. Plants (Basel) 11, 1601. |
| [81] | Takagi H, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Mitsuoka C, Utsushi H, Natsume S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Saitoh H, Yoshida K, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013). progeny bulk combined with de novo assembly of gap regions identifies the rice blast resistance gene Pii New Phytol 200, 276-283. |
| [82] | Tian DS, Wang JX, Zeng X, Gu KY, Qiu CX, Yang XB, Zhou ZY, Goh M, Luo YC, Murata-Hori M, White FF, Yin ZC (2014). The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497-515. |
| [83] | Uji Y, Kashihara K, Kiyama H, Mochizuki S, Akimitsu K, Gomi K (2019). Jasmonic acid-induced VQ-motif-containing protein OsVQ13 influences the OsWRKY45 signaling pathway and grain size by associating with OsMPK6 in rice. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2917. |
| [84] | Vidhyasekaran P, Ponmalar TR, Samiyappan R, Velazhahan R, Vimala R, Ramanathan A, Paranidharan V, Muthukrishnan S (1997). Host-specific toxin production by Rhizoctonia solani, the rice sheath blight pathogen. Phytopathology 87, 1258-1263. |
| [85] | Wang AJ, Ma L, Shu XY, Jiang YQ, Liang J, Zheng AP (2022a). Rice (Oryza sativa L.) cytochrome P450 protein 716A subfamily CYP716A16 regulates disease resistance. BMC Genomics 23, 343. |
| [86] | Wang AJ, Shu XY, Jing X, Jiao CZ, Chen L, Zhang JF, Ma L, Jiang YQ, Yamamoto N, Li SC, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zhu J, Liang YY, Zou T, Liu HN, Wang LX, Huang YB, Li P, Zheng AP (2021a). Identification of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genes involved in sheath blight resistance via a genome-wide association study. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1553-1566. |
| [87] | Wang CL, Zhang XP, Fan YL, Gao Y, Zhu QL, Zheng CK, Qin TF, Li YQ, Che JY, Zhang MW, Yang B, Liu YG, Zhao KJ (2015a). XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol Plant 8, 290-302. |
| [88] | Wang G, Chen X, Yu CZ, Shi XB, Lan WX, Gao CF, Yang J, Dai HL, Zhang XW, Zhang HL, Zhao BY, Xie Q, Yu N, He ZH, Zhang Y, Wang ET (2024). Release of a ubiquitin brake activates OsCERK1-triggered immunity in rice. Nature 629, 1158-1164. |
| [89] | Wang H, Li Y, Chern M, Zhu Y, Zhang LL, Lu JH, Li XP, Dang WQ, Ma XC, Yang ZR, Yao SZ, Zhao ZX, Fan J, Huang YY, Zhang JW, Pu M, Wang J, He M, Li WT, Chen XW, Wu XJ, Li SG, Li P, Li Y, Ronald PC, Wang WM (2021b). Suppression of rice miR168 improves yield, flowering time and immunity. Nat Plants 7, 129-136. |
| [90] | Wang J, Qu BY, Dou SJ, Li LY, Yin DD, Pang ZQ, Zhou ZZ, Tian MM, Liu GZ, Xie Q, Tang DZ, Chen XW, Zhu LH (2015b). The E3 ligase OsPUB15 interacts with the receptor-like kinase PID2 and regulates plant cell death and innate immunity. BMC Plant Biol 15, 49. |
| [91] | Wang L, Xu XK, Lin F, Pan QH (2009). Characterization of rice blast resistance genes in the Pik cluster and fine mapping of the Pik-p locus. Phytopathology 99, 900-905. |
| [92] | Wang LH, Chen J, Zhao YQ, Wang SP, Yuan M (2022b). OsMAPK6 phosphorylates a zinc finger protein OsLIC to promote downstream OsWRKY30 for rice resistance to bacterial blight and leaf streak. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 1116-1130. |
| [93] | Wang Y, Yue JL, Yang N, Zheng C, Zheng YN, Wu X, Yang J, Zhang HW, Liu LJ, Ning YS, Bhadauria V, Zhao WS, Xie Q, Peng YL, Chen Q (2023). An ERAD- related ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme boosts broad-spectrum disease resistance and yield in rice. Nat Food 4, 774-787. |
| [94] | Xie YJ, Wang YP, Yu XZ, Lin YL, Zhu YS, Chen JW, Xie HG, Zhang QQ, Wang LN, Wei YD, Xiao YJ, Cai QH, Zheng YM, Wang M, Xie HA, Zhang JF (2022). SH3P2, an SH3 domain-containing protein that interacts with both Pib and AvrPib, suppresses effector-triggered, Pib-mediated immunity in rice. Mol Plant 15, 1931-1946. |
| [95] | Xie Z, Yan BX, Shou JY, Tang J, Wang X, Zhai KR, Liu JY, Li Q, Luo MZ, Deng YW, He ZH (2019). A nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat receptor pair confers broad-spectrum disease resistance through physical association in rice. Philos Trans Royal Soc B Biol Sci 374, 20180308. |
| [96] | Xing JX, Zhang DY, Yin FY, Zhong QF, Wang B, Xiao SQ, Ke X, Wang LX, Zhang Y, Zhao CM, Lu YD, Chen L, Cheng ZQ, Chen LJ (2021). Identification and fine- mapping of a new bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa47(t), in G252, an introgression line of Yuanjiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon). Plant Dis 105, 4106-4112. |
| [97] | Xu DJ, Lin QX, Li ZK, Zhuang XQ, Ling Y, Lai ML, Chen XT, Lu GD (2024). OsOPR10 positively regulates rice blast and bacterial blight resistance. Chin J Rice Sci 38, 364-374. (in Chinese) |
| 许丹洁, 林巧霞, 李正康, 庄小倩, 凌宇, 赖美玲, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东 (2024). OsOPR10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性. 中国水稻科学 38, 364-374. | |
| [98] | Xu X, Hayashi N, Wang CT, Fukuoka S, Kawasaki S, Takatsuji H, Jiang CJ (2014a). Rice blast resistance gene Pikahei-1(t), a member of a resistance gene cluster on chromosome 4, encodes a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat protein. Mol Breed 34, 691-700. |
| [99] | Xu X, Lv QM, Shang JJ, Pang ZQ, Zhou ZZ, Wang J, Jiang GH, Tao Y, Xu Q, Li XB, Zhao XF, Li SG, Xu JC, Zhu LH (2014b). Excavation of Pid3 orthologs with differential resistance spectra to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice resource. PLoS One 9, 93275. |
| [100] | Yan YQ, Wang H, Bi Y, Song FM (2024). Rice E3 ubiquitin ligases: from key modulators of host immunity to potential breeding applications. Plant Commun 5, 101128. |
| [101] | Yang C, Li W, Cao JD, Meng FW, Yu YQ, Huang JK, Jiang L, Liu MX, Zhang ZG, Chen XW, Miyamoto K, Yamane H, Zhang JS, Chen SY, Liu J (2017). Activation of ethylene signaling pathways enhances disease resistance by regulating ROS and phytoalexin production in rice. Plant J 89, 338-353. |
| [102] | Yang S, Fu YW, Zhang Y, Yuan DP, Li S, Kumar V, Mei Q, Xuan YH (2023a). Rhizoctonia solani transcriptional activator interacts with rice WRKY53 and grassy tiller 1 to activate SWEET transporters for nutrition. J Adv Res 50, 1-12. |
| [103] | Yang Y, Li J, Li H, Ding Y, Wu W, Qin R, Ni J, Xu R, Wei P, Yang J (2023b). OsGSTU5 and OsGSTU37 encoding glutathione reductases are required for cadmium tolerance in rice. Int J Environ Sci Technol 20, 10253-10260. |
| [104] | Yang Y, Zhou YH, Sun J, Liang WF, Chen XY, Wang XM, Zhou J, Yu CL, Wang JM, Wu SL, Yao XM, Zhou YJ, Zhu J, Yan CQ, Zheng BS, Chen JP (2022). Research progress on cloning and function of Xa genes against rice bacterial blight. Front Plant Sci 13, 847199. |
| [105] | Yang YX, Ahammed GJ, Wu CJ, Fan SY, Zhou YH (2015). Crosstalk among jasmonate, salicylate and ethylene signaling pathways in plant disease and immune responses. Curr Protein Pept Sci 16, 450-461. |
| [106] | Yin X, Zou BH, Hong XX, Gao MJ, Yang WB, Zhong XB, He Y, Kuai P, Lou YG, Huang JR, Hua J, He ZH (2018). Rice copine genes OsBON1 and OsBON3 function as suppressors of broad-spectrum disease resistance. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 1476-1487. |
| [107] | Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang ZX, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998). Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 1663-1668. |
| [108] | Younas MU, Qasim M, Ahmad I, Feng ZM, Iqbal R, Abdelbacki AMM, Rajput N, Jiang XH, Rao B, Zuo SM (2024). Allelic variation in rice blast resistance: a pathway to sustainable disease management. Mol Biol Rep 51, 935. |
| [109] | Yu SB, Ali J, Zhang CP, Li ZK, Zhang QF (2020). Genomic breeding of green super rice varieties and their deployment in Asia and Africa. Theor Appl Genet 133, 1427-1442. |
| [110] | Yu XQ, Niu HQ, Liu C, Wang HL, Yin WL, Xia XL (2024). PTI-ETI synergistic signal mechanisms in plant immunity. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 2113-2128. |
| [111] | Yu Y, Ma L, Wang XY, Zhao Z, Wang W, Fan YX, Liu KQ, Jiang TT, Xiong ZW, Song QS, Li CQ, Wang PT, Ma WJ, Xu HN, Wang XY, Zhao ZJ, Wang JF, Zhang HS, Bao YM (2022). Genome-wide association study identifies a rice panicle blast resistance gene, Pb2, encoding NLR protein. Int J Mol Sci 23, 5668. |
| [112] | Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley SD (1991). Tagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81, 471-476. |
| [113] | Yuan DP, Yang S, Feng L, Chu J, Dong H, Sun J, Chen H, Li Z, Yamamoto N, Zheng AP, Li S, Yoon HC, Chen JS, Ma DR, Xuan YH (2023). Red-light receptor phytochrome B inhibits BZR1-NAC028-CAD8B signaling to negatively regulate rice resistance to sheath blight. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1249-1263. |
| [114] | Yuan DP, Zhang C, Wang ZY, Zhu XF, Xuan YH (2018). RAVL1 activates brassinosteroids and ethylene signaling to modulate response to sheath blight disease in rice. Phytopathology 108, 1104-1113. |
| [115] | Zhai C, Lin F, Dong ZQ, He XY, Yuan B, Zeng XS, Wang L, Pan QH (2011). The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication. New Phytol 189, 321-334. |
| [116] | Zhai C, Zhang Y, Yao N, Lin F, Liu Z, Dong ZQ, Wang L, Pan QH (2014). Function and interaction of the coupled genes responsible for Pik-h encoded rice blast resistance. PLoS One 9, 98067. |
| [117] | Zhai KR, Deng YW, Liang D, Tang J, Liu J, Yan BX, Yin X, Lin H, Chen FD, Yang DY, Xie Z, Liu JY, Li Q, Zhang L, He ZH (2019). RRM transcription factors interact with NLRs and regulate broad-spectrum blast resistance in rice. Mol Cell 74, 996-1009. |
| [118] | Zhang DD, Tian CJ, Yin KQ, Wang WY, Qiu JL (2019). Postinvasive bacterial resistance conferred by open stomata in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32, 255-266. |
| [119] | Zhao HJ, Wang XY, Jia YL, Minkenberg B, Wheatley M, Fan JB, Jia MH, Famoso A, Edwards JD, Wamishe Y, Valent B, Wang GL, Yang YN (2018). The rice blast resistance gene Ptr encodes an atypical protein required for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Nat Commun 9, 2039. |
| [120] | Zhao YD, Zhong XH, Xu GJ, Zhu XY, Shi YL, Liu MH, Wang RY, Kang HX, You XM, Ning YS, Wang GL, Wang XL (2024). The F-box protein OsFBX156 positively regulates rice defence against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae by mediating ubiquitination-dependent degradation of OsHSP71.1. Mol Plant Pathol 25, 13459. |
| [121] | Zhou XG, Liao HC, Chern M, Yin JJ, Chen YF, Wang JP, Zhu XB, Chen ZX, Yuan C, Zhao W, Wang J, Li WT, He M, Ma BT, Wang JC, Qin P, Chen WL, Wang YP, Liu JL, Qian YW, Wang WM, Wu XJ, Li P, Zhu LH, Li SG, Ronald PC, Chen XW (2018). Loss of function of a rice TPR-domain RNA-binding protein confers broad-spectrum disease resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 3174-3179. |
| [122] | Zhou YL, Shen XL, Zhou LS, Lin QX, Wang ZL, Chen J, Feng HJ, Zhang ZW, Chen XT, Lu GD (2022). OsLOX10 positively regulates defense responses of rice to rice blast and bacterial blight. Chin J Rice Sci 36, 348-356. (in Chinese) |
| 周永林, 申小磊, 周立帅, 林巧霞, 王朝露, 陈静, 冯慧捷, 张振文, 陈晓婷, 鲁国东 (2022). OsLOX10正调控水稻对稻瘟病和白叶枯病的抗性. 中国水稻科学 36, 348-356. | |
| [123] | Zhou ZZ, Pang ZQ, Zhao SL, Zhang LL, Lv QM, Yin DD, Li DY, Liu X, Zhao XF, Li XB, Wang WM, Zhu LH (2019). Importance of OsRac1 and RAI1 in signaling of nucleotide-binding site leucine-rich repeat protein-mediated resistance to rice blast disease. New Phytol 223, 828-838. |
| [124] | Zou T, Li GW, Liu MM, Liu R, Yang SY, Wang K, Lu LH, Ye QY, Liu JX, Liang J, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zhu J, Liang YY, Liu HN, Yu XM, Sun CH, Li P, Li SC (2023). A ubiquitin-specific protease functions in regulating cell death and immune responses in rice. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1312-1326. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |