

Advances in the Regulation and Evolutionary Mechanisms of Plant Gene Expression
Received date: 2024-11-22
Accepted date: 2025-02-09
Online published: 2025-02-10
Functional gene expression is a basic life process that connects the coding information of a gene to protein products. The level of gene expression is considered as a quantitative trait between genotype and phenotype and plays an important role in response to climatic and environmental changes. First, we systematically summarize regulatory elements of gene expression in plant species and empirical evidence, including the effects of transcription factors and small RNAs on gene expression regulation. Second, this review discusses the eQTL mapping for regulatory elements of gene expression through gene expression-based genome-wide association study (GWAS) and the limitations of this method. This review analyzes the intraspecific variation in gene expression in theory under the processes of mutation, drift and selection and the testing methods. This review also analyzes the interspecific evolution of gene expression under the mutation and drift processes or under the phylogeny-based drift-selection processes and the testing methods. Finally, this review discusses the regulation of gene expression by the plant mating system. Selfing reduces the effective population size, mutation rate, recombination rate and competition from exogenous pollen, and changes the efficacy of natural selection in the gametophytic and sporophytic phases. Selfing regulates intraspecific gene expression variation and interspecific gene expression evolution. This review comprehensively comments on theoretical and practical research progress and existing questions, which aids in our deep understanding of plant gene expression regulation and evolution mechanisms.
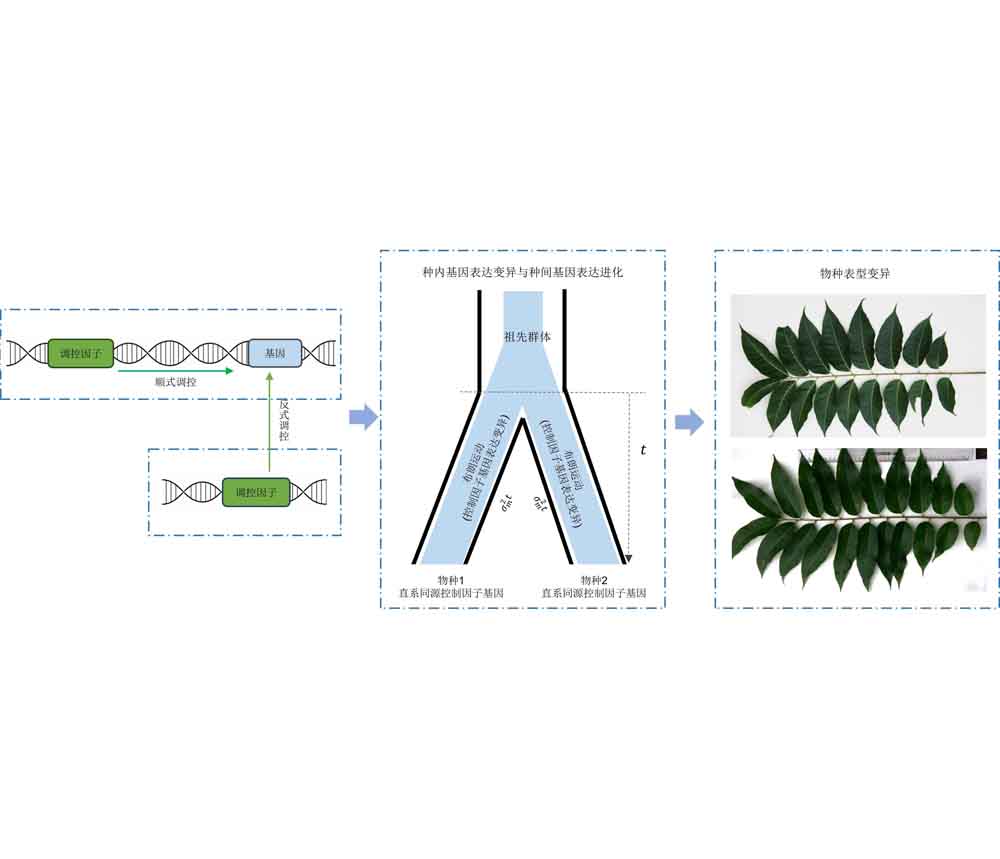
Ziyun Wang , Yanwen Lü , Yu Xiao , Chao Wu , Xinsheng Hu . Advances in the Regulation and Evolutionary Mechanisms of Plant Gene Expression[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025 , 60(4) : 621 -639 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB24175
| [1] | Andrew SC, Simonsen AK, Coppin CW, Arnold PA, Brice?o VF, McLay TGB, Jackson CJ, Gallagher RV, Mokany K (2024). Expression-environment associations in transcriptomic heat stress responses for a global plant lineage. Mol Ecol 33, e17473. |
| [2] | Arunkumar R, Josephs EB, Williamson RJ, Wright SI (2013). Pollen-specific, but not sperm-specific, genes show stronger purifying selection and higher rates of positive selection than sporophytic genes in Capsella grandiflora. Mol Biol Evol 30, 2475-2486. |
| [3] | Barton NH, Briggs DEG, Eisen JA, Goldstein DB, Patel NH (2007). Evolution. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. pp. 49-53. |
| [4] | Beaudry FEG, Rifkin JL, Barrett SCH, Wright SI (2020). Evolutionary genomics of plant gametophytic selection. Plant Commun 1, 100115. |
| [5] | Beaulieu JM, Jhwueng DC, Boettiger C, O’Meara BC (2012). Modeling stabilizing selection: expanding the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model of adaptive evolution. Evolution 66, 2369-2383. |
| [6] | Bedford T, Hartl DL (2009). Optimization of gene expression by natural selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 1133-1138. |
| [7] | Bernabè G, Dal Pra M, Ronca V, Pauletto A, Marzaro G, Saluzzo F, Stefani A, Artusi I, De Filippis V, Ferlin MG, Brun P, Castagliuolo I (2021). A novel aza-derivative inhibits agr quorum sensing signaling and synergizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to clindamycin. Front Microbiol 12, 610859. |
| [8] | Bonnet E, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P (2006). The small RNA world of plants. New Phytol 171, 451-468. |
| [9] | Brümmer A, Bergmann S (2024). Disentangling genetic effects on transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation through integrating exon and intron expression QTLs. Nat Commun 15, 3786. |
| [10] | Bustin SA (2000). Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25, 169-193. |
| [11] | Butler MA, King AA (2004). Phylogenetic comparative analysis: a modeling approach for adaptive evolution. Am Nat 164, 683-695. |
| [12] | Caballero A, Hill WG (1992). Effects of partial inbreeding on fixation rates and variation of mutant genes. Genetics 131, 493-507. |
| [13] | Cai WT, Zhang YP, Chang TP, Wang ZZ, Zhu B, Chen Y, Gao X, Xu LY, Zhang LP, Gao HJ, Song JZ, Li JY (2023). The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 14, 78. |
| [14] | Chen LG, Zhang LP, Xiang SY, Chen YL, Zhang HY, Yu DQ (2021). The transcription factor WRKY75 positively regulates jasmonate-mediated plant defense to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. J Exp Bot 72, 1473-1489. |
| [15] | Chen LL, Feng SS, Fan ZS, Gong C, Liu BY, Liu ZH, Li CW, Song EW, Sun SH, Wu GZ, Wu H, Wu M, Xu G, Yuan JX, Zeng CY, Zhu YM (2019). Progress in non- coding RNA research. Sci Sin Vitae 49, 1573-1605. (in Chinese) |
| 陈玲玲, 冯珊珊, 范祖森, 龚畅, 刘本宇, 刘子豪, 李传伟, 宋尔卫, 孙树汉, 吴庚泽, 吴煌, 吴缅, 许光, 袁继行, 曾春雨, 朱友明 (2019). 非编码RNA研究进展. 中国科学:生命科学 49, 1573-1605. | |
| [16] | Chen SS, Xie MH, Cui MK, Li WK, Xu ZG, Jia CX, Yang GY (2022). Identification of Broussonetia papyrifera transcription factor BpbZIP1 and analysis of its response to cadmium stress. Bull Bot Res 42, 394-402. (in Chinese) |
| 陈思思, 谢牧洪, 崔茂凯, 李文凯, 徐正刚, 贾彩霞, 杨桂燕 (2022). 构树转录因子BpbZIP1的鉴定及镉胁迫响应分析. 植物研究 42, 394-402. | |
| [17] | Chen YX (2020). Identification of WRKY Gene Family in Phyllostachys edulis and Their Correlation With Leaf Senescence Regulation. Master’s thesis. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University. pp. 1-72. (in Chinese) |
| 陈宇翔 (2020). 毛竹WRKY基因家族鉴定与叶片衰老调控的相关性分析. 硕士论文. 福州: 福建农林大学. pp. 1-72. | |
| [18] | Cheng X, Li LL, Xiao Y, Chen XY, Hu XS (2020). Advances in the methods of detecting interspecific gene introgression and their applications. Sci Sin Vitae 50, 1388-1404. (in Chinese) |
| 程祥, 李玲玲, 肖钰, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2020). 种间基因渐渗检测方法及其应用研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 50, 1388-1404. | |
| [19] | Dai ZH, Wang YF (2016). Genetics, 3rd edn. Beijing: Higher Education Press. pp. 338-346. (in Chinese) |
| 戴灼华, 王亚馥 (2016). 遗传学(第3版). 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 338-346. | |
| [20] | Dror I, Zhou TY, Mandel-Gutfreund Y, Rohs R (2014). Covariation between homeodomain transcription factors and the shape of their DNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res 42, 430-441. |
| [21] | Eppler E, Caelers A, Berishvili G, Reinecke MN (2005). The advantage of absolute quantification in comparative hormone research as indicated by a newly established real-time RT-PCR: GH, IGF-I, and IGF-II gene expression in the tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Ann NY Acad Sci 1040, 301-304. |
| [22] | Evans C, Hardin J, Stoebel DM (2018). Selecting between-sample RNA-Seq normalization methods from the perspective of their assumptions. Brief Bioinform 19, 776-792. |
| [23] | Farhangi S, Gòdia M, Derks MFL, Harlizius B, Dibbits B, González-Prendes R, Crooijmans RPMA, Madsen O, Groenen MAM (2024). Expression genome-wide association study identifies key regulatory variants enriched with metabolic and immune functions in four porcine tissues. BMC Genomics 25, 684. |
| [24] | Feng K, Liu YX, Sun J, Zhao CL, Duan YJ, Wang WJ, Yan KJ, Yan XJ, Sun H, Hu YH, Han JH (2021). Compound Danshen Dripping Pill inhibits doxorubicin or isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 138, 111-531. |
| [25] | Fleige S, Walf V, Huch S, Prgomet C, Sehm J, Pfaffl MW (2006). Comparison of relative mRNA quantification models and the impact of RNA integrity in quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1601-1613. |
| [26] | Frazee LJ, Rifkin J, Maheepala DC, Grant AG, Wright S, Kalisz S, Litt A, Spigler R (2021). New genomic resources and comparative analyses reveal differences in floral gene expression in selfing and outcrossing Collinsia sister species. G3-Genes Genom Genet 11, jkab177. |
| [27] | Gachon C, Mingam A, Charrier B (2004). Real-time PCR: what relevance to plant studies? J Exp Bot 55, 1445-1454. |
| [28] | Gilad Y, Oshlack A, Rifkin SA (2006). Natural selection on gene expression. Trends Genet 22, 456-461. |
| [29] | Gómez-Soto D, Ramos-Sánchez JM, Alique D, Conde D, Triozzi PM, Perales M, Allona I (2021). Overexpression of a SOC1-related gene promotes bud break in ecodormant poplars. Front Plant Sci 12, 670497. |
| [30] | Groen SC, ?ali? I, Joly-Lopez Z, Platts AE, Choi JY, Natividad M, Dorph K, Mauck III WM, Bracken B, Cabral CLU, Kumar A, Torres RO, Satija R, Vergara G, Henry A, Franks SJ, Purugganan MD (2020). The strength and pattern of natural selection on gene expression in rice. Nature 578, 572-576. |
| [31] | Gu X (2010). Statistical Theory and Methods for Evolutionary Genomics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 95-112. |
| [32] | Gutiérrez-Valencia J, Fracassetti M, Horvath R, Laenen B, Désamore A, Drouzas AD, Friberg M, Kolá? F, Slotte T (2022). Genomic signatures of sexual selection on pollen-expressed genes in Arabis alpina. Mol Biol Evol 39, msab349. |
| [33] | Hausser J, Syed AP, Bilen B, Zavolan M (2013). Analysis of CDS-located miRNA target sites suggests that they can effectively inhibit translation. Genome Res 23, 604-615. |
| [34] | Hill MS, Vande Zande P, Wittkopp PJ (2021). Molecular and evolutionary processes generating variation in gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 22, 203-215. |
| [35] | Hill WG, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2008). Data and theory point to mainly additive genetic variance for complex traits. PLoS Genet 4, e1000008. |
| [36] | Hu WG (2020). Preliminary Identification of Long Non-coding RNA in Wheat Powdery Mildew Resistance and Preliminary Analysis of its Regulatory Mechanism. PhD disser- tation. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 1-146. (in Chinese) |
| 胡卫国 (2020). 小麦白粉病抗性反应中长链非编码RNA的鉴定及其调控机制的解析. 博士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 1-146. | |
| [37] | Hu XS (2015). Mating system as a barrier to gene flow. Evolution 69, 1158-1177. |
| [38] | Hu XS, Chen XY, Yeh FC (2021). Forest Population Genetics. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. pp. 6-54. (in Chinese) |
| 胡新生, 陈晓阳, Yeh FC (2021). 林木群体遗传学. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 6-54. | |
| [39] | Hu XS, Ennos RA (1999). Impacts of seed and pollen flow on population genetic structure for plant genomes with three contrasting modes of inheritance. Genetics 152, 441-450. |
| [40] | Huang JL, Chen H, Chen YH, Yang ZQ (2024). Bioinformatics analysis and expression of PmWRKY2 and PmWRKY6 in Pinus massoniana. Guihaia http://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/45.1134.Q.20240705.1521.002.html. (in Chinese) |
| 黄金龙, 陈虎, 陈颖豪, 杨章旗 (2024). 马尾松PmWRKY2和PmWRKY6基因生物信息学及表达分析. 广西植物 http://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/45.1134.Q.20240705.1521.002.html. | |
| [41] | Huang SY, Yang TW, Zhang XJ, Tian SS, Gao MR, Li T, Shi Q, Zhang SW (2024). Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of WRKY genes family in Erythropalum scandens. Southwest China J Agr Sci 37, 1705-1714. (in Chinese) |
| 黄诗宇, 杨天为, 张向军, 田姗姗, 高曼熔, 李婷, 石前, 张尚文 (2024). 赤苍藤WRKY基因家族的全基因组鉴定及表达模式分析. 西南农业学报 37, 1705-1714. | |
| [42] | Husband BC (2016). Effect of inbreeding on pollen tube growth in diploid and tetraploid Chamerion angustifolium: do polyploids mask mutational load in pollen? Am J Bot 103, 532-540. |
| [43] | Immler S (2019). Haploid selection in “diploid” organisms. Annu Rev Ecol Evol S 50, 219-236. |
| [44] | Irving TB, Chakraborty S, Maia LGS, Knaack S, Conde D, Schmidt HW, Triozzi PM, Simmons CH, Roy S, Kirst M, Ané JM (2022). An LCO-responsive homolog of NODULE INCEPTION positively regulates lateral root formation in Populus sp. Plant Physiol 190, 1699-1714. |
| [45] | Jacob F, Monod J (1961). Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol 3, 318-356. |
| [46] | Khaitovich P, Weiss G, Lachmann M, Hellmann I, Enard W, Muetzel B, Wirkner U, Ansorge W, P??bo S (2004). A neutral model of transcriptome evolution. PLoS Biol 2, e132. |
| [47] | Kimura M (1962). On the probability of fixation of mutant genes in a population. Genetics 47, 713-719. |
| [48] | Lande R (1976). Natural selection and random genetic drift in phenotypic evolution. Evolution 30, 314-334. |
| [49] | Lemos B, Meiklejohn CD, Cáceres M, Hartl DL (2005). Rates of divergence in gene expression profiles of primates, mice, and flies: stabilizing selection and variability among functional categories. Evolution 59, 126-137. |
| [50] | Li J, Dai SY, Chen XJ, Liang XJ, Qu LZ, Jiang LY, Guo M, Zhou Z, Wei HD, Zhang HJ, Chen ZC, Chen L, Chen YH (2021). Mechanism of forkhead transcription factors binding to a novel palindromic DNA site. Nucleic Acids Res 49, 3573-3583. |
| [51] | Li JZ, Yang MK, Song XH, Wang Y, Wang YX, Wang SJ, Zhang MC, Deng X, Wang HY (2024). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SRS gene family in Panicum miliaceum. Pratacult Sci 41, 2035-2045. (in Chinese) |
| 李佳祯, 杨梦珂, 宋晓涵, 王月, 王禹茜, 王世纪, 张美春, 邓欣, 王红艳 (2024). 黍子SRS基因家族的全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 草业科学 41, 2035-2045. | |
| [52] | Li LL, Wang X, Xiao Y, Cheng X, Chen XY, Hu XS (2023). On the theories of plant mating system and molecular evolution and their applications. Sci Sin Vitae 53, 50-63. (in Chinese) |
| 李玲玲, 王茜, 肖钰, 程祥, 陈晓阳, 胡新生 (2023). 植物交配系统与分子进化理论及其应用研究. 中国科学: 生命科学 53, 50-63. | |
| [53] | Li LL, Xiao Y, Wang X, He ZH, Lv YW, Hu XS (2023). The Ka/Ks and πa/πs ratios under different models of gametophytic and sporophytic selection. Genome Biol Evol 15, evad151. |
| [54] | Li X, Lei JB (2015). Bioinformatics, 2nd edn. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House. pp. 236-257. (in Chinese) |
| 李霞, 雷健波 (2015). 生物信息学(第2版). 北京: 人民卫生出版社. pp. 236-257. | |
| [55] | Liu C, Zhu XY, Zhang J, Shen M, Chen K, Fu XK, Ma L, Liu XL, Zhou C, Zhou DX, Wang GW (2022). eQTLs play critical roles in regulating gene expression and identifying key regulators in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 2357-2371. |
| [56] | Liu JH (2023). Genome Wide Identification of WRKYs from Caragana korshinskii and Function Analysis of Four Group II Members. PhD dissertation. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. pp. 1-115. (in Chinese) |
| 柳金华 (2023). 柠条锦鸡儿WRKYs的全基因组鉴定及四个II组成员的功能探究. 博士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. pp. 1-115. | |
| [57] | Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408. |
| [58] | Luo J, Wu XY, Cheng Y, Chen G, Wang J, Song XJ (2023). Expression quantitative trait locus studies in the era of single-cell omics. Front Genet 14, 1182579. |
| [59] | Luo P, Di DW, Wu L, Yang JW, Lu YF, Shi WM (2022). MicroRNAs are involved in regulating plant development and stress response through fine-tuning of TIR1/AFB- dependent auxin signaling. Int J Mol Sci 23, 510. |
| [60] | Lv YW, Wang ZY, Xiao Y, He ZH, Wu C, Hu XS (2024). Advances in lineage sorting theories and their detection methods. Biodivers Sci 32, 121-138. (in Chinese) |
| 吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生 (2024). 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展. 生物多样性 32, 121-138. | |
| [61] | Mai J, Lu MM, Gao QW, Zeng JY, Xiao JF (2023). Transcriptome-wide association studies: recent advances in methods, applications and available databases. Commun Biol 6, 899. |
| [62] | Mallet J (2005). Hybridization as an invasion of the genome. Trends Ecol Evol 20, 229-237. |
| [63] | Mallory AC, Vaucheret H (2006). Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat Genet 38 (Suppl), S31-S36. |
| [64] | Mattick JS, Makunin IV (2006). Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 15, R17-R29. |
| [65] | Mcdonald JH, Kreitman M (1991). Adaptive protein evolution at the Adh locus in Drosophila. Nature 351, 652-654. |
| [66] | Meléndez-Rosa J, Bi K, Lacey EA (2019). Differential gene expression in relation to mating system in Peromyscine rodents. Ecol Evol 9, 5975-5990. |
| [67] | Meneksedag-Erol D, Tang T, Uluda? H (2015). Probing the effect of miRNA on siRNA-PEI polyplexes. J Phys Chem B 119, 5475-5486. |
| [68] | Meng LT, Su LW, Li XX, Xiong TS, Chang PP, Liu MZ, Zhou CG (2024). Functional analysis of ANT transcription factor of Populus trichocarpa based on CRISPR-dCas9 transcription activation system. Bull Bot Res 44, 431-440. (in Chinese) |
| 孟令桐, 苏丽伟, 李祥欣, 熊天圣, 常攀鹏, 刘孟卓, 周晨光 (2024). 基于CRISPR-dCas9转录激活系统的毛果杨ANT转录因子功能分析. 植物研究 44, 431-440. | |
| [69] | Mills JC, Taghert PH (2012). Scaling factors: transcription factors regulating subcellular domains. Bioessays 34, 10-16. |
| [70] | Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008). Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5, 621-628. |
| [71] | Mostafavi H, Spence JP, Naqvi S, Pritchard JK (2023). Systematic differences in discovery of genetic effects on gene expression and complex traits. Nat Genet 55, 1866-1875. |
| [72] | Mu XY, Yu LJ, Cheng ZH, Fan GF, Wang N, Cai JQ, Jia YY, Liu HZ (2024). Cloning and salt stress function analysis of the transcription factor WRKY23 gene of Populus simonii × P. nigra. Mol Plant Breeding http://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20240717.1719.014.html. (in Chinese) |
| 穆宣邑, 于莉婧, 程紫涵, 樊高峰, 王娜, 蔡静秋, 贾玉莹, 刘焕臻 (2024). 小黑杨转录因子PsnWRKY23基因的克隆及盐胁迫功能分析. 分子植物育种 http://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20240717.1719.014.html. | |
| [73] | Muyle A, Marais G (2016). Genome evolution and mating systems. In: Kliman RM, ed. Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Biology. Oxford: Academic Press. pp. 480-492. |
| [74] | Nica AC, Dermitzakis ET (2013). Expression quantitative trait loci: present and future. Phil Trans R Soc B 368, 20120362. |
| [75] | Nolan T, Hands RE, Bustin SA (2006). Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 1, 1559-1582. |
| [76] | Oleksiak MF, Churchill GA, Crawford DL (2002). Variation in gene expression within and among natural populations. Nat Genet 32, 261-266. |
| [77] | Palma-Silva C, Mortati AF, Chaves CJN, Sim?es Santos Leal B, Ribeiro RV, Pinheiro F, Ferro M, Ria?o-Pachón DM, de Mattos JS, Tavares MM, Aecyo P, da Costa Cacossi T, Sch?ngart J, Piedade MTF, André T (2024). Ecological transcriptomics reveals stress response pathways of a ground-herb species in a waterlogging gradient of Amazonian riparian forests. Mol Ecol 17, e17437. |
| [78] | Palos K, Nelson Dittrich AC, Yu LA, Brock JR, Railey CE, Wu HYL, Sokolowska E, Skirycz A, Hsu PY, Gregory BD, Lyons E, Beilstein MA, Nelson ADL (2022). Identification and functional annotation of long intergenic non- coding RNAs in Brassicaceae. Plant Cell 34, 3233-3260. |
| [79] | Pan Y (2019). Cloning and Functional Identification of Transcription Factor PeWRKY31 in Populus × euramericana. Master’s thesis. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University. pp. 1-43. (in Chinese) |
| 潘钰 (2019). 欧美杨转录因子PeWRKY31的克隆及功能鉴定. 硕士论文. 保定: 河北农业大学. pp. 1-43. | |
| [80] | Parikh TP, Malik M, Britten J, Aly JM, Pilgrim J, Catherino WH (2020). Steroid hormones and hormone antagonists regulate the neural marker neurotrimin in uterine leiomyoma. Fertil Steril 113, 176-186. |
| [81] | Peleke FF, Zumkeller SM, Gültas M, Schmitt A, Szymański J (2024). Deep learning the cis-regulatory code for gene expression in selected model plants. Nat Commun 15, 3488. |
| [82] | Pennell MW, Eastman JM, Slater GJ, Brown JW, Uyeda JC, FitzJohn RG, Alfaro ME, Harmon LJ (2014). geiger v2.0: an expanded suite of methods for fitting macroevolutionary models to phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 30, 2216-2218. |
| [83] | Pertermann R, Tamilarasan S, Gursinsky T, Gambino G, Schuck J, Weinholdt C, Lilie H, Grosse I, Golbik RP, Pantaleo V, Behrens SE (2018). A viral suppressor modulates the plant immune response early in infection by regulating microRNA activity. mBio 9, e00419-18. |
| [84] | Peters MAE, Weis AE (2018). Selection for pollen competitive ability in mixed-mating systems. Evolution 72, 2513-2536. |
| [85] | Pfaffl MW (2001). A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29, e45. |
| [86] | Price PD, Palmer Droguett DH, Taylor JA, Kim DW, Place ES, Rogers TF, Mank JE, Cooney CR, Wright AE (2022). Detecting signatures of selection on gene expression. Nat Ecol Evol 6, 1035-1045. |
| [87] | Qi YX, Wang L, Wang YY, Pu GB, Liu Q, Zhang YQ (2019). Function and mechanism of WRKY transcription factors of plants under abiotic stress. Mol Plant Breeding 17, 5973-5979. (in Chinese) |
| 戚莹雪, 王蕾, 王尧尧, 蒲高斌, 刘谦, 张永清 (2019). 植物WRKY类转录因子在非生物胁迫下的功能与作用机制. 分子植物育种 17, 5973-5979. | |
| [88] | Ren YJ, Wang DJ, Su YC, Wang L, Zhang X, Su WH, Que YX (2021). Structure, classification, evolution and function of plant WRKY transcription factors. J Agr Biotechnol 29, 105-124. (in Chinese) |
| 任永娟, 王东姣, 苏亚春, 王玲, 张旭, 苏炜华, 阙友雄 (2021). 植物WRKY转录因子: 结构、分类、进化和功能. 农业生物技术学报 29, 105-124. | |
| [89] | Renn SCP, Machado HE, Duftner N, Sessa AK, Harris RM, Hofmann HA (2018). Gene expression signatures of mating system evolution. Genome 61, 287-297. |
| [90] | Rifkin SA, Kim J, White KP (2003). Evolution of gene expression in the Drosophila melanogaster subgroup. Nat Genet 33, 138-144. |
| [91] | Roberge C, Guderley H, Bernatchez L (2007). Genomewide identification of genes under directional selection: gene transcription QST scan in diverging Atlantic salmon subpopulations. Genetics 177, 1011-1022. |
| [92] | Rohlfs RV, Nielsen R (2015). Phylogenetic ANOVA: the expression variance and evolution model for quantitative trait evolution. Syst Biol 64, 695-708. |
| [93] | Samad AFA, Sajad M, Nazaruddin N, Fauzi IA, Murad AMA, Zainal Z, Ismail I (2017). MicroRNA and transcription factor: key players in plant regulatory network. Front Plant Sci 8, 565. |
| [94] | Schwanh?usser B, Busse D, Li N, Dittmar G, Schuchhardt J, Wolf J, Chen W, Selbach M (2011). Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473, 337-342. |
| [95] | Sezen UU, Shue JE, Worthy SJ, Davies SJ, McMahon SM, Swenson NG (2024). Leaf gene expression trajectories during the growing season are consistent between sites and years in American beech. Proc R Soc B 291, 20232338. |
| [96] | Shamandi N, Zytnicki M, Charbonnel C, Elvira-Matelot E, Bochnakian A, Comella P, Mallory AC, Lepère G, Sáez-Vásquez J, Vaucheret H (2015). Plants encode a general siRNA suppressor that is induced and suppressed by viruses. PLoS Biol 13, e1002326. |
| [97] | Shea DJ, Nishida N, Takada S, Itabashi E, Takahashi S, Akter A, Miyaji N, Osabe K, Mehraj H, Shimizu M, Seki M, Kakizaki T, Okazaki K, Dennis ES, Fujimoto R (2019). Long noncoding RNAs in Brassica rapa L. following vernalization. Sci Rep 9, 9302. |
| [98] | Shriram V, Kumar V, Devarumath RM, Khare TS, Wani SH (2016). MicroRNAs as potential targets for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Plant Sci 7, 817. |
| [99] | Singh KP, Miaskowski C, Dhruva AA, Flowers E, Kober KM (2018). Mechanisms and measurement of changes in gene expression. Biol Res Nurs 20, 369-382. |
| [100] | Song L, Fang Y, Chen L, Wang J, Chen XW (2021). Role of non-coding RNAs in plant immunity. Plant Commun 2, 100180. |
| [101] | Stavast CJ, Erkeland SJ (2019). The non-canonical aspects of microRNAs: many roads to gene regulation. Cells 8, 1465. |
| [102] | Strader L, Weijers D, Wagner D (2022). Plant transcription factors—being in the right place with the right company. Curr Opin Plant Biol 65, 102136. |
| [103] | Su WJ, Cao RL, Zhou ZL, Zhao NH, Zhang YY, Hu DN, Liu J (2023). Identification and expression analysis of the WRKY gene family in Camellia oleifera under stress conditions. J Central South Univ Forestry Technol 43(3), 155-166, 174. (in Chinese) |
| 苏文娟, 曹瑞兰, 周增亮, 赵娜红, 张运煜, 胡冬南, 刘娟 (2023). 油茶WRKY基因家族鉴定及逆境胁迫表达分析. 中南林业科技大学学报 43(3), 155-166, 174. | |
| [104] | Tian F, Yang DC, Meng YQ, Jin JP, Gao G (2020). PlantRegMap: charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 48, D1104-D1113. |
| [105] | Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3, Research0034.1. |
| [106] | Vanguilder HD, Vrana KE, Freeman WM (2008). Twenty-five years of quantitative PCR for gene expression analysis. Biotechniques 44, 619-626. |
| [107] | V?sa U, Claringbould A, Westra HJ, Bonder MJ, Deelen P, Zeng B, Kirsten H, Saha A, Kreuzhuber R, Yazar S, Brugge H, Oelen R, De Vries DH, Van Der wijst MGP, Kasela S, Pervjakova N, Alves I, Favé MJ, Agbessi M, Christiansen MW, Jansen R, Sepp?l? I, Tong L, Teumer A, Schramm K, Hemani G, Verlouw J, Yaghootkar H, S?nmez Flitman R, Brown A, Kukushkina V, Kalnapenkis A, Rüeger S, Porcu E, Kronberg J, Kettunen J, Lee B, Zhang FT, Qi T, Hernandez JA, Arindrarto W, Beutner F, Dmitrieva J, Elansary M, Fairfax BP, Georges M, Heijmans BT, Hewitt AW, K?h?nen M, Kim Y, Knight JC, Kovacs P, Krohn K, Li S, Loeffler M, Marigorta UM, Mei HL, Momozawa Y, Müller-Nurasyid M, Nauck M, Nivard MG, Penninx BWJH, Pritchard JK, Raitakari OT, Rotzschke O, Slagboom EP, Stehouwer CDA, Stumvoll M, Sullivan P, ’t Hoen PAC, Thiery J, T?njes A, Van Dongen J, Van Iterson M, Veldink JH, V?lker U, Warmerdam R, Wijmenga C, Swertz M, Andiappan A, Montgomery GW, Ripatti S, Perola M, Kutalik Z, Dermitzakis E, Bergmann S, Frayling T, Van Meurs J, Prokisch H, Ahsan H, Pierce BL, Lehtim?ki T, Boomsma DI, Psaty BM, Gharib SA, Awadalla P, Milani L, Ouwehand WH, Downes K, Stegle O, Battle A, Visscher PM, Yang J, Scholz M, Powell J, Gibson G, Esko T, Franke L (2021). Large-scale cis- and trans- eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet 53, 1300-1310. |
| [108] | Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ (2012). Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory Biosci 131, 281-285. |
| [109] | Waheed S, Zeng LH (2020). The critical role of miRNAs in regulation of flowering time and flower development. Genes 11, 319. |
| [110] | Walsh B, Lynch M (2018). Evolution and Selection of Quantitative Traits. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 391-478. |
| [111] | Wang FF, Zhou ZX, Hong Y, Gu YY, Lv C, Guo BJ, Zhu J, Xu RG (2023). Identification of the NF-YC genes in Hordeum vulgare and expression analysis under salt stress. Chin Bull Bot 58, 140-149. (in Chinese) |
| 王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根 (2023). 大麦NF-YC基因鉴定及在盐胁迫下的表达分析. 植物学报 58, 140-149. | |
| [112] | Wang JL, Hou YG, Wang Y, Zhao HS (2021a). Integrative lncRNA landscape reveals lncRNA-coding gene networks in the secondary cell wall biosynthesis pathway of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). BMC Genomics 22, 638. |
| [113] | Wang T, Liu YZ, Ruan JP, Dong XJ, Wang YD, Peng JJ (2021b). A pipeline for RNA-seq based eQTL analysis with automated quality control procedures. BMC Bioinformatics 22, 403. |
| [114] | Wang X (2023). Phylogenomic Relationships Among Varieties of Tonna ciliata and the Strategy for Their Genetic Conservation. PhD dissertation. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University. pp. 1-173. (in Chinese) |
| 王茜 (2023). 红椿变种基因组进化关系和遗传资源保护研究. 博士论文. 广州: 华南农业大学. pp. 1-173. | |
| [115] | Wang Z (2014). The Structural Basis for the Specific DNA Recognition of Transcriptional Factor SATB1. PhD dissertation. Tianjin: NanKai University. pp. 1-126. (in Chinese) |
| 王峥 (2014). 转录因子SATB1特异性结合DNA的结构基础研究. 博士论文. 天津: 南开大学. pp. 1-126. | |
| [116] | Wright S (1943). Isolation by distance. Genetics 28, 114-138. |
| [117] | Wu JN, Del Duca E, Espino M, Gontzes A, Cueto I, Zhang N, Estrada YD, Pavel AB, Krueger JG, Guttman- Yassky E (2020). RNA sequencing keloid transcriptome associates keloids with Th2, Th1, Th17/Th22, and JAK3- skewing. Front Immunol 11, 597741. |
| [118] | Wu SH, Zhang SX, Chao JQ, Li Y, Yang SG, Deng XM, Shi MJ, Tian WM (2023). Differential miRNA expression profiling reveals a correlation between hbr-miR156 and laticifer differentiation in rubber trees. Ind Crop Prod 192, 116067. |
| [119] | Wu YQ, Sun RN, Huan T, Zhao YY, Yu DL, Sun YQ (2024). An insight into the gene expression evolution in Gossypium species based on the leaf transcriptomes. BMC Genomics 25, 179. |
| [120] | Xiao Y, Lv YW, Wang ZY, Wu C, He ZH, Hu XS (2024). Selfing shapes fixation of a mutant allele under flux equilibrium. Genome Biol Evol 16, evae261. |
| [121] | Yang JK (2023). Studies on the Stress Resistance of Transcription Factors PdPapERF34 and PdPapWRKY22 of Populus davidiana × P. alba var. pyramidalis. Master’s thesis. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University. pp. 1-95. (in Chinese) |
| 杨建坤 (2023). 山新杨转录因子PdPapERF34和PdPapWRKY22抗逆功能研究. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. pp. 1-95. | |
| [122] | Yang XQ, Zhang LC, Yang YZ, Schmid M, Wang YW (2021). miRNA mediated regulation and interaction between plants and pathogens. Int J Mol Sci 22, 2913. |
| [123] | Yu XY (2021). Cloning and Functional Identification of PeWRKY41 Gene from Populus × euramericana. PhD dissertation. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University. pp. 84-90. (in Chinese) |
| 于晓跃 (2021). 欧美杨PeWRKY41基因克隆及功能鉴定. 博士论文. 保定: 河北农业大学. pp. 84-90. | |
| [124] | Zhang L, Lu DY, Ge XL, Du JJ, Wen SS, Xiang XD, Du CJ, Zhou XL, Hu JJ (2023). Insight into growth and wood properties based on QTL and eQTL mapping in Populus deltoides ‘Danhong’ × Populus simonii ‘Tongliao1’. Ind Crop Prod 199, 116731. |
| [125] | Zhang XP, Wang W, Zhu WD, Dong J, Cheng YY, Yin ZJ, Shen FF (2019). Mechanisms and functions of long non- coding RNAs at multiple regulatory levels. Int J Mol Sci 20, 5573. |
| [126] | Zhang XX, Cheng X, Li LL, Wang X, Zhou W, Chen XY, Hu XS (2020). The wave of gene advance under diverse systems of mating. Heredity 125, 253-268. |
| [127] | Zhang YT (2022). Functional Study on Drought and Salt- alkali Tolerance of WRKY42 Gene in Amorpha fiuticosa. Master’s thesis. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University. pp. 27-34. (in Chinese) |
| 张艺腾 (2022). 紫穗槐WRKY42基因抗旱耐盐碱性的功能研究. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. pp. 27-34. | |
| [128] | Zhang YX, Han XJ, Chen SS, Zheng L, He XL, Liu MY, Qiao GR, Wang Y, Zhuo RY (2017). Selection of suitable reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR gene expression analysis in Salix matsudana under different abiotic stresses. Sci Rep 7, 40290. |
| [129] | Zhang ZB, Kryvokhyzha D, Orsucci M, Glémin S, Milesi P, Lascoux M (2022). How broad is the selfing syndrome? Insights from convergent evolution of gene expression across species and tissues in the Capsella genus. New Phytol 236, 2344-2357. |
| [130] | Zhao HM (2022). Molecular Mechanism of Long Noncoding RNA lncRNAW20 Regulating Drought Tolerance in Betula platyphylla. PhD dissertation. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University. pp. 1-146. (in Chinese) |
| 赵慧敏 (2022). 长链非编码RNA LncRNAW20调控白桦抗旱的分子机制. 博士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. pp. 1-146. | |
| [131] | Zheng GZ, Li W, Liu ZY (2019). Alternative role of noncoding RNAs: coding and noncoding properties. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 20, 920-927. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |