

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 353-362.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15094 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15094
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhishun Xiao, Cong Lin, Shuang Yang, Yan Liu, Yawen Fan*
Received:2015-06-01
Accepted:2015-09-25
Online:2016-05-01
Published:2016-05-24
Contact:
Fan Yawen
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
Zhishun Xiao, Cong Lin, Shuang Yang, Yan Liu, Yawen Fan. Community Structure of Phytoplankton and Its Relation with Environmental Factors in Xinhua Lake of China[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(3): 353-362.
| Season | Sampling sites | SD (cm) | Tempera- ture (°C) | SpCond (μS·cm-1) | DO (mg·L-1) | Chlorophyll a (mg·L-1) | NH3-N (mg·L-1) | TN (mg·L-1) | TP (mg·L-1) | COD (mg·L-1) | BOD (mg·L-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | I | 19 | 32.5 | 3770 | 4.18 | 10.20 | 0.64 | 2.9 | 0.56 | 8.56 | 21.00 | 9.06 |
| II | 18 | 31.4 | 3930 | 3.74 | 11.31 | 0.72 | 2.75 | 0.36 | 9.53 | 20.30 | 9.08 | |
| III | 16 | 33.7 | 3710 | 3.34 | 10.35 | 0.84 | 3.24 | 0.75 | 9.87 | 19.80 | 8.97 | |
| IV | 18 | 28.6 | 3370 | 3.02 | 15.40 | 0.70 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 10.31 | 17.90 | 8.91 | |
| V | 17 | 33.3 | 3730 | 4.33 | 11.65 | 0.70 | 3.55 | 0.42 | 9.00 | 18.30 | 9.01 | |
| VI | 20 | 27.4 | 3550 | 4.27 | 11.58 | 0.68 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 9.00 | 17.88 | 8.83 | |
| Summer | I | 23 | 29.6 | 3850 | 5.75 | 13.90 | 0.65 | 2.64 | 1.12 | 8.73 | 9.50 | 9.41 |
| II | 22 | 32.2 | 3850 | 7.61 | 12.70 | 0.69 | 2.55 | 0.71 | 9.01 | 10.20 | 9.39 | |
| III | 24 | 28.5 | 4010 | 6.70 | 14.80 | 0.84 | 3.52 | 0.94 | 11.4 | 18.10 | 9.42 | |
| IV | 23 | 32.6 | 3990 | 6.24 | 16.50 | 0.45 | 3.02 | 0.9 | 11.9 | 20.80 | 9.39 | |
| V | 18 | 33.6 | 3990 | 7.35 | 12.10 | 0.84 | 3.31 | 0.86 | 9.59 | 11.30 | 9.45 | |
| VI | 26 | 31.2 | 3960 | 8.20 | 11.80 | 0.83 | 3.15 | 0.82 | 9.01 | 8.70 | 9.43 | |
| Autumn | I | 18 | 11.6 | 3860 | 6.25 | 11.90 | 0.63 | 2.88 | 0.67 | 10.3 | 20.60 | 8.39 |
| II | 18 | 13.4 | 3940 | 6.05 | 12.80 | 0.75 | 2.95 | 0.45 | 10.2 | 18.10 | 7.79 | |
| III | 16 | 16.8 | 4100 | 5.54 | 12.90 | 0.84 | 3.01 | 0.76 | 14.2 | 23.90 | 8.45 | |
| IV | 16 | 14.0 | 3450 | 5.54 | 14.30 | 0.95 | 4.02 | 0.60 | 10.0 | 18.90 | 7.45 | |
| V | 16 | 13.5 | 4100 | 7.90 | 11.20 | 0.56 | 2.58 | 0.47 | 10.4 | 21.50 | 7.95 | |
| VI | 18 | 13.2 | 4050 | 7.96 | 12.00 | 0.53 | 2.49 | 0.58 | 10.6 | 20.10 | 7.96 |
Table 1 Physicochemical indexes of sampling sites in Xinhua Lake
| Season | Sampling sites | SD (cm) | Tempera- ture (°C) | SpCond (μS·cm-1) | DO (mg·L-1) | Chlorophyll a (mg·L-1) | NH3-N (mg·L-1) | TN (mg·L-1) | TP (mg·L-1) | COD (mg·L-1) | BOD (mg·L-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | I | 19 | 32.5 | 3770 | 4.18 | 10.20 | 0.64 | 2.9 | 0.56 | 8.56 | 21.00 | 9.06 |
| II | 18 | 31.4 | 3930 | 3.74 | 11.31 | 0.72 | 2.75 | 0.36 | 9.53 | 20.30 | 9.08 | |
| III | 16 | 33.7 | 3710 | 3.34 | 10.35 | 0.84 | 3.24 | 0.75 | 9.87 | 19.80 | 8.97 | |
| IV | 18 | 28.6 | 3370 | 3.02 | 15.40 | 0.70 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 10.31 | 17.90 | 8.91 | |
| V | 17 | 33.3 | 3730 | 4.33 | 11.65 | 0.70 | 3.55 | 0.42 | 9.00 | 18.30 | 9.01 | |
| VI | 20 | 27.4 | 3550 | 4.27 | 11.58 | 0.68 | 2.57 | 0.45 | 9.00 | 17.88 | 8.83 | |
| Summer | I | 23 | 29.6 | 3850 | 5.75 | 13.90 | 0.65 | 2.64 | 1.12 | 8.73 | 9.50 | 9.41 |
| II | 22 | 32.2 | 3850 | 7.61 | 12.70 | 0.69 | 2.55 | 0.71 | 9.01 | 10.20 | 9.39 | |
| III | 24 | 28.5 | 4010 | 6.70 | 14.80 | 0.84 | 3.52 | 0.94 | 11.4 | 18.10 | 9.42 | |
| IV | 23 | 32.6 | 3990 | 6.24 | 16.50 | 0.45 | 3.02 | 0.9 | 11.9 | 20.80 | 9.39 | |
| V | 18 | 33.6 | 3990 | 7.35 | 12.10 | 0.84 | 3.31 | 0.86 | 9.59 | 11.30 | 9.45 | |
| VI | 26 | 31.2 | 3960 | 8.20 | 11.80 | 0.83 | 3.15 | 0.82 | 9.01 | 8.70 | 9.43 | |
| Autumn | I | 18 | 11.6 | 3860 | 6.25 | 11.90 | 0.63 | 2.88 | 0.67 | 10.3 | 20.60 | 8.39 |
| II | 18 | 13.4 | 3940 | 6.05 | 12.80 | 0.75 | 2.95 | 0.45 | 10.2 | 18.10 | 7.79 | |
| III | 16 | 16.8 | 4100 | 5.54 | 12.90 | 0.84 | 3.01 | 0.76 | 14.2 | 23.90 | 8.45 | |
| IV | 16 | 14.0 | 3450 | 5.54 | 14.30 | 0.95 | 4.02 | 0.60 | 10.0 | 18.90 | 7.45 | |
| V | 16 | 13.5 | 4100 | 7.90 | 11.20 | 0.56 | 2.58 | 0.47 | 10.4 | 21.50 | 7.95 | |
| VI | 18 | 13.2 | 4050 | 7.96 | 12.00 | 0.53 | 2.49 | 0.58 | 10.6 | 20.10 | 7.96 |
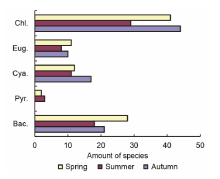
Fig. 3 The seasonal variations of the phytoplankton species in Xinhua Lake(Chl: Chlorophyta; Eug: Euglenophyta; Cya: Cyanophyta; Pyr: Pyrrhophyta; Bac: Bacillariophyta)
| Phylum | Species |
|---|---|
| Bacillariophyta | Cyclotella meneghiniana Kützing |
| Coscinodiscus lacustris Grun. | |
| Nitzschia palea (Kütz.) W. Smith | |
| Cyanophyta | Anabaena azotica Ley. |
| Raphidiopsis curvata Fritsch et Rich | |
| Chroococcus minutus (Kütz.) Näg. | |
| Arthrospira maxima Setch. et Gardner | |
| Merismopedia minima G. Beck | |
| Anabaenopsis circularis (G. S. West) Wolosz. et Miller | |
| Chlorophyta | Tetraëdron minimum (A. Braun) Hansgirg |
| Cosmarium depressum (Näg.) Lundell | |
| Scenedesmus bijuga (Turp.) Lagerheim | |
| Kirchneriella lunaris (Kirch. ) Moebius | |
| S. abundans (Kirchn.) Chodat | |
| Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck | |
| C. subprotumidum Nordstedt | |
| Pediastrum boryanum (Turp.) Meneghini | |
| Oocystis elliptica W. West | |
| O. solitaria Wittrock | |
| S. quadricauda (Turp.) Brébisson | |
| S. protuberans Fritsch. | |
| Ankistrodesmus angustus Bernard | |
| O. parva West & West | |
| Euglenophyta | Euglena viridis Ehrenberg |
Table 2 Dominant species of phytoplankton in Xinhua Lake
| Phylum | Species |
|---|---|
| Bacillariophyta | Cyclotella meneghiniana Kützing |
| Coscinodiscus lacustris Grun. | |
| Nitzschia palea (Kütz.) W. Smith | |
| Cyanophyta | Anabaena azotica Ley. |
| Raphidiopsis curvata Fritsch et Rich | |
| Chroococcus minutus (Kütz.) Näg. | |
| Arthrospira maxima Setch. et Gardner | |
| Merismopedia minima G. Beck | |
| Anabaenopsis circularis (G. S. West) Wolosz. et Miller | |
| Chlorophyta | Tetraëdron minimum (A. Braun) Hansgirg |
| Cosmarium depressum (Näg.) Lundell | |
| Scenedesmus bijuga (Turp.) Lagerheim | |
| Kirchneriella lunaris (Kirch. ) Moebius | |
| S. abundans (Kirchn.) Chodat | |
| Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck | |
| C. subprotumidum Nordstedt | |
| Pediastrum boryanum (Turp.) Meneghini | |
| Oocystis elliptica W. West | |
| O. solitaria Wittrock | |
| S. quadricauda (Turp.) Brébisson | |
| S. protuberans Fritsch. | |
| Ankistrodesmus angustus Bernard | |
| O. parva West & West | |
| Euglenophyta | Euglena viridis Ehrenberg |
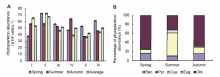
Fig. 4 The variations of phytoplankton abundance in different sampling sites (A) and the seasonal variations of phytoplankton abundance (B) in Xinhua Lake(I-VI see Table 1. Bac, Pry, Cya, Eug and Chl see Figure 3.)
| Season | Index | Sampling sites | Average value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | |||
| Spring | H′ | 2.407 | 2.205 | 2.144 | 1.845 | 1.698 | 2.005 | 2.051 |
| D | 0.808 | 0.792 | 0.763 | 0.670 | 0.642 | 0.734 | 0.735 | |
| J | 0.469 | 0.426 | 0.390 | 0.342 | 0.324 | 0.382 | 0.389 | |
| Summer | H′ | 2.345 | 2.510 | 2.236 | 2.097 | 2.471 | 2.111 | 2.295 |
| D | 0.810 | 0.851 | 0.779 | 0.779 | 0.771 | 0.859 | 0.748 | |
| J | 0.441 | 0.493 | 0.432 | 0.406 | 0.499 | 0.412 | 0.447 | |
| Autumn | H′ | 2.876 | 3.065 | 2.899 | 3.100 | 3.082 | 2.936 | 2.993 |
| D | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.915 | 0.928 | 0.927 | 0.911 | 0.918 | |
| J | 0.487 | 0.535 | 0.561 | 0.534 | 0.549 | 0.541 | 0.534 | |
Table 3 Seasonal variations of biodiversity indexes in Xinhua Lake
| Season | Index | Sampling sites | Average value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | |||
| Spring | H′ | 2.407 | 2.205 | 2.144 | 1.845 | 1.698 | 2.005 | 2.051 |
| D | 0.808 | 0.792 | 0.763 | 0.670 | 0.642 | 0.734 | 0.735 | |
| J | 0.469 | 0.426 | 0.390 | 0.342 | 0.324 | 0.382 | 0.389 | |
| Summer | H′ | 2.345 | 2.510 | 2.236 | 2.097 | 2.471 | 2.111 | 2.295 |
| D | 0.810 | 0.851 | 0.779 | 0.779 | 0.771 | 0.859 | 0.748 | |
| J | 0.441 | 0.493 | 0.432 | 0.406 | 0.499 | 0.412 | 0.447 | |
| Autumn | H′ | 2.876 | 3.065 | 2.899 | 3.100 | 3.082 | 2.936 | 2.993 |
| D | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.915 | 0.928 | 0.927 | 0.911 | 0.918 | |
| J | 0.487 | 0.535 | 0.561 | 0.534 | 0.549 | 0.541 | 0.534 | |
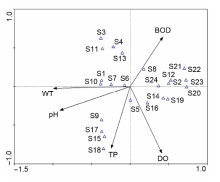
Fig. 5 Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) biplot of phytoplankton species and environmental factors in Xinhua Lake (F-ratio=3.091, P-value=0.018)(BOD: Biochemical oxygen demand; DO: Dissolved oxygen; TP: Total phosphorus; WT: Water temperature; pH: pH value; S1: Cosmarium depressum; S2: Scenedesmus abundans; S3: Anabaenopsis circularis; S4: S. bijuga; S5: Kirchneriella lunaris; S6: Tetraëdron minimum; S7: Cyclotella meneghiniana; S8: Chlorella vulgaris; S9: Anabaena azotica; S10: Coscinodiscus lacustris; S11: C. subprotumidum; S12: Nitzschia palea; S13: Pediastrum boryanum; S14: Oocystis elliptica; S15: Raphidiopsis curvata; S16: Chroococcus minutus; S17: Euglena viridis; S18: Arthrospira maxima; S19: O. solitaria; S20: S. quadricauda; S21: S. protuberans; S22: Merismopedia minima; S23: Ankistrodesmus angustus; S24: O. parva)
| [1] | 陈家长, 王菁, 裘丽萍, 孟顺龙, 范立民, 宋超 (2014). pH对鱼腥藻和普通小球藻生长竞争的影响. 生态环境学报 23, 289-294. |
| [2] | 陈立婧, 吴竹臣, 胡忠军, 彭自然, 刘其根 (2011). 上海崇明岛明珠湖浮游植物群落结构. 应用生态学报 22, 1599-1605. |
| [3] | 国家环境保护总局 (2002). 水和废水监测分析方法(第四版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. pp. 200-284. |
| [4] | 韩欢欢, 范亚文 (2012). 黑龙江省安兴湿地秋季浮游植物群落结构. 湖泊科学 24, 577-585. |
| [5] | 胡鸿钧, 魏印心 (2006). 中国淡水藻类——系统、分类及生态. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 23-900. |
| [6] | 金相灿, 屠清瑛 (1990). 湖泊富营养化调查规范(第2版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. pp. 239-244. |
| [7] | 况琪军, 马沛明, 胡征宇, 周广杰 (2005). 湖泊富营养化的藻类生物学评价与治理研究进展. 安全与环境学报 5(2), 87-91. |
| [8] | 李德亮, 张婷, 肖调义, 余建波, 王红权, 陈开健, 刘安民, 李祖军 (2011). 大通湖浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子关系. 应用生态学报 22, 2107-2113. |
| [9] | 李慧, 刘妍, 范亚文, 国超旋 (2014). 三江平原湿地同江地区水域夏季浮游植物群落结构特征. 植物学报 49, 440-449. |
| [10] | 梁培瑜, 王烜, 马芳冰 (2013). 水动力条件对水体富营养化的影响. 湖泊科学 25, 455-462. |
| [11] | 林秋奇, 胡韧, 韩博平 (2003). 流溪河水库水动力学对营养盐和浮游植物分布的影响. 生态学报 23, 2278-2284. |
| [12] | 刘春光, 金相灿, 孙凌, 钟远, 戴树桂, 庄源益 (2005). pH值对淡水藻类生长和种类变化的影响. 农业环境科学学报 24, 294-298. |
| [13] | 陆欣鑫, 刘妍, 范亚文 (2014). 呼兰河湿地夏、秋两季浮游植物功能分组演替及其驱动因子. 生态学报 34, 1264-1273. |
| [14] | 钱奎梅, 陈宇炜, 宋晓兰 (2008). 太湖浮游植物优势种长期演化与富营养化进程的关系. 生态科学 27(2), 65-70. |
| [15] | 沈韫芬, 章宗涉, 龚循矩, 顾曼如, 施之新, 魏印心 (1990). 微型生物监测新技术. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. pp. 119-139. |
| [16] | 田永强, 俞超超, 王磊, 黄邦钦 (2012). 福建九龙江北溪浮游植物群落分布特征及其影响因子. 应用生态学报 23, 2559-2565. |
| [17] | 王华, 逄勇 (2008). 藻类生长的水动力学因素影响与数值仿真. 环境科学 29, 884-889. |
| [18] | 王全喜, 曹建国, 刘妍, 钦娜 (2008). 上海九段沙湿地自然保护区及其附近水域藻类图集. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 55-70. |
| [19] | 吴世凯, 谢平, 倪乐意, 王松波, 徐军 (2014). 长江中下游地区湖泊中蓝藻及其与氮磷浓度的关系. 水生态学杂志 35(3), 19-25. |
| [20] | 吴晓辉, 李其军 (2010). 水动力条件对藻类影响的研究进展. 生态环境学报 19, 1732-1738. |
| [21] | 徐海, 刘兆普, 袁兰, 杨林章 (2009). pH对几种淡水藻类生长的影响. 环境科学与技术 32, 27-30. |
| [22] | 许海, 秦伯强, 朱广伟 (2012). 太湖不同湖区夏季蓝藻生长的营养盐限制研究. 中国环境科学 32, 2230-2236. |
| [23] | 颜润润, 逄勇, 赵伟, 李瑞玲, 晁建颖 (2008). 环流型水域水动力对藻类生长的影响. 中国环境科学 28, 813-817. |
| [24] | 杨宏伟, 高光, 朱广伟 (2012). 太湖蠡湖冬季浮游植物群落结构特征与氮、磷浓度关系. 生态学杂志 31(1), 1-7. |
| [25] | 朱广伟, 赵林林, 陈伟民, 谢纯刚, 高荣平 (2011). 低水位运行对天目湖水库水质与生态的影响. 生态与农村环境学报 27(4), 87-94. |
| [26] | APHA (1998). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater 20th Edition. Washington:APHA-AWWA- WEF. pp. 2810-3010. |
| [27] | Belaoussoff S, Kevan PG, Murphy S (2003). Assessing tillage disturbance on assemblages of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) by using a range of ecological indices.Biodivers Conserv 12, 851-882. |
| [28] | Camdevyren H, Demyr N, Kanik A (2005). Use of principal component scores in multiple linear regression models for prediction of chlorophylla in reservoirs.Ecol Model 181, 581-589. |
| [29] | Cardinale BJ, Palmer MA, Collins SL (2002). Species diversity enhances ecosystem functioning through interspecific facili- tation.Nature 415, 426-429. |
| [30] | Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1997a). Bacillariophyceae 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. Berlin: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg. pp. 488-857. |
| [31] | Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1997b). Bacillariophyceae. 2. Teil: Bacillariophyceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. Berlin: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg. pp. 224-585. |
| [32] | Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1997c). Bacillariophyceae. 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. Berlin: Spek- trum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg. pp. 232-560. |
| [33] | Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1997d). Bacillariophyceae. 4. Teil: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Ergänzunge zu Achnanthes s.l., Navicula s. str., Gomphonema Gesamtliteraturverzei- chnis Teil 1-4. Berlin: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidel- berg. pp. 250-425. |
| [34] | Lazorchak JM, Klemm DJ, Peck DV (1998). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment Program—Surface Waters: Field Operations and Methods for Measuring the Ecological Condition of Wadeable Streams. Washington, D.C: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. pp. 119-120. |
| [35] | Lepistö L, Holopainen AL, Vuoristo H (2004). Type-specific and indicator taxa of phytoplankton as a quality criterion for assessing the ecological status of Finnish boreal lakes.Limnologica 34, 236-248. |
| [36] | Marchetto A, Padedda BM, Marinani M (2009). Anumerical index for evaluation phytoplankton response to changes in nutrient levels in deep mediterranean reservoirs.J Limnol 68, 106-121. |
| [37] | Naselli-Flores L (2000). Phytoplankton assemblages in twenty one Sicilian reservoirs: relationship between species com- position and environment factors.Hydrobiologia 424, 1-11. |
| [38] | Naselli-Flores L, Barone R (1998). Phytoplankton dynamics in two reservoirs with different trophic state (Lake Rosamarina and Lake Arancio, Sicily, Italy).Hydrobiologia 369, 163-178. |
| [39] | Nwankwo DI, Akinsoji A (1992). Epiphyte community of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes (Mart) Solms in coastal waters of southwestern Nigeria.Archiv Für Hydrobiologie 124, 501-511. |
| [40] | Ortega-Mayagoitia E, Rojo C, Rodrigo MA (2003). Controlling factors of phytoplankton assemblages in wetlands: an exper- imental approach.Hydrobiologia 502, 177-186. |
| [41] | Parinet B, Lhote A, Legube B (2004). Principal component analysis: an appropriate tool for water quality evaluation and management application to a tropical lake system.Ecol Model 178, 295-311. |
| [42] | Reynolds CS (1998). What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status.Hydrobiologia 369, 11-26. |
| [43] | Singh PK, Malik A, Mohan D (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India) a case study.Water Res 38, 3980-3992. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||