

绿豆5个产量相关性状的QTL分析
收稿日期: 2022-05-25
录用日期: 2022-07-25
网络出版日期: 2022-07-25
基金资助
国家食用豆产业技术体系合肥综合试验站(CARS-08-Z11)
QTLs Analysis for Five Yield-related Traits in Mungbean
Received date: 2022-05-25
Accepted date: 2022-07-25
Online published: 2022-07-25
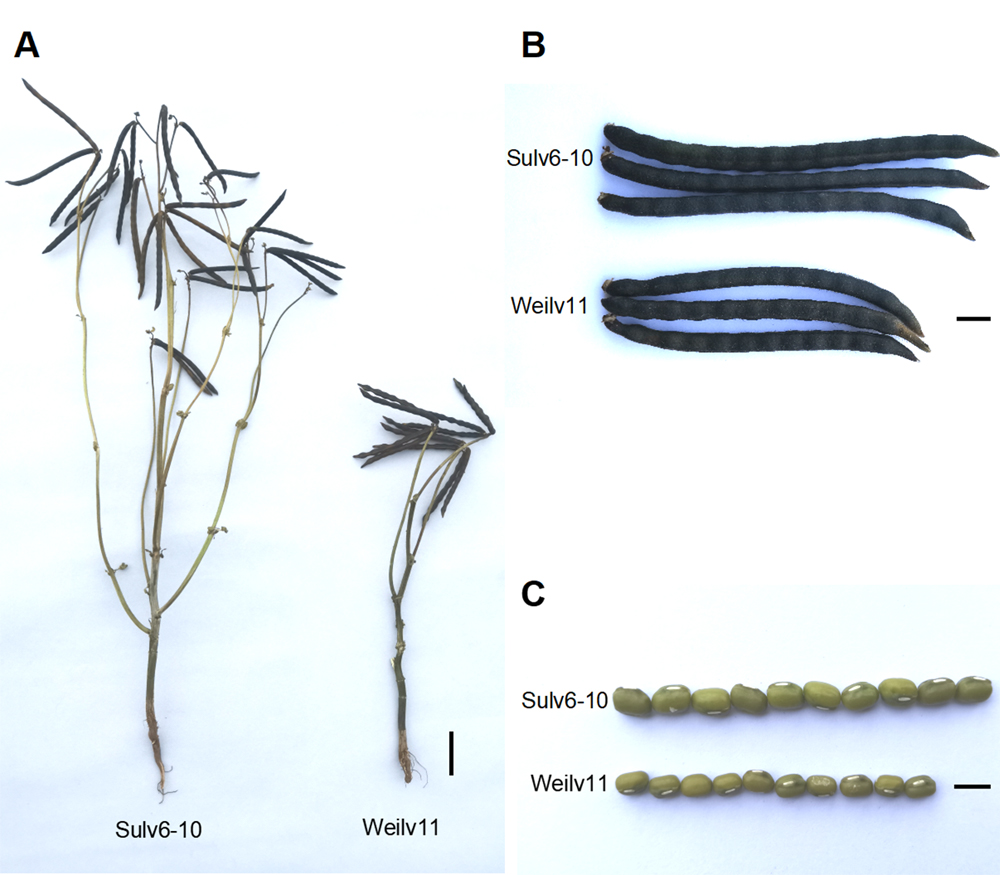
利用绿豆(Vigna radiata)品种苏绿16-10和潍绿11杂交构建的F2和F3群体发掘调控绿豆产量相关性状的遗传位点。同时对绿豆产量相关性状进行表型鉴定和相关性分析, 并利用构建的遗传连锁图谱进行QTL定位。结果表明, 单株产量与单株荚数、单荚粒数、百粒重和分枝数均呈正相关。单株产量与单株荚数的相关性最高, 这2个性状在F2和F3群体中的相关系数分别为0.950和0.914。在F2群体中, 共检测到8个与产量性状相关的QTL位点, 其中与单株荚数、单荚粒数和单株产量相关的QTL位点各1个, 分别解释11.09% (qNPP3)、17.93% (qNSP3)和14.18% (qYP3)的表型变异; 2个与分枝数相关的QTL位点qBMS3和qBMS11, 分别解释18.51%和7.06%的表型变异; 3个与百粒重相关的QTL位点qHSW3、qHSW7和qHSW10, 分别解释5.33%、46.07%和4.24%的表型变异。在F3群体中, qNSP3和qHSW7再次被检测到, 表明这2个QTLs有较好的遗传稳定性。同时, 开发了1个与百粒重主效QTL qHSW7紧密连锁的InDel标记R7-13.4, 并利用自然群体对该分子标记辅助筛选的有效性进行了验证。研究结果可为绿豆产量相关性状基因的定位、克隆及分子标记辅助育种提供参考。
叶卫军 , 张阴 , 王沛然 , 张玲玲 , 田东丰 , 吴泽江 , 周斌 . 绿豆5个产量相关性状的QTL分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023 , 58(1) : 150 -158 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB22108
The F2 and F3 populations derived from the cross between Sulv16-10 and Weilv11 were used to explore the genetic loci controlling yield-related traits in mungbean, and the phenotype identification and correlation analysis between yield-related traits were completed. The genetic linkage map was constructed and used for QTL analysis. The yield per plant was positively correlated with the number of pods per plant, the number of seeds per pod, hundred-seed weight and the number of branches on main stem. The correlation between the yield per plant and the number of pods per plant was the highest, and the correlation coefficient between these two traits were 0.950 and 0.914 in F2 and F3 population, respectively. A total of 8 QTLs for yield-related traits were detected in the F2 population. Among them, three traits including the number of pods per plant, number of seeds per pod and yield per plant were found only on one related QTL, and each QTL accounting for 11.09% (qNPP3), 17.93% (qNSP3) and 14.18% (qYP3) of phenotype variance, respectively. Two QTLs, qBMS3 and qBMS11 related to the branch number on main stem were detected, which could explain 18.51% and 7.06% of phenotype variance, respectively. Three QTLs, qHSW3, qHSW7 and qHSW10 controlling hundred-seed weight were identified, which could explain 5.33%, 46.07% and 4.24% of phenotype variance, respectively. qNSP3 and qHSW7 were detected again in the F3 population, demonstrating that the two QTLs were genetically stable. The InDel molecular marker R7-13.4 which closely linked to the major-effect QTL qHSW7 for hundred-seed weight was developed, and the validation of molecular marker-assisted selection was verified in natural populations. These studies provide reference for mapping, cloning of genes associated with yield-related traits as well as molecular marker-assisted selection in mungbean.

Key words: mungbean; yield-related traits; correlation analysis; QTL mapping
| [1] | 陈红霖, 胡亮亮, 杨勇, 郝曦煜, 李姝彤, 王素华, 王丽侠, 程须珍 (2020). 481份国内外绿豆种质农艺性状及豆象抗性鉴定评价及遗传多样性分析. 植物遗传资源学报 21, 549-559. |
| [2] | 陈吉宝 (2020). 绿豆产量性状的QTL定位. 中国农业科技导报 22(10), 38-48. |
| [3] | 程须珍, 王素华, 王丽霞 (2006). 绿豆种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 9-22. |
| [4] | 杜梦柯, 连文婷, 张晓, 李欣欣 (2021). 氮处理对大豆根瘤固氮能力及GmLbs基因表达的影响. 植物学报 56, 391-403. |
| [5] | 何恒斌, 贾桂霞 (2013). 豆科植物早期共生信号转导的研究进展. 植物学报 48, 665-675. |
| [6] | 侯小峰, 刘静, 王彩萍, 左联忠, 赵吉平, 郭鹏燕, 郭兆萍 (2015). 绿豆产量与主要农艺性状的灰色关联分析. 作物杂志 (1), 53-56. |
| [7] | 马秀杰 (2014). 间作对绿豆生物性状、产量和品质的影响. 核农学报 28, 546-551. |
| [8] | 梅丽, 程须珍, 王素华, 王丽侠, 蔡庆生, 刘春吉, 徐宁, 刘长友, 孙蕾 (2011). 绿豆产量相关农艺性状的QTL定位. 植物遗传资源学报 12, 948-956. |
| [9] | 王健康 (2009). 数量性状基因的完备区间作图方法. 作物学报 35, 239-245. |
| [10] | 王洁 (2020). 绿豆高密度遗传图谱构建及重要农艺性状QTL定位. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 22-26. |
| [11] | 徐东旭 (2015). 冀西北绿豆产量与主要农艺性状的灰色关联度分析. 农业科技通讯 (7), 96-98, 251. |
| [12] | 杨春玲, 王阔, 关立, 侯军红, 宋志均, 韩勇, 葛鹏飞 (2005). 绿豆主要农艺性状间的相关及通径分析. 杂粮作物 25, 314-315. |
| [13] | 杨芳, 杨媛, 冯高, 杨明君 (2012). 绿豆籽粒产量与主要农艺性状的相关分析. 农业科技通讯 (7), 95-97. |
| [14] | 杨勇, 周斌, 杨超华, 张丽亚 (2015). 夏播绿豆不同品种产量与主要农艺性状的相关分析. 作物杂志 (4), 65-68. |
| [15] | Alam MK, Islam MM, Salahin N, Hasanuzzaman M (2014). Effect of tillage practices on soil properties and crop productivity in wheat-mungbean-rice cropping system under subtropical climatic conditions. Sci World J 2014, 437283. |
| [16] | Chankaew S, Somta P, Sorajjapinun W, Srinives P (2011). Quantitative trait loci mapping of Cercospora leaf spot resistance in mungbean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Mol Breeding 28, 255-264. |
| [17] | Chen HM, Ku HM, Schafleitner R, Bains TS, Kuo CG, Liu CA, Nair RM (2013). The major quantitative trait locus for mungbean yellow mosaic Indian virus resistance is tightly linked in repulsion phase to the major bruchid resistance locus in a cross between mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] and its wild relative Vigna radiata ssp. sublobata. Euphytica 192, 205-216. |
| [18] | Chotechung S, Somta P, Chen JB, Yimram T, Chen X, Srinives P (2016). A gene encoding a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) is a candidate gene for bruchid (Coleoptera: bruchidae) resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata). Theor Appl Genet 129, 1673-1683. |
| [19] | Fatokun CA, Menancio-Hautea DI, Danesh D, Young ND (1992). Evidence for orthologous seed weight genes in cowpea and mungbean based on RFLP mapping. Genetics 132, 841-846. |
| [20] | Ha J, Satyawan D, Jeong H, Lee E, Cho KH, Kim MY, Lee SH (2021). A near-complete genome sequence of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) provides key insights into the modern breeding program. Plant Genome 14, e20121. |
| [21] | Humphry ME, Lambrides CJ, Chapman SC, Aitken EAB, Imrie BC, Lawn RJ, Mcintyre CL, Liu CJ (2005). Relationships between hard-seededness and seed weight in mungbean (Vigna radiata) assessed by QTL analysis. Plant Breeding 124, 292-298. |
| [22] | Humphry ME, Magner T, McIntyre CL, Aitken EAB, Liu CJ (2003). Identification of a major locus conferring resistance to powdery mildew (Erysiphe polygoni DC) in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) by QTL analysis. Genome 46, 738-744. |
| [23] | Isemura T, Kaga A, Tabata S, Somta P, Srinives P, Shimizu T, Jo U, Vaughan DA, Tomooka N (2012). Construction of a genetic linkage map and genetic analysis of domestication related traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata). PLoS One 7, e41304. |
| [24] | Kajonphol T, Sangsiri C, Somta P, Toojinda T, Srinives P (2012). SSR map construction and quantitative trait loci (QTL) identification of major agronomic traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). SABRAO J Breed Genet 44, 71-86. |
| [25] | Kang YJ, Kim SK, Kim MY, Lestari P, Kim KH, Ha BK, Jun TH, Hwang WJ, Lee T, Lee J, Shim S, Yoon MY, Jang YE, Han KS, Taeprayoon P, Yoon N, Somta P, Tanya P, Kim KS, Gwag JG, Moon JK, Lee YH, Park BS, Bombarely A, Doyle JJ, Jackson SA, Schafleitner R, Srinives P, Varshney RK, Lee SH (2014). Genome sequence of mungbean and insights into evolution within Vigna species. Nat Commun 5, 5443. |
| [26] | Keatinge JDH, Easdown WJ, Yang RY, Chadha ML, Shanmugasundaram S (2011). Overcoming chronic malnutrition in a future warming world: the key importance of mungbean and vegetable soybean. Euphytica 180, 129-141. |
| [27] | Kim SK, Nair RM, Lee J, Lee SH (2015). Genomic resources in mungbean for future breeding programs. Front Plant Sci 6, 626. |
| [28] | Kitsanachandee R, Somta P, Chatchawankanphanich O, Akhtar KP, Shah TM, Nair RM, Bains TS, Sirari A, Kaur L, Srinives P (2013). Detection of quantitative trait loci for mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV) resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) in India and Pakistan. Breeding Sci 63, 367-373. |
| [29] | Mei L, Cheng XZ, Wang SH, Wang LX, Liu CY, Sun L, Xu N, Humphry ME, Lambrides CJ, Li HB, Liu CJ (2009). Relationship between bruchid resistance and seed mass in mungbean based on QTL analysis. Genome 52, 589-596. |
| [30] | Sompong U, Somta P, Raboy V, Srinives P (2012). Mapping of quantitative trait loci for phytic acid and phosphorus contents in seed and seedling of mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczed). Breed Sci 62, 87-92. |
| [31] | Somta P, Chankaew S, Kongjaimun A, Srinives P (2015). QTLs controlling seed weight and days to flowering in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek], their conservation in azuki bean [V. angularis (Ohwi) Ohwi & Ohashi] and rice bean [V. umbellata (Thunb.) Ohwi & Ohashi]. Agrivita 37, 159-168. |
| [32] | Tuberosa R, Salvi S, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Maccaferri M, Conti S (2002). Mapping QTLs regulating morpho- physiological traits and yield: case studies, shortcomings and perspectives in drought-stressed maize. Ann Bot 89, 941-963. |
| [33] | Yaqub M, Mahmood T, Akhtar M, Iqbal MM, Ali S (2010). Induction of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] as a grain legume in the annual rice-wheat double cropping system. Pak J Bot 42, 3125-3135. |
| [34] | Ye WJ, Yang Y, Wang PR, Zhang Y, Zhang LY, Tian DF, Zhang L, Zhang LL, Zhou B (2021). InDel marker development and QTL analysis of agronomic traits in mung- bean [Vigna radiate (L.) Wilczek]. Mol Breeding 41, 66. |
| [35] | Yundaeng C, Somta P, Chen JB, Yuan XX, Chankaew S, Chen X (2021). Fine mapping of QTL conferring Cercospora leaf spot disease resistance in mungbean revealed TAF5 as candidate gene for the resistance. Theor Appl Genet 134, 701-714. |
| [36] | Zhang MC, Wang DM, Zheng Z, Humphry M, Liu CJ (2008). Development of PCR-based markers for a major locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata). Plant Breed 127, 429-432. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |