微区XRF技术分析无机元素在植物中的原位分布
- 自然资源部第三海洋研究所, 厦门 361005
收稿日期: 2020-03-25
录用日期: 2020-07-21
网络出版日期: 2020-07-21
基金资助
中国地质调查局国家专项(DD20190819)
Analysis of In Situ Distribution of Inorganic Elements in Plants by Micro-XRF
- Third Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Xiamen 361005, China
Received date: 2020-03-25
Accepted date: 2020-07-21
Online published: 2020-07-21
摘要
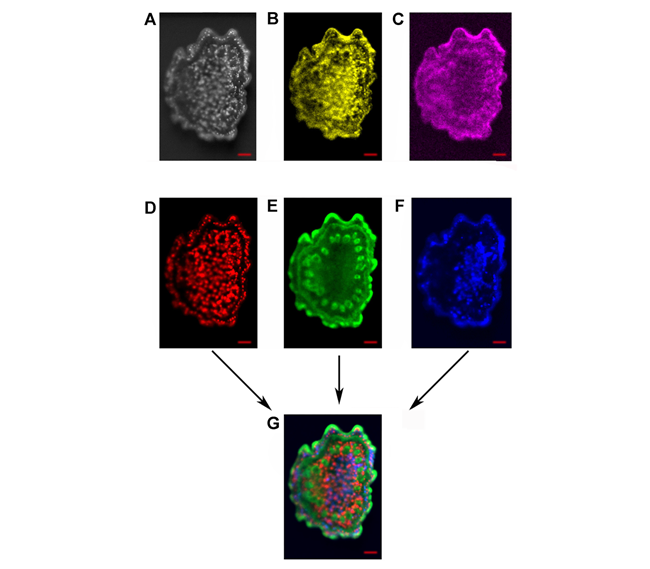
植物的无机元素分布特征对植物生理过程具有重要的指标作用, 可揭示营养物质分布、代谢途径及毒理耐受性等多种生命过程。用微区XRF技术测试样品中无机元素的分布, 具有原位无损、可进行较大面积样品连续成像分析以及前处理过程简单等诸多优势。将微区XRF技术应用于植物样品不同器官的无机元素分布检测, 旨在探讨该技术在植物样品测试中的仪器参数选择、样品前处理方法和数据后处理手段等对测试结果的影响。为得到可靠的实验结果, 对不同含水量的器官进行不同的前处理, 并比较不同驻留时间、测试腔体真空与否等仪器条件对测试结果的影响, 同时对数据处理方法进行探索, 包括对获得的数据进行图像叠加及对不同元素浓度比例进行半定量分析。研究结果表明, 微区XRF技术测试植物样品中无机元素分布具有一定的技术优势。
本文引用格式
林梵宇 , 尹希杰 , 梁毓娜 , 黄杰超 . 微区XRF技术分析无机元素在植物中的原位分布[J]. 植物学报, 2020 , 55(6) : 733 -739 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB20051
Abstract
The distribution characteristics of inorganic elements in plants play an important guiding role in the physiological, studies, which can reveal the distribution of nutrients, metabolic process, toxicity tolerance and other aspects in plants. Micro-XRF technology has many advantages to study inorganic elements, such as in situ, non-destructive, large area sample continuous mapping analysis, and simple pretreatment process. This study aims to explore the instrument parameters, pre-processing methods and data post-processing methods of micro-XRF in the distribution of inorganic elements of different plant organ samples. According to the difference of water content of different organs, we carried out different pretreatment schemes to obtain reliable experimental results. The influence of different point dwell time, chamber vacuum and other experimental conditions were compared. A variety of processing methods, such as image overlay, semi-quantitative analysis of concentration ratio of different elements, were carried out. The results show that micro-XRF technique has certain advantages in the determination of the distribution of inorganic elements in plant samples.

Key words: plant; micro-XRF; element distribution; in situ; nondestructive
参考文献
| [1] | 陈同斌, 黄泽春, 黄宇营, 谢华, 廖晓勇 (2003). 砷超富集植物中元素的微区分布及其与砷富集的关系. 科学通报 48, 1163-1168. |
| [2] | 丁广大, 刘佳, 石磊, 徐芳森 (2010). 植物离子组学: 植物营养研究的新方向. 植物营养与肥料学报 16, 479-484. |
| [3] | 梁述廷, 刘玉纯, 刘瑱, 林庆文 (2013). X射线荧光光谱微区分析在铅锌矿石鉴定上的应用. 岩矿测试 32, 897-902. |
| [4] | 凌雪, 吴萌蕾, 廖原, 周羿辰 (2018). 文物研究与保护中的无损分析技术. 光谱学与光谱分析 38, 2026-2031. |
| [5] | 罗立强, 沈亚婷, 马艳红, 许涛, 储彬彬, 曾远, 柳检 (2017). 微区X射线荧光光谱仪研制及元素生物地球化学动态分布过程研究. 光谱学与光谱分析 37, 1003-1008. |
| [6] | 沈亚婷 (2014). 原位微区同步辐射X射线荧光和近边吸收谱研究拟南芥幼苗及根际土壤中铅分布与形态特征. 光谱学与光谱分析 34, 818-822. |
| [7] | 王毅, 徐欣, 刘立新 (1994). 生物样品X射线微区分析样品制备技术分析. 植物学通报 11( 专辑), 85, 88. |
| [8] | 许涛, 罗立强 (2011). 原位微区X射线荧光光谱分析装置与技术研究进展. 岩矿测试 30, 375-383. |
| [9] | 余锦涛, 郭占成, 冯婷, 支歆 (2014). X射线光电子能谱在材料表面研究中的应用. 表面技术 43(11), 119-124. |
| [10] | 余志峰, 高永宏, 毛振才 (2005). 植物样品中多种微量元素的分析方法及应用研究. 见: 甘肃省化学会第二十四届年会论文集. 兰州: 甘肃省化学会. pp. 306-308. |
| [11] | Harvey MA, Erskine PD, Harris HH, Brown GK, Pilon-Smits EAH, Casey LW, Echevarria G, van der Ent A (2020). Distribution and chemical form of selenium in Neptunia amplexicaulis from Central Queensland, Australia. Metallomics 12, 514-527. |
| [12] | Modlitbová P, Po?ízka P, Kaiser J (2020). Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy as a promising tool in the elemental bioimaging of plant tissues. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 122, 115729. |
| [13] | van der Ent A, Przyby?owicz WJ, de Jonge MD, Harris HH, Ryan CG, Tylko G, Paterson DJ, Barnabas AD, Kopittke PM, Mesjasz-Przyby?owicz J (2018). X-ray elemental mapping techniques for elucidating the ecophysiology of hyperaccumulator plants. New Phytol 218, 432-452. |
| [14] | Wu B, Becker JS (2012). Imaging techniques for elements and element species in plant science. Metallomics 4, 403-416. |