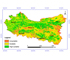
华中五味子(Schisandra sphenanthera)为我国三级保护野生药材物种, 在秦岭地区分布较广。采集秦岭地区19个样地307个采样点的华中五味子样本, 使用HPLC方法检测果实中五味子甲素和乙素含量, 基于模糊数学原理建立其与气候、土壤和地形三大类15个评价因子之间的隶属函数, 利用最大信息熵模型确定各评价指标权重, 使用加权平均法并参照GIS空间分析确定基于五味子甲素和乙素的秦岭地区野生华中五味子的潜在空间分布。研究结果显示, 秦岭地区华中五味子不适宜生境面积占研究区总面积的11.40%; 适宜生境面积占50.63%; 高适宜生境面积占37.97%, 主要集中在陕西南部、甘肃东部、河南西部、湖北神农架林区及其周边海拔800–2 000 m的山区。研究结果表明, 基于GIS与模糊数学构建的生境适宜性评价模型可以准确地对秦岭地区华中五味子生境适宜性作出科学且综合性评价, 并可量化适宜生境面积和空间分布, 为华中五味子野生抚育GAP基地选址和建设提供数据支撑, 为保护和可持续利用华中五味子野生资源提供参考。
Schisandra sphenanthera is the third-class conservation of wild medicinal species. It is widely distributed in Qinling Mountains. We collected S. sphenanthera samples at 307 sampling points in 19 sampling sites and extracted deoxyschizandrin and γ-schizandrin by high-performance liquid chromatography. We used “fuzzy theory” to determine the association of deoxyschizandrin and γ-schizandrin content and 15 assessment factors, including climate, soil and topographic factors. Then we used the maximum entropy model to determine the weight of each factor. Finally, we estimated the spatial distribution of S. sphenanthera in Qinling Mountains by the weighted average method and GIS spatial analysis. The proportion of unsuitable, suitable and high-suitable habitat for S. sphenanthera in Qinling Mountains was 11.40%, 50.63%, and 37.97%, respectively. The high-suitable habitat are mainly located in southern Shaanxi, eastern Gansu, western Henan, Shennongjia in Hubei, and the surrounding area, with elevation 800 to 2 000 m.This habitat-suitability assessment model based on GIS and fuzzy logic could be used to accurately determine the habitat suitability of S. sphenanthera, quantify the area of suitable habitat and analyze the spatial distribution. This information would supply scientific evidence for the choice of GAP and construction and advice for protection and sustainable utilization of resources.
陈斌, 丁世飞 (2007). 基于信息熵的模糊物元模型预测玉米螟种群动态. 数学的实践与认识 37, 78-82.
陈海生, 刘国顺, 刘大双, 陈伟强 (2009). GIS支持下的河南省烟草生态适宜性综合评价. 中国农业科学42, 2425-2433.
崔耀平, 刘纪远, 胡云锋, 王军邦, 匡文慧 (2012). 城市不同下垫面辐射平衡的模拟分析. 科学通报57, 465-473.
国家药典委员会 (2010). 中华人民共和国药典(2010年版一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社. pp. 227-228.
胡宝清 (2010). 模糊理论基础. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社. pp. 330-331.
黄林芳, 谢彩香, 陈士林, 段宝忠, 孙成忠, 凯撒?苏来曼, 王丽芝 (2010). 沙生药用植物锁阳产地适宜性的定量评价. 植物学报45, 205–211.
康慕谊, 朱源 (2007). 秦岭山地生态分界线的论证. 生态学报 27, 2774-2784.
中国科学院中国自然地理编辑委员会 (1985). 中国自然地理总论. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 270-276.
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1996). 中国植物志(第30卷第1分册). 北京:科学出版社. pp. 258-260.
张义, 谢永生, 郝明德 (2011). 黄土沟壑区王东沟流域苹果品质限制性生态因子探析. 中国农业科学44, 1184-1190.
Dussault C, Courtois R, Ouellet J (2006). A habitat suitability index model to assess moose habitat selection at multiple spatial scales. Can J Forest Res 36, 1097-1107.
Gu W, Wei NY, Wang ZZ (2008). LC analysis of lignans from Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. Chromatographia 67, 979-983.
Li J, Heap A D (2011). A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in envi-ronmental sciences: performance and impact factors. Ecol Inform 6, 228-241.
Lu CY, Gu W, Dai AH, Wei HY (2012). Assessing habitat suitability based on geographic in-fomation system (GIS) and fuzzy: a case study of Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. in Qinling Mountains, China. Ecol Model 242, 105-115.
Nguyen TT, Qiu JJ, Ann V, LI H, EricVan Ranst (2011). Temperature and precipitation suitabil-ity evaluation for the winter wheat and summer maize cropping system in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain of China. Agr Sci in China 10, 275-288.
Podchong S, Schmidt-Vogt D, Honda K (2009). An improved approach for identifying suitable habitat of Sambar Deer (Cervus unicolor Kerr) using ecological niche analysis and environ-mental categorization: case study at Phu-Khieo Wildlife Sanctuary, Thailand. Ecol Model 220, 2103-2114.
Rinaldi M, Losavio N, Flagella Z (2003). Evaluation and application of the OILCROP–SUN model for sunflower in southern Italy. Agr Syst 78, 17-30.
Saunders RMK (2000). Monograph of Schisandra (Schisandraceae). Syst Bot Monogr 58, 1-146.
Smith A C (1947). The families Illiciaceae and Schisandraceae. Sargentia 7, 1-244.
Tian SQ, Chen XJ, Chen Y, Xu LX , Dai XJ (2009). Evaluating habitat suitability indices drived from CPUE and fishing effort data for Ommatrphes bratramii in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Fish Res 95, 181-188.
Weber TC (2011). Maximum entropy modeling of mature hardwood forest distribution in four U.S. states. Forest Ecol Manag 261, 779-788.



