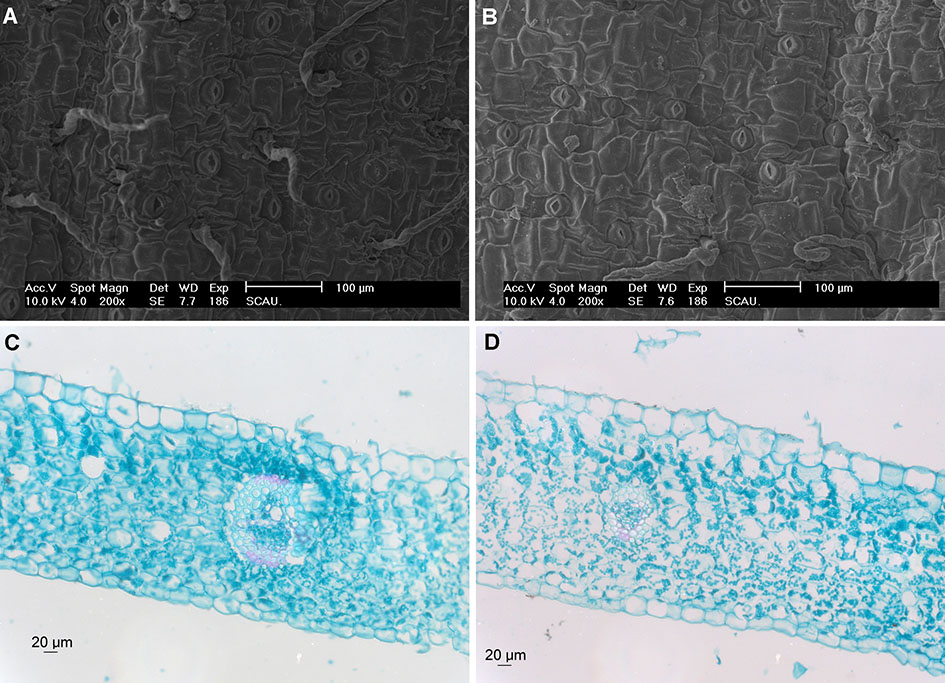
以黑毛组的黑毛石斛(Dendrobium williamsonii)和长距石斛(D. longicornu)为材料, 对其光合生理特性进行了系统研究。2种石斛叶片的解剖结构为异面叶, 气孔仅分布在下表面, 具气孔盖, 叶脉维管束鞘不含叶绿体, 无花环型结构。2种石斛的光强、CO2浓度和温度的响应研究表明, 它们的光补偿点(LCP)和光饱和点(LSP)分别为5–10 μmol·m−2·s−1和800–900μmol·m−2·s−1,表观量子效率为0.02; CO2补偿点和CO2饱和点分别为80–90 μmol·mol−1和800 μmol·mol−1, 羧化效率在0.015–0.021之间; 光合作用的最适温度为28–30°C。光合特性的研究表明, 2种石斛的净光合速率(Pn)日变化均呈双峰型曲线, 首峰出现在12:00, 最大光合速率为5 μmolCO2·m−2·s−1, 次峰出现在15:00, 夜间不吸收CO2。2种石斛叶片的叶绿素a/叶绿素b比值在2.51–2.66之间。酶活性的测定结果表明, 2种石斛的PEPCase活性极低, 但RuBPCase和GO酶活性较高。以上的研究结果均表明, 黑毛石斛和长距石斛光合作用碳同化途径属C3植物类型, 具有半阴生植物的特点。
We examined the photosynthetic physiology of Dendrobium williamsonii and D. longicornu. Cross-sections of the leaves of the 2 Dendrobium species showed that they were bifacial. The abaxial epidermis showed a large amount of stomata, covered by the waxy stomata; vascular bundles showed no chloroplast or Kranz structures. Photosynthesis of the 2 species responded to light intensity, CO2 concentration and temperature. Light compensation points were 5–10 μmol·m−2·s−1, light saturation points were 800–900 μmol·m−2·s−1; apparent quantum yields were ~0.02; CO2 compensation points and saturation points were 80–90 μmol·mol−1 and 800 μmol·mol−1, respectively; and carboxylation efficiencies were 0.015–0.021. The optimal temperature for photosynthesis was 26–30°C. The diurnal variation in net photosynthetic rates (Pn) were all bimodal curves, with the first peaks at ~5 μmol CO2·m−2·s−1 and emerging at between 11:00–12:00, and the second peaks emerging at about 15:00; no CO2 absorption occurred at night. Additionally, the chlorophyll a/b (Chl a/b) ratios of leaves were 2.51–2.66. Measurement of key enzymes in the photosynthetic pathway indicated relatively high RuBPCase and GO activities but low PEPCase activities. D. williamsonii and D. longicornu are typical semi-shade C3 plants.
吕芳德, 徐德聪, 侯红波(2003). 5种红山茶叶绿素荧光特性的比较研究经济林业研究, 21(4):4-7.
蔡永萍,李玲,李合生等(2005).霍山县3种石斛叶片光合光合作特性及其对光强的响应中草药,36(4): 586~590.
曹军胜,刘广全(2005). 刺槐光合特性的研究[J].西北农业学报,14 (3): 519~524.
丑敏霞,朱利泉,张玉进等(2001).不同光照强度和温度对金钗石斛生长的影响.植物生态学报,23(5):325-330.
潘瑞炽,叶庆生(2006).国兰生理,北京:科学出版社.
苏文华,张光飞(2003).金钗石斛光合作用特征的初步研究.中药材,26(3):157-159.
苏文华,张光飞(2003).铁皮石斛叶片光合作用的碳代谢途径.植物生态学报,27(5):631-637.
许大全(1994).光合作用及其有关过程对长期高CO2浓度的响应.植物生理学通讯,30(2):81~87.
徐云鹃,于力文,吴庆生等(1993).安徽省霍山县3种石斛的光合特征.应用生态学报,4(1):18-21.
叶庆生,潘瑞炽,丘才新(1992).墨兰叶片结构及光合作用的研究.植物学报,34(10):771-776.
叶庆生,潘瑞炽,丘才新(1993).墨兰光合途径的研究.植物学报,35(6):441-446.
叶庆生,潘瑞炽,丘才新(1996).兰属植物光合途径的研究.热带亚热带植物学报,6(1):25-29.
郁昭(1998).大棚黄瓜CO2 施肥的研究[J].土壤肥料,(5):47~48.
张方,迟伟,金成哲等(2003).高粱C4型磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶基因的分子克隆及其转基因水稻的培育.科学通报,48:1542~1546.
张志良(1990).植物生理学实验指导(第二版).北京:高等教育出版社.
中国科学院植物研究所形态学及细胞学研究室情报资料室(1974).扫描电子显微镜在植物学上的应用(第1版).
Blanke MM(1987).Comparative SEM study of stomata and surface morphology in apple. Angewandte Botanik, 61:433~438.
Critchley C, Russell AW(1994). Photoinhibition of photo synthesis invivo: The role of protein turnover in photo systemll. Physiol Plant, 92:188-196.
Demmig-Adams B , Adams III WW(1992). Photoprotection and other responses of plants to high light stress. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 43:599-626.
Edwards G Walker D(1983).C3,C4:Mechanisms,Cellular and Environmental Regulatlon of Photosynthesis, Oxford.Blackwell, 542
Hew CS, Ye QS, Pan RC(1989). Pathway of carbon fixation in some thin-leaved orchids. Lindleyana,4(3): 154-157.
Holden M(1973). Chloroplast pigment in plants with the C4-dicaboryllic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica,7:14-49.
Krause GH, Weis E(1984). Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in plant physiology II. Interpretation of fluorescence signals. Photosynthesis Research , 5: 139-157.
Krause GH , Weis E(1991). Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis:The Basics, Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology., 42 :313-349.
Pan RC, Ye QS, Hew CS(1997). Physiology of Cymbidium sinense:a review. Scientia Horticlturea,70:123-129.
Ye QS, Hew CS Pan RC(1993).Translocation of photosynthetically assimilated 14C in Cymbidium sinense.J. Singapore .Nat1.Acadeny Sci.,20&21:6-9.
Ye QS, Pan RC, Hew CS(1994). Study on respiration of Cymbidium sinense.Chinese J.of Botany,6(1):36-41.
Powles SB(1984). Photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by visible light. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology., 35:15-44.
Wintermans JFGM & De Mots A(1965). Spectrophotometric characteristic of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and their pheophytins in ethanol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 109-453



