

脯氨酸转运相关基因的研究进展
收稿日期: 2017-10-18
网络出版日期: 2018-01-02
Recent Progress in Research of Proline Transport Genes
Received date: 2017-10-18
Online published: 2018-01-02
陈颖, 王婷, 华学军 . 脯氨酸转运相关基因的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018 , 53(6) : 754 -763 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB17192
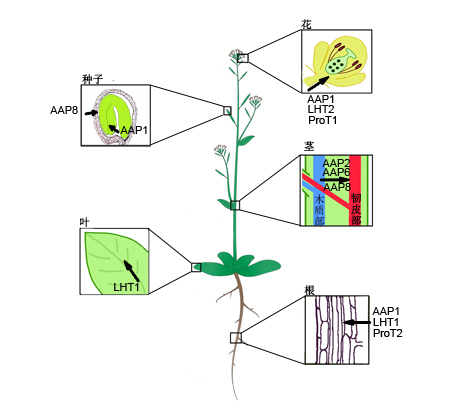
As a wide-spread stress adaption in plants, proline accumulation is thought to result from increased biosynthesis and decreased degradation. However, accumulating reports showed that proline transport also plays a role in stress-induced proline accumulation. In plants, several amino acid transporter protein families, such as AAPs, LHTs and ProTs, can transport proline. In this review, we summarize the expression pattern, function and expression regulation of these families in terms of proline transport, with an aim to provide some useful information on proline transport and accumulation research in plants.
| [1] | 全先庆, 张渝洁, 单雷, 毕玉平 (2007). 高等植物脯氨酸代谢研究进展. 生物技术通报 (1), 14-18. |
| [2] | 赵瑞雪, 朱慧森, 程钰宏, 董宽虎 (2008). 植物脯氨酸及其合成酶系研究进展. 草业科学 25, 90-97. |
| [3] | Andréasson C, Neve EPA, Ljungdahl PO (2004). Four permeases import proline and the toxic proline analogue azetidine-2-carboxylate into yeast.Yeast 21, 193-199. |
| [4] | Bäumlein H, Nagy I, Villarroel R, Inzé D, Wobus U (1992). Cis-analysis of a seed protein gene promoter: the conser- vative RY repeat CATGCATG within the legumin box is essential for tissue-specific expression of a legumin gene. Plant J 2, 233-239. |
| [5] | Breitkreuz KE, Shelp BJ, Fischer WN, Schwacke R, Rentsch D (1999). Identification and characterization of GABA, proline and quaternary ammonium compound transporters fromArabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 450, 280-284. |
| [6] | Cassab GI (1998). Plant cell wall proteins.Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49, 281-309. |
| [7] | Chang HC (1998). NAT2/AAP1 as A Prototypical Example of the AAP amino Acid Transporter Gene Family: From Protein Topology to Regulation of Gene Expression. Ph.D. thesis. Urbana: University of Illinois at Urbana-Cham- paign. pp. 33-52. |
| [8] | Chen JG, Zhang YQ, Wang CP, Lü WT, Jin JB, Hua XJ (2011). Proline induces calcium-mediated oxidative burst and salicylic acid signaling.Amino Acids 40, 1473-1484. |
| [9] | Chen LS, Bush DR (1997). LHT1, a lysine- and histidine- specific amino acid transporter in Arabidopsis.Plant Phy- siol 115, 1127-1134. |
| [10] | Chen NH, Reith MEA, Quick MW (2004). Synaptic uptake and beyond: the sodium- and chloride-dependent neuro- transmitter transporter family SLC6.Pflügers Arch 447, 519-531. |
| [11] | Couturier J, de Fay E, Fitz M, Wipf D, Blaudez D, Chalot M (2010). PtAAP11, a high affinity amino acid transporter specifically expressed in differentiating xylem cells of poplar.J Exp Bot 61, 1671-1682. |
| [12] | Csonka LN (1989). Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic-stress.Microbiol Rev 53, 121-147. |
| [13] | Deuschle K, Funck D, Forlani G, Stransky H, Biehl A, Leister D, van der Graaff E, Kunze R, Frommer WB (2004). The role of Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydro genase in proline degradation.Plant Cell 16, 3413-3425. |
| [14] | Di Martino C, Pizzuto R, Pallotta ML, De Santis A, Passarella S (2006). Mitochondrial transport in proline catabolism in plants: the existence of two separate trans- locators in mitochondria isolated from durum wheat seed- lings.Planta 223, 1123-1133. |
| [15] | Fischer WN, André B, Rentsch D, Krolkiewicz S, Tegeder M, Breitkreuz K, Frommer WB (1998). Amino acid transport in plants.Trends Plant Sci 3, 188-195. |
| [16] | Fischer WN, Kwart M, Hummel S, Frommer WB (1995). Substrate-specificity and expression profile of amino-acid transporters (AAPs) in Arabidopsis.J Biol Chem 270, 16315-16320. |
| [17] | Fischer WN, Loo DDF, Koch W, Ludewig U, Boorer KJ, Tegeder M, Rentsch D, Wright EM, Frommer WB (2002). Low and high affinity amino acid H+-cotransporters for cellular import of neutral and charged amino acids.Plant J 29, 717-731. |
| [18] | Foster J, Lee YH, Tegeder M (2008). Distinct expression of members of the LHT amino acid transporter family in flowers indicates specific roles in plant reproduction.Sex Plant Reprod 21, 143-152. |
| [19] | Frommer WB, Hummel S, Riesmeier JW (1993). Expres- sion cloning in yeast of a cDNA encoding a broad speci- ficity amino acid permease from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 5944-5948. |
| [20] | Girousse C, Bournoville R, Bonnemain JL (1996). Water deficit-induced changes in concentration in proline and some other amino acids in the phloem sap of Alfalfa.Plant Physiol 111, 109-113. |
| [21] | Grallath S, Weimar T, Meyer A, Gumy C, Suter-Grote- meyer M, Neuhaus JM, Rentsch D (2005). The AtProT family. Compatible solute transporters with similar sub- strate specificity but differential expression patterns.Plant Physiol 137, 117-126. |
| [22] | Grenson M, Hou C, Crabeel M (1970). Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IV. Evidence for a general amino acid permease. J Bacteriol 103, 770-777. |
| [23] | Guether M, Volpe V, Balestrini R, Requena N, Wipf D, Bonfante P (2011). LjLHT1.2-a mycorrhiza-inducible plant amino acid transporter from Lotus japonicus. Biol Fertil Soils 47, 925-936. |
| [24] | Guo MJ (2004). Molecular and Genomic Analysis of Nitrogen Regulation of Amino Acid Permease I (AAP1) in Arabi- dopsis. Ph.D. thesis. Urbana: University of Illinois at Urba- na-Champaign. pp. 90-102. |
| [25] | Hammes UZ, Nielsen E, Honaas LA, Taylor CG, Schacht- man DP (2006). AtCAT6, a sink-tissue-localized transpor- ter for essential amino acids in Arabidopsis.Plant J 48, 414-426. |
| [26] | Hatanaka T, Hatanaka Y, Setou M (2006). Regulation of amino acid transporter ATA2 by ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2.J Biol Chem 281, 35922-35930. |
| [27] | Heazlewood JL, Durek P, Hummel J, Selbig J, Weckwerth W, Walther D, Schulze WX (2008). PhosPhAt: a database of phosphorylation sites in Arabidopsis thaliana and a plant-specific phosphorylation site predictor. Nucleic Acids Res 36, D1015-D1021. |
| [28] | Hirner A, Ladwig F, Stransky H, Okumoto S, Keinath M, Harms A, Frommer WB, Koch W (2006). Arabidopsis LHT1 is a high-affinity transporter for cellular amino acid uptake in both root epidermis and leaf mesophyll.Plant Cell 18, 1931-1946. |
| [29] | Hu CAA, Delauney AJ, Verma DPS (1992). A bifunctional enzyme (Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase) cataly- zes the first two steps in proline biosynthesis in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 9354-9358. |
| [30] | Hunt E, Gattolin S, Newbury HJ, Bale JS, Tseng HM, Barrett DA, Pritchard J (2010). A mutation in amino acid permease AAP6 reduces the amino acid content of the Arabidopsis sieve elements but leaves aphid herbivores unaffected.J Exp Bot 61, 55-64. |
| [31] | Igarashi Y, Yoshiba Y, Takeshita T, Nomura S, Otomo J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2000). Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding proline transporter in rice.Plant Cell Physiol 41, 750-756. |
| [32] | Jauniaux JC, Vandenbol M, Vissers S, Broman K, Grenson M (1987). Nitrogen catabolite regulation of pro- line permease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning of the PUT4 gene and study of PUT4 RNA levels in wild-type and mutant strains. Eur J Biochem 164, 601-606. |
| [33] | Kiyosue T, Yoshiba Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinoz- aki K (1996). A nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial proline dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in proline metabolism, is upregulated by proline but downregulated by dehydration in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 8, 1323-1335. |
| [34] | Koch W, Kwart M, Laubner M, Heineke D, Stransky H, Frommer WB, Tegeder M (2003). Reduced amino acid content in transgenic potato tubers due to antisense inhibition of the leaf H+/amino acid symporter StAAP1.Plant J 33, 211-220. |
| [35] | Lasko PF, Brandriss MC (1981). Proline transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 148, 241-247. |
| [36] | Lee YH, Foster J, Chen J, Voll LM, Weber APM, Tegeder M (2007). AAP1 transports uncharged amino acids into roots of Arabidopsis.Plant J 50, 305-319. |
| [37] | Lee YH, Tegeder M (2004). Selective expression of a novel high-affinity transport system for acidic and neutral amino acids in the tapetum cells of Arabidopsis flowers.Plant J 40, 60-74. |
| [38] | Lehmann S, Funck D, Szabados L, Rentsch D (2010). Proline metabolism and transport in plant development.Amino Acids 39, 949-962. |
| [39] | Liu X, Bush DR (2006). Expression and transcriptional regulation of amino acid transporters in plants.Amino Acids 30, 113-120. |
| [40] | Lv WT, Lin B, Zhang M, Hua XJ (2011). Proline accumula- tion is inhibitory to Arabidopsis seedlings during heat stress.Plant Physiol 156, 1921-1933. |
| [41] | Marella HH, Nielsen E, Schachtman DP, Taylor CG (2013). The amino acid permeases AAP3 and AAP6 are involved in root-knot nematode parasitism of Arabidopsis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26, 44-54. |
| [42] | Matskevitch I, Wagner CA, Stegen C, Bröer S, Noll B, Risler T, Kwon HM, Handler JS, Waldegger S, Busch AE, Lang F (1999). Functional characterization of the betaine/γ-aminobutyric acid transporter BGT-1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 274, 16709-16716. |
| [43] | Miranda M, Borisjuk L, Tewes A, Heim U, Sauer N, Wobus U, Weber H (2001). Amino acid permeases in developing seeds of Vicia faba L: expression precedes storage protein synthesis and is regulated by amino acid supply. Plant J 28, 61-71. |
| [44] | Morbach S, Krämer R (2002). Body shaping under water stress: osmosensing and osmoregulation of solute trans- port in bacteria.Chembiochem 3, 384-397. |
| [45] | Okumoto S, Schmidt R, Tegeder M, Fischer WN, Rentsch D, Frommer WB, Koch W (2002). High affinity amino acid transporters specifically expressed in xylem parenchyma and developing seeds of Arabidopsis.J Biol Chem 277, 45338-45346. |
| [46] | Ortiz-Lopez A, Chang HC, Bush DR (2000). Amino acid transporters in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta 1465, 275-280. |
| [47] | Peng B, Kong HL, Li YB, Wang LQ, Zhong M, Sun L, Gao GJ, Zhang QL, Luo LJ, Wang GW, Xie WB, Chen JX, Yao W, Peng Y, Lei L, Lian XM, Xiao JH, Xu CG, Li XH, He YQ (2014). OsAAP6 functions as an important regu- lator of grain protein content and nutritional quality in rice. Nat Commun 5, 4847. |
| [48] | Perchlik M, Foster J, Tegeder M (2014). Different and overlapping functions of Arabidopsis LHT6 and AAP1 transporters in root amino acid uptake.J Exp Bot 65, 5193-5204. |
| [49] | Popova OV, Dietz KJ, Golldack D (2003). Salt-dependent expression of a nitrate transporter and two amino acid transporter genes in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant Mol Biol 52, 569-578. |
| [50] | Pratelli R, Pilot G (2014). Regulation of amino acid meta- bolic enzymes and transporters in plants.J Exp Bot 65, 5535-5556. |
| [51] | Regenberg B, Düring-Olsen L, Kielland-Brandt MC, Holmberg S (1999). Substrate specificity and gene exp- ression of the amino-acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 36, 317-328. |
| [52] | Rentsch D, Hirner B, Schmelzer E, Frommer WB (1996). Salt stress-induced proline transporters and salt stress- repressed broad specificity amino acid permeases identified by suppression of a yeast amino acid permease- targeting mutant.Plant Cell 8, 1437-1446. |
| [53] | Rentsch D, Schmidt S, Tegeder M (2007). Transporters for uptake and allocation of organic nitrogen compounds in plants.FEBS Lett 581, 2281-2289. |
| [54] | Sanders A, Collier R, Trethewy A, Gould G, Sieker R, Tegeder M (2009). AAP1 regulates import of amino acids into developing Arabidopsis embryos.Plant J 59, 540-552. |
| [55] | Santiago JP, Tegeder M (2016). Connecting source with sink: the role of Arabidopsis AAP8 in phloem loading of amino acids.Plant Physiol 171, 508-521. |
| [56] | Savouré A, Jaoua S, Hua XJ, Ardiles W, Van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (1995). Isolation, characterization, and chromosomal location of a gene encoding the Δ1-pyrroline- 5-carboxylate synthetase in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 372, 13-19. |
| [57] | Schmidt R, Stransky H, Koch W (2007). The amino acid permease AAP8 is important for early seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 226, 805-813. |
| [58] | Schwacke R, Grallath S, Breitkreuz KE, Stransky E, Stransky H, Frommer WB, Rentsch D (1999). LeProT1, a transporter for proline, glycine betaine, and γ-amino butyric acid in tomato pollen.Plant Cell 11, 377-391. |
| [59] | Su YH, Frommer WB, Ludewig U (2004). Molecular and functional characterization of a family of amino acid transporters from Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 136, 3104-3113. |
| [60] | Suzuki A, Mochizuki T, Uemura S, Hiraki T, Abe F (2013). Pressure-induced endocytic degradation of the Saccha- romyces cerevisiae low-affinity Tryptophan Permease Tat1 is mediated by Rsp5 ubiquitin ligase and functionally red- undant PPxY motif proteins. Eukaryot Cell 12, 990-997. |
| [61] | Svennerstam H, Ganeteg U, Näsholm T (2008). Root uptake of cationic amino acids by Arabidopsis depends on functional expression of amino acid permease 5.New Phytol 180, 620-630. |
| [62] | Szabados L, Savouré A (2010). Proline: a multifunctional amino acid.Trends Plant Sci 15, 89-97. |
| [63] | Tan QM, Grennan AK, Pélissier HC, Rentsch D, Tegeder M (2008). Characterization and expression of French bean amino acid transporter PvAAP1. Plant Sci 174, 348-356. |
| [64] | Tanner JJ (2008). Structural biology of proline catabolism.Amino Acids 35, 719-730. |
| [65] | Tilsner J, Kassner N, Struck C, Lohaus G (2005). Amino acid contents and transport in oilseed rape (Brassica na- pus L.) under different nitrogen conditions. Planta 221, 328-338. |
| [66] | Tuskan GA, DiFazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A, Schein J, Sterck L, Aerts A, Bhalerao RR, Bhalerao RP, Blaudez D, Boerjan W, Brun A, Brunner A, Busov V, Campbell M, Carlson J, Chalot M, Chapman J, Chen GL, Cooper D, Coutinho PM, Couturier J, Covert S, Cronk Q, Cunningham R, Davis J, Degroeve S, Déjardin A, Depamphilis C, Detter J, Dirks B, Dubchak I, Duplessis S, Ehlting J, Ellis B, Gendler K, Goodstein D, Gribskov M, Grimwood J, Groover A, Gunter L, Hamberger B, Heinze B, Helariutta Y, Henrissat B, Holligan D, Holt R, Huang W, Islam-Faridi N, Jones S, Jones-Rhoades M, Jorgensen R, Joshi C, Kangasjärvi J, Karlsson J, Kelleher C, Kirkpatrick R, Kirst M, Kohler A, Kalluri U, Larimer F, Leebens-Mack J, Leplé JC, Locascio P, Lou Y, Lucas S, Martin F, Montanini B, Napoli C, Nelson DR, Nelson C, Nieminen K, Nilsson O, Pereda V, Peter G, Philippe R, Pilate G, Poliakov A, Razumovskaya J, Richardson P, Rinaldi C, Ritland K, Rouzé P, Ryaboy D, Schmutz J, Schrader J, Segerman B, Shin H, Siddiqui A, Sterky F, Terry A, Tsai CJ, Uberbacher E, Unneberg P, Vahala J, Wall K, Wessler S, Yang G, Yin T, Douglas C, Marra M, Sandberg G, Van de Peer Y, Rokhsar D (2006). The genome of black cottonwood,Populus trichocarpa(Torr. & Gray). Science 313, 1596-1604. |
| [67] | Ueda A, Shi WM, Sanmiya K, Shono M, Takabe T (2001). Functional analysis of salt-inducible proline transporter of barley roots.Plant Cell Physiol 42, 1282-1289. |
| [68] | Ueda A, Shi WM, Shimada T, Miyake H, Takabe T (2008). Altered expression of barley proline transporter causes different growth responses in Arabidopsis.Planta 227, 277-286. |
| [69] | Verbruggen N, Hermans C (2008). Proline accumulation in plants: a review.Amino Acids 35, 753-759. |
| [70] | Verbruggen N, Hua XJ, May M, Van Montagu M (1996). Environmental and developmental signals modulate pro- line homeostasis: evidence for a negative transcriptional regulator.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 8787-8791. |
| [71] | Verslues PE, Sharp RE (1999) Proline accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) primary roots at low water potentials. II. Metabolic source of increased proline deposition in the elongation zone. Plant Physiol 119, 1349-1360. |
| [72] | Waditee R, Hibino T, Tanaka Y, Nakamura T, Incharoens akdi A, Hayakawa S, Suzuki S, Futsuhara Y, Kawam itsu Y, Takabe T, Takabe T (2002). Functional charac- terization of betaine/proline transporters in betaine-accu- mulating mangrove.J Biol Chem 277, 18373-18382. |
| [73] | Wood JM (2006). Osmosensing by bacteria.Sci STKE 2006, pe43. |
| [74] | Wood JM, Bremer E, Csonka LN, Kraemer R, Poolman B, van der Heide T, Smith LT (2001). Osmosensing and osmoregulatory compatible solute accumulation by bac- teria.Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 130, 437-460. |
| [75] | Zhang LZ, Garneau MG, Majumdar R, Grant J, Tegeder M (2015). Improvement of pea biomass and seed productivity by simultaneous increase of phloem and embryo loading with amino acids.Plant J 81, 134-146. |
| [76] | Zhang LZ, Tan QM, Lee R, Trethewy A, Lee YH, Tegeder M (2010). Altered xylem-phloem transfer of amino acids affects metabolism and leads to increased seed yield and oil content in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 22, 3603-3620. |
| [77] | Zhang R, Zhu J, Cao HZ, Xie XL, Huang JJ, Chen XH, Luo ZY (2013). Isolation and characterization of LHT-type plant amino acid transporter gene from Panax ginseng Meyer. J Ginseng Res 37, 361-370. |
| [78] | Zhao HM, Ma HL, Yu L, Wang X, Zhao J (2012). Genome- wide survey and expression analysis of amino acid trans- porter gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One 7, e49210. |
| [79] | Zhou YZ, Zhu WD, Bellur PS, Rewinkel D, Becker DF (2008). Direct linking of metabolism and gene expression in the proline utilization A protein from Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 35, 711-718. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |