

一种优化的测定水稻硅含量的方法
# 共同第一作者
收稿日期: 2015-10-10
录用日期: 2016-02-14
网络出版日期: 2016-09-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.30170236)和山西省基础研究项目(No.2012011032)
An Optimized Method to Determine Silicon Content in Rice
# Co-first authors
Received date: 2015-10-10
Accepted date: 2016-02-14
Online published: 2016-09-27
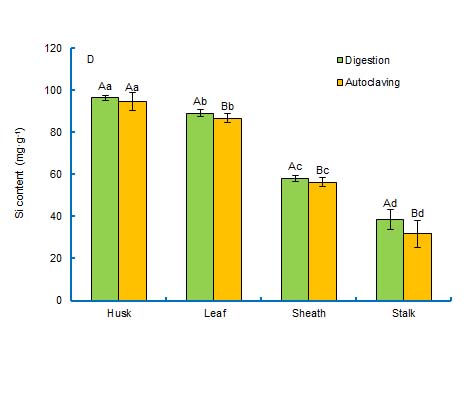
为建立一种更为简便且准确的水稻(Oryza sativa)硅含量测定方法, 对硅钼蓝分光光度法的多个实验条件进行了优化, 并对水稻样品的前处理——消解法和高压灭菌法进行了比较研究。结果表明, 还原剂为抗坏血酸、测定波长为600 nm、硅钼黄显色时间和硅钼蓝稳定时间分别为5和25分钟为最佳测定条件, 样品的前处理则是消解法优于高压灭菌法, 前者提取硅的效果好于后者。该优化方法为深入研究水稻和其它植物中硅的吸收和转运机制奠定了基础。
张洋 , 陈惠 , 贾雨薇 , 房娟娟 , 杨瑞林 . 一种优化的测定水稻硅含量的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2016 , 51(5) : 679 -683 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB15181
To establish an easier and more accurate method to determine silicon content in rice, several main parameters of silicon molybdenum-blue spectrophotometry were optimized in combination with 2 sample pretreatments, digestion and autoclaving. By using ascorbic acid as a reductant, with the color development time of the silicon molybdenum yellow and the stable time of silicon molybdenum blue for 5 and 25 min, respectively, optimal silicon content in rice was achieved at 600 nm wavelength by molybdenum-blue spectrophotometry. For sample pretreatment, the digestion method was more effective for silicon extraction than autoclaving. Briefly, the optimized method facilitates the determination of silicon content in rice and other plants and could lay a theoretical foundation for further research of the mechanism of silicon absorbance and transportation.

| 1 | 白淑琴, 阿木日沙那, 那人高娃, 杨帆, 王媛, 王桂花, 横山拓史 (2012). 水稻中硅元素的分布及存在状态. 应用与环境生物学报 18, 444-449. |
| 2 | 戴伟明, 张克勤, 段彬伍, 孙成效, 郑康乐, 蔡润, 庄杰云 (2005). 测定水稻硅含量的一种简易方法. 中国水稻科学 19, 460-462. |
| 3 | 石海强, 白淑云, 刘秉钺, 鲁杰 (2011). 稻草制浆中硅含量测定方法的改进. 大连工业大学学报 30, 126-128. |
| 4 | 童国林, 陆琦, 汪鋆, 周彩虹 (2005). 硅钼蓝光度法测定稻草原料及烧碱法制浆黑液的硅含量. 中华纸业 26, 64-66. |
| 5 | 王思哲, 温圣贤, 邓文, 蒲熙, 刘灿辉, 崔巍 (2007). 硅肥在水稻上的应用研究进展. 作物研究 21, 620-624. |
| 6 | 邢雪荣, 张蕾 (1998). 植物的硅素营养研究综述. 植物学通报 15, 33-40. |
| 7 | 翟庆洲, 金永哲, 邵长路, 张宗韬, 肖丰收, 裘式纶 (1998). 硅钼蓝光度法测定沸石分子筛中的硅. 光谱实验室 15, 82-84. |
| 8 | 张遴, 蔡砚, 王昌钊, 乐爱山 (2011). 硅钼蓝光度法测定钼铁中硅含量方法的条件优化设计. 化学试剂 33, 829-832. |
| 9 | 朱智伟, 林榕辉 (1990). 碱氧化消化法快速测定谷壳中的硅. 中国水稻科学 4, 89-91. |
| 10 | Liebig JV (刘更另译) (1983). 化学在农业和生理学上的应用(第1版). 北京: 农业出版社. pp. 189-191. |
| 11 | Ma JF, Higashitani A, Takeda K (2003). Genotypic variation in silicon concentration of barley grain.Plant Soil 249, 383-387. |
| 12 | Ma JF, Mitani N, Nagao S, Konishi S, Tamai K, Lwashita T, Yano M (2004). Characterization of the silicon uptake system and molecular mapping of the silicon transporter gene in rice.Plant Physiol 136, 3284-3289. |
| 13 | Meyer ML, Bloom PR (1993). Lithium metaborate fusion for silicon, calcium, magnesium, and potassium analysis of wild rice.Plant Soil 153, 281-285. |
| 14 | Okuda A, Takahashi E (1961). Studies on the physiological role of silicon in crop plants. Part1 on the method of silicon-free culture.J Sci Soil Manure Jpn 32, 475-480. |
| 15 | Okuda A, Takahashi E (1965). The role of silicon. In: Chandler RF, ed. The Mineral Nutrition of the Rice Plant. Baltimore: John Hopkins Press. pp. 126-146. |
| 16 | Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976). Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. 3 rd edn. Los Banos, Laguna: International Rice Research Institute. pp. 17-22. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |